Abstract
Provided herein are novel emopamil-binding protein (EBP) inhibitors, their pharmaceutical compositions, the use of such compounds in treating multiple sclerosis, and processes for preparing such compounds.
Important Compound Classes

Title
Emopamil-Binding Protein Inhibitors and Uses Thereof
Patent Publication Number
WO 2023/164063 A1
Publication Date
August 31, 2023
Priority Application
US 63/314,095
Priority Date
February 25, 2022
Inventors
Gilfillan, R.; Himmelbauer, M.; Gonzalez Lopez De Turiso, F.; Lin, E. Y. S.; Pattaropong, V.; Xin, Z.; Chen, T. Y.; Jones, J. H.; Bansal, N.
Assignee Company
Biogen Ma Inc., USA
Disease Area
Multiple sclerosis
Biological Target
Emopamil-binding protein (EBP)
Summary
Emopamil-binding protein (EBP) is a Δ8−Δ7 sterol isomerase enzyme which isomerizes the double bond in sterol molecules, moving the double bond from the 8–9 position to the 7–8 position. Specifically, EBP converts either zymostenol to lathosterol or zymosterol to dehydrolathosterol during the biosynthesis of cholesterol. It has been shown that an accumulation of 8–9 unsaturated sterols activates oligodendrocyte formation and remyelination.
Myelin is a lipid-based molecule which forms protective layers (myelin sheathes) around nerve cell axons and insulates the axons. Demyelinating diseases, or myelin-related diseases, are a result of these sheathes being damaged, degraded, or reduced in thickness. The loss of the myelin sheathes disrupts the electronic signals from the brain and can lead to nerve damage, vision loss, numbness, muscle weakness, cognitive decline, loss of motor functions, and other similar symptoms. In some myelin-related diseases, such as multiple sclerosis, a subject’s immune system targets and breaks down their own myelin sheathes. The ability to repair and regenerate the myelin sheathes is key to treating these myelin-related diseases. Due to its function converting 8–9 sterols, inhibition of EBP is a potential target for activating remyelination, as its inhibition leads to an increase of these 8–9 sterol starting materials.
The present application describes a series of novel emopamil-binding protein (EBP) inhibitors for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Further, the application discloses compounds, their preparation, use, and pharmaceutical composition, and treatment.
Definitions
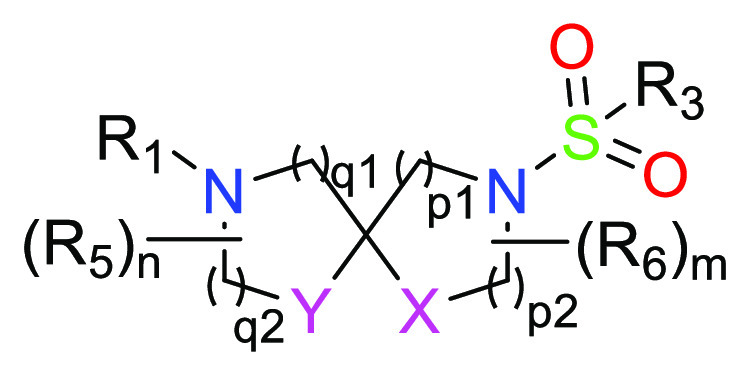
X = CH2 or O; Y = CH2 or O;
R1 = C2–6alkyl, Het, or -Z-Het, wherein C2–6alkyl is optionally substituted with one or more RA and Het is optionally substituted with one or more R2;
R3 = C1–6alkyl-phenyl, phenyl, 5 or 6-membered monocyclic heteroaryl, or 9 or 10-membered bicyclic heteroaryl, wherein phenyl, 5 or 6-membered monocyclic heteroaryl, and 9 or 10-membered bicyclic heteroaryl is optionally substituted with one or more substituent R4;
R5 = H, halo, C1–3alkyl or C1–3haloalkyl;
R6 = H, halo, C1–3alkyl or C1–3haloalkyl;
q1 = 1 or 2;
q2 = 0 or 1 when Y = CH2, or q2 = 2 when Y = O;
p1 = 1 or 2;
p2 = 0 or 1 when X = CH2, or p2 = 2 when X = O; and
m = 1 or 2; n = 1 or 2.
Key Structures
Biological Assay
The EBP functional assay was performed. The compounds described in this application were tested for their ability to inhibit EBP. The EBP IC50 values (nM) are shown in the following table.
Biological Data
The table below shows representative compounds that were tested for EBP inhibition and the biological data obtained from testing representative examples. For IC50, + + + means <100 nM.
Claims
Total claims: 72
Compound claims: 67
Pharmaceutical composition claims: 1
Method of treatment claims: 4
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
References
- Long T.; Debler E. W.; Li X. Structural enzymology of cholesterol biosynthesis and storage. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2022, 74, 102369. 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madan B.; Virshup D. M.; Nes W. D.; Leaver D. J. Unearthing the Janus-face cholesterogenesis pathways in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 196, 114611. 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J.; Wang D.; Ma X.; Dong Z.; Wu J.; Wang F.; Wu Y. Impaired metabolism of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and axons in demyelinated lesion and in the aged CNS. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 64, 102205. 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabnis R. W. Emopamil-Binding Protein Inhibitors for Treating Multiple Sclerosis. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 1318–1319. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer B. A.; Lairson L. L. Promoting remyelination: A case study in regenerative medicine. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2022, 70, 102201. 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




