Abstract
Many neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by cellular deposits such as Abeta, Tau, alpha-synuclein, and huntingtin. The ability to image alpha-synuclein deposits in the human brain is essential to support diagnosis and research for Parkinson’s disease. This patent application describes the development of novel small molecules showing high affinity to alpha-synuclein.
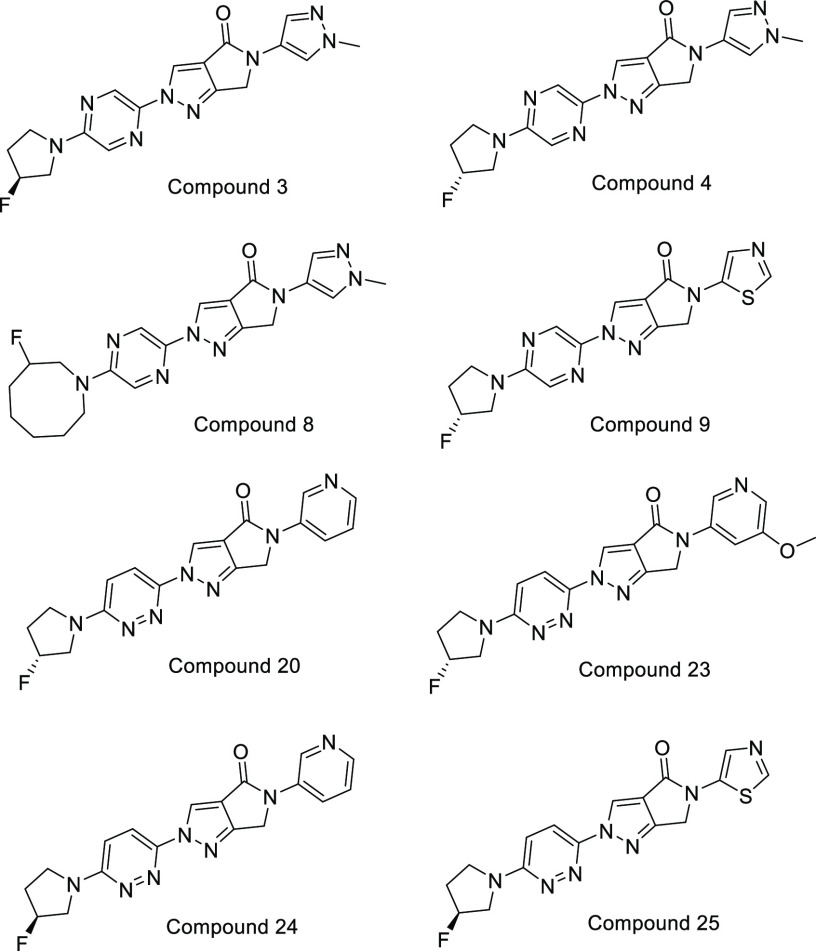
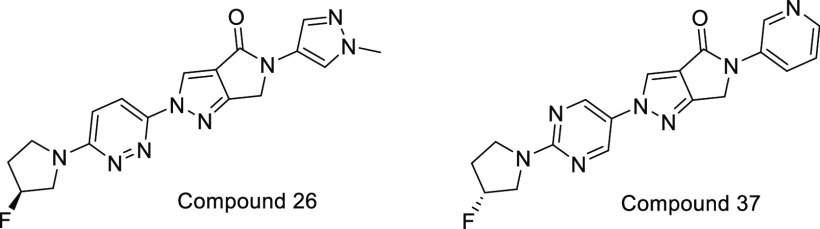
Important Compound Classes

Title
Dihydropyrrolo[3,4-C]pyrazole Derivatives and Their Use in Diagnosis
Patent Publication Number
WO 2023/083961 Al
URL
https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2023083961A1/en?oq=WO+2023%2f083961+Al
Publication Date
May 19, 2023
Priority Application
EP2021-207636
Priority Date
November 10, 2021
Inventor
Molette, J.
Assignee Company
AC Immune SA
Disease Area
Parkinson’s disease
Biological Target
Alpha-synuclein aggregates
Summary
Many neurodegenerative diseases are characterized by cellular deposits such as Abeta, Tau, alpha-synuclein, and huntingtin. The ability to image alpha-synuclein deposits in the human brain is essential to support diagnosis and research for Parkinson’s disease. This patent application describes the development of novel small molecules showing high affinity to alpha-synuclein.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
Compounds were assessed for their
potency to compete with the binding of a tritiated reference alpha-synuclein
ligand to Parkinson’s disease patient brain-derived alpha-synuclein
aggregates. The results of the microradiobinding competition assay
for the determination of binding affinity are given in the table below.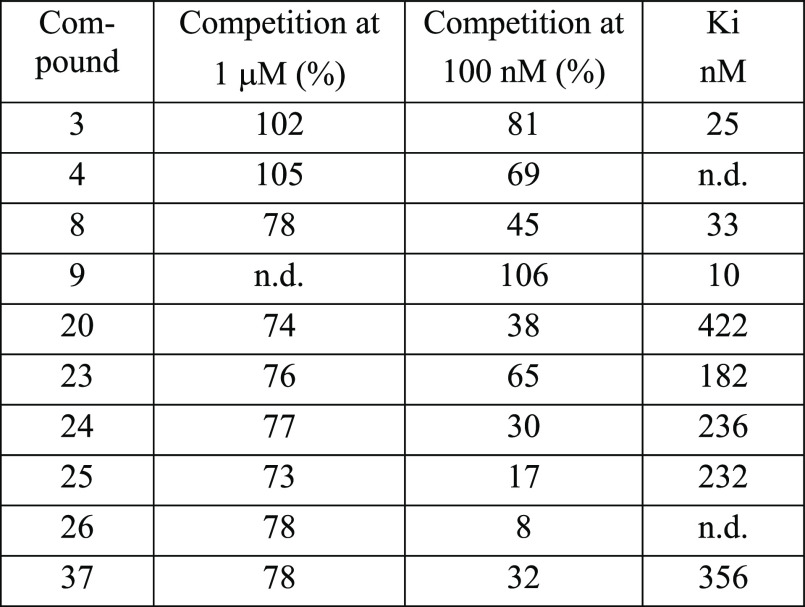
Claims
37 compounds are exemplified
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
References
- Tofaris G. K. Initiation and progression of α-synuclein pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79 (4), 210. 10.1007/s00018-022-04240-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nwabufo C. K.; Aigbogun O. P. Diagnostic and therapeutic agents that target alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2022, 269 (11), 5762–5786. 10.1007/s00415-022-11267-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]