Figure 7. HIF1A recruits RAD21 to CTCF-bound sites to upregulate NOS1.
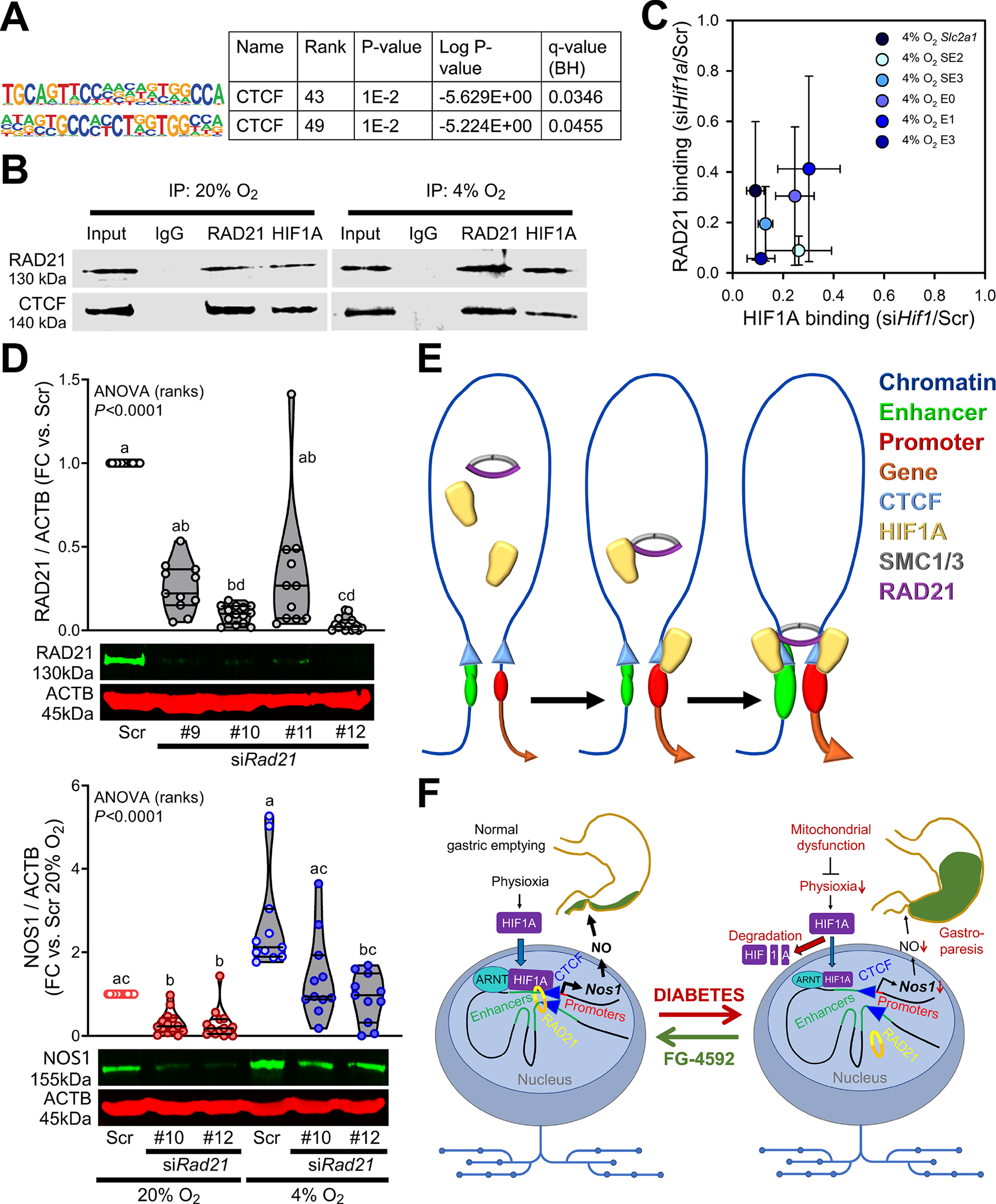
(A) Enrichment of known CTCF motifs in HIF1A-bound cis-regulatory elements of the Nos1 TAD in N1E-115 cells. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of RAD21 and CTCF with RAD21 and HIF1A. Representative immunoblots from 3 (RAD21) or 2 (CTCF) experiments. (C) Concordant reduction in HIF1A and RAD21 binding in the promoter of the canonical HIF1A target Slc2a1 gene and key HIF1A-bound SEs and enhancers of the sub-TAD containing Nos1 in HIF1A-silenced N1E-115 cells cultured at 4% O2. The loci targeted for analysis are indicated by pink bars in Supplementary Figure 10D and a pink vertical line in Supplementary Figure 7A. (D) Top: Silencing efficiencies of 4 siRNAs targeting Rad21. nScr=14, n#9=11, n#10=14, n#11=11, n#12=14. P, Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA. Groups not sharing the same superscript are different by Dunn’s test. Bottom: Effects of Rad21 knockdown using the two most efficacious siRNAs on NOS1 protein in N1E-115 cells. nScr;20%=14, n#10;20%=14, n#12;20%=14, nScr;4%=11, n#10;4%=11, n#12;4%=11. P, Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA. Groups not sharing the same superscript are different by Dunn’s test. (E) Schematic illustration showing the formation of architectural enhancer-promoter loops triggered by HIF1A recruitment of RAD21 to CTCF-bound sites. (F) Overview of the proposed main roles of HIF1A in gastroparesis.
