Abstract
This work was undertaken to determine the kinds and amount of substances that would account for the previously demonstrated differential growth of Claviceps purpurea on guttation fluids from Rosen rye, Genesee wheat, and Traill barley seedlings. Chromatographic methods were used for determining amino acids and sugars, spot tests and spectrometric methods for inorganic materials, and microbiological methods for vitamins.
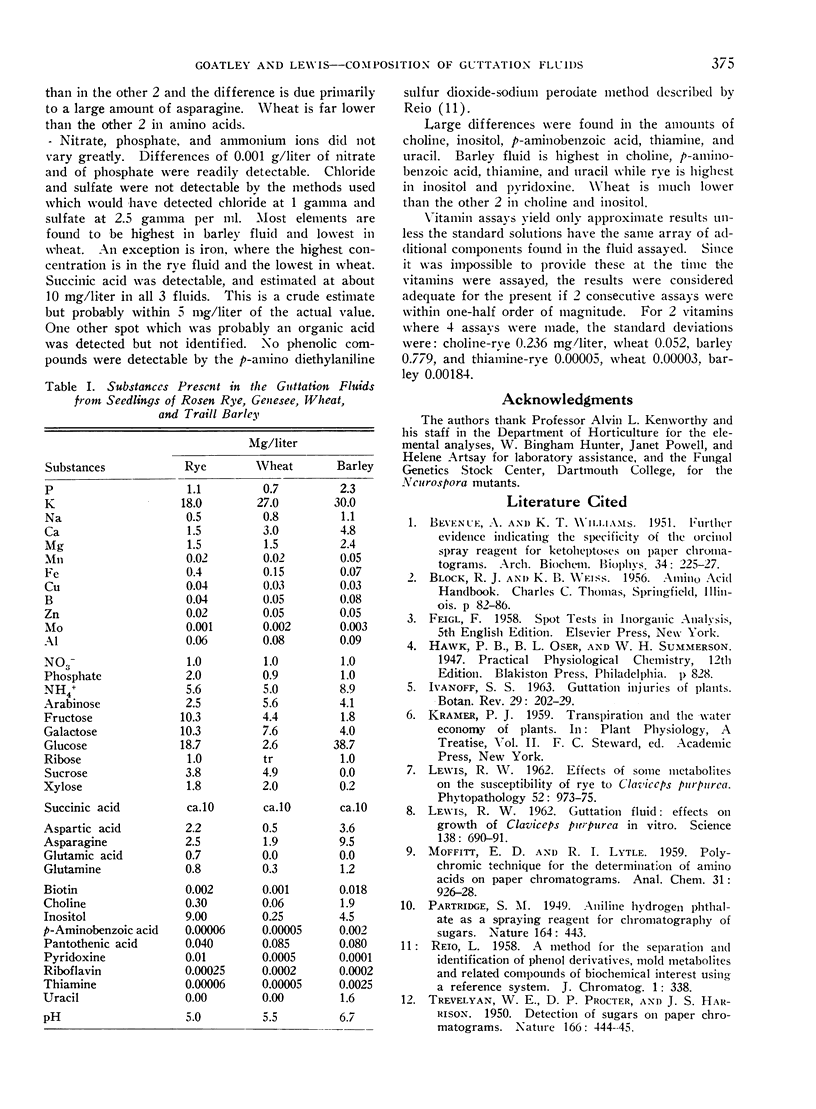
Total sugar content is about equal in rye and barley fluids, but lower in wheat. Glucose is the principal sugar component of the rye and barley fluids and galactose highest in wheat. Most of the amino acid in all 3 fluids is aspartic acid or asparagine. Barley fluid is far higher than the other 2 in total amino acids, with wheat the lowest. Most inorganic elements are found to be highest in barley and lowest in wheat, with the exception of iron where rye is highest and barley lowest. Barley fluid is highest in choline, p-aminobenzoic acid, thiamine, and uracil, while rye is highest in inositol and pyridoxine. Wheat is much lower than the other 2 in choline and inositol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


