Abstract
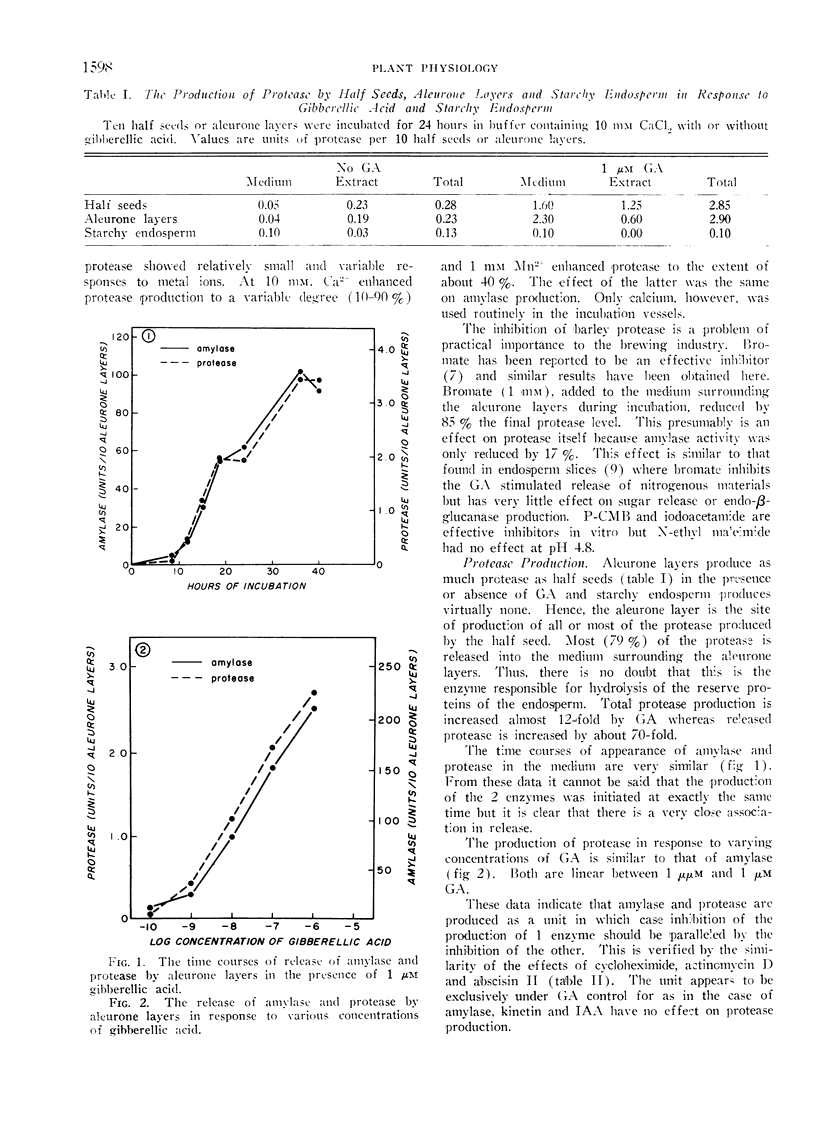
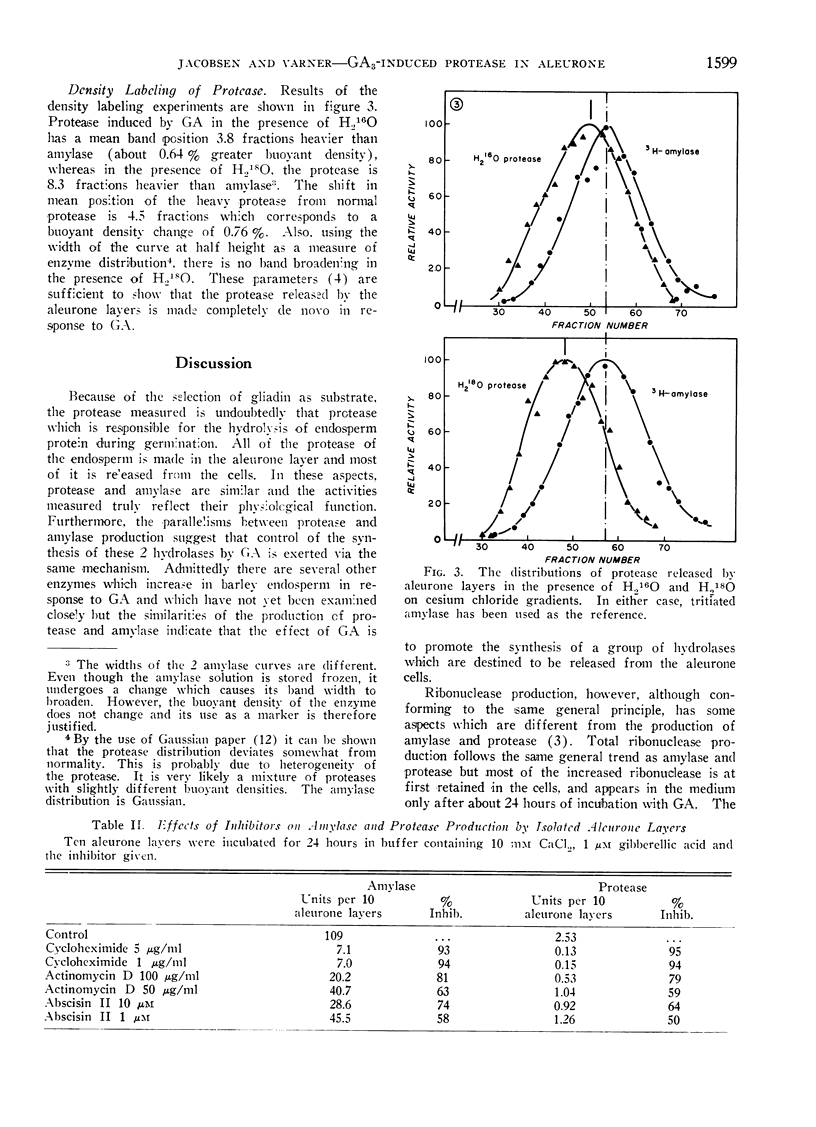
The production of protease by isolated aleurone layers of barley in response to gibberellic acid has been examined. The protease arises in the aleurone layer and is mostly released from the aleurone cells. The courses of release of amylase and protease from aleurone layers, the dose responses to gibberellic acid and the effects of inhibitors on the production of both enzymes are parallel. As is the case for amylase, protease is made de novo in response to the hormone. These data give some credence to the hypothesis that the effect of gibberellic acid is to promote the simultaneous synthesis and secretion of a group of hydrolases.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chrispeels M. J., Varner J. E. Gibberellic Acid-enhanced synthesis and release of alpha-amylase and ribonuclease by isolated barley and aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1967 Mar;42(3):398–406. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.3.398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUSTER L., GIFFORD R. H. Changes in 3'-nucleotidase during the germination of wheatembryos. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Mar;96:534–540. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


