Abstract
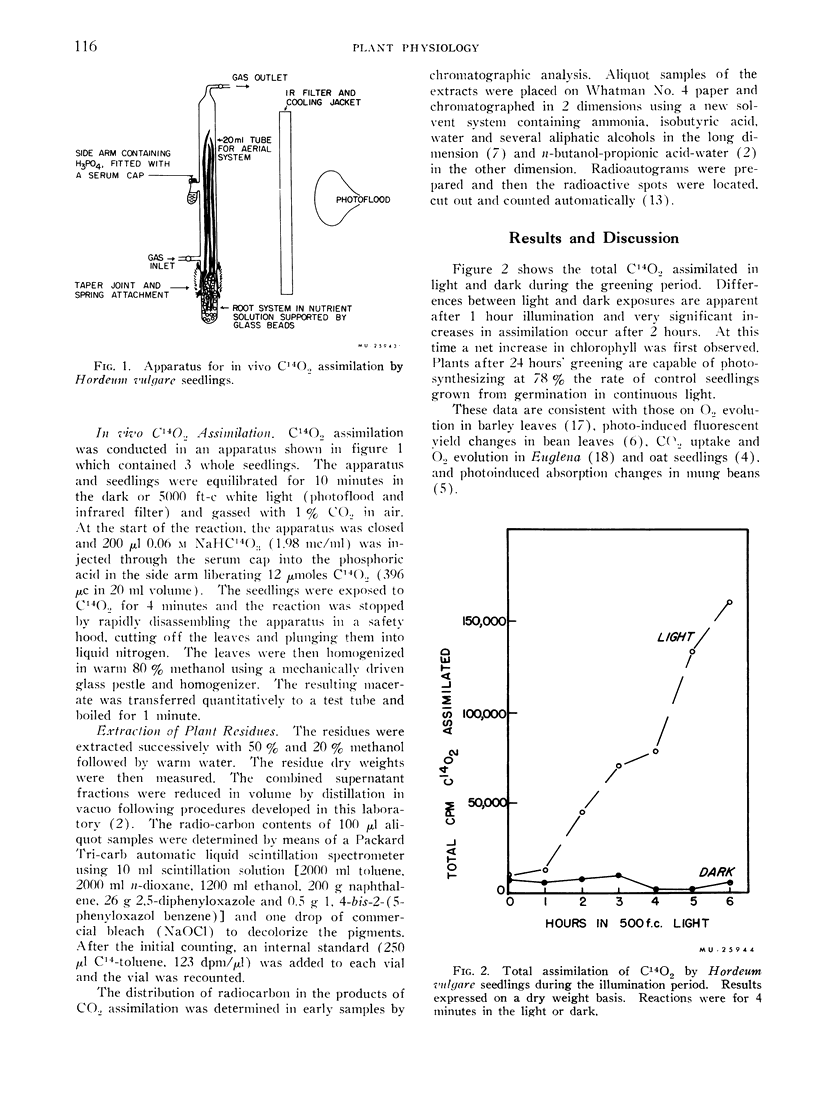
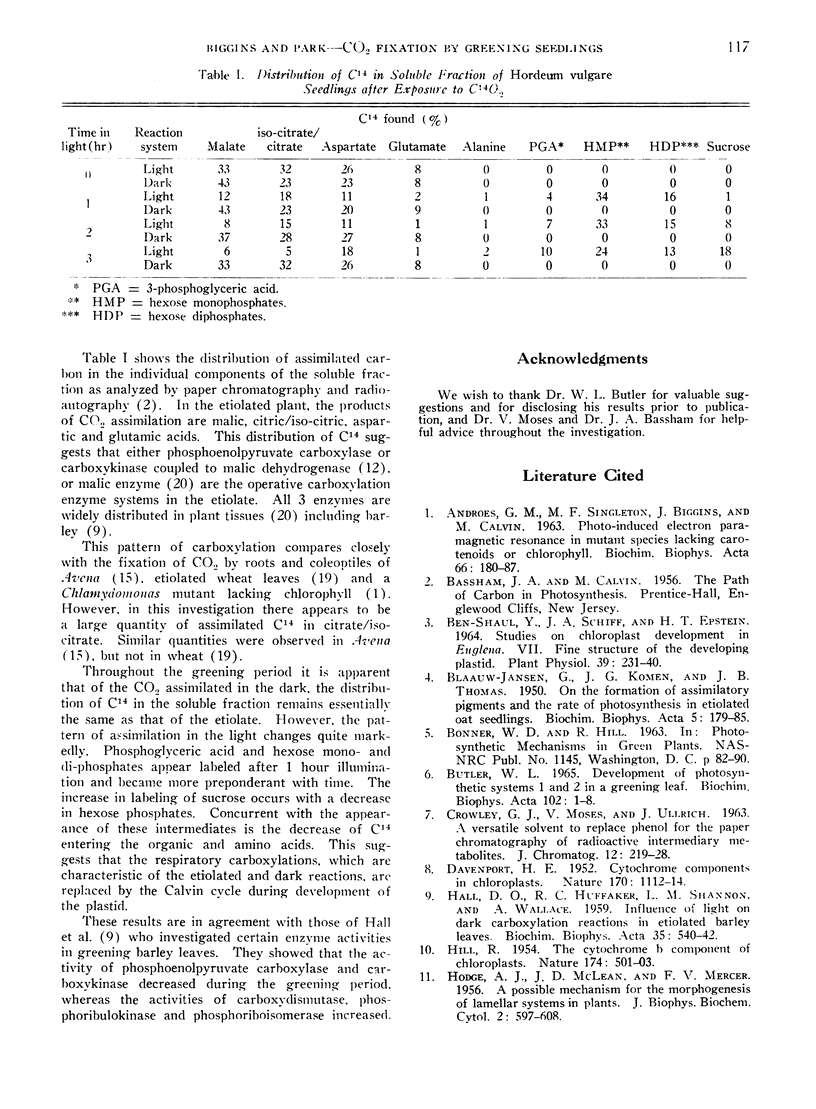
The assimilation of CO2 by etiolated Hordeum vulgare seedlings during an illumination period indicates a conversion of the organisms to autotrophy.
After 1 hour illumination, increases in the photo-assimilation of CO2 are observed and the distribution of C14 in the soluble fraction of the plants is predominantly in intermediates of the Calvin cycle.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDROES G. M., SINGLETON M. F., BIGGINS J., CALVIN M. Photo-induced electron paramagnetic resonance in mutant photosynthetic species lacking carotenoids or chlorophyll. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 19;66:180–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLAAUW-JANSEN G., KOMEN J. G., THOMAS J. B. On the relation between the formation of assimilatory pigments and the rate of photosynthesis in etiolated oat seedlings. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Apr;5(2):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shaul Y., Schiff J. A., Epstein H. T. Studies of Chloroplast Development in Euglena. VII. Fine Structure of the Developing Plastid. Plant Physiol. 1964 Mar;39(2):231–240. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. L. Development of photosynthetic system 1 and 2 in a greening leaf. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 25;102(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROWLEY G. J., MOSES V., ULLRICH J. A VERSATILE SOLVENT TO REPLACE PHENOL FOR THE PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF RADIOACTIVE INTERMEDIARY METABOLITES. J Chromatogr. 1963 Oct;12:219–228. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)83673-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVENPORT H. E. Cytochrome components in chloroplasts. Nature. 1952 Dec 27;170(4339):1112–1114. doi: 10.1038/1701112b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta A. S., Sen S. P. Carbon dioxide fixation by auxin treated tissues. Plant Physiol. 1961 May;36(3):374–380. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.3.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGE A. J., MCLEAN J. D., MERCER F. V. A possible mechanism for the morphogenesis of lamellar systems in plant cells. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Sep 25;2(5):597–608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.5.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSES V., LONBERG-HOLM K. K. A semiautomatic device for measuring radioactivity on two-dimensional paper chromatograms. Anal Biochem. 1963 Jan;5:11–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(63)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazelis M., Vennesland B. Carbon Dioxide Fixation into Oxalacetate in Higher Plants. Plant Physiol. 1957 Nov;32(6):591–600. doi: 10.1104/pp.32.6.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern A. I., Schiff J. A., Epstein H. T. Studies of Chloroplast Development in Euglena. V. Pigment Biosynthesis, Photosynthetic Oxygen Evolution and Carbon Dioxide Fixation during Chloroplast Development. Plant Physiol. 1964 Mar;39(2):220–226. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.2.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolbert N. E., Gailey F. B. Carbon Dioxide Fixation by Etiolated Plants after Exposure to White Light. Plant Physiol. 1955 Nov;30(6):491–499. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


