The authors would like to apologize for a paragraph that is missing from the Materials and Methods section of this article. The paragraph is given below, and should have appeared between the ‘Electron microscopy’ and ‘Inhibition assay and western blot analysis’ paragraphs.
Chemotaxis assay
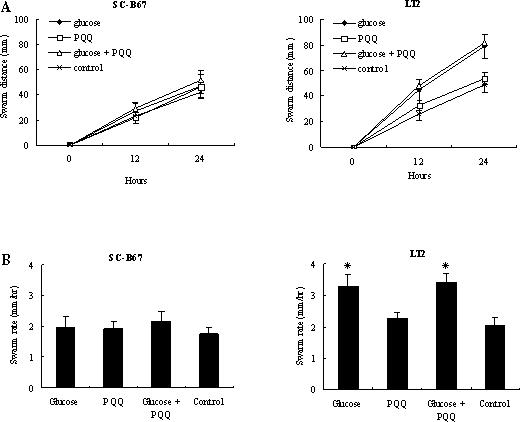
Chemotaxis of S.Choleraesuis SC-B67 and S.Typhimurium LT2 towards chemotactic attractants, glucose and pyrroloquinolone quinone (PQQ), was investigated by using the tube swarming assay (20, 21). The agar tube was consisted of two layers: both upper and lower layers contained tryptone (10 g/l), NaCl (5 g/l), and 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (0.05 g/l) in a agar base, while only the lower layer was added with either glucose (1 mM) and/or PQQ (10 (M). The 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (0.05 g/l) acts as a color indicator when bacteria grew and moved. For each test, approximately 3 × 106 CFU of bacteria, pre-grown to late log phase, were transferred to the top of the agar tube. The tube was then incubated at 37°C and the swarming length of the bacteria (red area) was measured every hour.
The authors would also like to apologize for an error in Figure 3. Two asterisks were missing in Figure 3B. The complete corrected Figure is given below.