Abstract
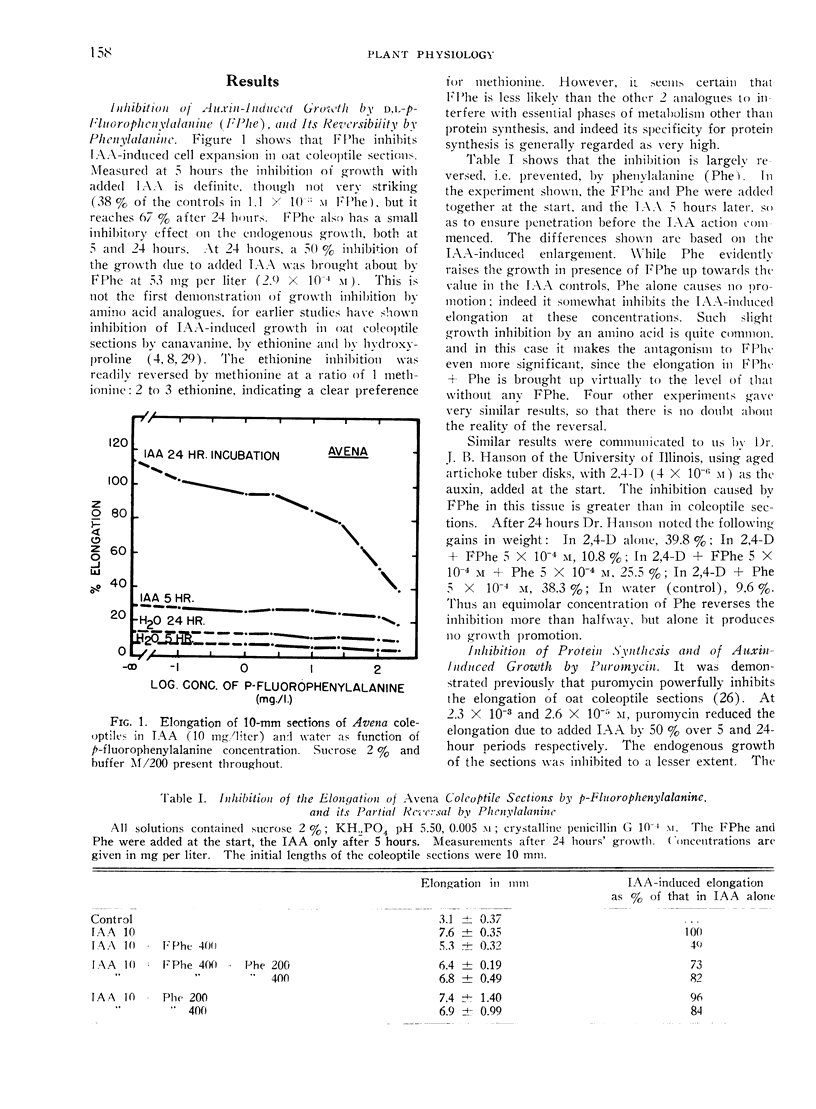
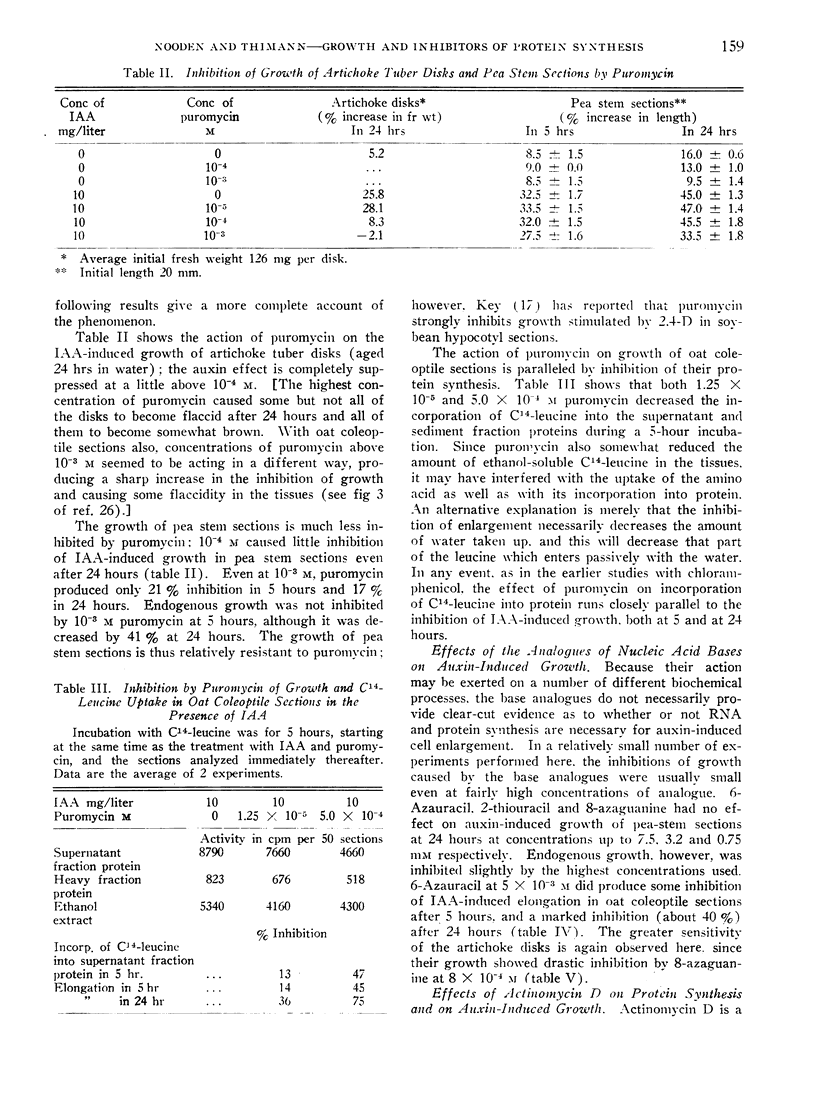
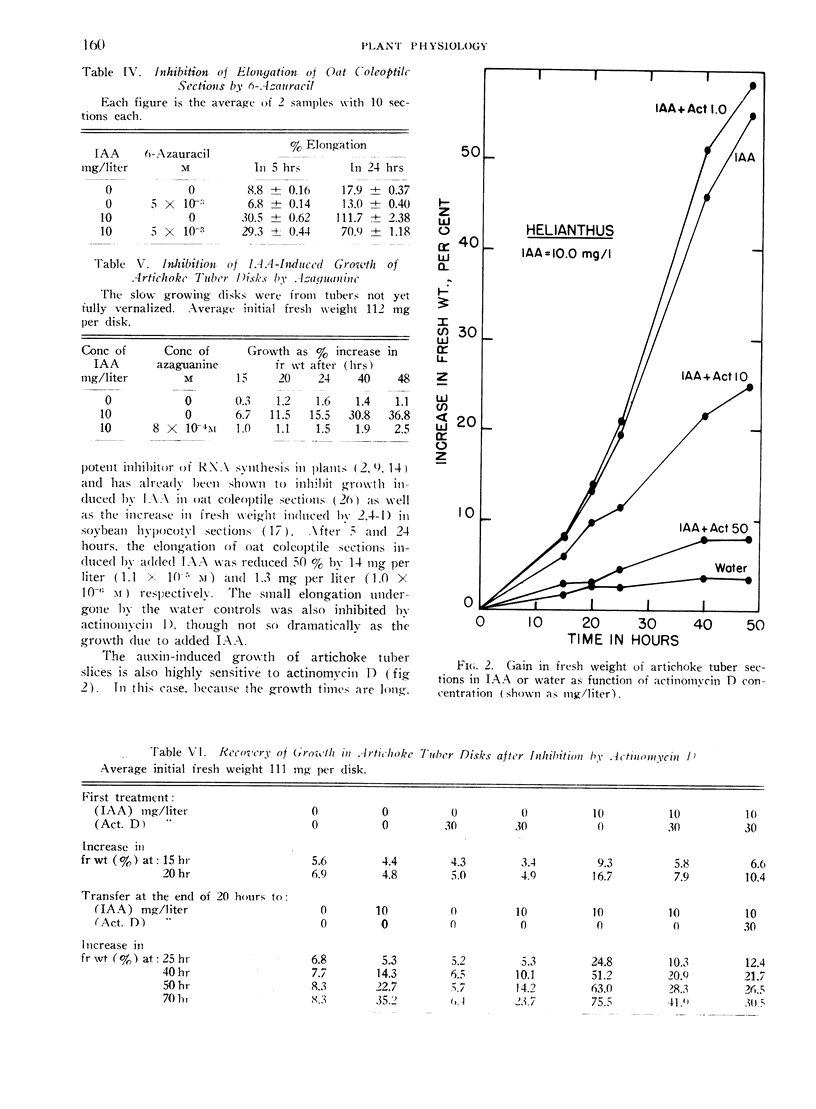
Further studies with inhibitors of protein synthesis are presented to support the conclusion, drawn from work with chloramphenicol, that protein synthesis is a critical limiting factor in auxin-induced cell expansion. The indoleacetic acid-induced elongation of oat coleoptile sections was strongly inhibited by dl-p-fluorophenylalanine, and the inhibition is antagonized by phenylalanine. Puromycin at 10−4 m very strongly inhibited the indoleacetic acid-induced growth of oat coleoptile and artichoke tuber sections and exerted a less powerful effect on pea stem sections. As found earlier with chloramphenicol, concentrations of puromycin effective in inhibiting the growth of coleoptile sections had quantitatively similar effects on protein synthesis, as measured by the incorporation of C14-leucine into protein of the coleoptile tissue. Several analogues of RNA bases were also tested, but while 8-azaguanine very strongly inhibited growth of artichoke tuber disks, 6-azauracil was the only one of this group clearly inhibitory to growth in coleoptile or pea stem sections. Actinomycin D actively inhibited both elongation and the incorporation of C14-leucine into protein in oat coleoptile sections. Inhibition of the 2 processes went closely parallel. Actinomycin D also powerfully inhibited growth of artichoke tuber disks. All the compounds effective in inhibiting growth generally inhibited the uptake of leucine as well.
The possibility that auxin causes cell enlargement in plants by inducing the synthesis of a messenger RNA and of one or more new but unstable enzymes, is discussed. Possible but less favored alternative explanations are: A) that auxin induces synthesis of a wall protein, or B) that the continued synthesis of some other unstable protein (by a process independent of auxin) may be a prerequisite for cell enlargement.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIRNSTIEL M. L., HYDE B. B. Protein synthesis by isolated pea nucleoli. J Cell Biol. 1963 Jul;18:41–50. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCKMAN R. W., ANDERSON E. P. BIOCHEMISTRY OF CANCER (METABOLIC ASPECTS). Annu Rev Biochem. 1963;32:463–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.32.070163.002335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D. B., Ray P. M. Direct and Indirect Effects of Auxin on Cell Wall Synthesis in Oat Coleoptile Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1965 Mar;40(2):345–352. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bal A. K., Gross P. R. Mitosis and Differentiation in Roots Treated with Actinomycin. Science. 1963 Feb 15;139(3555):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3555.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CERRONI R. E., ZEUTHEN E. Inhibition of macromolecular synthesis and of cell division in synchronized Tetrahymena. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Mar;26:604–605. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLELAND R. HYDROXYPROLINE AS AN INHIBITOR OF AUXIN-INDUCED CELL ELONGATION. Nature. 1963 Nov 30;200:908–909. doi: 10.1038/200908a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLICK R. E., HACKETT D. P. THE ROLE OF PROTEIN AND NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF RESPIRATION IN POTATO TUBER SLICES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50:243–250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GALE E. F. MECHANISMS OF ANTIBIOTIC ACTION. Pharmacol Rev. 1963 Sep;15:481–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTTA Y., STERN H. SYNTHESIS OF MESSENGER-LIKE RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND PROTEIN DURING MEIOSIS IN ISOLATED CELLS OF TRILLIUM ERECTUM. J Cell Biol. 1963 Oct;19:45–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.19.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen W. A. THE INCORPORATION OF C-ADENINE AND C-PHENYLALANINE BY DEVELOPING ROOT-TIP CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1957 Dec 15;43(12):1038–1046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.43.12.1038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARAKASHIAN M. W., HASTINGS J. W. The inhibition of a biological clock by actinomycin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2130–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L. Ribonucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis as Essential Processes for Cell Elongation. Plant Physiol. 1964 May;39(3):365–370. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klenow H., Frederiksen S. Differential inhibition of RNA synthesis by actinomycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Oct 14;17(3):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL H. G., ALTMAN R. L. The depression of the incorporation of sulfur amino acids into Bacillus cereus by 8-Azaguanine. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2029–2035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER C. Reversible inhibition of cell division and enlargement in plant tissues by 2,6-diaminopurine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Jul;83(3):561–565. doi: 10.3181/00379727-83-20418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton R. K., Raison J. K. The separate incorporation of amino acids into storage and soluble proteins catalysed by two independent systems isolated from developing wheat endosperm. Biochem J. 1964 Jun;91(3):528–539. doi: 10.1042/bj0910528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHANS D. PUROMYCIN INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS: INCORPORATION OF PUROMYCIN INTO PEPTIDE CHAINS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Apr;51:585–592. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noodén L. D., Thimann K. V. Inhibition of protein synthesis and of auxin-induced growth by chloramphenicol. Plant Physiol. 1965 Jan;40(1):193–201. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomisek A., Reid M. R., Short W. A., Skipper H. E. Studies on the Photosynthetic Reaction. III. The Effects of Various Inhibitors upon Growth and Carbonate-Fixation in Chlorella Pyrenoidosa. Plant Physiol. 1957 Jan;32(1):7–10. doi: 10.1104/pp.32.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmolinsky M. B., Haba G. L. INHIBITION BY PUROMYCIN OF AMINO ACID INCORPORATION INTO PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1721–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



