Abstract
Gossypol was examined in relation to its effect on certain enzymes and enzyme complexes associated with the tricarboxylic acid cycle and the electron transport system. Succinic dehydrogenase and cytochrome oxidase activity from sweet potato was completely inhibited by gossypol at 7.5 × 10−3 m and 2.0 × 10−3 m, respectively. Succinoxidase activity of the same preparations was fully inhibited at a lower concentration, 2.5 × 10−4 m. This concentration did not affect either succinic dehydrogenase or cytochrome oxidase, the primary and terminal enzymes of the succinoxidase complex. The nature of the intermediate step or steps inhibited at this concentration is not yet known. Gossypol was further shown to inhibit phosphorylation at concentrations having no appreciable effect on oxidation. Inhibition in general was not reduced by increased substrate concentrations in the enzyme systems examined, with the exception of cytochrome c for cytochrome oxidase. Bovine serum albumin was partially effective in reducing gossypol inhibition, provided that it was present before enzyme exposure to gossypol.
Full text
PDF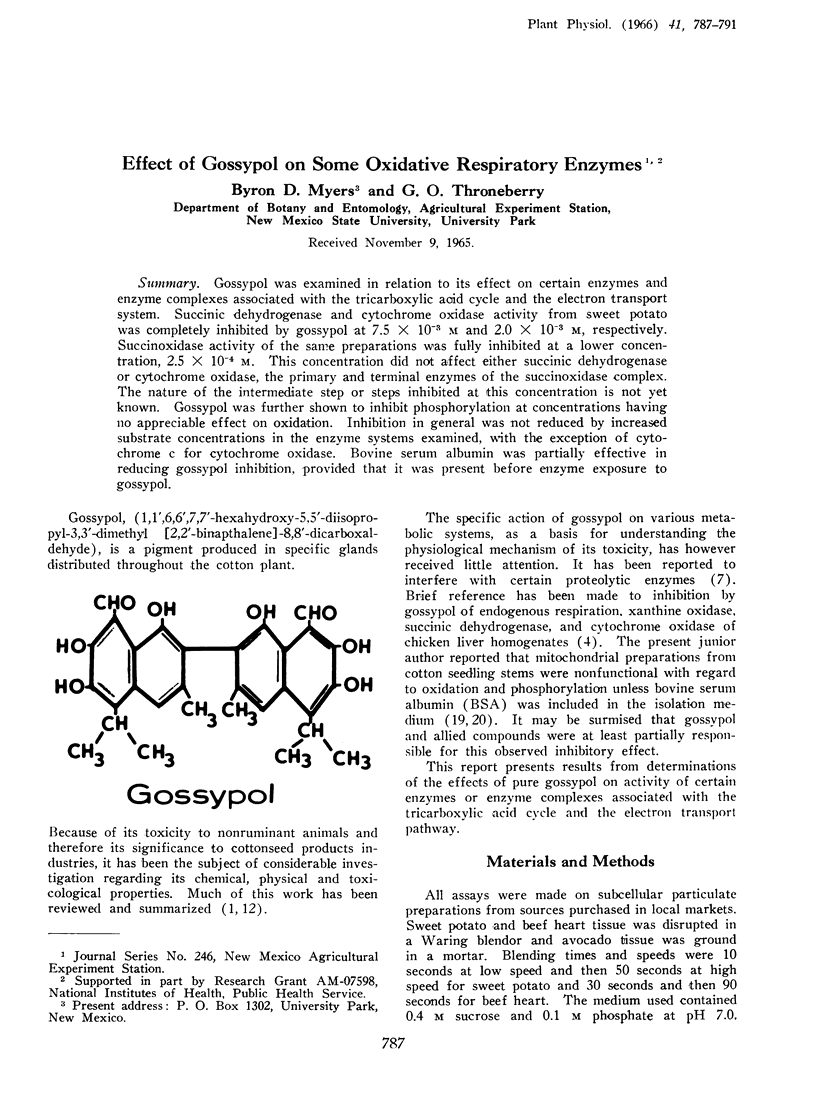

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHMAD K., SCHNEIDER H. G., STRONG F. M. Studies on the biological action of antimycin A. Arch Biochem. 1950 Sep;28(2):281–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HACKETT D. P., RICE B., SCHMID C. The partial dissociation of phosphorylation from oxidation in plant mitochondria by respiratory chain inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2140–2144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEILIN D., KING T. E. Effect of inhibitors on the activity of soluble succinic dehydrogenase and on the reconstitution of the succinic dehydrogenase-cytochrome system from its components. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1960 May 17;152:163–187. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1960.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIGHTBOWN J. W., JACKSON F. L. Inhibition of cytochrome systems of heart muscle and certain bacteria by the antagonists of dihydrostreptomycin: 2-alkyl-4-hydroxyquinoline N-oxides. Biochem J. 1956 May;63(1):130–137. doi: 10.1042/bj0630130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYMAN C. M., BALIGA B. P., SLAY M. W. Reactions of proteins with gossypol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Oct;84:486–497. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90610-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER V. R., REIF A. E. Inhibition of an electron transport component by antimycin A. J Biol Chem. 1952 Jan;194(1):287–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUMPHREY A. M. Studies on the electron transfer system. XLV. Some effects of antimycin on cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2384–2390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REIF A. E., POTTER VAN R. Studies on succinoxidase inhibition. I. Pseudoirreversible inhibition by a naphthoquinone and by antimycin A. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):279–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMON E. W. The effect of digitonin on the cytochrome c oxidase activity of plant mitochondria. Biochem J. 1958 May;69(1):67–74. doi: 10.1042/bj0690067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGER T. P., KEARNEY E. B. Determination of succinic dehydrogenase activity. Methods Biochem Anal. 1957;4:307–333. doi: 10.1002/9780470110201.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Throneberry G. O. Factors affecting oxidative phosphorylation by subcellular particles isolated from cotton seedling hypocotyls. Plant Physiol. 1962 Nov;37(6):781–784. doi: 10.1104/pp.37.6.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Throneberry G. O. Isolation of metabolically-active subcellular particles from etiolated cotton seedling hypocotyls using bovine serum albumin in preparative medium. Plant Physiol. 1961 May;36(3):302–309. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


