Abstract
Primary roots of solution-grown, 5-day-old or 6-day-old seedlings of corn (Zea mays L.) 10 to 14 cm in length were used to study radial salt transport. Measurements were made of the volume of root pressure exudation, salt concentration of the exudate, and rate of salt movement into the xylem exudate. The 32P uptake, O2 consumption, and dehydrogenase activity of the root cortex and stele also were studied.
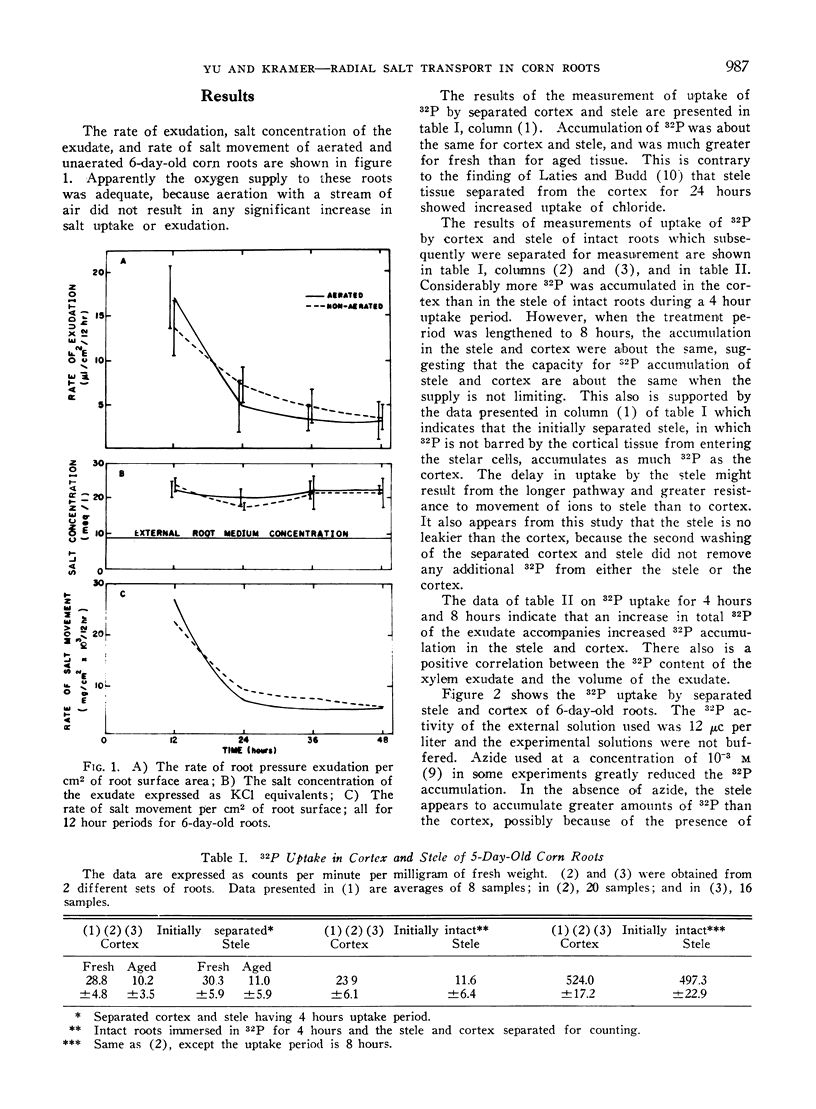
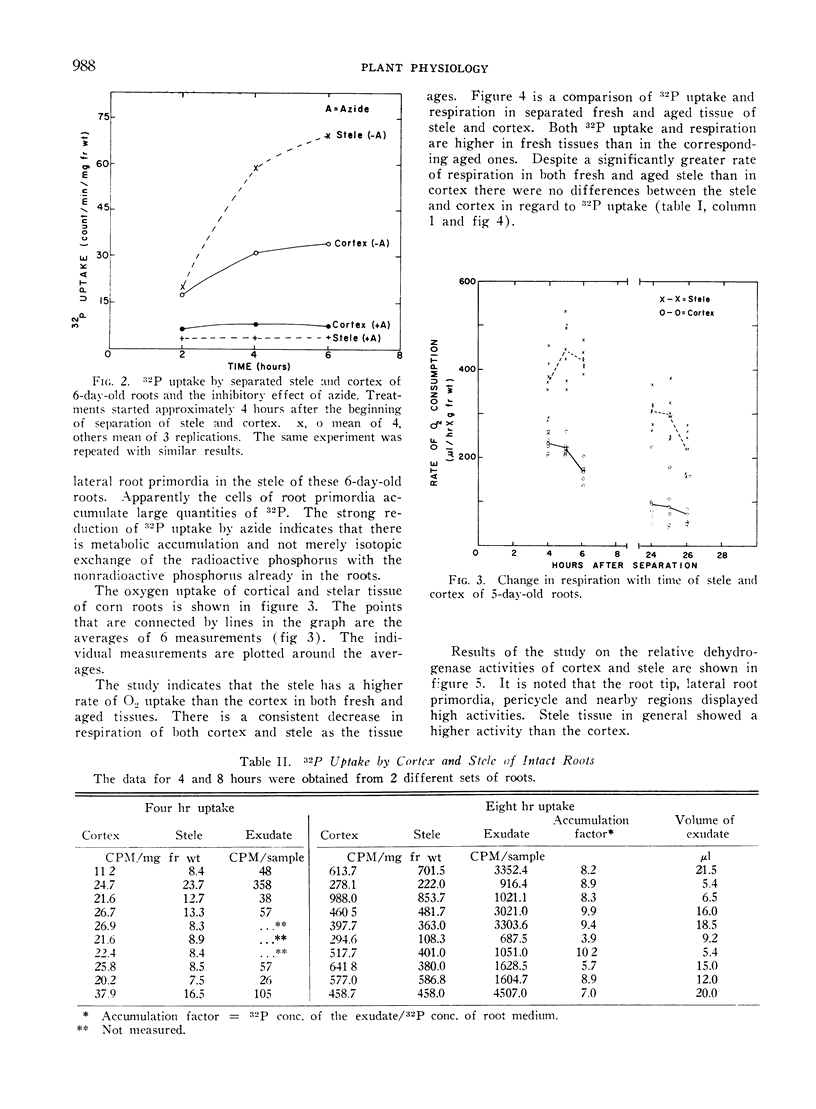
These roots produced copious root pressure exudate containing 4 to 10 times the concentration of 32P in the external solution. Freshly separated stele from 5-day-old roots accumulated 32P as rapidly as the cortex from which it was separated and the stele of intact roots also accumulated 32P. Separated stele has a higher oxygen uptake than cortex. It also shows strong dehydrogenase activity with the tetrazolium test. The high oxygen consumption, 32P uptake and strong dehydrogenase activity indicate that the cells of the stele probably play a direct role in salt transport.
These data raise doubts concerning theories of radial salt transport into the xylem based on the assumption that the stele is unable to accumulate salt vigorously.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laties G. G., Budd K. THE DEVELOPMENT OF DIFFERENTIAL PERMEABILITY IN ISOLATED STELES OF CORN ROOTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52(2):462–469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



