Abstract
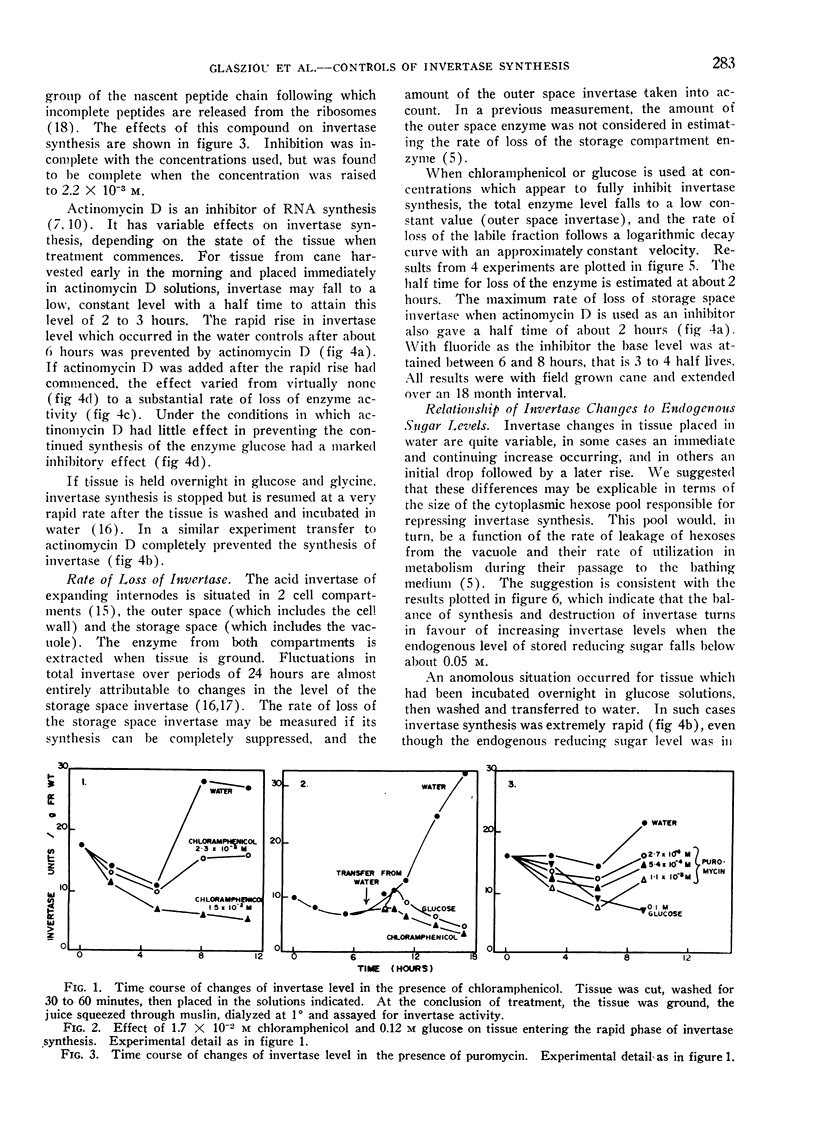
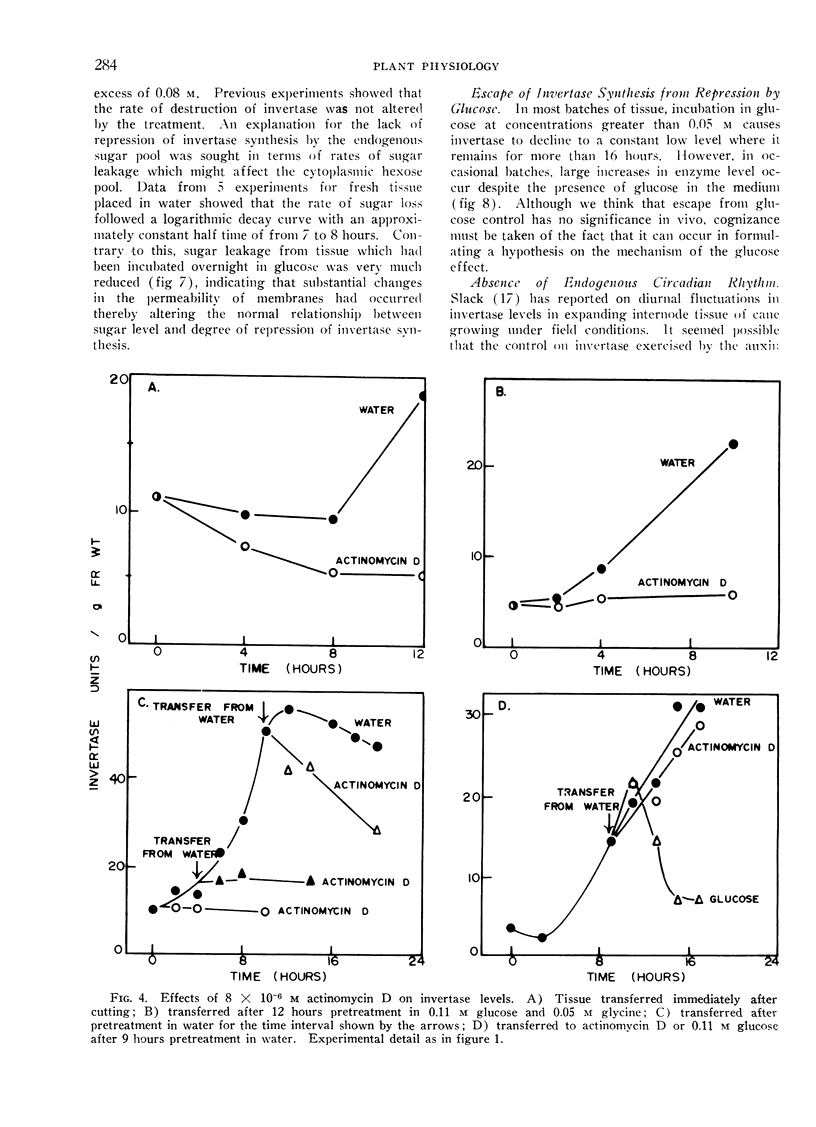
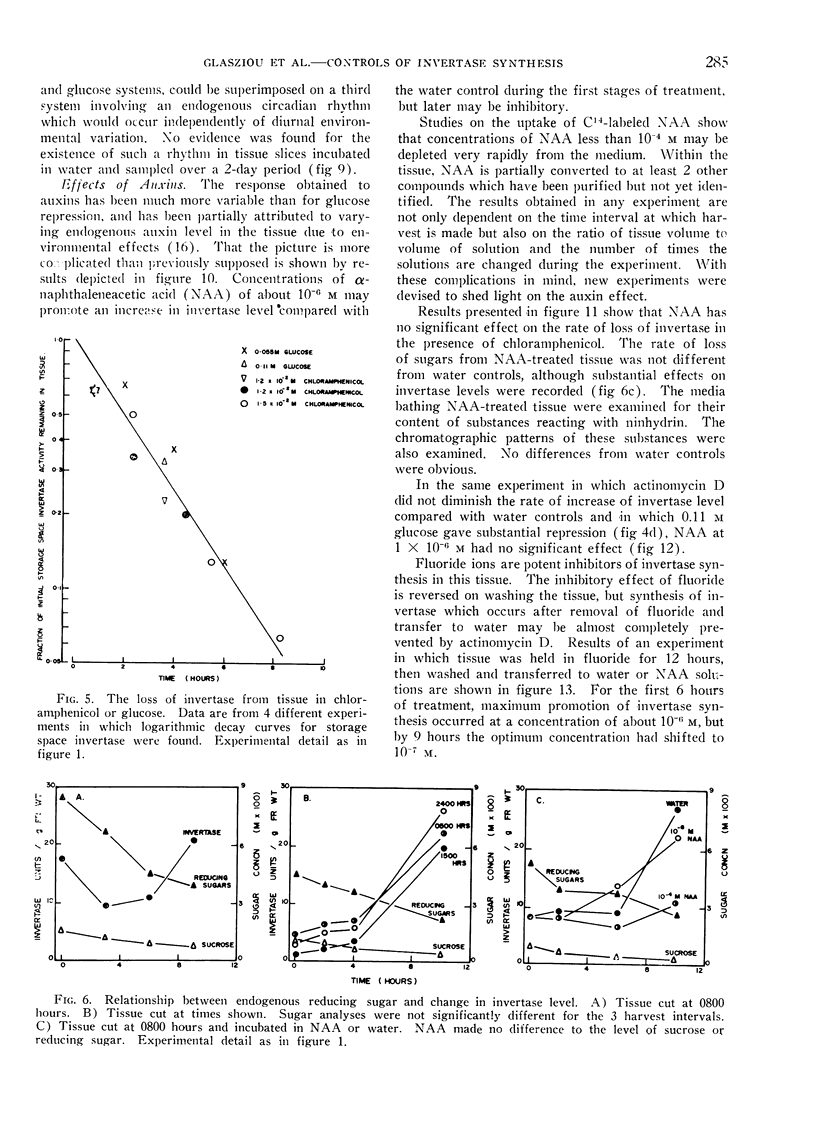
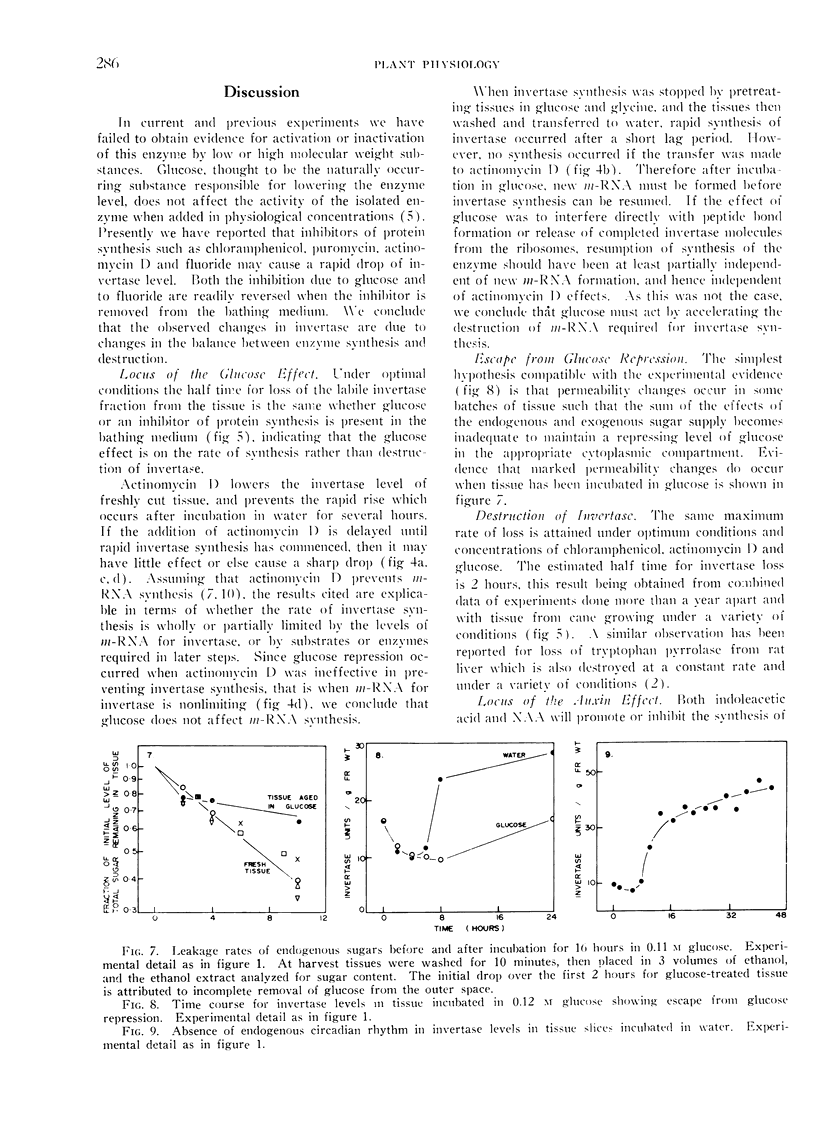
In tissue slices from rapidly expanding internodes of sugar cane the vacuolar invertase level is a function of the balance between synthesis and destruction. The enzyme is destroyed in the tissue at an approximately constant rate with a half time of 2 hours. Invertase synthesis is regulated by both auxin and glucose. From studies with inhibitors of protein and RNA synthesis we conclude that auxin alters the rate of synthesis and glucose increases the rate of destruction of messenger RNA required for the production of invertase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COLOMBO B., FELICETTI L., BAGLIONI C. INHIBITION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS BY CYCLOHEXIMIDE IN RABBIT RETICULOCYTES. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Feb 3;18:389–395. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90719-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARREN L. D., HOWELL R. R., TOMKINS G. M., CROCCO R. M. A PARADOXICAL EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D: THE MECHANISM OF REGULATION OF ENZYME SYNTHESIS BY HYDROCORTISONE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1121–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H., RABINOWITZ M., REICH E. Basis of actinomycin action. I. DNA binding and inhibition of RNA-polymerase synthetic reactions by actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2094–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ J., FURTH J. J., MALAMY M., ALEXANDER M. The role of deoxyribonucleic acid in ribonucleic acid synthesis. III. The inhibition of the enzymatic synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid by actinomycin D and proflavin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1222–1230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch M. D., Glasziou K. T. Sugar Accumulation Cycle in Sugar Cane. II. Relationship of Invertase Activity to Sugar Content & Growth Rate in Storage Tissue of Plants Grown in Controlled Environments. Plant Physiol. 1963 May;38(3):344–348. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L., Ingle J. REQUIREMENT FOR THE SYNTHESIS OF DNA-LIKE RNA FOR GROWTH OF EXCISED PLANT TISSUE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52(6):1382–1388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Key J. L. Ribonucleic Acid and Protein Synthesis as Essential Processes for Cell Elongation. Plant Physiol. 1964 May;39(3):365–370. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.3.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noodén L. D., Thimann K. V. EVIDENCE FOR A REQUIREMENT FOR PROTEIN SYNTHESIS FOR AUXIN-INDUCED CELL ENLARGEMENT. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Aug;50(2):194–200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacher J. A., Hatch M. D., Glasziou K. T. Sugar Accumulation Cycle in Sugar Cane. III. Physical & Metabolic Aspects of Cycle in Immature Storage Tissues. Plant Physiol. 1963 May;38(3):348–354. doi: 10.1104/pp.38.3.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON A. R., SCHWEET R. ROLE OF THE GENETIC MESSAGE IN INITIATION AND RELEASE OF THE POLYPEPTIDE CHAIN. Nature. 1964 May 2;202:435–437. doi: 10.1038/202435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


