Abstract
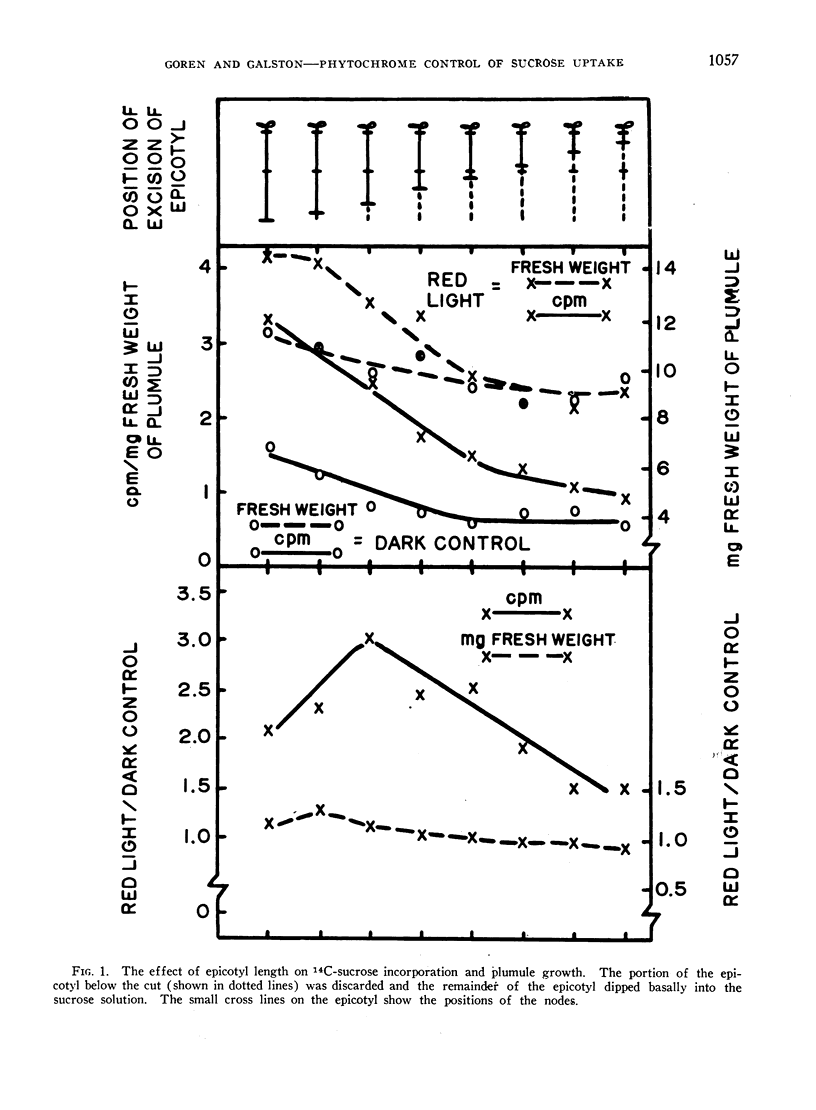
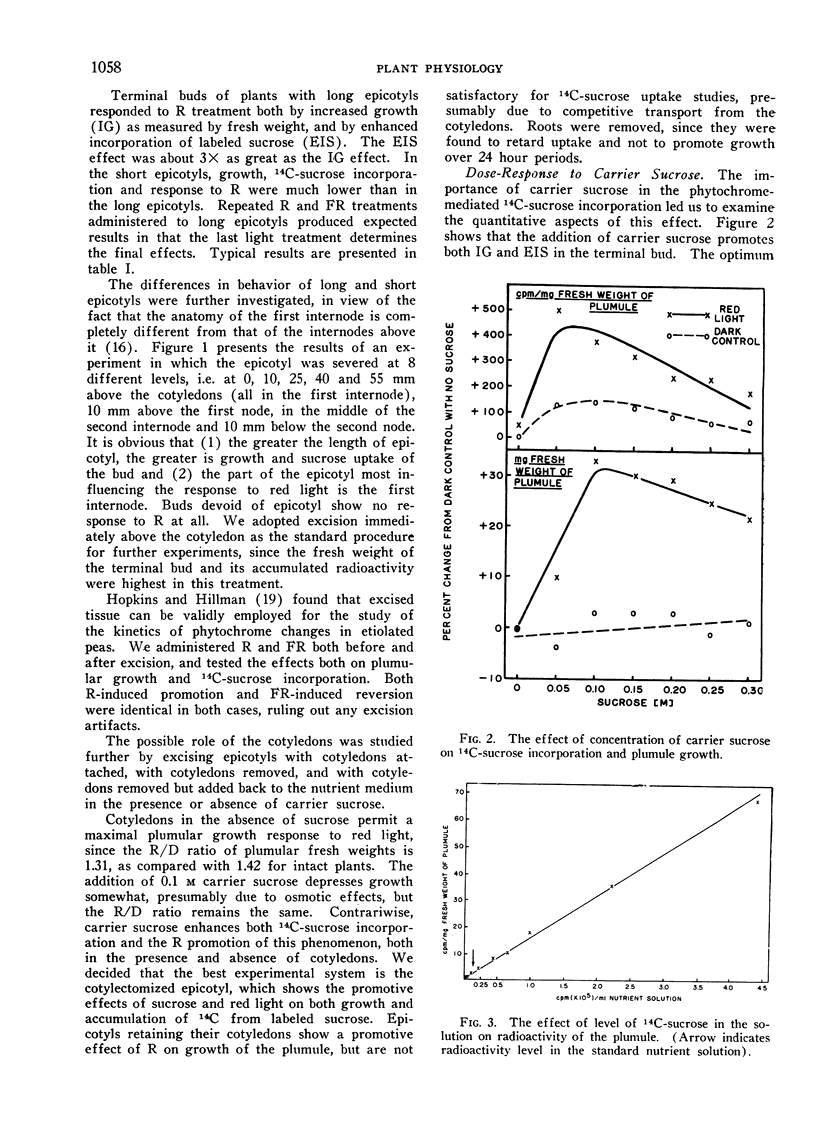
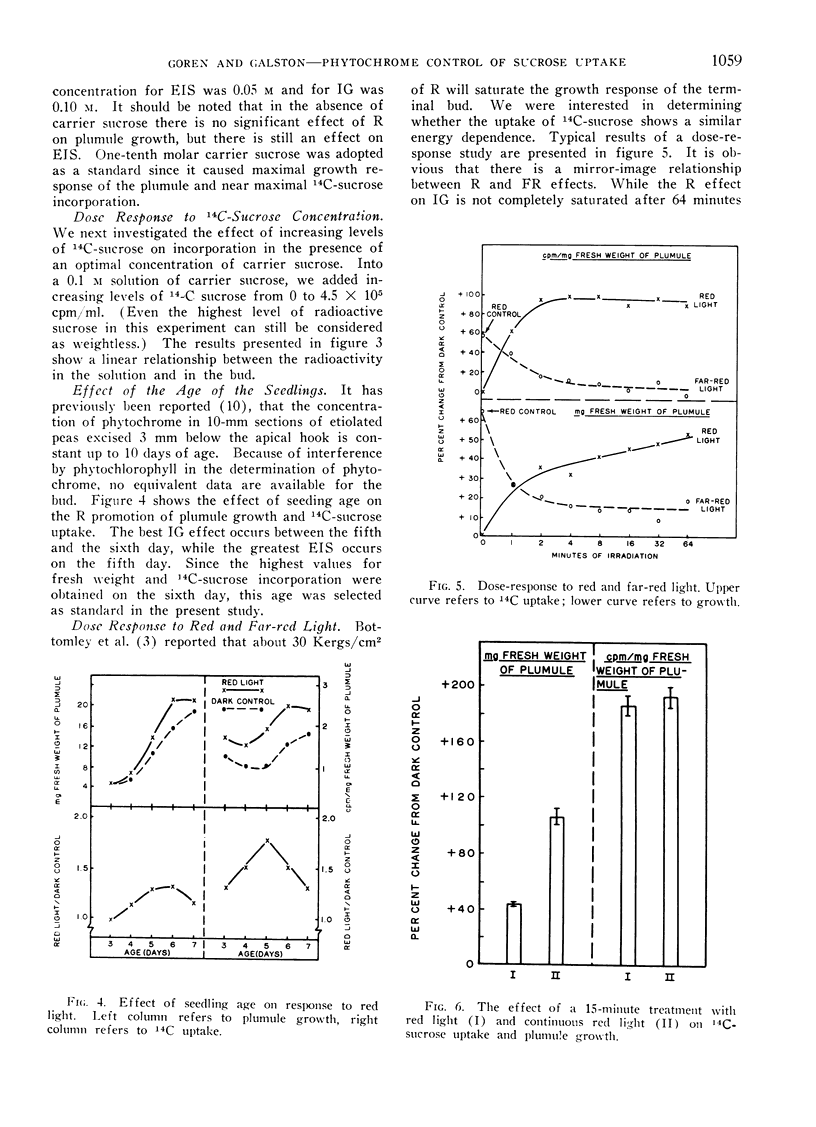
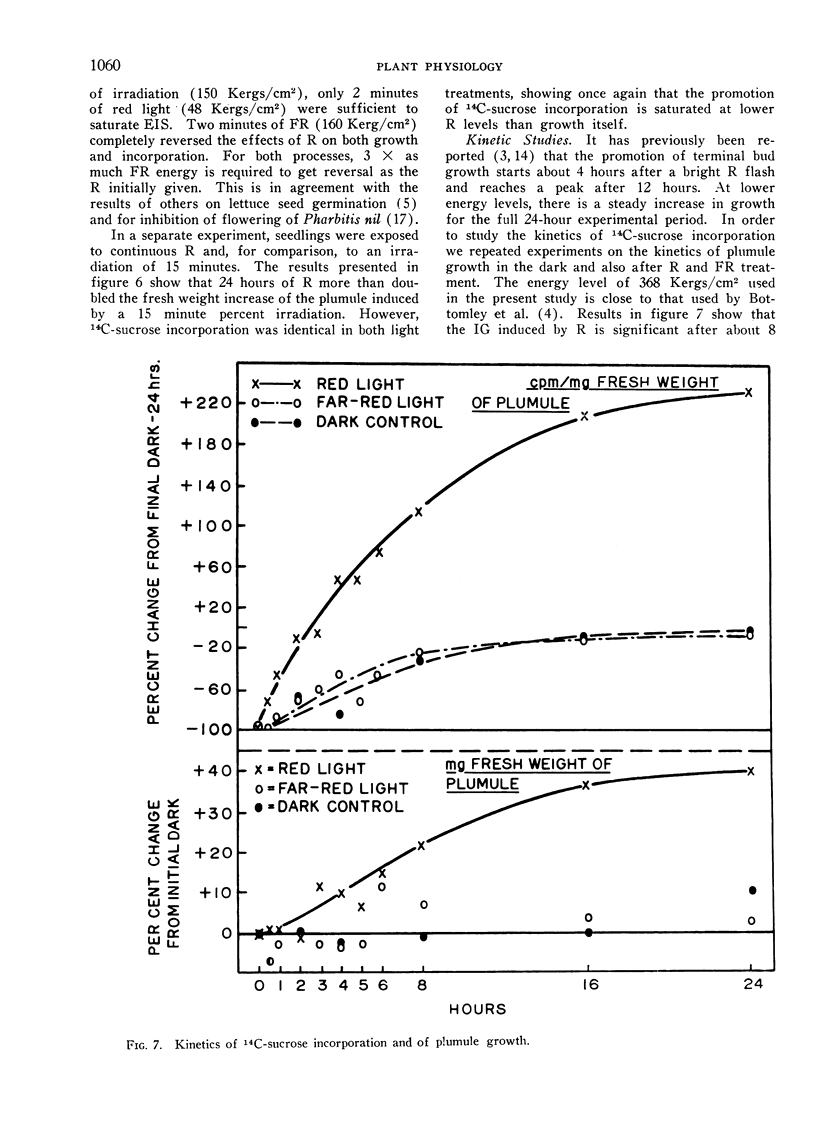
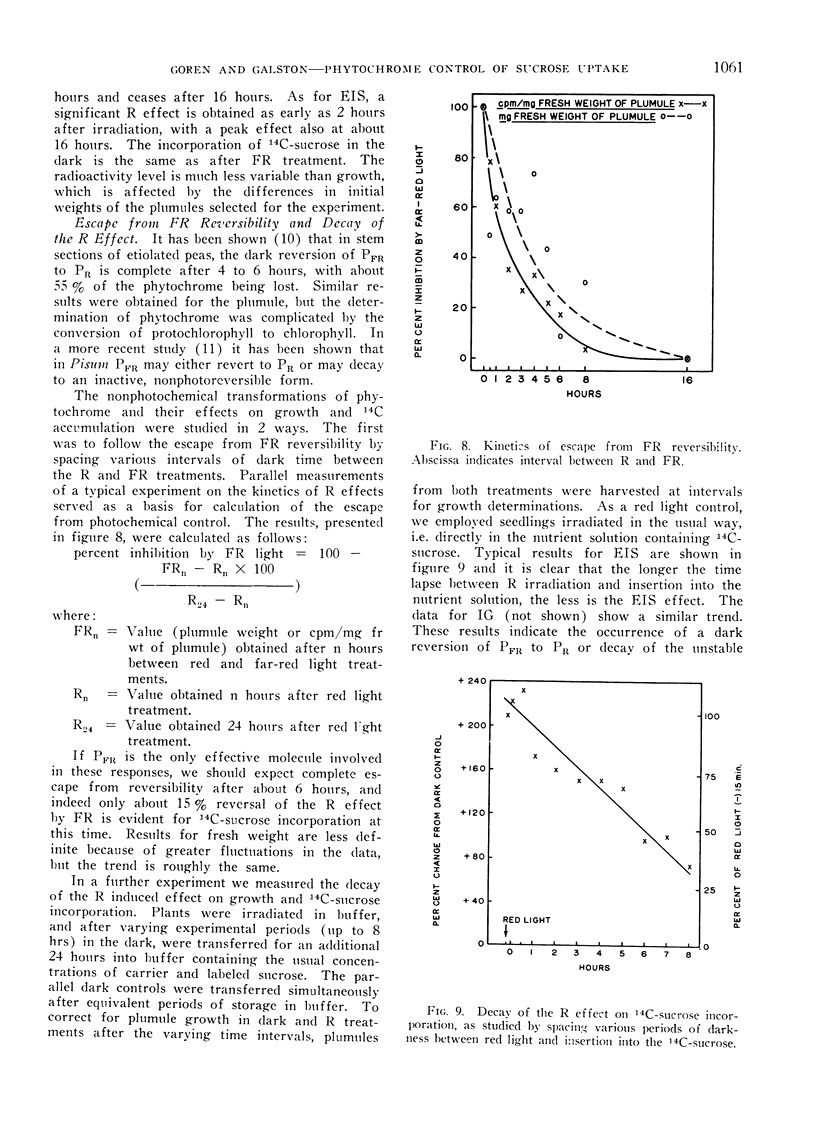
When etiolated pea epicotyls are excised immediately above the cotyledons and dipped basally into 14C-sucrose, their terminal buds respond to red light by increased growth (IG) and enhanced incorporation of sucrose (EIS). Both phenomena are phytochrome controlled, showing typical kinetics, reversal by far-red light, escape from photochemical control and limitation to leaf tissue. EIS is of greater magnitude, occurs more rapidly and is saturated by lower energies of red light than IG, suggesting its possible importance as a controlling reaction in phytochrome-mediated growth. Both IG and EIS are best shown in the presence of a long epicotyl derived from a 5 to 6-day-old seedling in the presence of about 0.1 m unlabeled sucrose in the medium.
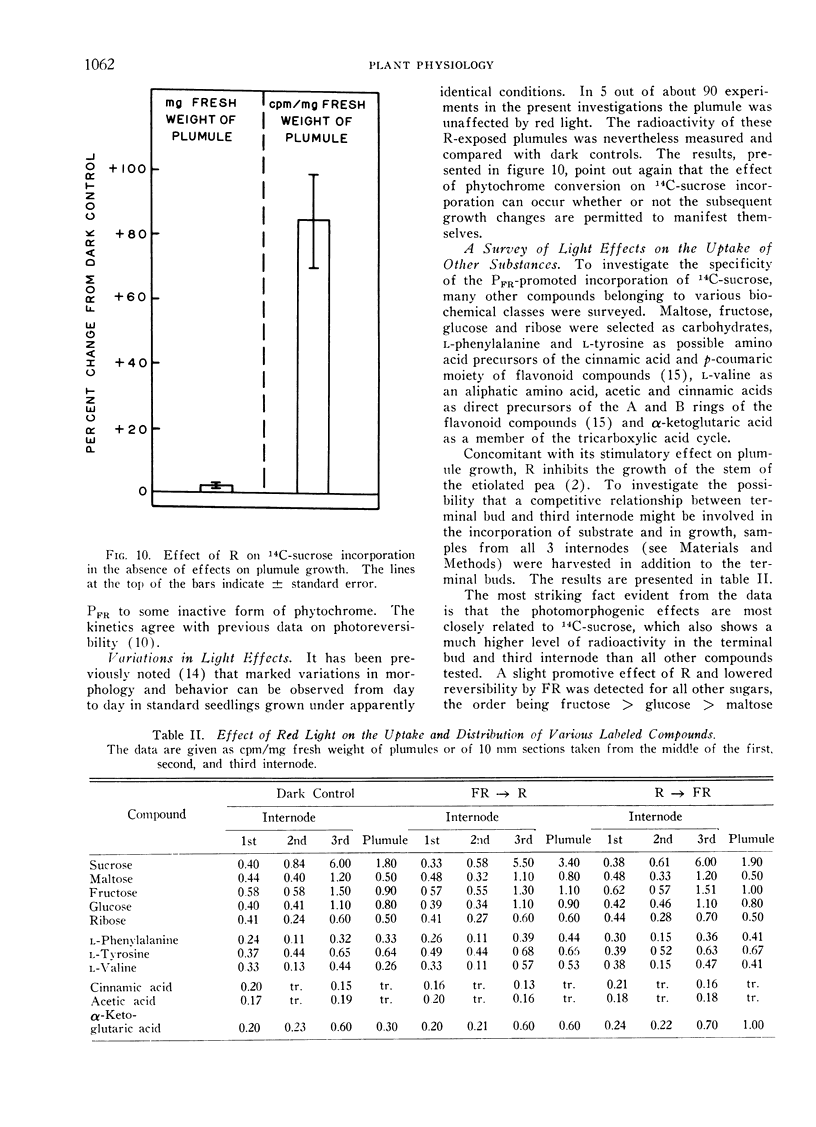
Enhanced incorporation is most dramatic with sucrose; lesser effects are shown with fructose, glucose, maltose and ribose in that order. Both level of incorporation and red light effects are poor for labeled tyrosine, phenylalanine, valine, acetic acid, cinnamic acid and α-ketoglutaric acid. The possible connection between carbohydrates and phytochrome-mediated photomorphogenesis is considered.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borthwick H. A., Hendricks S. B., Parker M. W., Toole E. H., Toole V. K. A Reversible Photoreaction Controlling Seed Germination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Aug;38(8):662–666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.8.662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs W. R., Siegelman H. W. Distribution of Phytochrome in Etiolated Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):934–941. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


