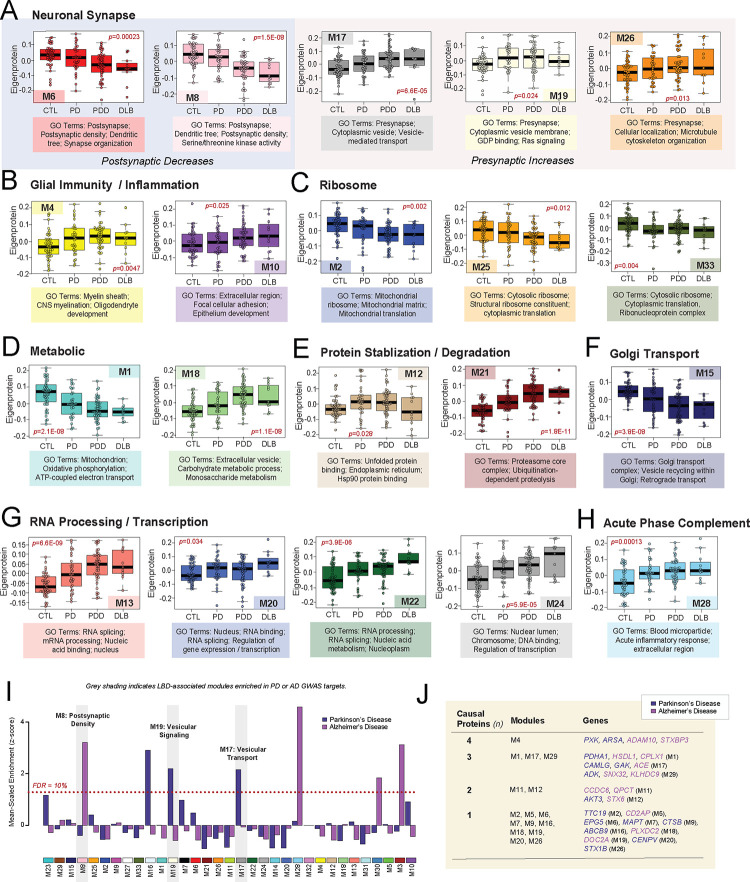
Figure 2. Module abundances of UPenn LBD network reflect significant disease-associated alterations across diverse biological ontologies.
(A-I) Abundance levels (eigenproteins) of select modules across control and disease groups with their top associated biological ontologies. ANOVA p values are provided for each abundance plot. All modules depicted were significantly altered (p<0.05) across the four groups. Box plots represent the median and 25th and 75th percentiles, while data points up to 1.5 times the interquartile range from the box hinge define the extent of error bar whiskers. (J) Module enrichment of PD (dark blue) and AD (purple) genetic risk factor proteins identified by GWAS. The dashed red line indicates a z score of 1.28, above which enrichment was significant (p=0.05) with an FDR of <10%. Gray shading indicates those modules with significant LBD-associated alterations in disease that were also significantly enriched with GWAS targets. Modules are ordered by relatedness as showed in Fig. 1D. (K) Table highlighting modules containing proteins identified by integrative multi-omic analysis as maintaining a causal role in PD (dark blue) and AD (purple). Abbreviations: FDR, false discovery rate.