Abstract
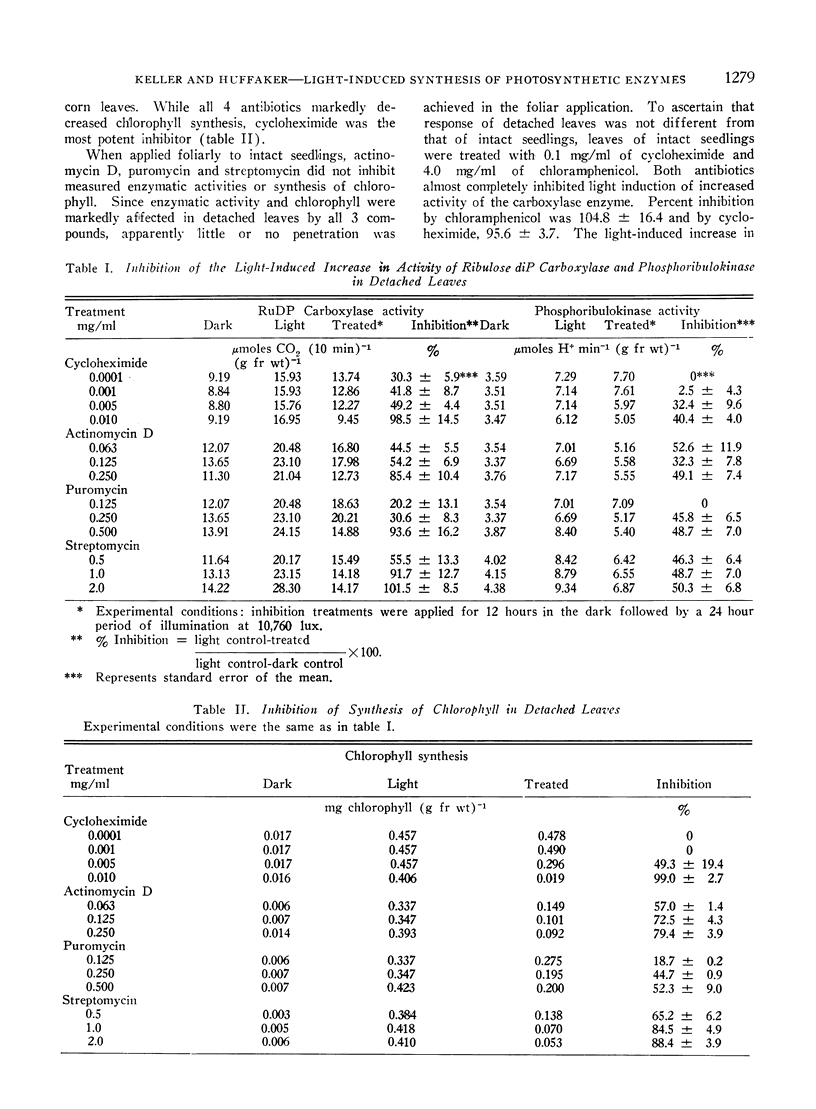
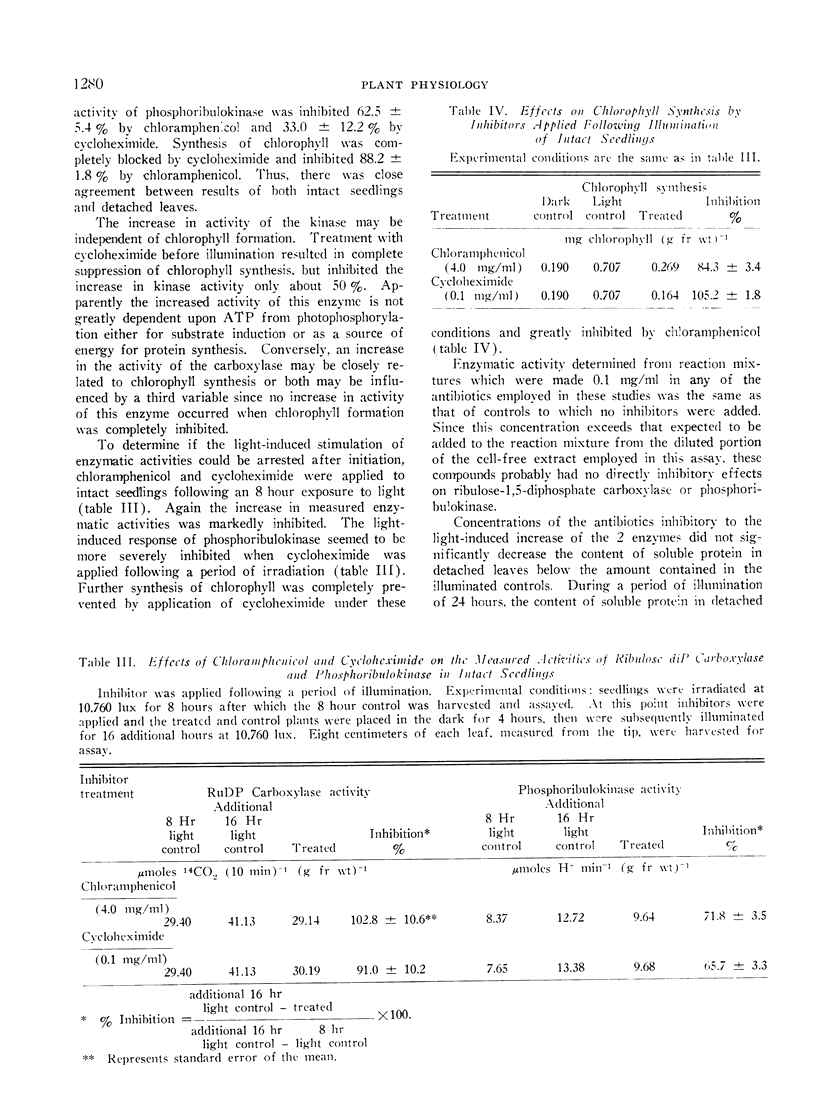
When actinomycin D, puromycin, streptomycin, chloramphenicol, and cycloheximide, known inhibitors of protein synthesis, were applied to leaves of intact seedlings or detached leaves of barley prior to their greening, the same general response resulted: the light-induced increase in activity of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase was prevented while that of phosphoribulokinase was only partially suppressed; synthesis of chlorophyll was arrested. This is taken as preliminary evidence that de novo synthesis of protein may be responsible for the observed increase in ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase activity during greening. However, other factors may be involved with the light-induced stimulation of phosphoribulokinase.
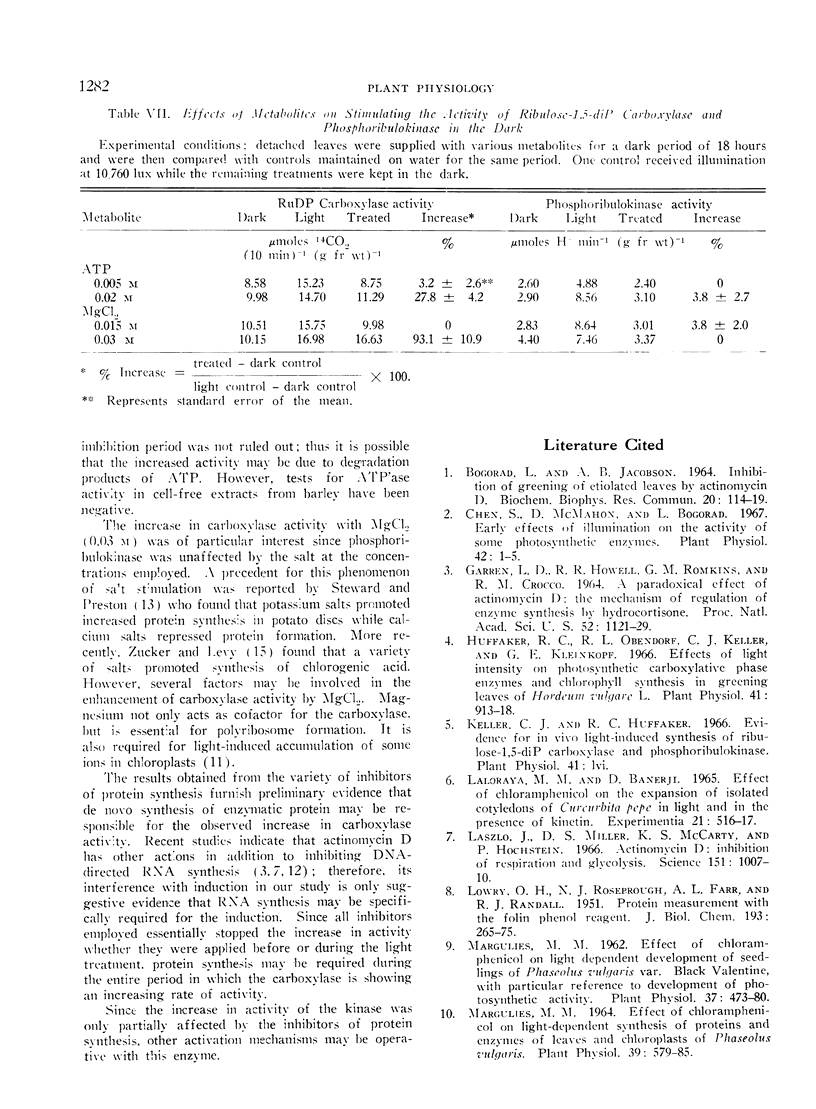
Carbohydrate metabolites and substrates of the enzymes failed to induce the formation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase and phosphoribulokinase in the dark. No evidence was found for the presence of inhibitors in etiolated seedlings or activators in illuminated leaves of barley. Carboxylase activity almost equal to that of the illuminated water control was stimulated by MgCl2 in the dark; MgCl2 had no effect on the activity of the kinase.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GARREN L. D., HOWELL R. R., TOMKINS G. M., CROCCO R. M. A PARADOXICAL EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D: THE MECHANISM OF REGULATION OF ENZYME SYNTHESIS BY HYDROCORTISONE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1121–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huffaker R. C., Obendorf R. L., Keller C. J., Kleinkopf G. E. Effects of Light Intensity on Photosynthetic Carboxylative Phase Enzymes and Chlorophyll Synthesis in Greening Leaves of Hordeum vulgare L. Plant Physiol. 1966 Jun;41(6):913–918. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.6.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo J., Miller D. S., McCarty K. S., Hochstein P. Actinomycin D: inhibition of respiration and glycolysis. Science. 1966 Feb 25;151(3713):1007–1010. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3713.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M. M. Effect of Chloramphenicol on Light Dependent Development of Seedlings of Phaseolus vulgaris var. Black Valentine, With Particular Reference to Development of Photosynthetic Activity. Plant Physiol. 1962 Jul;37(4):473–480. doi: 10.1104/pp.37.4.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nobel P. S., Packer L. Light-Dependent Ion Translocation in Spinach Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1965 Jul;40(4):633–640. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.4.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REVEL M., HIATT H. H., REVEL J. P. ACTINOMYCIN D: AN EFFECT ON RAT LIVER HOMOGENATES UNRELATED TO ITS ACTION ON RNA SYNTHESIS. Science. 1964 Dec 4;146(3649):1311–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3649.1311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward F. C., Preston C. THE EFFECT OF SALT CONCENTRATION UPON THE METABOLISM OF POTATO DISCS AND THE CONTRASTED EFFECT OF POTASSIUM AND CALCIUM SALTS WHICH HAVE A COMMON ION. Plant Physiol. 1941 Jan;16(1):85–116. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROWN P. W. AN IMPROVED METHOD FOR THE ISOLATION OF CARBOXYDISMUTASE. PROBABLE IDENTITY WITH FRACTION I PROTEIN AND THE PROTEIN MOIETY OF PROTOCHLOROPHYLL HOLOCHROME. Biochemistry. 1965 May;4:908–918. doi: 10.1021/bi00881a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


