Abstract
Staphylococcus and Streptococcus, two groups of major human pathogens, are equipped with a fatty acid kinase (Fak) machinery to scavenge host fatty acids. The Fak complex is contains an ATP-binding subunit FakA, which interacts with varied FakB isoforms, and synthesizes acyl-phosphate from extracellular fatty acids. However, how FakA recognizes its FakB partners and then activates different fatty acids is poorly understood. Here, we systematically describe the Fak system from the zoonotic pathogen, Streptococcus suis. The crystal structure of SsFakA complexed with SsFakB2 was determined at 2.6 Å resolution. An in vitro system of Fak-PlsX (phosphate: acyl-ACP transacylase) was developed to track acyl-phosphate intermediate and its final product acyl-ACP. Structure-guided mutagenesis enabled us to characterize a mechanism for streptococcal FakA working with FakB partners engaged in host fatty acid scavenging. These findings offer a comprehensive description of the Fak kinase machinery, thus advancing the discovery of attractive targets against deadly infections with Streptococcus.
Structure and function of Fak system shed light on how the opportunistic pathogen Streptococcus suis scavenges host fatty acids.
INTRODUCTION
Bacterial type II fatty acid synthesis (FAS II) is an attractive target for antibiotic development (1, 2). The essentiality of FAS II pathway mainly relies on two facts: (i) β-hydroxyl-fatty acids are required for lipid A moiety of lipopolysaccharides in Gram-negative microorganisms (3) and (ii) Ile (Leu)–derived pentadecanoic acid (C15:0) is acylated on the 2-position of phosphatidic acids in Gram-positive Staphylococcus (4). Continuing efforts to discover FAS II–targeted antibacterial agents have returned an arsenal of potent lead compounds. Among them, triclosan (an additive of soap) (5, 6) and isoniazid (a frontline drug against tuberculosis) (7, 8) are two broadly used inhibitors. However, the validity of FAS II as an effective drug target is still debated vigorously. This is because certain Gram-positive pathogen (exemplified with Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus) circumvents the dependence of de novo fatty acid (FA) synthesis by scavenging host/environmental FA to construct its membrane phospholipids (9, 10). Parsons et al. (4) found that the feedback by exogenous FAs represses acetyl–coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylase and turns off FAS II in Streptococcus, but not in Staphylococcus. This explains partially the discrepancy and validates the rationale for bacterial FAS II as a feasible drug target against certain Gram-positive pathogens.
In general, exogenous FAs are assimilated and then activated, before the incorporation into bacterial membrane phospholipids. So far, three types of different machineries by which extracellular FA is scavenged have been found in bacteria: (i) production of acyl-CoA thioesters by acyl-CoA synthetase FadD (11), following the entry of exogenous FA via FadL porin (12, 13) in γ-proteobacteria; (ii) formation of fatty acyl–ACP (acyl carrier protein) species by acyl-ACP synthetase (AasS) in certain species [including AasS of Vibrio harveyi (14, 15), AasC in Chlamydia (16), and Neisseria AasN (17)]; and (iii) conversion of acyl-phosphate by fatty acid kinase (Fak) systems in Firmicutes, a phylum of Gram-positive bacteria, exemplified with S. aureus (the order Bacillales) (18) and Streptococcus pneumoniae (the order Lactobacillales) (19). The Fak route is a newly identified kinase system, consisting of two dissociable protein subunits, FakA and FakB (18). FakA refers to a Fak domain that phosphorylates exogenous FA species carried by FakB (fatty acid–binding protein) (18). The leading pathogen S. aureus has two distinct but related FakB modules: FakB1 preferring saturated FA (C14:0 to C17:0) (20) and FakB2 favoring monounsaturated FA (oleate, C18:1, Δ9) (21). Unlike S. aureus, the other major pathogen S. pneumoniae produces an additional FakB3 subunit, which enables the utilization of polyunsaturated FAs that are rich in host niche, i.e., linoleic acid (C18:2, Δ9/11) (19). The product of the Fak kinase system, fatty acyl-phosphates (FA-P), is then transferred to PlsY [glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) acyltransferase] to begin membrane phospholipid synthesis at 1-position of G3P (22). In addition, FA-P can be trans-acylated with ACP by PlsX (phosphate: acyl-ACP transacylase) to yield acyl-ACP intermediates (22). Apart from the entry into FAS II cycles, the resultant acyl-ACP pool can be fixed by PlsC (1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase) at 2-position of 1-acyl-glycerolphosphate (23, 24). Moreover, the elongated acyl-ACP species can be used by the PlsX/Y system to construct membrane phospholipid (Fig. 1). So far, the availability of structural information for the Fak system is limited to the FakB subunits of S. aureus (20, 21) and S. pneumoniae (19). Although crystal structures of the separate domains [N-terminal domain of FakA (FakA_N) or C-terminal domain of FakA (FakA_C)] of SaFakA are released during the revision of this manuscript, the full-length architecture of FakA remains unclear. Structural dissection of the FakA/FakB complex, which could help to explain how bacterial pathogen scavenges exogenous FAs for control of lipid homeostasis (20, 25, 26) or adaptation to host niches (27–29), is lacking.
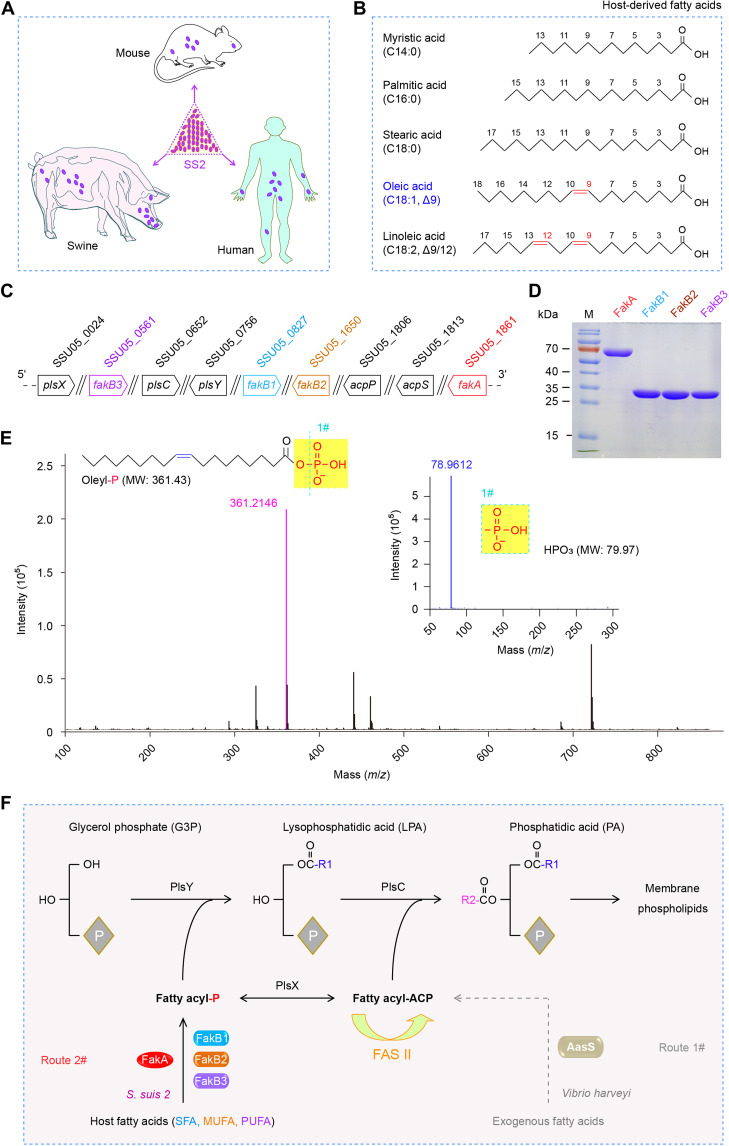
Fig. 1. A scheme for the S. suis FakA-FakB1 (FakB2 and FakB3) system to scavenge host fatty acids.
(A) Cartoon illustration for the zoonotic pathogen S. suis 2 (SS2) and its hosts. Oval purple symbol denotes the bacterium SS2. (B) Chemical structures of five representative host FAs. (C) Genetic environment for the FakA-FakB system and PlsX/Y/C path in SS2. (D) SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) (12%) profile for four components of the FakA/FakB system from SS2. (E) Use of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to analyze the phosphorylated oleic acid generated by the FakA-FakB2 kinase system. MW, molecular weight. (F) Proposed model of host FA activation by the S. suis FakA-FakB2 (FakB1 and FakB3) system, before the entry into the PlsX/Y/C-based steps of membrane phospholipid formation. Unlike the FakA-FakB2 (FakB1 and FakB3) system of the Gram-positive Streptococcus, the Gram-negative bacterium V. harveyi develops the AasS system to activate host/environmental FAs. Oleyl-P, oleyl-phosphate; acpS, the locus that encodes holo-ACP synthase/phosphopantetheinyl transferase; acpP, acyl carrier protein-encoding gene.
As the closely related cousin of S. pneumoniae, the zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis is a group of swine colonizers (Fig. 1A) and comprises 35 varied serotypes (1, 1/2, and 2 to 34) (30, 31), of which serotype 2 [S. suis 2 (SS2)] is the most relevant to clinical infections (32–34). As predicted, it also harbors a Fak system to activate diverse environmental FAs (Fig. 1B), in which three FakB homologs are involved (Fig. 1, C and D). Here, we report the complex structure of a dimeric FakA bound to an oleate-liganded FakB2. The structure reveals that FakA is a chimeric/fusion protein consisting of three distinct domains (namely, FakA_N, FakA_M, and FakA_C) with extensive interdomain interactions. Also, the binding interface between FakA and FakB is functionally defined. Collectively, this study advances our understanding of host FA salvage by the human streptococcal pathogens.
RESULTS
Occurrence of the Fak system in S. suis 2
Streptococcal Fak is a dissociable two-component system, comprising the adenosine triphosphate (ATP)–binding protein FakA and certain FakB FA-binding subunits. Genome-wide comparison of two representatives of virulent SS2 (P1/7, a European strain, and 05ZYH33, an epidemic strain in China) suggested the presence of four FakB candidates in addition to a single FakA (fig. S1). Here, SSU05_1861 (554 amino acids) from 05ZYH33 strain was named FakA (Fig. 1A and figs. S2 and S3) because it is highly similar to its counterparts [i.e., 50.92% identity to SaFakA (548 amino acids) of S. aureus Newman (SAR1202) and 82.85% identity to SpFakA (555 amino acids) of S. pneumoniae TIGR4 (Sp_0443); fig. S2B]. Accordingly, SSU05_0827 (283 amino acids) of 05ZYH33 strain was termed FakB1, since its identity is 31.1% to SaFakB1 (SAR0803, 288 amino acids) and 67.5% to SpFakB1 (Sp_1557, 282 amino acids), respectively (Fig. 1C and fig. S1A). The locus SSU05_1650 (277 amino acids) was termed FakB2 in that it separately is 29.35% identical to SaFakB2 (SAR1438, 279 amino acids) and 74.01% identical to SpFakB2 (Sp_1112, 279 amino acids) (fig. S4). FakB3 of S. suis 05ZYH33 is denoted SSU05_0561 (283 amino acids), which is 68.6% identical to SpFakB3 (Sp_0743, 281 amino acids) (fig. S1A). The identity among the above three FakB (FakB1 to FakB3) of S. suis ranges from 17.52 to 29.82% (fig. S5). The fourth FakB protein of 05ZYH33 strain (FakB4) corresponds to SSU05_1899 (fig. S1B), having appreciable similarity to the other three cousins (30.2% identity to SsFakB1, 29.6% identity to SsFakB2, and 19.4% identity to SsFakB3). Unlike S. pneumoniae TIGR4 that features three FakA-centering FakB cousins (FakB1 to FakB3), genetic arrangement of S. suis Fak loci is equivalent to that of Streptococcus pyogenes M1 GAS (fig. S1). However, the function of the Fak system in S. suis requires experimental validation.
Salvage of host FAs by the Fak system
Host serum contains a spectrum of FA species like oleic acid and linoleic acid (Fig. 1B). Presumably, the Fak system facilitates the survival of the zoonotic pathogen S. suis during the bloodstream infections through scavenging exogenous FAs from either pigs or humans (Fig. 1A). To address this hypothesis, we attempted to construct a series of fak mutants of S. suis through allelic replacement. It seemed likely that fakA (SSU05_1861) is an essential gene for S. suis viability, and our long-term continued efforts failed to obtain the ΔfakA mutant. A similar scenario was seen with its counterpart (Sp_0443) in S. pneumoniae (35). Except for fakB3 (SSU05_0561; Fig. 1C), we had success in generating single mutants of both fakB1 (SSU05_0827) and fakB2 (SSU05_1650). In principle, FakB1 specifically binds saturated FAs (C14:0 to C18:0), whereas FakB2 prefers mono-unsaturated FA, i.e., oleic acid (Fig. 1B). The removal of either fakB1 or fakB2 influenced bacterial growth of S. suis in liquid Todd-Hewitt broth (THB) medium (fig. S6A) and on solid THB agar plates (fig. S6B). As expected, the supplementation of swine serum stimulated robust growth of SS2 (fig. S6, A and C). Compared with the wild-type strain 05ZYH33, the two fakB mutants, i.e., ΔfakB1 and ΔfakB2, exhibited a relatively delayed lag phase (fig. S6C) as well as smaller colony size (fig. S6D). This hints that the improved growth of S. suis relies on the presence of FakB1/FakB2, a determinant of full Fak activity. Subsequently, gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC/MS)–aided lipidomic analysis verified that S. suis uses Fak machinery to scavenge host serum lipid-derived FAs (especially C18:0 and C18:1) to construct bacterial membrane phospholipid (fig. S6, E and F). Thus, it is plausible that Fak system benefits the survival of SS2 within diverse host niches, assuring competition advantage at infection sites. However, how streptococcal Fak machinery cross-talks with host FAs is incompletely understood.
Action of the Fak-PlsX system
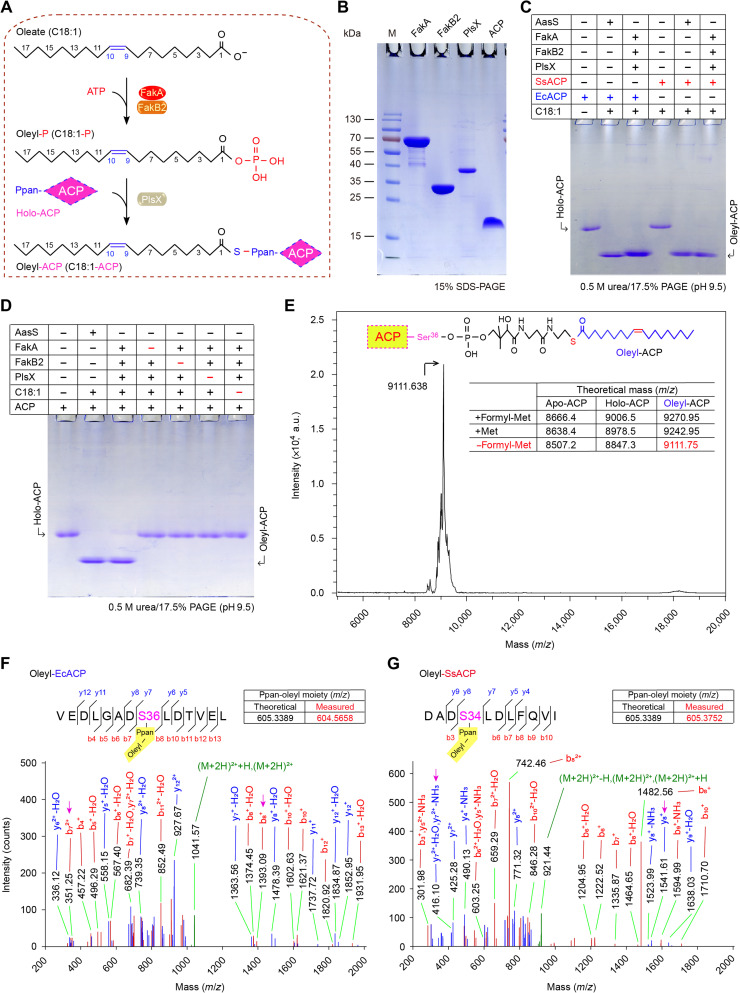
Given the fact that FA-P arising from FakA-FakB action can be converted by PlsX to acyl-ACP (Figs. 1F and 2A) (22), we aimed to reconstitute the in vitro enzymatic system that reproduces Fak activity. In addition to FakA-FakB pairs, the purified components of this assay involved PlsX and ACP (Fig. 2B). Except for FakB4 (SSU05_1899) that appears as inclusion bodies in vitro (i.e., not biochemically amenable), all the other three (FakB1 to FakB3) were purified to homogeneity (Fig. 1D). First, liquid chromatography–MS (LC-MS) analysis enables us to detect the occurrence of oleyl-phosphate (oleyl-P) intermediate due to FakA-FakB2 action (Fig. 1E). In principle, the production of acyl-ACP initiated by FA-P could be differentiated from its acceptor holo-ACP using conformation-sensitive 17.5% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) (pH 9.5) supplemented with 0.5 M urea. Here, the V. harveyi AasS functioned as a positive control (14, 36). As expected, the FakB2-centering Fak-PlsX system produced an acyl-ACP candidate, whose migration is almost identical to that of AasS in the presence of oleic acid plus ACP (Fig. 2, C and D). In addition to its native acceptor, the Escherichia coli ACP seemed to be effectively exploited by FakB2 in the activation of oleic acids (Fig. 2C). Not surprisingly, the oleyl-ACP of interest cannot appear if any individual element of the Fak-PlsX system is missing (e.g., PlsX; Fig. 2D). This was further validated by the closeness of measured [9111.638, mass/charge ratio (m/z)] and theoretical (9111.75, m/z) mass values of oleyl-EcACP (Fig. 2E). MS/MS identification illustrated that oleyl moiety is loaded on certain serine residue of ACP, namely, S36 for E. coli (Fig. 2F) and S34 for S. suis (Fig. 2F). As expected, the replacement of FakB2 with FakB1 enabled the Fak-PlsX system to be active in the utilization of three saturated FAs, namely, C14:0 (fig. S7, A and C), C16:0 (fig. S7, A and D), and C18:0 (fig. S7, A and E). The addition of FakB3 protein also allowed us to visualize the formation of linoleyl-ACP in the in vitro enzymatic system (fig. S7, B and F). This biochemical finding is fully consistent with the nomenclature of various FakB subunits of S. aureus (20, 21) and S. pneumoniae (19). Hence, it represents the first functional proof for an active FakA-FakB system in the human pathogen S. suis. This in vitro reconstituted Fak-PlsX system might represent a promising tool to track a wide repertoire of acyl-ACP pool, which was also used by a recent study with Enterococcus (37).
Fig. 2. Biochemical evidence that the Fak-PlsX system catalyzes the production of oleyl-ACP via the phosphorylated oleate intermediate.
(A) Scheme for catalytic actions by the Fak-PlsX reaction system. (B) Components used for the in vitro reconstitution of FakA/FakB2-PlsX enzymatic system. (C and D) In vitro reconstitution of FakA/FakB2-FlsX system to produce oleyl-ACP in the presence of SsACP (and/or EcACP). Conformationally sensitive 0.5 M urea/17.5% PAGE (pH 9.5) was used to track the oleyl-ACP product from FakA-FakB2 reaction system in the presence of PlsX. The symbol of plus (+) refers to addition of protein (and/or oleic acid), whereas minus (−) denotes no addition. (E) Use of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time of flight (MALDI-TOF) to measure molecular mass of the oleyl-ACP product. Molecular mass for the form of oleyl-ACP lacking its initial formyl-Met residue is measured to be 9111.638, close to its theoretical value of 9111.74. LC-MS identity for oleyl-EcACP (F) and oleyl-SsACP (G). Posttranslational modification with oleyl moiety occurs on the residue S36 of EcACP (F) and on S34 of SsACP (G). The actual mass of Ppan-oleyl moiety is separately measured by LC-MS to be 604.5658 and 605.3752, which matches its theoretical value of 605.3389. C18:1-P, oleyl-P; EcACP, E. coli ACP; SsACP, S. suis ACP; Met, methionine; formyl-Met, n-formyl-methionine.
Architecture of the FakA-FakB2 machinery
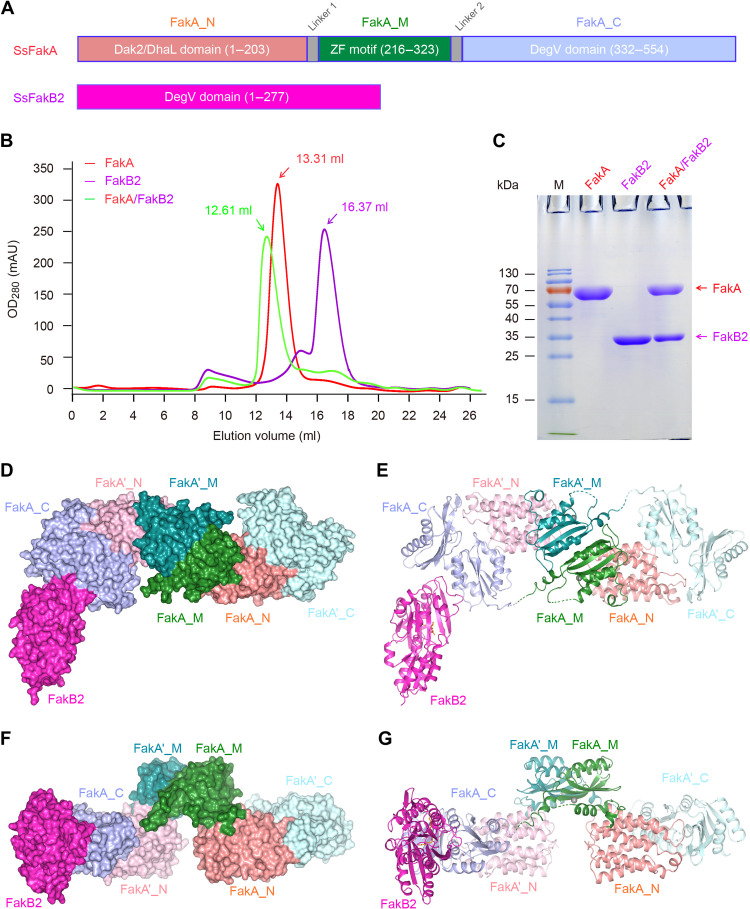
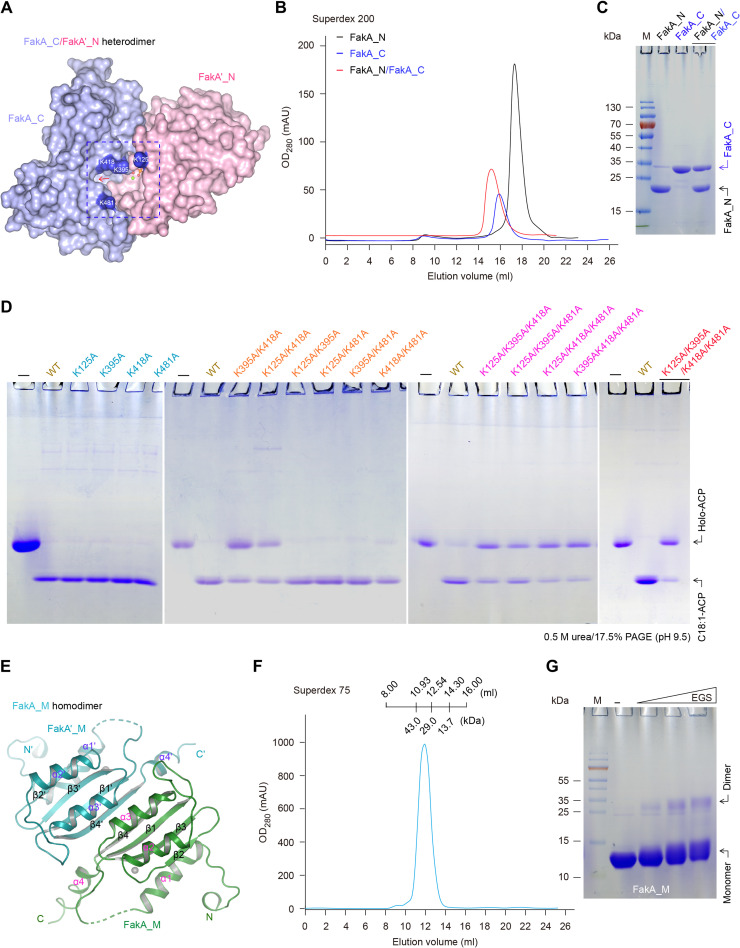
Before this study, we are only aware of five ligand-bound FakB structures, consisting of two S. aureus FakBs [SaFakB1 (20) and SaFakB2 (21)] and three S. pneumoniae FakBs (SpFakB1, SpFakB2, and SpFakB3) (19). To gain further mechanistic insights into Fak activation of host FA assimilation, we attempted to resolve crystal structures of FakA alone and in complex with various partners (FakB1 to FakB3). Along with the full-length FakA (554 residues, ~60 kDa) of SS2, three sets of distinct but related FA-binding proteins (e.g., FakB2) were overexpressed and purified to homogeneity (Fig. 3, A to C). Using a Superdex 200 increase column, gel filtration experiments showed that FakA appears at an elution volume of 13.31 ml, suggesting an apparent molecular weight (~130 kDa) as a dimer form (Fig. 3B). This generally agrees with the fact that FakA does form a dimer in the ethylene glycol bis(succinimidyl succinate) (EGS) cross-linking assay (fig. S2). Size exclusion chromatography revealed that all the three FakB proteins consistently elutes out as a monomer in solution (Fig. 3B and fig. S8). Moreover, FakA and FakB2 formed a stable complex and eluted earlier than FakA alone in gel filtration columns (Fig. 3B). The molar ratio of FakA versus FakB2 is estimated to be around 1:1 in the complex based on the intensity of bands on SDS-PAGE gels (Fig. 3C). Similar results were also obtained with FakA in the presence of either FakB1 (fig. S8, A and B) or FakB3 (fig. S8, C and D).
Fig. 3. Biochemical and structural characterization of FakA-FakB2 complex.
(A) Linear diagrams for SsFakA kinase and SsFakB2, an oleate-binding protein. (B) Gel filtration analysis for FakA binding to FakB2. (C) SDS-PAGE profile of FakA complexed with FakB2. FakA is indicated with a red arrow, and FakB2 is shown with a magenta arrow. Surface illustration [front view in (D), top view in (F)] for the overall structure of the dimeric FakA with one FakB2 bound. Ribbon representation [front view in (E), top view in (G)] of the FakA-FakB2 complex. FakA appears as a dimer. The FakA protomer consists of three subunits, including FakA_N (colored salmon), FakA_M (green), and FakA_C (light blue), respectively. In the other protomer, they are separately designated as FakA′_N (colored pink), FakA′_M (teal), and FakA′_C (light cyan). FakA_C not only interacts with FakB2 (in magenta) but also binds to FakA′_N, producing a heterodimer. In addition, FakA_M forms a homodimer with FakA′_M. The complex structure of FakA-bound FakB2 was deposited under accession number [Protein Data Bank (PDB): 7W7H]. SsFakA, S. suis FakA; DAK2, dihydroxyacetone kinase; DhaL, dihydroxyacetone kinase ADP-binding subunit L; ZF, zinc finger.
We managed to crystalize FakA-FakB2 complex and solved its structure at 2.6 Å (table S1). The space group is P 43 21 2, and each asymmetric unit contains a FakA dimer and one FakB2 molecule (Fig. 3, D to G). FakA consists of three distinct domains (designated FakA_N, FakA_M, and FakA_C; Fig. 3A) and adopts an elongated conformation (Fig. 3, D and F). Two FakA molecules form a dimer in a head-to-tail manner, mostly through interactions between FakA_M/FakA′_M and FakA′_N/FakA_C (Fig. 3, E and G). Unexpectedly, only a single FakB2 molecule binds to one of the FakA_C domains (chain A), and we failed to observe any electron density for the second FakB2, although there is enough space near FakA′_C (chain B) in the crystal packing to accommodate another FakB2 (Fig. 3, D to G). The two FakA molecules are almost identical and appear to be in the same conformation. Presumably, the relatively high concentration of ammonium sulfate (2.4 M) in the crystallization buffer might weaken FakB2-FakA association and drives the crystallization toward a 2:1 (FakA:FakB2) configuration despite that the protein ratio of the complex in solution is 2:2.
Characterization of FakA, a chimeric kinase
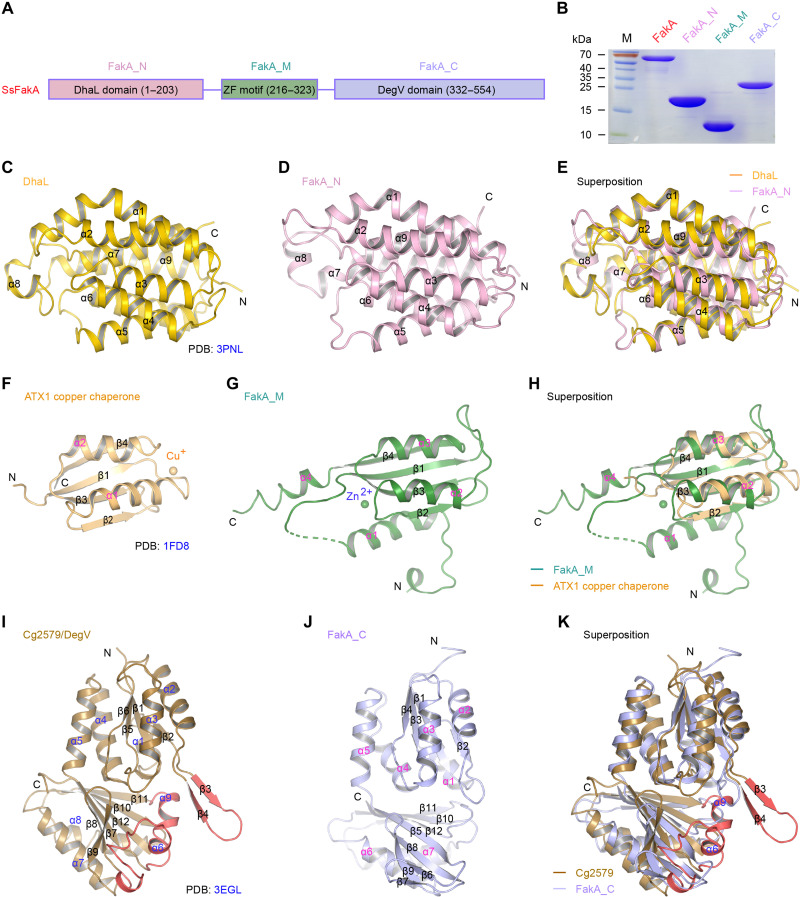
FakA seemed to evolve through the recruitment of three unrelated domains connected by two flexible linkers (Fig. 4A). Briefly, the zinc finger–containing FakA_M (216 to 323 amino acids) is centered by the N-terminal DhaL [dihydroxyacetone kinase adenosine diphosphate (ADP)–binding subunit L] domain (FakA_N, 1 to 203 amino acids) and a DegV subunit at C terminus (FakA_C, 332 to 554 amino acids). Despite that they are tightly associated in the complex structure (Fig. 3, D to G), all three subunits of FakA kinase can be individually expressed and purified (Fig. 4B). The FakA_N domain consists of nine α helices and resembles the DhaL subunit (210 amino acids) of the heterodimeric E. coli dihydroxyacetone kinase (DhaK)–DhaL (Fig. 4, C and D, and fig. S9) (38), although their sequence identity is less than 15%. DALI server–based structural superposition yielded a root mean square deviation (RMSD) of 1.75 Å between DhaL and FakA_N (Fig. 4E and fig. S9E) (39, 40). In DhaK structure, DhaL has Mg2+ and ADP bound (fig. S10A). The alignment of DhaL-Mg2+/ADP with FakA_N showed that (i) the adenine moiety of ADP fits well in a pocket of FakA_N and (ii) the two aspartate residues (D35 and D37) of DhaL that coordinate Mg2+ have two equivalent residues (D37 and D39) in FakA_N (fig. S10B). A similar scenario was also seen with FakA_N from S. aureus [Protein Data Bank (PDB): 7RM7], termed as SaFakA_N (fig. S11). D38 and D40 of SaFakA_N are equivalent to D37 and D39 in FakA_N of S. suis (fig. S11, A to C). Thus, we anticipated that FakA_N is where ATP could likely bind. To test this hypothesis, we created a panel of single mutants of FakA (fig. S10C), namely, D37A, D39A, D39R, D39G, D39E, D39V, D39S, and D39L. Except with D39A, all the remaining mutants markedly lost FakA activity in vitro (fig. S10D). It underscored the physiological relevance of D37 and D39 to the coordination of Mg2+/ATP, a prerequisite for FakA kinase activity. Surprisingly, the D39A mutant was still active, and this indicates that D39A might be able to maintain the local conformation and water molecules could substitute for the carboxyl group oxygen atoms to coordinate Mg2+ (fig. S11B). Together, these results provided structural and functional evidence that FakA_N of S. suis has a similar role as the DhaL subunit of E. coli DhaK (fig. S9, A to D).
Fig. 4. Structural evidence that FakA is reminiscent of the dihydroxyacetone kinase (Dak) system.
(A) Linear scheme for SsFakA kinase consisted of three distinct functional motifs. FakA_M, the ZF motif of 108 residues, is centered between the N-terminal DhaL domain of 203 amino acids (designated FakA_N) and the C-terminal DegV domain of 223 amino acids (termed as FakA_C). (B) Electrophoresis analyses of the full-length FakA protein and its three domains (FakA_N, FakA_M, and FakA_C). (C) Ribbon diagram of the DhaL subunit of the E. coli dihydroxyacetone (Dha) kinase (PDB: 3PNL). (D) FakA_N and DhaL display similar folding patterns. (E) Superposition of FakA_N with DhaL. (F) Solution structure of ATX1 copper chaperone (PDB: 1FD8). (G) Structural characterization of FakA_M domain. (H) Structural alignment of FakA_M domain with ATX1. (I) Crystal structure of DegV-type protein Cg2579 from C. glutamicum, the prototype of palmitic acid–binding protein family (PDB: 3EGL). (J) Ribbon structure of FakA_C. (K) Structural comparison suggests that an extra insert motif (colored red) exists in Cg2579, but not in FakA_C. α, α helix; β, β strand.
FakA_M, the central domain of FakA, is composed of four α helices, four β strands, and several long loops (fig. S12A). Structural comparison with DALI server (39, 40) revealed that FakA_M adopts a similar folding pattern as yeast copper chaperone ATX1, a paradigm metallochaperone/metal-binding protein (Fig. 4F), but has two extra connecting helices (α1 and α4; Fig. 4G). Structural alignment of FakA_M with ATX1 (PDB: 1FD8) yielded an RSMD of 2.53 Å over 65 Cα atoms (Fig. 4, F to H). A “C1H3” zinc finger motif is detected in FakA_M, which is formed by C244, H289, H291, and H226 from β1, β3, and α1 (fig. S12, A and B). FakA_M is connected to FakA_N through α1, the linker region before α1, as well as a few residues from β3 and the loop between β2 and β3 (fig. S12C). The zinc finger motif appears to benefit stapling of FakA_M α3 and β4 regions to its α1 helix, which sits on top of FakA_N (fig. S12C). Mutational analyses determined that three of the four zinc finger residues could affect FakA activity, namely, C244, H289, and H291 (fig. S12D). Therefore, FakA_M most likely plays a structural role in the maintenance of FakA dimerization and its action.
The DegV family refers to a group of diversified FA-binding proteins, which includes distinct FakB members. Although S. suis FakA_C exhibits limited sequence identity (9.2%) to Cg2579 (274 amino acids), a prototypic DegV member from Corynebacterium glutamicum (Fig. 4I), it also seemed to adopt a DegV-like fold (Fig. 4J and fig. S9, C and D). The structural superposition of FakA_C with Cg2579 (PDB: 3EGL) gave an RMSD of 2.59 Å over 192 Cα atoms (Fig. 4K). A similar scenario was also observed in comparison with the DhaK subunit of E. coli DhaK (fig. S9, E and F). Compared with FakA_C, Cg2579 has an extra insertion sequence (β3 and β4) in the loops between α2 and β2, and an α helix insertion (α9) between β11 and β12 (Fig. 4, I to K). In addition, the two short β strands (β6 and β7) in FakA_C are replaced with an α helix (α6) and a flexible loop in Cg2579. Of note, the two insertions as well as the replacement region (colored red in Cg2579) are involved in FA binding (Fig. 4K). In contrast to FakA_C having a relatively shallow and wide hydrophobic pocket (fig. S13A), the extra insertions of Cg2579 enable the formation of a narrow (around 5 Å in diameter) and deep hydrophobic tunnel to accommodate FAs (fig. S13B). Unlike the counterparts in Cg2579, the hydrophobic residues potentially involved in FA binding of FakA_C are relatively closer to each other (fig. S13C), presumably due to the lack of ligands at the current state. Compared with different FA-binding FakBs of S. aureus (20, 21) and S. pneumoniae (19) having known structures (fig. S14, A and B), FakA_C lacks the conserved arginine residue that stabilizes the carboxyl group of FAs at the tunnel entrance (fig. S13C). In contrast, FakA_N interface lysines might play that role. Collectively, the structural organization of three FakA modules suggested that FakA resembles an evolutionary mimic of the DhaK-DhaL kinase system (fig. S9, A to F), and FakA_C acts as a recipient of FAs transferred from FakB in the context of Fak activity (Fig. 3, D to G).
Molecular dissection of FakA dimerization
The dimeric nature of FakA is mainly attributed to the formation of FakA_C/FakA′_N heterodimer (Fig. 5, A to C) and FakA_M homodimer (Fig. 5, E to G). Structural analysis of FakA dimer revealed that the interaction interface between FakA′_N and FakA_C buries an area of 900 Å2 (Fig. 5A). This agreed with the fact that FakA′_N forms a stable complex with FakA_C on a gel filtration column (Fig. 5, B and C). The cross-chain interaction of FakA′_N with FakA_C is categorized into two interfaces, termed interface I and interface II (fig. S15A). Interface I involves FakA′_N residues from α2, α3, α4, loopα3–4, and loopα5–6 with FakA_C residues from α2 and α3. Briefly, (i) N81 forms hydrogen bonds with K395 and M399 main-chain atoms; (ii) R79 interacts with D375 side chain as well as N370 main-chain carbonyl group and M399 side chain inserts into a hydrophobic pocket formed by A122, V123, I85, and V84; and (iii) the two residues (M76 and L75) of FakA′_N α3 also forms hydrophobic contacts with V377 and V402 in FakA_C (fig. S15B). Interface II involves certain residues in FakA_N (loopα1–2 and α8) and those of FakA_C (β6, β5, loopβ5–6, and loopβ11–12). Specifically, (i) E179 forms two hydrogen bonds with the main-chain amide group of D465 and G466, (ii) R460 forms a hydrogen bond with main-chain carbonyl group of FakA′_N N31, and (iii) five residues from FakA_C (I464, I482, I469, L475, and M477) forms a hydrophobic patch and interact with a group of hydrophobic residues in FakA′_N (F33, V176, V35, and V32) (fig. S15C). Not surprisingly, the newly resolved SaFakA_C domain (PDB: 6W6B) is similar to the FakA_C subunit from the S. suis FakA-FakB2 complex (fig. S15D) (41).
Fig. 5. Structural and biochemical analysis for SsFakA dimerization.
(A) Surface diagram for the heterodimer formed by FakA′_N and FakA_C, illustrating a substrate-loading cavity. The substrate-loading cavity is formed by the two domains FakA_C and FakA′_N, which is marked with dashed lines, and indicated with a red arrow. Four critical lysine residues surrounding this cavity are highlighted blue and marked with white letters. Different from K125 occurring in FakA′_N domain, all the other three residues (K395, K418, and K481) are located in the opposite domain FakA_C. (B) Use of size exclusion chromatography to assay binding of FakA_C to FakA′_N. (C) SDS-PAGE (15%) profile for the complex of FakA_C and FakA′_N. (D) Fak-PlsX system–based functional analyses for all the 15 FakA mutants. (E) Ribbon representation of the FakA_M homodimer. (F) Gel filtration analysis of the recombinant FakA_M. (G) EGS-based chemical cross-linking experiments indicated that FakA_M can form a dimer. The symbol “minus” denotes no addition of EGS, and the triangle on the right hand indicates the varied level of EGS (10, 100, and 1000 μM). Gel filtration was conducted with either a Superdex 200 column (B) or a Superdex 75 column (F).
The interdomain association between FakA_C and FakA′_N enables formation of a putative FA substrate–loading cavity (Fig. 5A). Four basic amino acids on the surface surround the entrance of the potential FA-binding pocket, suggesting functional relevance to FakA activity. Among them, three lysine residues (K395, K418, and K481) arise from FakA_C, whereas K125 is located in FakA′_N (Fig. 5A). These lysine residues point to the solvent and appear to be not involved in interdomain interactions. To evaluate their roles, we constructed 15 FakA mutants in total, including 4 single mutants, 6 double mutants, 4 triple mutants, and a quadruple mutant. Before Fak-PlsX system–based enzymatic assay, all the resultant FakA derivatives were overexpressed and purified to homogeneity (fig. S16). None of the single mutants (like K125A) was functionally defective in FakA activity, whereas two of six double mutants lost partial enzymatic activity, namely, K125A/K418 and K395A/K418A (Fig. 5D). All the four triple mutants exhibited functional loss at varied levels, and the quadruple mutant (K125A/K395A/K418A/K481A) was almost completely inactivated (Fig. 5D). These data combined with structural comparison functionally define a substrate channel of FakA that is important in Fak catalysis.
The subunit of FakA_M sits in the middle of FakA and forms an “antiparallel” dimer (Fig. 5E). Structural analysis of FakA indicated that the dimerization of FakA_M is mainly driven by a slew of hydrophobic residues (between α3-to-α3′ and β4-to-β4′) and hydrogen bond networks. The three residues (N315, Y243, and Q300) form hydrogen bonds with backbone atoms of L308′ and G296′ and the carboxyl group of D294′ from the other protomer (fig. S17, A and B). Purified FakA_M alone eluted as a single peak on a Superdex 75 column, displaying an apparent molecular weight of ~30 kDa (Fig. 5F). This was consistent with the fact that a dimeric band appears in our EGS-based chemical cross-linking trials (Fig. 5G). With FakA_M dimer in the middle, the two heterodimeric catalytic domains (FakA′_C-FakA_N and FakA_C-FakA′_N) are fixed in place through FakA_M-FakA_N and FakA′_M-FakA′_N interfaces (Fig. 3, D to G, and fig. S12B). Without FakA_M-FakA′_M dimer, the heterodimers of FakA′_C-FakA_N or FakA_C-FakA′_N would only be connected by flexible loops, independent of each other. The combined structural and functional data suggested that FakA dimerization assures formation of FA substrate–loading tunnel, a prerequisite for FA exchange with its FakB partners.
Insights into FakA-FakB interplay
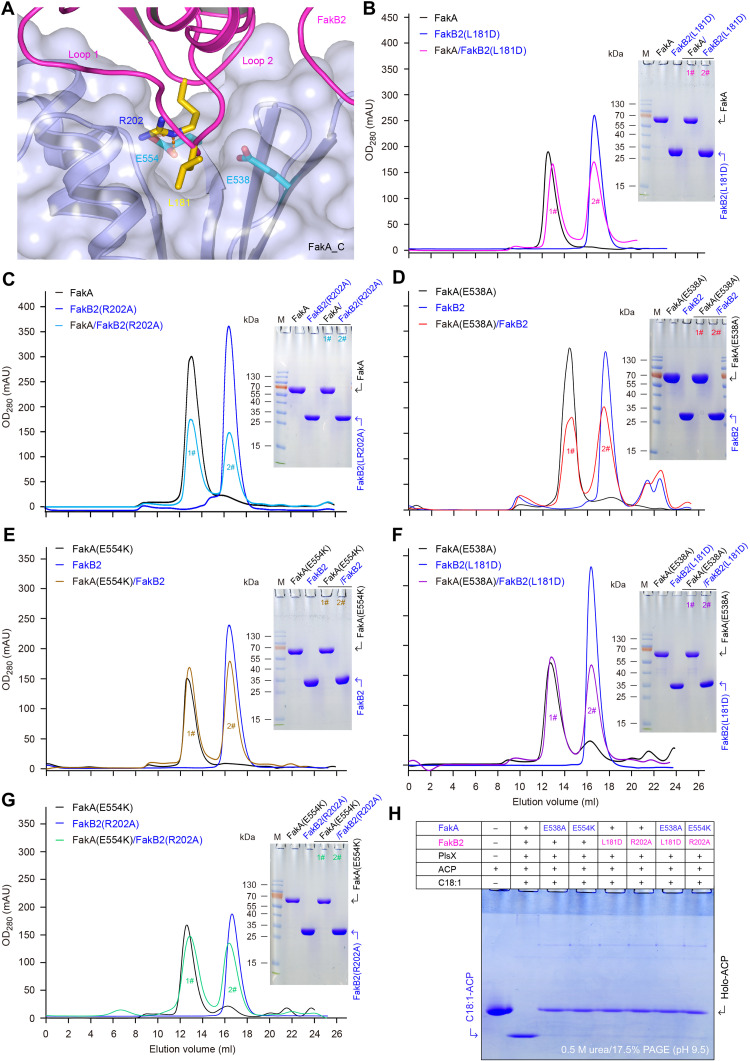
Complex structure of FakA-FakB2 provides a snapshot for the activation of host FA by the Fak machinery. FakA_C is the FakB2-binding subunit (Fig. 6A and fig. S18A). The binding of FakA_C to FakB2 partner involves two interfaces, namely, interface I and interface II (fig. S18, A to C). Purified FakA_C domain formed a stable complex with FakB2 during gel filtrations (fig. S18, D and E), verifying the role of FakA_C as FakB2 partner. Two loops of FakB2 participate in its interaction with FakA_C, namely, loop 1 between α7 and β9 (loopβ9-α7) and loop 2 between β10 and α8 (loopβ10-α8) (Fig. 6A and fig. S18A). First, several residues in loop 1 form an extensive hydrogen bond network with five residues of FakA_C (E538, H540, Q357, D431, and S356). Five conserved hydrophobic residues in loop 1 (L181, L182, M177, V174, and L178) interact with the hydrophobic patch formed by five FakA_C residues (Y511, I353, F424, L427, and V359) (fig. S18B). Second, the residues in loop 2 (α8-β10) adopt a “V” shape and insert into the same V-shaped groove in FakA_C domain (fig. S18C). The V-shaped conformation of loop 2 is stabilized via hydrogen bond networks as well as charge-charge interactions.
Fig. 6. Functional analysis for FakA binding to FakB2.
(A) Enlarged view of FakB2-bound FakA_C. (B) Gel filtration combined with SDS-PAGE revealed that the L181D mutation of FakB2 impairs its ability to bind FakA kinase. (C) Biochemical evidence for an essential role of R202 in FakB2 binding to FakA. (D) Inability of FakA(E538A) mutant to interact with FakB2 protein. (E) E554D substitution of FakA disables its capability of binding FakB2. (F) Gel filtration unveiled that the two mutants, FakA(E538A) and FakB2(L181D), cannot interact with each other. (G) Inability of FakA(E554D) to bind FakB2(R202A). (H) No detectable enzymatic activity for the FakA/FakB2-PlsX system containing mutated FakA (and/or FakB2) components. Conformationally sensitive gel suggested that (i) the in vitro reconstituted system with the wild-type version of FakA/FakB2-PlsX can attach oleic acid to ACP carrier, producing oleyl-ACP with faster migration compared to holo-ACP, and (ii) the site-directed mutagenesis of FakA/FakB2 component markedly impairs the activity to produce oleyl-ACP. This agreed with the fact that FakA fails to bind certain FakB2 mutant and vice versa. The plus (+) symbol denotes the presence of protein (and/or oleic acid) component, whereas the minus (−) represents no addition.
Among them, two pairs of critical residues were selected through fine mapping of FakA-FakB2 interface, namely, E538 and E554 from FakA and L181 and R202 from FakB2 (Fig. 6A). Not only the two residues of E538 and E554 are extremely conserved among FakA homologs (fig. S1) but also the two sites (L181 and R202) are prevalent across various FakB members (figs. S3, S4, and S14). R202 of FakB2 is sandwiched between L428 and I507, and sits on top of the carbon chain of E554 (Fig. 6A and fig. S18C). The guanidino group of R202 is coordinated by the carboxyl group of E554 and Q357 (fig. S18C). To address the importance of the FakA-FakB2 interface, we created four single mutants, FakB2(L181D), FakB2(R202A), FakA(E538A), and FakA(E554K). As expected, the two mutated versions of FakB2, namely, L181D (Fig. 6B) and R202A (Fig. 6C), cannot associate with FakA on the gel filtration column. Accordingly, the two FakA mutants [E538A (Fig. 6D) and E554K (Fig. 6E and fig. S18F)] completely lost the abilities to bind FakB2 partner. Not surprisingly, FakB2(L181D) failed to bind FakA(E538A) (Fig. 6F), and FakB2(R202A) cannot interact with FakA(E554K) (Fig. 6G and fig. S18F). Subsequently, the use of the Fak-PlsX system reconstituted in vitro indicated that each of the aforementioned four single mutations fully abolishes FakA-FakB2 activity (Fig. 6H). These data confirmed that all the four conserved residues (L181 and R202 of FakB2 and E538 and E554 of FakA) are involved in FakB2-FakA interaction, a prerequisite for activation of host oleic acid by the Fak system.
To evaluate whether the specific interface is universal or not, we extended our functional investigation of FakA binding to both FakB1 (fig. S8, A and B) and FakB3 (fig. S8, C and D). Given that both FakB1 and FakB3 display FakA-interacting abilities, sequence alignment of different FakB members enabled us to predict the conserved residues involved in FakA binding. Accordingly, L183 and R205 are detected in FakB1, and L185 plus R207 are proposed for FakB3 (fig. S4). As seen in the superposition/comparison of FakB members with known structures (figs. S14B and S21), the two residues of L185 and R205 in FakB1 (i.e., L185 and R207 in FakB3) are also located at the tip of the V-shaped structure. In general consistency with those of FakB2-FakA (Fig. 6), a single mutation of either L183D (fig. S19A) or R205A (fig. S19B) abolished FakB1-FakA association on the gel filtration column. Similar results were obtained with the two FakB3 derivatives that separately contain an L185D mutation (fig. S19C) or an alanine substitution of R207A (fig. S19D). Further enzymatic analysis revealed that the two FakB1 mutants (L183D and R205A) consistently impair the ability of FakA-FakB1 to activate the bellowed three types of saturated FAs: myristic acid (C14:0; fig. S20A), palmitic acid (C16:0; fig. S20B), and steric acid (C18:0, fig. S20C). As anticipated, none of the two mutations (L185D and R207A) enables FakB3-including Fak machinery to retain the activity of phosphorylating linoleic acids (C18:2; fig. S20D). Together, these results demonstrated that the FakA-FakB interface, of which the critical residues are evolutionarily conserved, is functionally unified across the family of Fak kinase.
Parallels in FA-loading tunnel of FakB
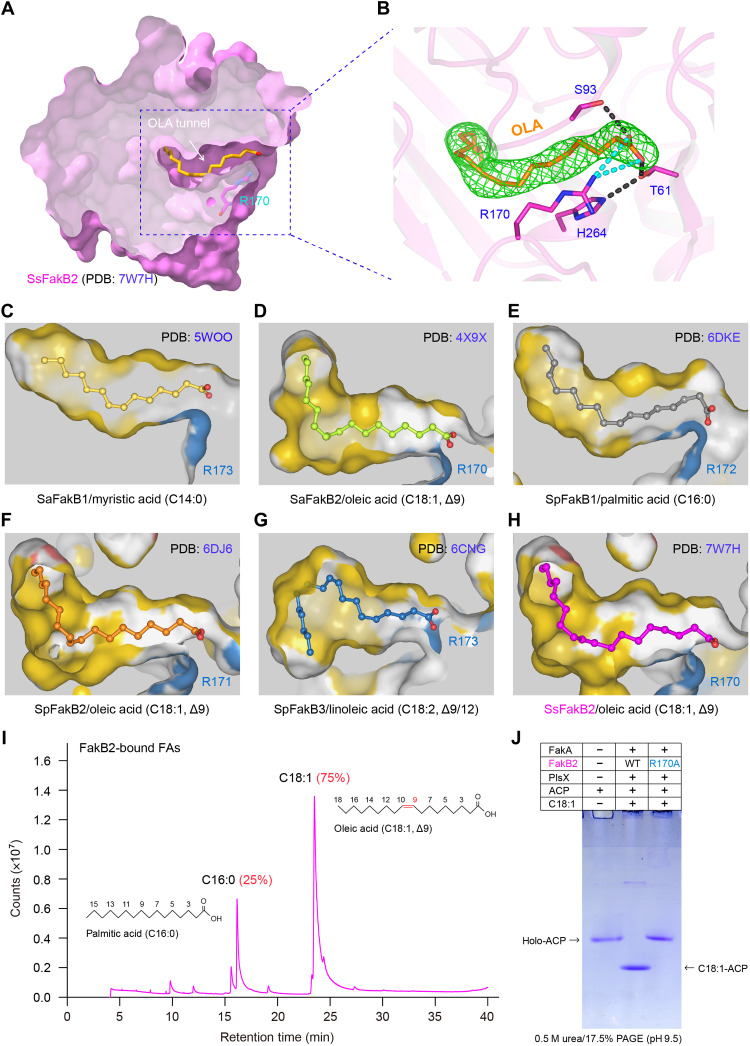
The overall structure of S. suis FakA-FakB2 complex revealed that a single FakB2 monomer is present in the asymmetric unit (table S1). The architecture of SsFakB2 resembles a paradigm DegV member, consisting of two unique domains (fig. S21). First, the N-terminal domain refers to a typical EDD fold (42), connected with a three-stranded antiparallel β sheet along with one α helix. Second, the C-terminal motif is a six-stranded β sheet neighbored by two α helices on one side, and three on the other side (fig. S21F). SsFakB2 is structurally similar to all the other known FakB cousins (FakB1 to FakB3) restricted to S. aureus and S. pneumoniae (fig. S21, A to F). Structural alignment of SsFakB2 with SaFakB2 returned an RMSD of 1.66 Å over 254 Cα atoms (fig. S14B), despite limited sequence identity (29%) that occurred (fig. S14A).
Although we had never added any FA during the process of protein purification, clear electron density of a ligand in FakB2 was observed in the crystal, which we built as oleate, C18:1 (Fig. 7, A and B). As we know, similar surface charge distribution occurs among different FakB isoforms having parallel overall architectures (fig. S21). This assured a common mechanism by which FakB isoforms interchangeably cross-talk with FakA kinase domain (19–21). However, systematic comparison of FakB structures unveiled that the interior FA-loading tunnels are pretty distinguishable in their size and shape, which explains in part, if not all, their distinct FA selectivity and/or preference (Fig. 7, C to H). Briefly, both C14:0-binding cavity of SaFakB1 (PDB: 5WOO) and C16:0-occuping channel of SpFakB1 (PDB: 6DKE) are relatively short, and of gently curved shape. A notable variation of the two channels denotes a kink at the mouth of tunnel that appears in SpFakB1 (Fig. 7E), but not in SaFakB1 (Fig. 7C). Similar to the counterparts in SaFakB2 (Fig. 7D) and SpFakB2 (Fig. 7F), the C18:1-loading pocket within SsFakB2 features with a kinked cavity of L shape, which is suitable to accommodate the double bond in the middle of oleate (Fig. 7H). Not surprisingly, a unique gourd-like tunnel is located within the SpFakB3 interior, benefiting its adaption to the folded-back shape of linoleic acid with two double bonds (Fig. 7G).
Fig. 7. Identification of an oleate-loading tunnel from SsFakB2 and its comparison with the counterparts in diverse FakB proteins.
(A) Sliced view of the substrate oleic acid (C18:1, Δ9)–loading tunnel of SsFakB2. (B) Fo-Fc omit map contoured at 2.0σ for the oleic acid molecule occupied within SsFakB2. (C) Sliced view of the myristic acid (C14:0)–loading cavity within SaFakB1 (PDB: 5WOO). (D) Structural insight into the oleic acid (C18:1, Δ9)–recognizing pocket of SaFakB2 (PDB: 4X9X). (E) Structural snapshot for the palmitic acid (C16:0)–loading tunnel from SpFakB1 protein (PDB: 6DKE). (F) Structural visualization for the oleic acid (C18:1, Δ9)–occupied funnel from SpFakB2 (PDB: 6DJ6). (G) Structural illustration for the linoleic acid (C18:1, Δ9/12)–binding tunnel within SpFakB3 (PDB: 6CNG). (H) Structural characterization of the oleate-loading pocket from SsFakB2 (PDB: 7W7H). (I) GC analysis suggested the presence of oleic acids predominantly bound in the FakB2 protein. (J) The FakB2 (R170A) substitution inactivates the ability of FakA/FakB2-PlsX in transferring exogenous oleic acids to ACP carrier.
Like the other two known FakB2, the C18:1 ligand sits in a deep hydrophobic tunnel inside SsFakB2 (Fig. 7). This generally agrees with our observation that C18:1 is predominantly bound by FakB2 (Fig. 7I). The carboxyl group of C18:1 is coordinated by a group of conserved residues (H264, T61, and S93) through extensive hydrogen bond networks (Fig. 7B). Of note, the positively charged R170 is presumed to stabilize the negatively charged carboxyl group of oleic acid via electrostatic interactions (Fig. 7B). In addition to its equivalents, R170 in SaFakB2 (Fig. 7, D and H) and R171 in SpFakB2 (Fig. 7F), other FakB isoforms also harbor this conserved residue, namely, R173 in SaFakB1 (Fig. 7C), R172 in SpFakB1 (Fig. 7E), and R173 in SpFakB3 (Fig. 7G). Given the fact that it consistently locates at the entrance of FA tunnel, we speculated that R170 might have a critical role in extracellular FA fixation, essential for Fak activity. To test this prediction, we prepared three mutated FakB isoforms with origin of S. suis (fig. S22). Namely, they included FakB1(R172A) (fig. S22A), FakB2(R170A) (fig. S22B), and FakB3(R174A) (fig. S22C). All the three mutant proteins remained to be monomeric in solution (fig. S22). Enzymatic analysis confirmed that a single R170A mutation of FakB2 abolishes full activity of FakA-FakB2 machinery with oleic acids (Fig. 7J). As expected, Fak kinase system failed to facilitate the activation of different saturated FAs (C14:0, C16:0, and C18:0) in the presence of FakB1(R172A) mutant (fig. S23A). Similarly, the FakA-FakB3(R174A) mixture lost its enzymatic activity with linoleic acids (fig. S23B). Collectively, our results represented a functional and structural proof for FA-binding tunnel paralleled in various FakB isoforms.
Activation of host oleate by the FakA-FakB2 system
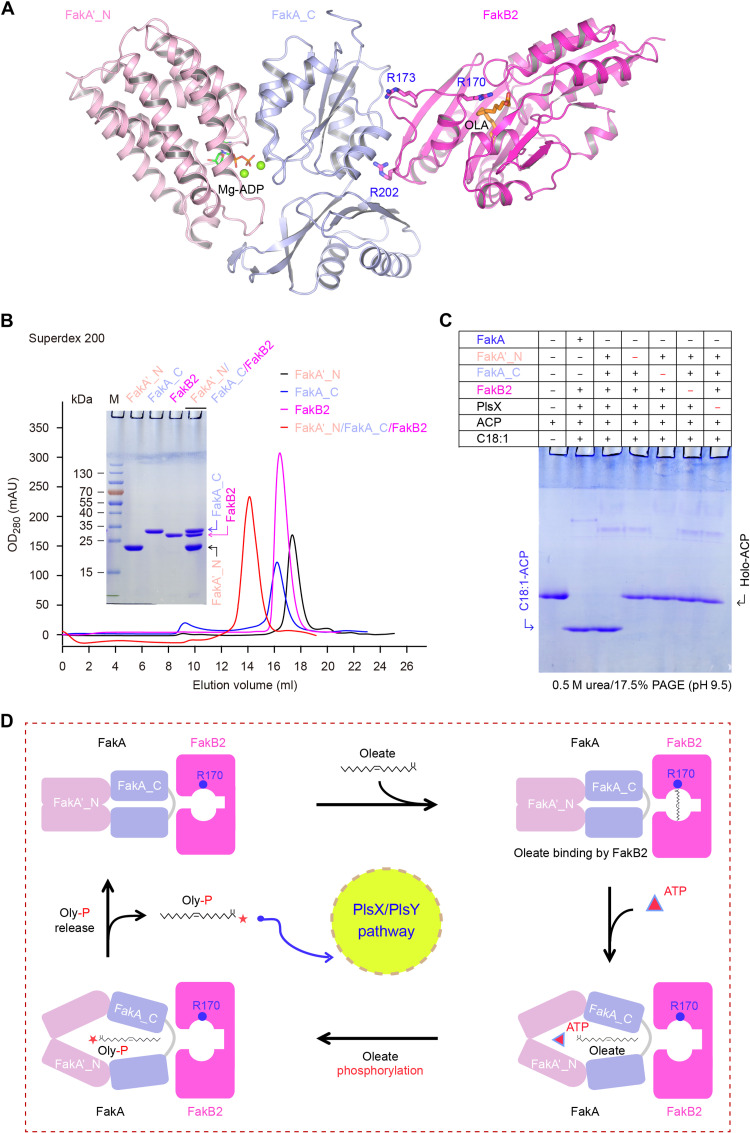
Regardless of the FakA_M domain (Figs. 3 to 5), FakA_C can interact with FakA′_N at its two binding interfaces (Fig. 5 and fig. S15), formulating a FA substrate–loading pocket (Fig. 5A). Along with the fact that FakA_C subunit is a FakB2 partner (fig. S18), this prompted us to speculate that the two disconnected domains (FakA_N and FakA_C) can form a heterotrimer with FakB2 protein (Fig. 8A), reproducing full-length FakA activity for oleate activation. As predicted, the mixture of three components (FakA_N, FakA_C, and FakB2) formed a stable complex on a gel filtration column (Fig. 8B). The two subunits of FakA_N and FakA_C did reconstitute Fak kinase activity in vitro, giving an oleyl-ACP product in the presence of PlsX (Fig. 8C), whereas no oleyl-ACP was produced, if neither FakA_C nor FakA_N was supplemented (Fig. 8C). Thus, we propose a working model for oleate activation by the FakA-FakB2 machinery as follows (Fig. 8D): Oleate loading induces conformational alteration of FakB2 in adaption to binding FakA. The interaction of FakB2 with FakA_C involves its two conserved residues (R202 and L182). Connection of FakA_C with FakA′_N relies on two contact surfaces (Fig. 8D and fig. S15). The occupation of FakA′_N by Mg2+/ATP would likely lead to expansion of its ATP-binding pocket and loops, which results in the movement of the two domains of FakA_C connected to FakA′_N (figs. S10B and S15). One of the FakA_C domains associates with a loop in FakB2 where R170 is located (Fig. 8A and fig. S18B, interface I). It is possible that the expanded FakA_C subunit further triggers the movement of R170 and renders FakB2 to release the bound oleate (Fig. 8D). As we stated earlier, FakA′_N and FakA_C form a heterodimer in parallel to that of DhaK/DhaL kinase. Here, FakA′_N accounts for ATP-binding and FakA_C recognizes the FA substrate (Fig. 8D). The released oleate molecule could fit into the pocket formed by FakA_C and FakA′_N where many hydrophobic residues reside (figs. S13 and S15, B and C). The compact FakA_C (no extra insertions compared to FakBs) allows its binding to a wide range of FAs. The pocket formed by FakA′_N and FakA_C is also where the γ-phosphate of ATP is transferred to oleate carboxyl group (Fig. 8D). Release of products allows FakA′_N, FakA_C, and FakB2 to revert to their initial states. The phosphorylated oleate (Oly-P) is subsequently transferred to the PlsX/PlsY system for phospholipid synthesis (Fig. 8D). It is reasonable that this proposal might partially explain the recognition and utilization of other saturated (and/or polyunsaturated) FAs by streptococcal Fak kinase machinery.
Fig. 8. A working model for oleate phosphorylation by Fak kinase system.
(A) Ribbon structure illustrating the interplay of FakA_C with both FakA′_N and FakB2. As for FakB2, three critical residues are highlighted, namely, (i) R170 required for fixation of oleate carboxyl group and (ii) R202 and R173 interacting with FakA_C domain. Mg-ADP is modeled into FakA_N′ based on the DhaL–Mg-ADP structure (PDB: 3PNL). (B) Gel filtration analysis of the ternary complex of FakA′_N, FakA_C, and FakB2. The inside gel denotes the protein identity. Size exclusion chromatography was conducted with a Superdex 200 increase column. (C) The in vitro reconstituted Fak system in which the full-length FakA is replaced with its two separated domains (FakA′_N plus FakA_C) retains the ability to produce oleyl-ACP. Given the fact that FakA_C binds to both FakA′_N domain and its partner FakB2, we attempted to test if the two domains (FakA′_N plus FakA_C) can partially replace the dimeric FakA in vitro. Relative to the full-length FakA (60 nM), each of the two domains (FakA′_N plus FakA_C) was supplemented at 500 to 600 nM in this in vitro reconstituted system. (D) Assignment of putative reaction steps to oleate phosphorylation by the FakA-FakB2 system.
DISCUSSION
The emergence and rapid dissemination of antimicrobial resistance [such as tetM (43) and tetO (44)]–producing SS2 variants might compromise the clinical effectiveness of tigecycline, a “last resort” antibiotic (45–47). As a successful zoonotic pathogen, S. suis has evolved certain mechanisms to undergo the transition between carrier/asymptomatic and disease/virulent stages (48). In particular, host factors (especially FAs-rich blood serum) are hijacked to stimulate the production of bacterial virulence factors. Lopez and coworkers (49) found that (i) certain host FAs activate the expression of type VII secretion system (T7SS), a well-known virulence weapon in the major human pathogen S. aureus, and (ii) the sensing and incorporation of exogenous FAs into bacterial membrane is exclusively dependent on the Fak kinase system. The T7SS apparatus also facilitates streptococcal colonization, virulence, and disease development (50, 51). We might ask the question whether the zoonotic pathogen S. suis requires the Fak machinery to carry out its cross-talk with hosts. However, how SS2 senses the host environment and scavenges FAs at the infection site remains unclear. It is reasonable that a functional characterization of the S. suis Fak system might facilitate the discovery of attractive targets against SS2 interspecies transmission and virulence, considering the limited availability of specific antivirulence therapy against deadly SS2 infections.
The structural and biochemical study of the S. suis Fak kinase complex reported here represents an important step toward understanding how the streptococcal pathogens scavenge host FAs for survival and successful infection. The overall structure of SsFakA kinase appears as a domain-swapped dimer (Fig. 3 and fig. S24), mimicking domain organization of certain DhaK to some extent (fig. S9). It is known that the DhaK kinase transfers a phosphate group to Dha, producing Dha phosphate (DhaP) (52). In general, the phosphoryl moiety arises from either (i) ATP molecule or (ii) phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) molecule. Unlike the Citrobacter freundii DhaK (CfDhaK) that relies on ATP (53), the E. coli DhaK/DhaL subunit along with a third phosphoryl carrier DhaM features a PEP-dependent kinase complex (38). The E. coli DhaK/DhaL is a heterotetramer formed by a heterodimer of DhaK/DhaL (fig. S24A). The CfDhaK comprises an N terminus Dha_K domain fused with its C terminus Dha_L domain by a loop, and exhibits a domain-swapped homodimer (fig. S24B). The domain organization of CfDhaK is different from FakA in that the N terminus of CfDhaK is equivalent to FakA_C, and the C-terminal DhaL domain is similar to FakA′_N. By contrast, the domain-swapped organization of FakA_C/FakA′_N catalytic center resembles the E. coli DhaK/DhaL complex rather than CfDhaK kinase (fig. S24C). The three kinases (E. coli DhaK/DhaL, CfDhaK, and SsFakA) consistently feature a dimeric structure fulfilled with two catalytic centers, giving an advantage of efficient catalysis. Different from the E. coli DhaK/DhaL and CfDhaK, which both exploit the DhaK motif for dimerization (Fig. 4, A and B), SsFakA has evolved a specialized subunit FakA_M to dimerize (Fig. 4C). The in vitro reconstituted Fak-PlsX assay suggested that the FakA_M domain is not required for FA activation (Fig. 8C). One explanation could be that the DhaK equivalent, FakA_C, is required to form a heterodimer with FakB2 and not able to dimerize with another FakA_C at the same time. Another advantage of using a separate FakA_M domain for dimerization might be that even if FakA_C/FakA′_N undergoes large conformational changes during reaction, FakA would remain as a dimer, assuring its dynamic stability. Therefore, FakA seems to have several essential elements from the DhaK family protein and then recruits a panel of DegV-like FakB members for FA binding. The highly conserved FakA_N domain is found in all three systems, indicating its critical role in binding ATP/ADP and acting as a phosphate donor. On the other hand, although the core fold of FakA_C is similar to the DhaK domain of EcDhaK/CfDhaK, it is much simpler and more closely related to DegV family (Fig. 4, I to K, and fig. S9E), indicating a possibility that it is more suitable for FA substrate delivered by FakB family members. Structural and functional snapshot of FakA_C-FakB2 interaction reported here represents an important expansion of our knowledge on host FA scavenging by bacterial pathogens.
It was noted that individual domain structures of SaFakA_C (PDB: 6W6B) and SaFakA_N–Mg-ADP (PDB: 7RM7) were released during the revision of this manuscript (41). Overall, the SaFakA_C structure alone is similar to SsFakA_C in the SsFakA-FakB2 complex, and the major differences lie in the interface I and II regions, which are involved in binding to FakA′_N (fig. S15). SaFakA_N–Mg-ADP is nearly identical to SsFakA_N, with the loop between α1 and α2 (loops 1 and 2) in SsFakA′_N shifted upward (fig. S11), which largely supports our working model proposed for FakA action (Fig. 8D). Also, Subramanian and coworkers (41) speculated that FakM has a catalytic triad (C240, H282, and H284) based on AlphaFold prediction. By contrast, the equivalent residues (C244, H226, H289, and H289) of SsFakA_M form a zinc finger (fig. S12), unlikely acting as a catalytic center. In addition, in our complex structure of FakA-FakB2, the ATP-binding site of FakA_N is away from FakA_M. Thus, Subramanian et al.’s hypothesis of FakA_M as a catalytic center based on individual domains is questionable considering the overall arrangement of the complex. As we observed, FakA_M plays important structural roles in the organization of FakA-FakB2 complex as well as its enzymatic activity (fig. S12).
The FakA-FakB system is an evolutionarily conserved apparatus by which exogenous FAs are activated and then used within the phylum Firmicutes. A single FakA subunit is consistently present, whereas the number of FakB belonging to DegV family (COG1307) varies markedly in individual members of Firmicutes. Database mining combined with sequence alignment allowed us to provisionally group the FakB variants into five subtypes (FakB1 to FakB5; fig. S1A). Of these, FakB4 and FakB5 are two predicted FakB homologs without functional assignment, warranting further experimental validation. Not surprisingly, a proteome-wide interaction screen of S. pneumoniae TIGR4 revealed that not only FakA (SP_0443) binds to FakB2 (SP_1112; fig. S1) but also PlsX (SP_0037) (54). This finding suggests a metabolic link between the Fak system and membrane phospholipid synthesis. Compared with S. pneumoniae TIGR4, Streptococcus agalactiae 2603V/R lacks FakB3 but retains FakB4 (SAG0211; fig. S1B). Surprisingly, two species of Enterococcus that contain four FakB paralogs contain a previously unidentified FakB5 (e.g., EF_1191 for Enterococcus faecalis V583) in place of FakB3 (fig. S1). FakB5 displays limited similarity (less than 27.1%) to the four FakB proteins of S. suis 05ZYH33, it is of much interest to investigate the biochemical roles of the two newly identified FakB members (FakB4 and FakB5) in extracellular FA selectivity. Collectively, these findings indicate unexpected complexity of the Fak system, suggesting diverse recognition, but convergent activation, of extracellular FA pools.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and growth conditions
SS2 and E. coli were used in this study. In addition to the wild-type strain of S. suis (i.e., 05ZYH33), two isogenic mutants were generated, namely, FYJ902 (ΔfakB1) and FYJ903 (ΔfakB2) (table S2). The S. suis strains were cultivated on THB agar plates or liquid THB medium at 37°C. If necessary, 10% swine serum was supplemented. The THB medium was purchased from RPI (Research Products International). Except for DH5α that acted as a cloning host, all the other E. coli strains were derived from BL21(DE3) for production of various recombinant proteins (table S2). The strain FYJ582 (BL21 carrying pET28a::aasS) was used to prepare AasS, which subsequently functioned as the positive control in our enzymatic assays for Fak activity. The strain DK574 carrying pJT93 was an E. coli dedicated to overexpress holo form of ACP (55). Apart from the fakA-expressing strain FYJ571, three additional strains were engineered to make distinct FakB isoforms, namely, FYJ572 for FakB1, FYJ573 for FakB2, and FYJ5700 for FakB3 (table S2). Unlike the FakB isoform (B1 to B3) that has single mutants, FakA was designed to create a variety of mutants (single to quadruple). The three strains of FYJ5131, FYJ5132, and FYJ5133 were constructed to express different domains of FakA, namely, FakA_N, FakA_M, and FakA_C (table S2). FYJ5134 was the E. coli strain that we engineered to produce PlsX, the FakA partner (table S2). In general, most of the E. coli strains were kept on LB (Luria-Bertani) agar plates or LB liquid medium at 37°C. When required to acquire soluble proteins, the growth temperature was reduced to 16°C, and appropriate antibiotics were added as follows: kanamycin (50 μg/ml) and ampicillin (100 μg/ml).
Molecular manipulations
Homologous recombination was used to knock out fakB1 (and/or fakB2) from the 05ZYH33 strain of SS2. Briefly, the upstream and downstream region (~1 kb) of fakB1 (and/or fakB2) was amplified with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and inserted directionally into the suicide vector pUC19-Spc, giving pUC19::fakB1-LSR (and/or pUC19::fakB2-LSR), the knockout plasmid for fakB1 (and/or fakB2) (table S2). The resultant plasmid was electroporated into competent cells of 05ZYH33 strains, and the spectinomycin-resistant colonies were determined with multiplex PCR (table S3). The mutant of ΔfakB1 (and/or ΔfakB2) was further confirmed with sequencing of the PCR products. The genes encoding fakA and/or fakB were introduced into expression vector to produce recombinant protein. Except for fakB3 that was inserted into pET21(a) to give pET21a::fakB3, all the other fakB isoforms and fakA were cloned into pET28(a), generating pET28a::fakB1, pET28a::fakB2, and pET28a::fakA, respectively (table S2). In particular, three domains of FakA (FakA_N, FakA_M, and FakA_C) were engineered via homologous recombination strategy into the expression vector by using PCR with three sets of specific primers (table S3). The resultant plasmids included pET21a::fakA_N, pET21a::fakA_M, and pET28a::fakA_C, respectively (table S2).
Structure-guided site-directed mutagenesis was routinely conducted with fakA and three fakB (B1 to B3) members. Briefly, as for fakA(E538A), a pair of specific primers that carries a certain point mutation [i.e., fakA(E538A)-F and fakA(E538A)-R] was introduced into the system of PCR with a wild-type fakA-bearing plasmid as a template. The resultant PCR products were purified and then digested with Dpn I (New England Biolabs Inc.) to eliminate the trace plasmid template, which was followed by transformation into DH5α-competent cells. Eventually, the acquired colonies of interest were subjected to Sanger DNA sequencing. Three types of point mutations were generated for each of three fakB isoforms (table S2), whereas the mutations of fakA were categorized into four groups, namely, 10 single mutants like E554K, 6 double mutants (such as K125A/K395A), 4 triple mutants (e.g., K125A/K395A/K418A), and 1 quadruple mutant of K125A/K395A/K418A/K481A (fig. S2). Using the homologous recombination strategy (table S3), the locus SSU05_0024 that encodes PlsX was inserted into the pET28(a) vector, yielding pET28a::plsX. Before functional assays, all these recombinant plasmids were verified with direct DNA sequencing.
Evaluation of S. suis growth
Given that swine serum is rich in diverse FAs, bacterial growth of S. suis on the routine cultivation condition was compared with that of the condition with the addition of porcine serum. Two methods are involved: (i) growth curves in liquid THB medium and (ii) series dilution on THB solid agar plates. Briefly, an epidemic strain 05ZYH33 of SS2 and its two isogenic mutants (ΔfakB1 plus ΔfakB2) were inoculated on THB agar plate at 37°C overnight. As for each strain, three single colonies were transferred to 2 ml of fresh THB (and/or 10% porcine serum plus THB) medium and kept in a shaker (180 rpm) at 37°C. The bacterial growth was monitored for over 14 hours. Using a spectrophotometer (Spectrum Lab, S32A), the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) was measured at a regular 1-hour internal, except for the initial value recorded at the second hour. In addition, liquid cultures of S. suis were adjusted to OD600 of 1.2 and spotted (8 μl each) on THB agar plates alone (or supplemented with 10% porcine serum) in series of 10-fold dilution (10−1 to 10−6). The size of single SS2 colony on different growth conditions was evaluated.
GC-MS identification of FAs
To evaluate the alteration of membrane lipid composition by swine serum, the phospholipids of S. suis were extracted. Log-phage culture (20 ml) of SS2 grown in THY [THB containing 2% yeast extract (OXOID)] medium with or without swine serum was harvested (40-mg weight) and washed with 1× phosphate-buffered saline three times. The bacterial cells were suspended in 1 ml of solution I (45 g of sodium hydroxide, 150 ml of methanol, and 150 ml of ddH2O). The samples were gently shaken and then incubated at 100°C for 5 min. FA saponification proceeded via 0.5-hour incubation at the same temperature. For FA methylation, the samples were subjected to 10 min of incubation at 80°C, followed by the treatment with 2 ml of solution II (325 ml of 6 N hydrochloric acid and 275 ml of methanol). Then, the FA methyl esters were extracted by adding 1.25 ml of solution III (200 ml of n-hexane and 200 ml of methyl tert-butyl ether). Last, the resultant organic phase containing lipids on the bottom was washed with 3 ml of solution IV (1.08 g of sodium hydroxide dissolved by 90 ml of ddH2O), transferred to a clean glass tube, and dried under nitrogen evaporation.
The dried sample was dissolved with 50 μl of chloroform and injected into an Agilent HP-5MS column (30 m by 0.25 mm by 0.25 μm) on a GC-MS system (Agilent Technologies,7890B-7000C). The GC conditions were set as follows: injection volume, 1 μl; constant speed, 1 ml/min; injection temperature, 270°C; split ratio, 20:1. Column temperature program was described as follows: initial temperature of 50°C, 2 min; temperature of 200°C, 10 min; temperature of 215°C, 8 min; and final temperature of 270°C, 5 min. The MS parameters were set as follows: detector temperature 250°C; scan range (m/z) 50 to 550 Da. The identities of various FA methyl esters were verified by comparing their retention times with a panel of standard FAs (Sigma-Aldrich).
Similarly, the FA profile of swine serum and FakB2-bound FAs was characterized. Briefly, swine serum (~1 ml) and FakB2 protein (10 mg/ml) were treated identically as conducted with bacterial membrane lipids and identified with GC-MS.
Protein expression, purification, and gel filtration
In total, 40 proteins (and/or domains) were overexpressed and purified for the reconstitution of protein complex as well as enzymatic assays. In addition to the two well-studied tool proteins, V. harveyi AasS (14) and holo-ACP carried (56), they included 25 FakA derivatives [1 wild type, 21 mutants, and 3 FakA domains (FakA_N, FakA_M, and FakA_C)], 12 versions of three FakB isoforms (B1 to B3; 1 wild type and 3 single mutants each), and PlsX. In general, the midlog phase culture (OD600: 0.6 to 0.8) of BL21 carrying the aforementioned expression plasmid (table S2) was induced at 16°C in 1 liter of LB medium containing 0.3 to 0.5 mM isopropyl β-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG) for around 12 hours. The bacterial cells were collected by centrifugation (7000 rpm, 20 min) at 4°C, washed once with wash buffer [20 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 300 mM NaCl, and 5% glycerol], resuspended with binding buffer [20 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 300 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 20 mM imidazole, and 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF)], and then subjected to two rounds of lysis with mini-French press (JNBIO, Guangzhou, China). After removing bacterial debris by 0.5 hours of centrifugation (16,800 rpm, at 4°C), the supernatant was incubated for 0.5 hours with Nickel–nitrilotriacetic acid agarose beads (QIAGEN) equilibrated with binding buffer. Following 3× column volumes of wash with washing buffer [20 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 300 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 50 mM imidazole, and 1 mM PMSF], the Fak (and/or PlsX) protein was eluted with elution buffer [20 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 300 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 300 mM imidazole, and 1 mM PMSF].
The acquired protein was checked with SDS-PAGE (12 or 15%) and dialyzed with the GF buffer [20 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, and 2 mM dithiothreitol (DTT)]. To examine whether FakA binds its partner, the mixture of FakA and distinct FakB isoforms (B1 to B3) was subjected to size exclusion chromatography using a Superdex 200 increase column (GE). Similarly, gel filtrations with a Superdex 200 increase column were also conducted with the potential Fak mixtures as follows: (i) FakA_N/FakA_C, (ii) FakA_N/FakA_C/FakB2, (iii) FakA mutants/FakB (B1 to B3), (iv) FakA/FakB mutants (B1 to B3), and (v) FakA mutants/FakB mutants (B1 to B3). In addition, a Superdex 75 column (GE) was used to probe the dimerization of FakA_M subunit due to its small size. All the protein samples collected from representative peaks of gel filtration were analyzed with SDS-PAGE (12 or 15%). The purified proteins were stored at −80°C before the enzymatic assays.
In vitro reconstituted Fak-PlsX system
To detect Fak activity, an in vitro reconstituted Fak-PlsX system was established. The Fak-PlsX system consisted of two successive steps, termed step I and step II. In principle, step I is dedicated to formation of FA-P intermediate, and step II is destined to acyl-ACP product. In general, step I proceeded in a 50-μl reaction system [containing 100 mM tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 20 mM MgCl2, 10 mM ATP, 1 mM FA, 30 to 60 nM FakA, and 300 to 500 nM FakB] at 37°C for 1 hour (20). Subsequently, step II (50 μl in total) began with the reaction mixture of step I (30 μl) supplemented with a second reaction mixture (20 μl) that included 5 mM DTT, 4 μg of ACP, and 400 nM PlsX (22). Following 1-hour incubation of step II at 37°C, the reaction mixtures (10 μl) were separated with conformationally sensitive gel of 0.5 M urea/17.5% PAGE (pH 9.5). The acyl-ACP product was supposed to migrate faster than its reactant holo-ACP. It was noted that aforementioned steps I and II can proceed in a single test tube within half an hour, offering an alternative reaction process for the Fak-PlsX system.
Oleate (C18:1) was applied to detect the in vitro activity of FakA-FakB2, three saturated FAs (C14:0, C16:0, and C18:0) substrates were tested for FakB1, and linoleic acid (C18:2) was examined for FakB3. In addition to series of FakA mutants with defects in either catalysis or FakB recognition, a panel of FakB mutants devoid of either FA loading or FakA interaction was introduced into the in vitro reconstituted Fak-PlsX system to determine their roles in Fak activities. To see if they are functionally equivalent, a modified Fak-PlsX system was established, in which the full-length FakA (30 to 60 nM) was replaced with its two interacting subunits of FakA_N and FakA_C at relatively high concentration (500 to 600 nM each). The positive control here referred to the acylated ACP species by AasS (14, 36), and the reaction system proceeded at 37°C for 1 hour, comprising the following components: 0.4 mM FA, 100 mM tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 10 mM MgSO4, 10 mM ATP, 5 mM DTT, 4 μg of ACP, and 0.2 μg of AasS.
Crystallization, data collection, and structural determination
To explore crystallization conditions suitable for FakA-FakB (B1 to B3), the harvested bacterial cells that separately produced FakA and different FakB isoforms were lysed in a lysis buffer [containing 20 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl, 10 mM imidazole, 0.1 mM PMSF, 10% glycerol, and 0.3 mM tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP)]. Following nickel affinity pull-down, both FakA and various FakB samples were sequentially purified by anion exchange and gel filtration chromatography. Peak fractions of FakA or FakB (B1 to B3) were collected and concentrated to around 20 mg/ml in a buffer containing 20 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl, and 0.3 mM TCEP. Before crystal screen, all the concentrated samples were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored in −80°C.
The purified proteins of FakA and FakB (B1 to B3) were mixed in a 1:1.2 molar ratio and injected into a Superdex 200 increase column. FakA-FakB (B1 to B3) complex fractions were pooled, concentrated to 15 mg/ml, and then subjected to crystallization screens. Screen kits were purchased from Hampton Research, including (i) Crystal Screen, (ii) Index Crystallization Screen, (iii) PEG/Ion Screen, (iv) PEGRx, and (v) Natrix. FakA-FakB complex (0.2 μl) and reservoir solution (0.2 μl) were mixed on 96-well plates, sealed, and stored at 16°C. The use of hanging-drop vapor diffusion method enabled microcrystals of FakA-FakB2 to appear from a condition of Index A6 [100 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.5) and 2.0 M ammonium sulfate] after 2 weeks. To improve these crystals, 1 μl of FakA-FakB2 complex was mixed with 1 μl of reservoir solution on a cover slide that was sealed over 1 ml of well buffer [100 mM tris-HCl (pH 8.5), 2.4 M ammonium sulfate, and 0.3 mM TCEP]. The resultant crystals were harvested and cryoprotected with reservoir solution supplemented with 30% glycerol and flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen for x-ray diffraction.
Diffraction data were collected at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility in China beamline BL17U1 at a wavelength of 0.9792 Å at 100 K. Data were indexed, integrated, and scaled using the XDS and CCP4 program Pointless and Aimless (57–59). For molecular replacement with Phaser (60), initial models of SsFakA and SsFakB2 were generated with AlphaFold (61) and manually curated. After multiple rounds of molecular replacement search, two copies of SsFakA and one copy of SsFakB2 were found, and the structural models were built using Coot and refined using PHENIX (62). The statistics of the data collection and refinement are shown in table S1. Structural graphs were generated using PyMOL (The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0, Schrödinger, LLC) and UCSF Chimera (63).
LC-MS of phosphorylated oleic acid
To acquire enough amount of phosphorylated form of oleic acid, oleyl-P, the FakA-FakB2 reaction system (2 ml in total) was established and maintained at 37°C for 2 hours. The reaction components contained 100 mM tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 20 mM MgCl2, 10 mM ATP, 1 mM oleic acid, 100 nM FakA, and 1 mM FakB2. Then, 7.2 ml of chloroform/methanol/HCl (1:2:0.2) and 2.4 ml of chloroform were successively added to the reaction mixture. Vigorous vortex and spin enabled phase separation (of note, organic phase in bottom). After washing twice respectively by 2.4 ml of 2 M KCl and ddH2O, the organic phase was dried under nitrogen evaporation.
To detect oleyl-P, LC-MS was performed as recently described by Parsons et al. (18) with little change. Briefly, 3 μl of sample (dissolved in 100 μl of methanol) was injected into ACQUITY UPLC HSS-T3 column (1.8 μm, 2.1 × 150 mm; Waters Corp.) on a Waters UPLC system (Waters Corp, Milford, MA, USA) connected with AB Triple TOF 5600+ System (AB SCIEX, Framingham, USA). The mobile phases were 0.1% formic acid–water (A) and 0.1% formic acid–methanol (B). The chromatographic parameters were set as follows: (i) linear gradient programs, 0/5, 35/95, and 42/95 (min/B%); (ii) column oven temperature, 50°C; (iii) flow rate, 0.3 ml/min; and (iv) ultraviolet detector, 254 nm. The optimal MS/MS conditions were described as follows: (i) negative ion mode; (ii) source voltage, −4.5 kV; (iii) source temperature, 550°C; (iv) a cycle of full scan, 1 s; (v) collision energy, 40 ± 20 V; (vi) ion release delay, 67; and (vii) ion release width (IRW), 25. The scan range of m/z of precursor ion and product ion was set as 100 to 1500 Da and 50 to 1500 Da, respectively.
MALDI-TOF determination of acyl-ACP
As AasS catalyzes the acylation of ACP (14), the in vitro reconstituted Fak-PlsX system could modify ACP to give an array of acyl-ACP species (18, 19, 21). Namely, they corresponded to (i) myristoyl-ACP (C14:0-ACP), (ii) palmitoyl-ACP (C16:0-ACP), (iii) steroyl-ACP (C18:0-ACP), (iv) oleyl-ACP (C18:1-ACP, Δ9), and (v) linoleyl-ACP (C18:2-ACP, Δ9/12). The use of conformationally sensitive gel of 0.5 M urea/17.5% PAGE (pH 9.5) rendered the various acyl-ACP products distinguishable from the ACP reactant. After the removal of contaminated proteins by precipitation with cold isopropyl alcohol, the reaction mixtures were resuspended with 0.2 ml of ammonium acetate (20 mM) and then dialyzed overnight in a 200-ml solution of 20 mM ammonium acetate at 4°C.
Following concentration by freeze-drying, the purified acyl-ACP species were subjected to matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization–time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) as routinely recommended by manufacturer (Bruker, ultraflextreme). Briefly, the sample was dissolved with 50 μl of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid and then mixed with an equal volume of SA2 solution (saturated solution of sinapic acid in 30% acetonitrile). One microliter of the mixed solution was placed on the substrate thin layer [1 μl of matrix SA1 solution (saturated solution of sinapic acid in ethanol) on the MALDI target plate] and kept dry naturally. Samples were tested with positive ion mode, and the resultant data were analyzed with flexAnalysis software.
LC-MS identification of acyl-ACP
To finely localize the acylated residue of ACP, LC-MS was conducted as described with the BioZ reaction (64). Five acyl-ACP thioesters were analyzed by LC-MS: (i) three species for FakB1 (C14:0-ACP, C16:0-ACP, and C18:0-ACP), (ii) an oleyl-ACP (C18:1-ACP, Δ9) for FakB2, and (iii) linoleyl-ACP (C18:2-ACP, Δ9/12) for FakB3. First, the acyl-ACP bands of interest were cut from the urea/PAGE gel and digested with pepsin (rather than the routine trypsin). Then, the resultant peptide mixture was injected into the trap column (Thermo Fisher Scientific Easy-nLC 1000) before its entry into an analytical column (50 μm × 15 cm, nanoViper, C18, 2 μM,100 Å). Together with FTMS (Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass) analyzer, Thermo LTQ-Orbitrap Elite Ion Trap analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) was applied in data collection. Using the software of Proteome Discoverer 2.0, database search enabled numbers of MS spectrum to match certain peptides arising from acylated ACP with reliable value (65).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the beamline staff of BL17U1 at Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility (SSRF) for help with data collection and Y. Xu (Analysis Center for Agrobiology and Environmental Sciences, Zhejiang University) for technical assistance in mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS and MALDI-TOF). We thank laboratory members (H. Ye, S. Lei, K. Ji, L. Liu, J. Ma, and L. Su) for their help on this project.
Funding: This work was supported by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholar (32125003, to Y.F.), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32141001, 81772142 and 31830001, to Y.F.; 22193061, to H.L.), and the Research Fund of Non-coding RNA and Drug Discovery Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu Medical College (FB20-01, to Y.F.).
Author contributions: Y.F., C.Z., and H.L. designed the research. Y.F., Y.S., C.Z., N.Z., N.L., H.Z., H.L., Y.X., M.H., and J.S. conducted the research and analyzed the data. Y.F., C.Z., H.Z., Y.S., and H.L. wrote the paper.
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Data and materials availability: The coordinates and structure factors of FakA-FakB2 complex of S. suis were deposited in the RCSB Protein Data Bank with accession code: 7W7H. All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper and/or the Supplementary Materials. Bacterial strains of S. suis 05ZYH33 and recombinant plasmids carrying either fakA or fakB are provided by Zhejiang University pending scientific review and a completed material transfer agreement (MTA). Requests for the strains and plasmids should be submitted to Y.F. (fengyj@zju.edu.cn).
Supplementary Materials
This PDF file includes:
Tables S1 to S3
Figs. S1 to S24
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Yao J., Rock C. O., How bacterial pathogens eat host lipids: Implications for the development of fatty acid synthesis therapeutics. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 5940–5946 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Campbell J. W., Cronan J. E. Jr., Bacterial fatty acid biosynthesis: Targets for antibacterial drug discovery. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 55, 305–332 (2001). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Raetz C. R., Reynolds C. M., Trent M. S., Bishop R. E., Lipid A modification systems in Gram-negative bacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 76, 295–329 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Parsons J. B., Frank M. W., Subramanian C., Saenkham P., Rock C. O., Metabolic basis for the differential susceptibility of Gram-positive pathogens to fatty acid synthesis inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 15378–15383 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McMurry L. M., Oethinger M., Levy B., Triclosan targets lipid synthesis. Nature 394, 531–532 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Heath R. J., Yu Y. T., Shapiro M. A., Olson E., Rock C. O., Broad spectrum antimicrobial biocides target the FabI component of fatty acid synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 30316–30320 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dessen A., Quémard A., Blanchard J. S., Jacobs W. R. Jr., Sacchettini J. C., Crystal structure and function of the isoniazid target of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science 267, 1638–1641 (1995). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chollet A., Mourey L., Lherbet C., Delbot A., Julien S., Baltas M., Bernadou J., Pratviel G., Maveyraud L., Bernardes-Génisson V., Crystal structure of the enoyl-ACP reductase of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (InhA) in the apo-form and in complex with the active metabolite of isoniazid pre-formed by a biomimetic approach. J. Struct. Biol. 190, 328–337 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brinster S., Lamberet G., Staels B., Trieu-Cuot P., Gruss A., Poyart C., Type II fatty acid synthesis is not a suitable antibiotic target for Gram-positive pathogens. Nature 458, 83–86 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Balemans W., Lounis N., Gilissen R., Guillemont J., Simmen K., Andries K., Koul A., Essentiality of FASII pathway for Staphylococcus aureus. Nature 463, E3 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rock C. O., Jackowski S., Pathways for the incorporation of exogenous fatty acids into phosphatidylethanolamine in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 12720–12724 (1985). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nunn W. D., Simons R. W., Transport of long-chain fatty acids by Escherichia coli: Mapping and characterization of mutants in the fadL gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 3377–3381 (1978). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nunn W. D., Colburn R. W., Black P. N., Transport of long-chain fatty acids in Escherichia coli. Evidence for role of fadL gene product as long-chain fatty acid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 167–171 (1986). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jiang Y., Chan C. H., Cronan J. E., The soluble acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase of Vibrio harveyi B392 is a member of the medium chain acyl-CoA synthetase family. Biochemistry 45, 10008–10019 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Byers D. M., Holmes C. G., A soluble fatty acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase from the bioluminescent bacterium Vibrio harveyi. Biochem. Cell Biol. 68, 1045–1051 (1990). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yao J., Dodson V. J., Frank M. W., Rock C. O., Chlamydia trachomatis scavenges host fatty acids for phospholipid synthesis via an acyl-acyl carrier protein synthetase. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 22163–22173 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yao J., Bruhn D. F., Frank M. W., Lee R. E., Rock C. O., Activation of exogenous fatty acids to acyl-acyl carrier protein cannot bypass FabI Inhibition in Neisseria. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 171–181 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Parsons J. B., Broussard T. C., Bose J. L., Rosch J. W., Jackson P., Subramanian C., Rock C. O., Identification of a two-component fatty acid kinase responsible for host fatty acid incorporation by Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 10532–10537 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gullett J. M., Cuypers M. G., Frank M. W., White S. W., Rock C. O., A fatty acid-binding protein of Streptococcus pneumoniae facilitates the acquisition of host polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. 294, 16416–16428 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cuypers M. G., Subramanian C., Gullett J. M., Frank M. W., White S. W., Rock C. O., Acyl-chain selectivity and physiological roles of Staphylococcus aureus fatty acid-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 294, 38–49 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Broussard T. C., Miller D. J., Jackson P., Nourse A., White S. W., Rock C. O., Biochemical roles for conserved residues in the bacterial fatty acid-binding protein family. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 6292–6303 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lu Y. J., Zhang Y. M., Grimes K. D., Qi J., Lee R. E., Rock C. O., Acyl-phosphates initiate membrane phospholipid synthesis in Gram-positive pathogens. Mol. Cell 23, 765–772 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yao J., Rock C. O., Exogenous fatty acid metabolism in bacteria. Biochimie 141, 30–39 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yao J., Rock C. O., Phosphatidic acid synthesis in bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1831, 495–502 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Delekta P. C., Shook J. C., Lydic T. A., Mulks M. H., Hammer N. D., Staphylococcus aureus utilizes host-derived lipoprotein particles as sources of fatty acids. J. Bacteriol. 200, e00728-17 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Adams F. G., Trappetti C., Waters J. K., Zang M., Brazel E. B., Paton J. C., Snel M. F., Eijkelkamp B. A., To make or take: Bacterial lipid homeostasis during infection. mBio 12, e0092821 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Teoh W. P., Chen X., Laczkovich I., Alonzo F. III, Staphylococcus aureus adapts to the host nutritional landscape to overcome tissue-specific branched-chain fatty acid requirement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 118, e2022720118 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ridder M. J., Daly S. M., Triplett K. D., Seawell N. A., Hall P. R., Bose J. L., Staphylococcus aureus fatty acid kinase FakA modulates pathogenesis during skin infection via proteases. Infect. Immun. 88, e00163-20 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Frank M. W., Yao J., Batte J. L., Gullett J. M., Subramanian C., Rosch J. W., Rock C. O., Host fatty acid utilization by Staphylococcus aureus at the infection site. mBio 11, e00920-20 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Segura M., Fittipaldi N., Calzas C., Gottschalk M., Critical Streptococcus suis virulence factors: Are they all really critical? Trends Microbiol. 25, 585–599 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Staats J. J., Feder I., Okwumabua O., Chengappa M. M., Streptococcus suis: past and present. Vet. Res. Commun. 21, 381–407 (1997). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Feng Y., Zhang H., Wu Z., Wang S., Cao M., Hu D., Wang C., Streptococcus suis infection: An emerging/reemerging challenge of bacterial infectious diseases? Virulence 5, 477–497 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Feng Y., Zhang H., Ma Y., Gao G. F., Uncovering newly emerging variants of Streptococcus suis, an important zoonotic agent. Trends Microbiol. 18, 124–131 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lun Z. R., Wang Q. P., Chen X. G., Li A. X., Zhu X. Q., Streptococcus suis: An emerging zoonotic pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 7, 201–209 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.van Opijnen T., Camilli A., A fine scale phenotype-genotype virulence map of a bacterial pathogen. Genome Res. 22, 2541–2551 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jiang Y., Morgan-Kiss R. M., Campbell J. W., Chan C. H., Cronan J. E., Expression of Vibrio harveyi acyl-ACP synthetase allows efficient entry of exogenous fatty acids into the Escherichia coli fatty acid and lipid A synthetic pathways. Biochemistry 49, 718–726 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zou Q., Dong H., Zhu L., Cronan J. E., The Enterococcus faecalis FabT transcription factor regulates fatty acid biosynthesis in response to exogeneous fatty acids. Front. Microbiol. 13, 877582 (2022). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Shi R., McDonald L., Cui Q., Matte A., Cygler M., Ekiel I., Structural and mechanistic insight into covalent substrate binding by Escherichia coli dihydroxyacetone kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 1302–1307 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Holm L., Rosenstrom P., Dali server: Conservation mapping in 3D. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, W545–W549 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Holm L., Laakso L. M., Dali server update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, W351–W355 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Subramanian C., Cuypers M. G., Radka C. D., White S. W., Rock C. O., Domain architecture and catalysis of the Staphylococcus aureus fatty acid kinase. J. Biol. Chem. , 101993 (2022). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kinch L. N., Cheek S., Grishin N. V., EDD, a novel phosphotransferase domain common to mannose transporter EIIA, dihydroxyacetone kinase, and DegV. Protein Sci. 14, 360–367 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dong X., Chao Y., Zhou Y., Zhou R., Zhang W., Fischetti V. A., Wang X., Feng Y., Li J., The global emergence of a novel Streptococcus suis clade associated with human infections. EMBO Mol. Med. 13, e13810 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Palmieri C., Varaldo P. E., Facinelli B., Streptococcus suis, an emerging drug-resistant animal and human pathogen. Front. Microbiol. 2, 235 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Umar Z., Chen Q., Tang B., Xu Y., Wang J., Zhang H., Ji K., Jia X., Feng Y., The poultry pathogen Riemerella anatipestifer appears as a reservoir for Tet(X) tigecycline resistance. Environ. Microbiol. 23, 7465–7482 (2021). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sun J., Chen C., Cui C. Y., Zhang Y., Liu X., Cui Z. H., Ma X. Y., Feng Y., Fang L. X., Lian X. L., Zhang R. M., Tang Y. Z., Zhang K. X., Liu H. M., Zhuang Z. H., Zhou S. D., Lv J. N., du H., Huang B., Yu F. Y., Mathema B., Kreiswirth B. N., Liao X. P., Chen L., Liu Y. H., Plasmid-encoded tet(X) genes that confer high-level tigecycline resistance in Escherichia coli. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 1457–1464 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ji K., Xu Y., Sun J., Huang M., Jia X., Jiang C., Feng Y., Harnessing efficient multiplex PCR methods to detect the expanding Tet(X) family of tigecycline resistance genes. Virulence 11, 49–56 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Murray G. G. R., Charlesworth J., Miller E. L., Casey M. J., Lloyd C. T., Gottschalk M., Tucker A. W. (D.), Welch J. J., Weinert L. A., Genome reduction is associated with bacterial pathogenicity across different scales of temporal and ecological divergence. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38, 1570–1579 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lopez M. S., Tan I. S., Yan D., Kang J., McCreary M., Modrusan Z., Austin C. D., Xu M., Brown E. J., Host-derived fatty acids activate type VII secretion in Staphylococcus aureus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 114, 11223–11228 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Taylor J. C., Gao X., Xu J., Holder M., Petrosino J., Kumar R., Liu W., Höök M., Mackenzie C., Hillhouse A., Brashear W., Nunez M. P., Xu Y., A type VII secretion system of Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. Gallolyticus contributes to gut colonization and the development of colon tumors. PLOS Pathog. 17, e1009182 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Lai L., Dai J., Tang H., Zhang S., Wu C., Qiu W., Lu C., Yao H., Fan H., Wu Z., Streptococcus suis serotype 9 strain GZ0565 contains a type VII secretion system putative substrate EsxA that contributes to bacterial virulence and a vanZ-like gene that confers resistance to teicoplanin and dalbavancin in Streptococcus agalactiae. Vet. Microbiol. 205, 26–33 (2017). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Erni B., Siebold C., Christen S., Srinivas A., Oberholzer A., Baumann U., Small substrate, big surprise: Fold, function and phylogeny of dihydroxyacetone kinases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 890–900 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Siebold C., Arnold I., Garcia-Alles L. F., Baumann U., Erni B., Crystal structure of the Citrobacter freundii dihydroxyacetone kinase reveals an eight-stranded alpha-helical barrel ATP-binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 48236–48244 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Meier M., Sit R. V., Quake S. R., Proteome-wide protein interaction measurements of bacterial proteins of unknown function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 477–482 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Cronan J. E., Thomas J., Bacterial fatty acid synthesis and its relationships with polyketide synthetic pathways. Methods Enzymol. 459, 395–433 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Flugel R. S., Hwangbo Y., Lambalot R. H., Cronan J. E. Jr., Walsh C. T., Holo-(acyl carrier protein) synthase and phosphopantetheinyl transfer in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 959–968 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Evans P. R., Murshudov G. N., How good are my data and what is the resolution? Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 69, 1204–1214 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kabsch W., XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 125–132 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Winn M. D., Ballard C. C., Cowtan K. D., Dodson E. J., Emsley P., Evans P. R., Keegan R. M., Krissinel E. B., Leslie A. G. W., McCoy A., McNicholas S. J., Murshudov G. N., Pannu N. S., Potterton E. A., Powell H. R., Read R. J., Vagin A., Wilson K. S., Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 67, 235–242 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.McCoy A. J., Grosse-Kunstleve R. W., Adams P. D., Winn M. D., Storoni L. C., Read R. J., Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Cryst. 40, 658–674 (2007). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Jumper J., Evans R., Pritzel A., Green T., Figurnov M., Ronneberger O., Tunyasuvunakool K., Bates R., Žídek A., Potapenko A., Bridgland A., Meyer C., Kohl S. A. A., Ballard A. J., Cowie A., Romera-Paredes B., Nikolov S., Jain R., Adler J., Back T., Petersen S., Reiman D., Clancy E., Zielinski M., Steinegger M., Pacholska M., Berghammer T., Bodenstein S., Silver D., Vinyals O., Senior A. W., Kavukcuoglu K., Kohli P., Hassabis D., Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596, 583–589 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Liebschner D., Afonine P. V., Baker M. L., Bunkóczi G., Chen V. B., Croll T. I., Hintze B., Hung L. W., Jain S., McCoy A. J., Moriarty N. W., Oeffner R. D., Poon B. K., Prisant M. G., Read R. J., Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C., Sammito M. D., Sobolev O. V., Stockwell D. H., Terwilliger T. C., Urzhumtsev A. G., Videau L. L., Williams C. J., Adams P. D., Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: Recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 75, 861–877 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pettersen E. F., Goddard T. D., Huang C. C., Couch G. S., Greenblatt D. M., Meng E. C., Ferrin T. E., UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612 (2004). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Zhang S., Xu Y., Guan H., Cui T., Liao Y., Wei W., Li J., Hassan B. H., Zhang H., Jia X., Ouyang S., Feng Y., Biochemical and structural characterization of the BioZ enzyme engaged in bacterial biotin synthesis pathway. Nat. Commun. 12, 2056 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ren J., Sang Y., Tan Y., Tao J., Ni J., Liu S., Fan X., Zhao W., Lu J., Wu W., Yao Y. F., Acetylation of lysine 201 inhibits the DNA-binding ability of PhoP to regulate Salmonella virulence. PLOS Pathog. 12, e1005458 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Tables S1 to S3
Figs. S1 to S24