Abstract
Herein, we report the synthesis and characterization of a novel set of substituted indazole-ethanamines and indazole-tetrahydropyridines as potent serotonin receptor subtype 2 (5-HT2) agonists. Specifically, we examine the 5-HT2 pharmacology of the direct indazole analogs of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT) and related serotonergic tryptamines, and highlight the need for rigorous characterization of 5-HT2 subtype selectivity for these analogs, particularly for the 5-HT2B receptor subtype. Within this series, the potent analog VU6067416 (19d) was optimized to have suitable preclinical pharmacokinetic properties for in vivo dosing, although potent 5-HT2B agonist activity precluded further characterization for this series. Additionally, in silico docking studies suggest that the high potency of 19d may be a consequence of a halogen-bonding interaction with Phe2345.38 in the 5-HT2A orthosteric pocket.
Keywords: Serotonin, psychedelic, tryptamine, indazole, SAR
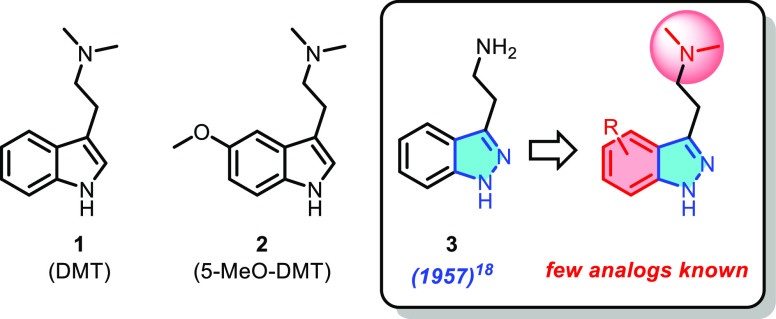
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT) are among the most powerful canonical agonists for the serotonin receptor 2A (5-HT2A) and are known to produce profound changes in perception and mood after systemic dosing.1−3 These compounds, along with many other classical psychedelics, have recently seen a resurgence in clinical profiling for a number of indications including depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), cluster headaches, end of life anxiety, and many others.4−6 Indeed, a number of encouraging clinical reports, highlighting the efficacy of these and related psychedelics, have begun to emerge in the literature, and as of 2021 at least 70 registered clinical studies using psychedelics have been reported.4 Results of a phase 3 clinical study evaluating 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), a phenethylamine in the entactogen class of psychedelics,7 were recently published and demonstrated that the compound was a safe and effective treatment for severe symptoms observed in PTSD patients.8
In addition to DMT and 5-MeO-DMT, the tryptamine class of psychedelics includes psilocybin (a phosphate ester prodrug of the active 5-HT2A agonist psilocin)9 and LSD (a semisynthetic ergoline alkaloid),10 and the first specific associations of tryptamine structures with psychedelic experiences were first described in the literature at least as early as the 1940s.6,11,12 Given the long history of this class of compounds and the number of recent reports detailing various tryptamine analogs as novel 5-HT2A agonists,13−17 it is therefore perhaps surprising that very few reports exist of a direct indazole analog of a serotonergic-type tryptamine. The first such report, published in 1957, describes a synthetic method by which to access the direct 1H-indazole analog of tryptamine itself (3, see Figure 1), although no pharmacology data are reported.18 In keeping with the recent resurgence in psychedelic research, this manuscript remained one of the only reports describing an indazole-substituted serotonergic until very recently, when a selection of patent applications emerged in the literature which describe a wide variety of N-substituted tryptamines and tryptamine isosteres19,20 (including the direct 1H-indazole analog of 5-MeO-DMT).20
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of DMT, 5-MeO-DMT, and 1H-indazole 3.
Incorporation of the indazole motif has yielded compounds with excellent properties across a number of drug discovery programs21−25 and is present in no less than 43 compounds undergoing clinical evaluation (as of 2021).26 Additionally, indazoles are known to act as effective bioisosteres for indoles and phenols, and are often superior with respect to plasma clearance, oral bioavailability, and metabolic stability.27−29 We were therefore also interested in examining the indazole isosteres of classical psychedelics (including 5-MeO-DMT) to ultimately (1) profile the 5-HT2A potency and serotonin-subtype selectivity of 2-aza-5-MeO-DMT and compare our data to the known literature (with a parallel emphasis on the generation of novel analogs) and (2) understand the overall properties of an indazole series of tryptamines with respect to preclinical pharmacokinetics (PK).
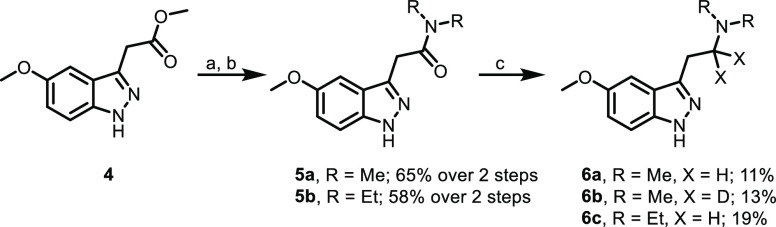
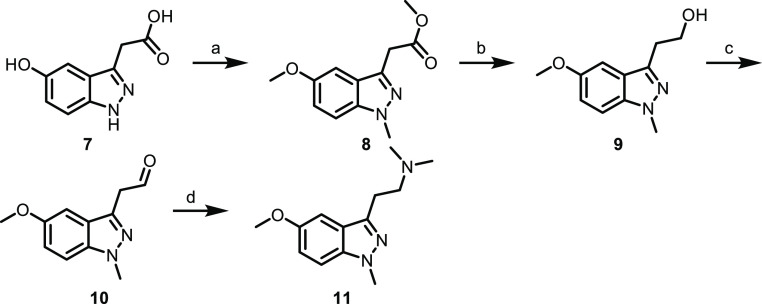
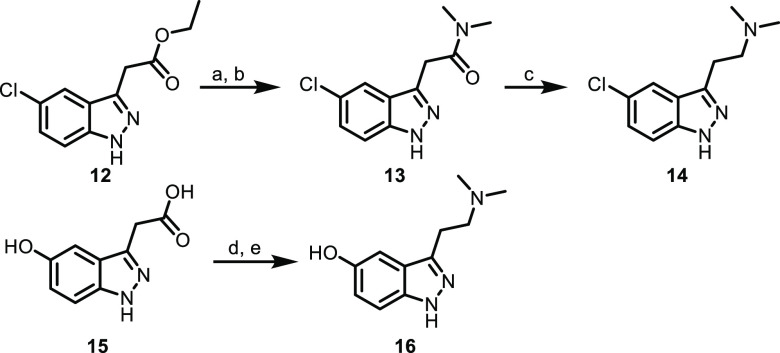
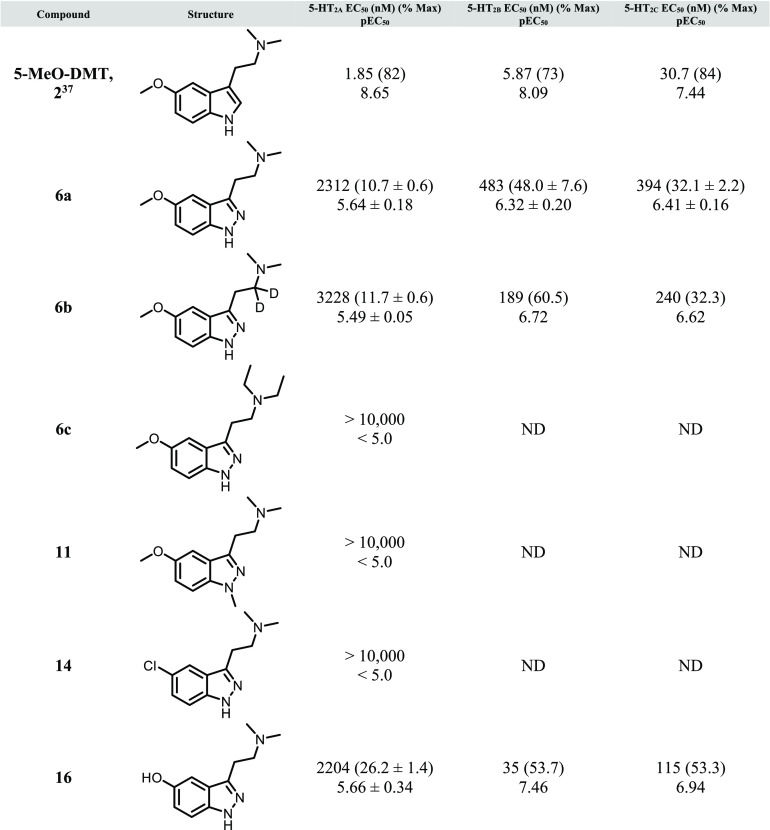
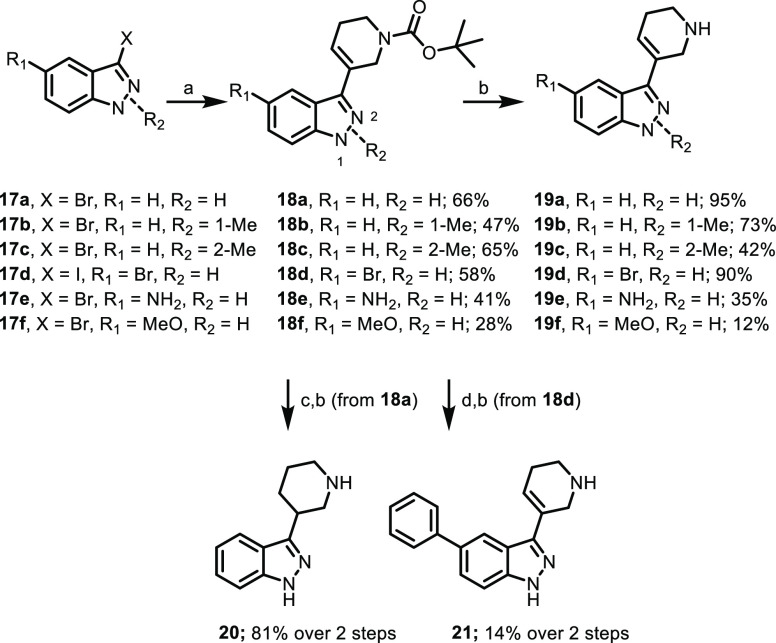
The direct 1H-indazole analog of 5-MeO-DMT, compound 6a, was accessed as shown in Scheme 1. Tertiary amides 5a and 5b were generated from commercially available methyl ester 4 via hydrolysis and amide coupling, followed by reduction with either lithium aluminum hydride or lithium aluminum deuteride to generate amines 6a–6c. 1-Methylindazole analog 11 was synthesized as shown in Scheme 2. Briefly, triple alkylation of carboxylic acid 7, followed by ester reduction, oxidation, and reductive amination gave 11 (attempts to generate 1H-indazoles 6a–6c using a similar sequence were unsuccessful owing to the apparent instability of indazole aldehydes similar to 10 but lacking the 1-methyl substitution). 5-Chloro- and 5-hydroxyindazoles (14 and 16, respectively) were generated using a similar amide reduction sequence to 6a–6c, as shown in Scheme 3. All analogs were then assessed for functional potency across all 5-HT2 subtypes (Table 1).
Scheme 1. Synthesis of Indazoles 6a–6c.
(a) LiOH, THF, H2O, rt; (b) dimethylamine hydrochloride or diethylamine, HATU, DIPEA, DMF, rt; (c) LiAlH4, or LiAlD4, THF, rt.
Scheme 2. Synthesis of indazole 11.
(a) MeI, Cs2CO3, DMF, rt, 27%; (b) DIBAL, DCM, −78 °C to rt, 67%; (c) Dess–Martin periodinane, DCM, rt, 91%; (d) dimethylamine hydrochloride, NaBH(OAc)3, DCM, rt, 33%.
Scheme 3. Synthesis of Indazoles 14 and 16.
(a) LiOH, THF, H2O, rt.; (b) dimethylamine hydrochloride, HATU, DIPEA, DMF, rt, 26% over 2 steps; (c) LiAlH4, THF, rt, 14%; (d) dimethylamine hydrochloride, HATU, DIPEA, THF, DMF, rt; (e) LiAlH4, THF, rt, 11% over 2 steps.
Table 1. In Vitro Functional Potency for Compounds 2, 6a–c, 11, 14, and 16a.
Calcium mobilization assays using human 5-HT2A-CHO, 5-HT2B-HEK293, and 5-HT2C-CHO cells. Data represent (n = 1 to 3) independent experiments performed in duplicate (data are ±SEM). See Supporting Information for additional details. ND = not determined.
In our hands, compound 6a (the direct 1H-indazole analog of 5-MeO-DMT) was found to have low micromolar activity for 5-HT2A, with higher potency at 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C (and was less potent than the indole parent compound across all 5-HT2 subtypes). 1-Methyl analog 11 was markedly less potent at 5-HT2A compared to both 5-MeO-DMT and 6a. gem-Deutero analog 6b was approximately equipotent at 5-HT2A relative to its proteo-counterpart 6a. (Recently, this type of deuterium incorporation was found to increase the in vitro stability for a series of DMT analogs in human hepatocyctes.16 In the case of the present indazole analogs, 6b was found to have only marginally lower predicted clearance in human hepatic microsomes compared to 6a (human CLhep = 11.7 and 12.1 (mL/min)/kg, respectively), although a more complete metabolic picture (the effect of deuterium on MAO-mediated oxidation, etc.) would likely be obtained using hepatocytes.) Diethylamine 6c and 5-chloroindazole 14 displayed no appreciable 5-HT2A functional activity up to 10 μM, whereas 5-hydroxy analog 16 displayed similar potency to 6a for 5-HT2A (with higher potency for the other subtypes). Within this set, the relatively higher potency observed for 6a and 16 align with the available published data for the corresponding tryptamines, in which a 5-MeO or 5-OH substitution in the context of the N,N-dimethylamine motif (5-MeO-DMT and bufotenin, respectively) are among the most potent tryptamines described in the literature.30,31 Because the more potent analogs in the present series do not show appreciable selectivity for 5-HT2A relative to 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C, and in fact are largely 5-HT2B-preferring, this appreciable 5-HT2B agonist activity may elicit problematic cardiotoxicities for these and related tryptamines.32 Historically, there are no examples of orthosteric tryptamines with high selectivity across 5-HT2 subtypes due to the highly conserved nature of the orthosteric binding pocket, although examples of substituted phenethylamines with higher 5-HT2A selectivity have been reported.33−35 Recently, additional chemotypes with some degree of 5-HT2A subtype selectivity have started to emerge in the literature, and an allosteric approach may prove fruitful toward this end.19,20,36
Interestingly, the direct 1H-indazole analog of 5-MeO-DMT, compound 6a, was previously described to be moderately potent for 5-HT2A (5-HT2A EC50 = 203 nM, Emax = 70%), with high selectivity relative to 5-HT2B (EC50 > 10 μM) and, to a lesser extent, 5-HT2C (EC50 = 532 nM, Emax = 72%).20 This large discrepancy between reports for the 5-HT2B subtype selectivity profile for this compound is noteworthy (483 nM in our hands vs >10 μM), given that agonist activity (nor-dexfenfluramine and related clinical 5-HT2B agonists) at this receptor presents a well-validated risk for cardiotoxicity.32 Although it is possible that differences in cell line background and/or receptor expression levels may partially account for this disparate selectivity data (see Supporting Information), this finding highlights the need for rigorous characterization of 5-HT2A agonists (both known and novel) across multiple cell backgrounds and functional readouts if such compounds are to be safely profiled in the clinic.
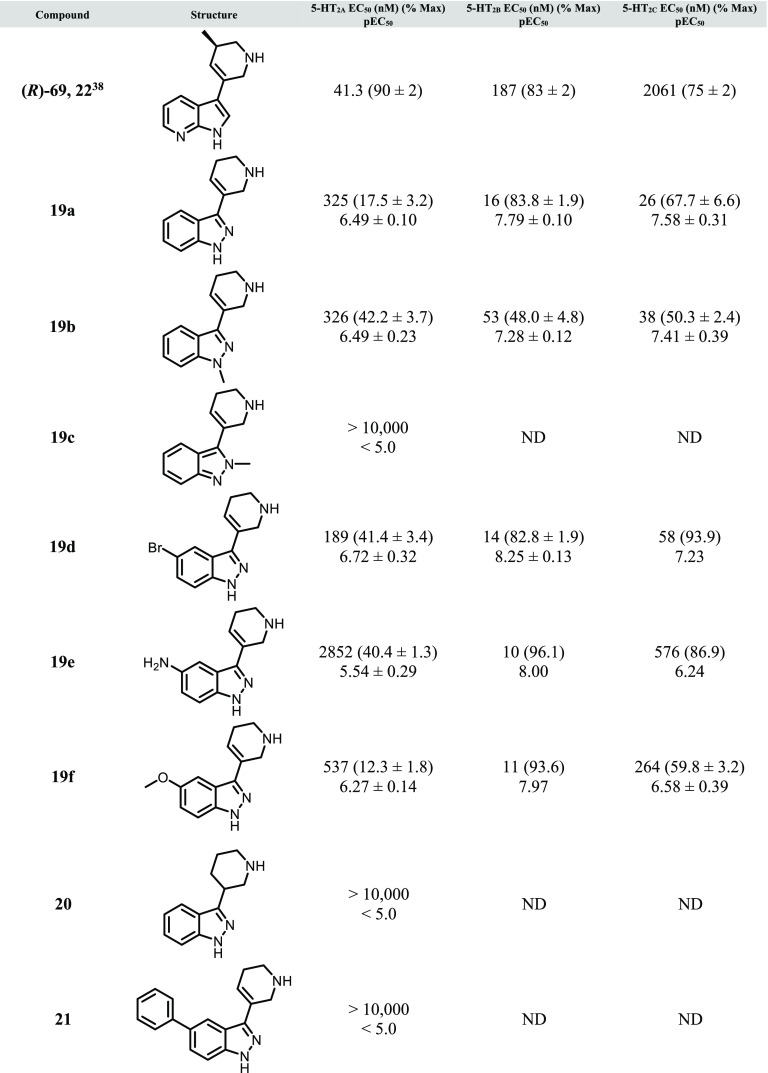
Recently, Kaplan and colleagues utilized an ultralarge virtual docking approach to discover, among other novel 5-HT2A chemical scaffolds, a series of aza-tryptamines in which the ethanamine pendant is cyclized to give a tetrahydropyridine moiety (see Table 2 for representative example (R)-69).38 Interested in examining this type of modification in the context of our indazole series, we synthesized tetrahydropyridine-indazoles 19a–f and 21 as shown in Scheme 4. Briefly, commercially available substituted indazoles 17a–f were coupled to tert-butyl 5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-3,6-dihydropyridine-1(2H)-carboxylate using standard Suzuki–Miyaura chemistry, followed by Boc-deprotection to give compounds 19a–f. Piperidine 20 was synthesized from 18a via olefin hydrogenation prior to Boc-deprotection, and 5-phenyl analog 21 was synthesized via Suzuki–Miyaura coupling/Boc-deprotection from 18d. Functional potency across all 5-HT2 subtypes is summarized in Table 2.
Table 2. In Vitro Functional Potency for Compounds 19a–f and 20–22a.
Calcium mobilization assays using human 5-HT2A-CHO, 5-HT2B-HEK293, and 5-HT2C-CHO cells. Data represent (n = 1 to 3) independent experiments performed in duplicate (data are ±SEM). See Supporting Information for additional details. ND = not determined.
Scheme 4. Synthesis of Indazoles 19a-f, 20, and 21.
(a) tert-Butyl 5-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)-3,6-dihydropyridine-1(2H)-carboxylate, K2CO3, PdCl2(dppf)·DCM, 1,4-dioxane, H2O, 110 °C; (b) HCl, DCM, rt; (c) 10% Pd/C, ammonium formate, MeOH, 60 °C; (d) phenylboronic acid, K2CO3, PdCl2(dppf)·DCM, 1,4-dioxane, H2O, 110 °C.
In contrast to the acyclic series (Table 1), 1H-indazole 19a and its 1-methyl counterpart 19b were found to be equipotent with respect to 5-HT2A, with both displaying approximately 10-fold higher agonist potency for 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C (2-methylindazole 19c was found to be inactive at 5-HT2A up to 10 μM, indicating the importance of the spatial arrangement of the methyl group on the indazole scaffold). All substitutions examined at the 5-position, with the exception of 5-phenyl analog 21, were found to be tolerated (19d–f), with 5-bromo analog 19d in particular showing high agonist potency across all 5-HT2 subtypes (189 nM for 5-HT2A). Ring reduction to give saturated piperidine analog 20 was not tolerated, indicating the necessity of the olefin constraint for 5-HT2A activity. During the preparation of this manuscript, a related patent application containing a series of tetrahydropyridine-linked indoles and indazoles was disclosed, in which additional SAR around this type of 5-HT2A scaffold is detailed.19 Within this report, the structures and functional 5-HT2A potency data for 19a and 19f are reported, and interestingly, each compound appears significantly more potent compared to our findings (5-HT2A EC50 values of 9.9 and 17.8 nM, respectively), although no selectivity relative to 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C is reported for these analogs. In our hands, 19a and 19f appear to be strongly 5-HT2B-preferring relative to 5-HT2A, indicating that the selectivity for 5-HT2A in the context of the tetrahydropyridine series may prove challenging. As with the acyclic analogs described in Table 1, this potent 5-HT2B agonist activity is concerning with respect to the potential to induce pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), valvular heart disease (VHD), and related cardiopathies.32 A functional agonist profile at 5-HT2B, however, does not necessarily guarantee cardiotoxicity, and in fact partial agonists for this receptor have been shown to prevent and treat Sugen-hypoxia-induced PAH in mice.39 Furthermore, signaling bias may play a role in determining the cardiotoxic potential of a given compound; compounds including ropinirole and BW723C86 are not known to induce cardiotoxicity despite being potent functional agonists in the Ca2+ calcium flux assay.40,41 Further characterization of the present compounds will be needed in order to fully understand any associated risks.32
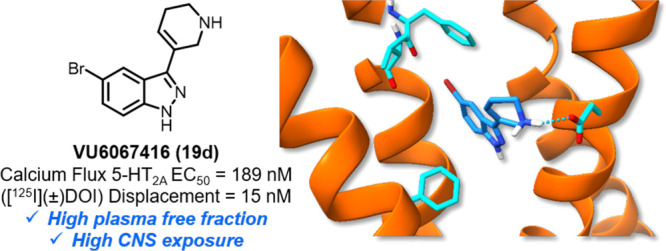
Encouraged by the high potency of 5-bromo analog 19d (VU6067416), we examined this analog in a battery of in vitro and in vivo pharmacokinetic (PK) assays. VU6067416 (19d) was found to have low predicted hepatic clearance (CLhep) in human microsomes, with higher turnovers observed for rodent species. Additionally, 19d displayed a high fraction unbound (fu) in plasma across species, as well as a low predicted P-gp efflux, indicating high potential for brain penetration in human. In a rat iv PK study utilizing cassette dosing, 19d showed moderate plasma clearance (CLp) and high Vss, with a 2.8 h half-life and a high total brain to plasma ratio (Kp) of 5.4. These parameters, which are summarized in Table 3, are encouraging with respect to the high potential for brain exposure and free drug across species.
Table 3. In Vitro and in Vivo PK Parameters for VU6067416 (19d)a.
| parameter | value |
|---|---|
| in vitro | |
| CLhep ((mL/min)/kg) | 5.6 (human); 58 (rat); 57 (mouse) |
| fu | 0.12 (human); 0.13 (rat); 0.12 (mouse) |
| P-gp efflux ratio (PappA-B (10–6 cm/s)) | 1.3 (7.9) |
| rat PK cassette (iv, 0.2 mg/kg) | |
| CLp ((mL/min)/kg) | 34.2 |
| Vss (L/kg) | 6.33 |
| t1/2 (h) | 2.8 |
| Kp (measured at 0.25 h) | 5.4 |
See Supporting Information for additional experimental information.
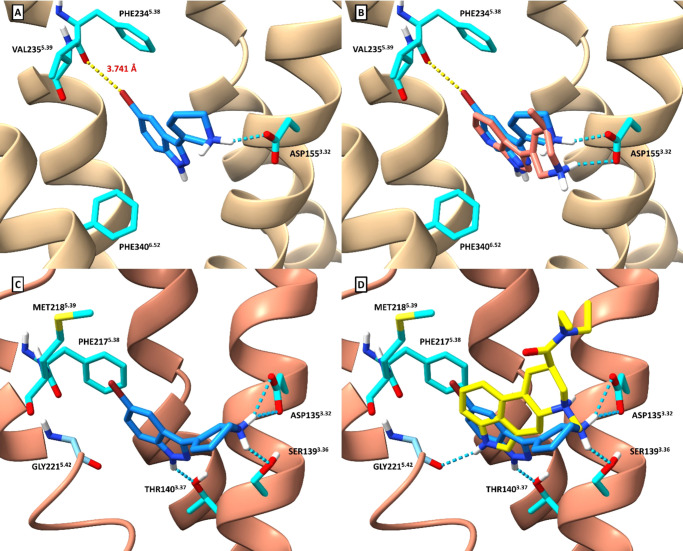
19d was found to fully displace radiolabeled racemic 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodomethamphetamine ([125I](±)DOI) in a competition binding experiment for the 5-HT2A receptor (19d IC50 = 15 nM),42 suggesting an orthosteric binding profile. Previous literature has demonstrated the potential for halogenated 5-HT2AR substrates to form a halogen bond with either or both of the backbone carbonyls of Phe2345.38 and Val2355.39 in the 5-HT2A orthosteric pocket.43 To explore this possibility in the context of the present series, VU6067416 (19d) was docked to an active state of 5-HT2AR (PDB code 7RAN)38 using AutoDock VinaXB (Figure 2A).44 While traditional 5-HT2AR agonist binding interactions with Phe3406.52 (π–π with indazole) and Asp1553.32 (salt bridge with amine) are retained, the distance between the bromine and Phe2345.38 backbone carbonyl oxygen is slightly outside the typical cutoff for halogen bond formation between a bromine and a carbonyl oxygen (3.74 vs 3.37 Å),45 rendering the occurrence of this phenomenon uncertain in this context. Given the potency of 19d relative to other compounds in the present series and the limitations of rigid docking, though, it is possible that a halogen bond does form. Furthermore, an overlay of the cryo-EM bound pose of 5-HT2AR agonist (R)-69(38) with the docked pose of 19d indicates a high degree of similarity between the two conformations, lending credence to this proposed docking mode given the structural similarity of these two agonists (Figure 2B). Definitive structural data, however, are needed to validate this proposed binding mode and any existence of a halogen bond. 19d was also docked to an active state of 5-HT2BR (PDB code 7SRR; orthosteric ligand: LSD)46 in the same manner (Figure 2C,D). Given that des-bromo analog 19a exhibits nearly identical activity at 5-HT2B compared to 19d (EC50 = 16 nM vs 14 nM, respectively), it follows that there were no docking results indicative of a potential halogen bond between the bromine of 19d and the backbone carbonyls of Phe2175.38 or Met2185.39. Rather, the activity at this receptor is likely driven by a combination of ionic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and π–π interactions.
Figure 2.
(A) Compound 19d docked to 5-HT2AR, with predicted halogen bonding interaction (yellow dashes) with Phe2345.38. (B) Compound 19d docking pose overlaid with (R)-69 (pink) cryo-EM pose. (C) Compound 19d docked to 5-HT2BR. (D) Compound 19d 5-HT2BR docking pose overlaid with the LSD (yellow) cryo-EM pose. Blue dashes depict salt bridges and hydrogen bonds.
In summary, we report herein a novel series of 5-HT2 agonists containing an indazole core in place of the traditionally indole-containing tryptamines and show that while many compounds in this series are 5-HT2A agonists, selectivity relative to the other 5-HT2 subtypes remains difficult to achieve (and needs to be rigorously profiled, particularly for safety concerns related to 5-HT2B agonism). Although nonselective, VU6067416 (19d) is a potent 5-HT2A agonist (possibly due in part to a halogen bonding interaction with Phe2345.38 in the 5-HT2A orthosteric pocket), with favorable PK properties for systemic dosing in rats, and is predicted to be brain-penetrant in human. It is our hope that these results will serve to inform the development of next-generation modulators for the 5-HT2A receptor.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the William K. Warren Family and Foundation for funding the William K. Warren Jr. Chair in Medicine and endowing the WCNDD, and support of our programs.
Supporting Information Available
The Supporting Information is available free of charge at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00566.
Experimental procedures and characterization for new compounds; experimental details for all assays (PDF)
Author Contributions
A.M.B., N.J., and C.J.D. performed synthetic chemistry and compound characterization. M.A.M. and H.P.C. performed and analyzed molecular pharmacology experiments. D.C.S. performed and analyzed docking studies. A.T.G., O.B., and C.K.J. performed and analyzed PK experiments. A.M.B., C.W.L., H.P.C., C.K.J, and O.B. oversaw experimental design. A.M.B. wrote the manuscript with input from all authors.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Barsuglia J.; Davis A. K.; Palmer R.; Lancelotta R.; Windham-Herman A.-M.; Peterson K.; Polanco M.; Grant R.; Griffiths R. R. Intensity of Mystical Experiences Occasioned by 5-MeO-DMT and Comparison With a Prior Psilocybin Study. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2459. 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron L. P.; Olson D. E. Dark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT). ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2344–2357. 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reckweg J. T.; Uthaug M. V.; Szabo A.; Davis A. K.; Lancelotta R.; Mason N. L.; Ramaekers J. G. The Clinical Pharmacology and Potential Therapeutic Applications of 5-Methoxy-N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT). J. Neurochem. 2022, 162, 128–146. 10.1111/jnc.15587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel A. N.; Meshkat S.; Benitah K.; Lipsitz O.; Gill H.; Lui L. M. W.; Teopiz K. M.; McIntyre R. S.; Rosenblat J. D. Registered Clinical Studies Investigating Psychedelic Drugs for Psychiatric Disorders. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2021, 139, 71–81. 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D. E. The Promise of Psychedelic Science. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 413–415. 10.1021/acsptsci.1c00071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carhart-Harris R. L.; Goodwin G. M. The Therapeutic Potential of Psychedelic Drugs: Past, Present and Future. Neuropsychopharmacology 2017, 42, 2105–2113. 10.1038/npp.2017.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols D. E. Differences Between the Mechanism of Action of MDMA, MBDB, and the Classic Hallucinogens: Identification of a New Therapeutic Class: Entactogens. J. Psychoactive Drugs. 1986, 18, 305–313. 10.1080/02791072.1986.10472362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. M.; Ot’alora G. M.; van der Kolk B.; Shannon S.; Bogenschutz M.; Gelfand Y.; Paleos C.; Nicholas C. R.; Quevedo S.; Balliett B.; Hamilton S.; Mithoefer M.; Kleiman S.; Parker-Guilbert K.; Tzarfaty K.; Harrison C.; de Boer A.; Doblin R.; Yazar-Klosinski B.; MDMA-Assisted Therapy for Moderate to Severe PTSD: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2473–2480. 10.1038/s41591-023-02565-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passie T.; Seifert J.; Schneider U.; Emrich H. M. The Pharmacology of Psilocybin. Addict. Biol. 2002, 7, 357–364. 10.1080/1355621021000005937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols D. E. Dark Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Lysergic Acid Diethylamide (LSD). ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2331–2343. 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch A. K.; Johnson W. C. L.S.D. 25 as an Aid in Psychotherapy; Preliminary Report of a New Drug. Dis. Nerv. Syst. 1950, 11, 241–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A.; Heim R.; Brack A.; Kobel H. Psilocybin, a Psychotropic Substrance from the Mexican Mushroom Psilicybe Mexicana. Experientia 1958, 14, 107–109. 10.1007/BF02159243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein A. K.; Chatha M.; Laskowski L. J.; Anderson E. I.; Brandt S. D.; Chapman S. J.; McCorvy J. D.; Halberstadt A. L. Investigation of the Structure-Activity Relationships of Psilocybin Analogues. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 533–542. 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap L. E.; Azinfar A.; Ly C.; Cameron L. P.; Viswanathan J.; Tombari R. J.; Myers-Turnbull D.; Taylor J. C.; Grodzki A. C.; Lein P. J.; Kokel D.; Olson D. E. Identification of Psychoplastogenic N,N-Dimethylaminoisotryptamine (isoDMT) Analogs through Structure-Activity Relationship Studies. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1142–1155. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatfelter G. C.; Naeem M.; Pham D. N. K.; Golen J. A.; Chadeayne A. R.; Manke D. R.; Baumann M. H. Receptor Binding Profiles for Tryptamine Psychedelics and Effects of 4-Propionoxy-N,N-Dimethyltryptamine in Mice. ACS Pharmacol. Transl Sci. 2023, 6, 567–577. 10.1021/acsptsci.2c00222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layzell M.; Rands P.; Good M.; Joel Z.; Cousins R.; Benway T.; James E.; Routledge C. Discovery and In Vitro Characterization of SPL028: Deuterated N,N-Dimethyltryptamine. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 14, 1216–1223. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.3c00143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein L. M.; Cozzi N. V.; Daley P. F.; Brandt S. D.; Halberstadt A. L. Receptor Binding Profiles and Behavioral Pharmacology of Ring-Substituted N,N-Diallyltryptamine Analogs. Neuropharmacology 2018, 142, 231–239. 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ainsworth C. Indazole Analog of Tryptamine: A New Synthesis of Indazoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 5242–5245. 10.1021/ja01576a047. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar J. M.; Slocum S.; Skiniotis G.; Barros X.; Jin J.; Kaniskan U. H.; Sun N.; Sun R.; Xiong Y.; Shen Y.; Xu Z.; Qui X.; Qian C.; Song X.; Deng Z.; Roth B.; Diberto J.; Kuglae K.; Suomivuori C.-M.; Daemgen M. A.; Dror R.; Shoichet B.; Kaplan A. L.. Heterocyclic Compounds as 5HT2A Biased Agonists. Patent, International Publication Number WO2023/114472, 2023.
- Banister S.; Jorgensen W.; Tan J. Patent, International Publication Number WO2023/115165, 2023.
- Unoh Y.; Uehara S.; Nakahara K.; Nobori H.; Yamatsu Y.; Yamamoto S.; Maruyama Y.; Taoda Y.; Kasamatsu K.; Suto T.; Kouki K.; Nakahashi A.; Kawashima S.; Sanaki T.; Toba S.; Uemura K.; Mizutare T.; Ando S.; Sasaki M.; Orba Y.; Sawa H.; Sato A.; Sato T.; Kato T.; Tachibana Y. Discovery of S-217622, a Noncovalent Oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL Protease Inhibitor Clinical Candidate for Treating COVID-19. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 6499–6512. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada Y.; Nakano S.; Morimoto A.; Kasahara K.; Hayashi T.; Takada Y.; Suzuki H.; Niwa-Sakai M.; Ohashi S.; Mori M.; Hirokawa T.; Shuto S. Discovery of Novel Indazole Derivatives as Orally Available β3-Adrenergic Receptor Agonists Lacking Off-Target-Based Cardiovascular Side Effects. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3252–3265. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugar S.; Hollinger F. P.; Mahajan D.; Sen S.; Kuila B.; Arora R.; Pawar Y.; Shinde V.; Rahinj M.; Kapoor K. K.; Bhumkar R.; Rai S.; Kulkarni R. Discovery of Novel and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitors of PI3 Kinase Based on Indazole Substituted Morpholino-Triazines. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 1190–1194. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moehle M. S.; Bender A. M.; Dickerson J. W.; Foster D. J.; Qi A.; Cho H. P.; Donsante Y.; Peng W.; Bryant Z.; Stillwell K. J.; Bridges T. M.; Chang S.; Watson K. J.; O’Neill J. C.; Engers J. L.; Peng L.; Rodriguez A. L.; Niswender C. M.; Lindsley C. W.; Hess E. J.; Conn P. J.; Rook J. M. Discovery of the First Selective M4 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonists with In Vivo Anti-Parkinsonian and Anti-Dystonic Efficacy. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1306–1321. 10.1021/acsptsci.0c00162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A. M.; Cho H. P.; Nance K. D.; Lingenfelter K. S.; Luscombe V. B.; Gentry P. R.; Voigtritter K.; Berizzi A. E.; Sexton P. M.; Langmead C. J.; Christopoulos A.; Locuson C. W.; Bridges T. M.; Chang S.; O’Neill J. C.; Zhan X.; Niswender C. M.; Jones C. K.; Conn P. J.; Lindsley C. W. Discovery and Optimization of Potent and CNS Penetrant M5-Preferring Positive Allosteric Modulators Derived from a Novel, Chiral N-(Indanyl)piperidine Amide Scaffold. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1572–1581. 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin J.; Cheng W.; Duan Y.-T.; Yang H.; Yao Y. Indazole as Privileged Scaffold: The Derivatives and their Therapeutic Applications. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 839–860. 10.2174/1871520620999200818160350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüken J.; Goerges G.; Ritter N.; Disse P.; Schreiber J. A.; Schmidt J.; Frehland B.; Schepmann D.; Seebohm G.; Wünsch B. Indazole as a Phenol Bioisostere: Structure-Affinity Relationships of GluN2B-Selective NMDA Receptor Antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 11573–11588. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamborough P.; Angell R. M.; Bhamra I.; Brown D.; Bull J.; Christopher J. A.; Cooper A. W. J.; Fazal L. H.; Giordano I.; Hind L.; Patel V. K.; Ranshaw L. E.; Sims M. J.; Skone P. A.; Smith K. J.; Vickerstaff E.; Washington M. N-4-Pyrimidinyl-1H-Indazol-4-Amine Inhibitors of Lck: Indazole as Phenol Isosteres with Improved Pharmacokinetics. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4363–4368. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2007.04.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang D.-J.; He Y.; Ponnusamy S.; Thiyagarajan T.; Mohler M. L.; Narayanan R.; Miller D. D. Metabolism-Guided Selective Androgen Receptor Antagonists: Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation for Activity Against Enzalutamide-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 3372–3392. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glennon R. A.; Gessner P. K. Serotonin Receptor Binding Affinities of Tryptamine Analogs. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 428–432. 10.1021/jm00190a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough B. E.; Landavazo A.; Decker A. M.; Partilla J. S.; Baumann M. H.; Rothman R. B. Interaction of Psychoactive Tryptamines with Biogenic Amine Transporters and Serotonin Receptor Subtypes. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 4135–4144. 10.1007/s00213-014-3557-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A. M.; Parr L. C.; Livingston W. B.; Lindsley C. W.; Merryman W. D. 2B Determined: The Future of the Serotonin Receptor 2B in Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 11027–11039. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroteaux L.; Ayme-Dietrich E.; Aubertin-Kirch G.; Banas S.; Quentin E.; Lawson R.; Monassier L. New Therapeutic Opportunities for 5-HT2 Receptor Ligands. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 170, 14–36. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.10.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juncosa Jr J. I.; Hansen M.; Bonner L. A.; Cueva J. P.; Maglathlin R.; McCorvy J. D.; Marona-Lewicka D.; Lill M. A.; Nichols D. E. Extensive Rigid Analogue Design Maps the Binding Conformation of Potent N-Benzylphenethylamine 5-HT2A Serotonin Agonist Ligands. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 96–109. 10.1021/cn3000668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallach J.; Cao A. B.; Calkins M. M.; Heim A. J.; Lanham J. K.; Bonniwell E. M.; Hennessey J. J.; Bock H. A.; Anderson E. I.; Sherwood A. M.; Morris H.; de Klein R.; Klein A. K.; Cuccurazzu B.; Gamrat J.; Fannana T.; Zauhar R.; Halberstadt A. L.; McCorvy J. D. Identification of 5-HT2A Receptor Signaling Pathways Associated with Psychedelic Potential. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8221. 10.1038/s41467-023-44016-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J.; Garcia E. J.; Merritt C. R.; Zamora J. C.; Bolinger A. A.; Pazdrak K.; Stafford S. J.; Mifflin; Wold E. A.; Wild C. T.; Chen H.; Anastasio N. C.; Cunningham K. A.; Zhou J. Discovery of Novel Oleamide Analogues as Brain-Penetrant Positive Allosteric Serotonin 5-HT2C Receptor and Dual 5-HT2C/5-HT2A Receptor Modulators. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 9992–10009. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c00908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron L. P.; Tombari R. J.; Lu J.; Pell A. J.; Hurley Z. Q.; Ehinger Y.; Vargas M. V.; McCarroll M. N.; Taylor J. C.; Myers-Turnbull D.; Liu T.; Yaghoobi B.; Laskowski L. J.; Anderson E. I.; Zhang G.; Viswanathan J.; Brown B. M.; Tjia M.; Dunlap L. E.; Rabow Z. T.; Fiehn O.; Wulff H.; McCorvy J. D.; Lein P. J.; Kokel D.; Ron D.; Peters J.; Zuo Y.; Olson D. E. A Non-Hallucinogenic Psychedelic Analogue with Therapeutic Potential. Nature 2021, 589, 474–479. 10.1038/s41586-020-3008-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. L.; Confair D. N.; Kim K.; Barros-Álvarez X.; Rodriguiz R. M.; Yang Y.; Kweon O. S.; Che T.; McCorvy J. D.; Kamber D. N.; Phelan J. P.; Martins L. C.; Pogorelov V. M.; DiBerto J. F.; Slocum S. T.; Huang X.-P.; Kumar J. M.; Robertson M. J.; Panova O.; Seven A. B.; Wetsel A. Q.; Wetsel W. C.; Irwin J. J.; Skiniotis G.; Shoichet B. K.; Roth B. L.; Ellman J. A. Bespoke Library Docking for 5-HT2A Receptor Agonists with Antidepressant Activity. Nature 2022, 610, 582–591. 10.1038/s41586-022-05258-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine M. S.; Bender A. M.; Shay S.; Paffenroth K. C.; Gladson S.; Dickerson J. W.; Watson K. J.; Kapolka N. J.; Boutaud O.; Rook J. M.; Blackwell T. S.; Roth B. L.; Harrison F. E.; Austin E. D.; West J. D.; Lindsley C. W.; Merryman W. D. Development of a Peripherally Restricted 5-HT2B Partial Agonist for Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. Basic Trans. Science. 2023, 8, 1379–1388. 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.06.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X.-P.; Setola V.; Yadav P. N.; Allen J. A.; Rogan S. C.; Hanson B. J.; Revankar C.; Robers M.; Doucette C.; Roth B. L. Parallel Functional Activity Profiling Reveals Valvulopathogens Are Potent 5-Hydroxytryptamine2B Receptor Agonists: Implications for Drug Safety Assessment. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 76, 710–722. 10.1124/mol.109.058057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnoux A.; Ayme-Dietrich E.; Dieterle S.; Goy M.-A.; Schann S.; Frauli M.; Monassier L.; Dupuis L. Evaluation of a 5-HT2B Receptor Agonist in a Murine Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23582. 10.1038/s41598-021-02900-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- https://www.eurofinsdiscovery.com/catalog/5-ht2a-human-serotonin-gpcr-binding-agonist-radioligand-leadhunter-assay-fr/471.
- Fierro A.; Matthies D. J.; Cassels B. K.; Jaque P.; Zapata-Torres G. 5-HT2 Receptor Subfamily and the Halogen Bond Promise. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 5001–5012. 10.1021/acs.jcim.1c00466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koebel M. R.; Schmadeke G.; Posner R. G.; Sirimulla S. AutoDock VinaXB: Implementation of XBSF, New Empirical Halogen Bond Scoring Function, into AutoDock Vina. J. Cheminf. 2016, 8, 27. 10.1186/s13321-016-0139-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z.; Yang Z.; Liu Y.; Lu Y.; Chen K.; Zhu W. Halogen Bond: Its Role beyond Drug-Target Binding Affinity for Drug Discovery and Development. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 69–78. 10.1021/ci400539q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao C.; Barros-Álvarez X.; Zhang S.; Kim K.; Dämgen M. A.; Panova O.; Suomivuori C.-M.; Fay J. F.; Zhong X.; Krumm B. E.; Gumpper R. H.; Seven A. B.; Robertson M. J.; Krogan N. J.; Hüttenhain R.; Nichols D. E.; Dror R. O.; Skiniotis G.; Roth B. L. Signaling Snapshots of a Serotonin Receptor Activated by the Prototypical Psychedelic LSD. Neuron 2022, 110, 3154–3167. 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.