Abstract
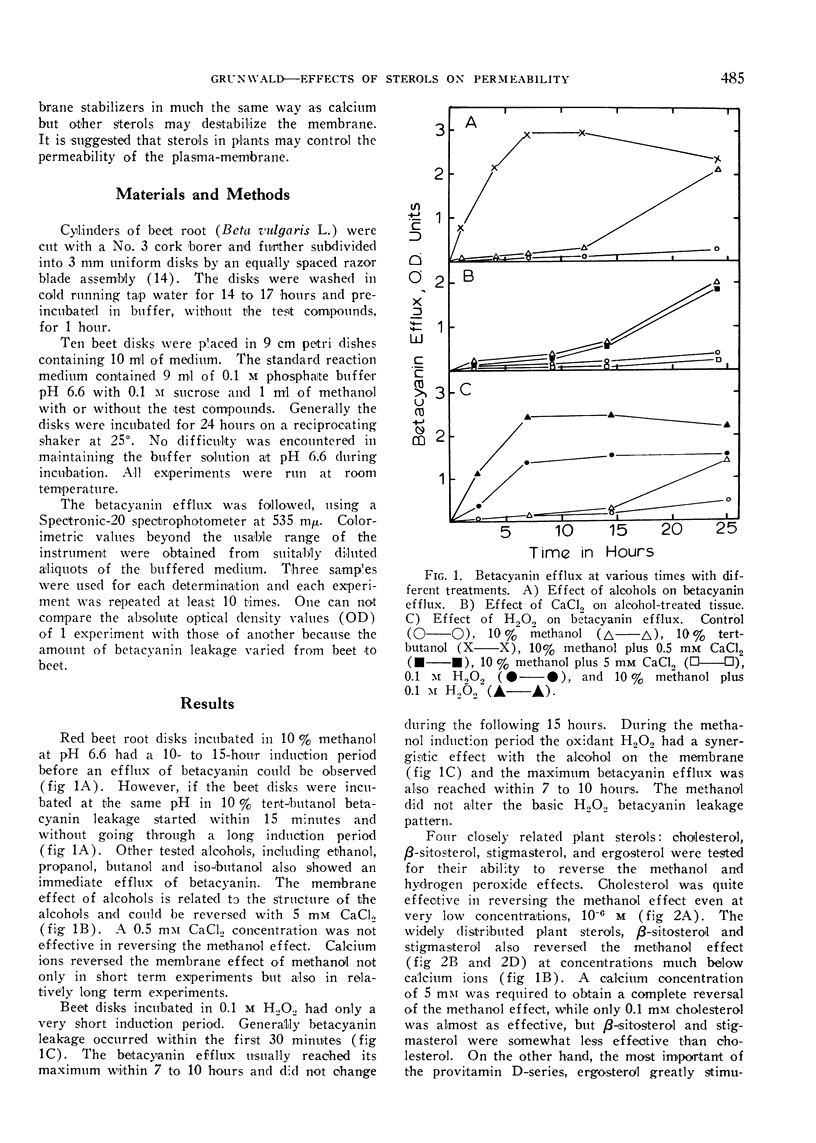
Alcohols and hydrogen peroxide altered the permeability of membranes of Beta vulgaris root cells. Generally alcohols increased the permeability of membranes without going through an induction period except methanol which required a 10- to 15-hour induction period. The membrane effect of methanol could be inhibited with CaCl2, cholesterol, β-sitosterol, and stigmasterol. Cholesterol was the most effective inhibitor, followed by β-sitosterol and stigmasterol; and at the same concentration, the sterols were more effective than CaCl2, the classic membrane stabilizer.
Ergosterol increased the methanol-initiated betacyanin leakage. Since none of the tested sterols reversed the betacyanin efflux induced by hydrogen peroxide, the sterols do not apparently act as antioxidants. The results are explained in terms of sterol-phospholipid interaction, based on stereochemistry and charge distribution.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GERSHFELD N. L., HEFTMANN E. Steroil hormones and monolayers. Experientia. 1963 Jan 15;19:2–2. doi: 10.1007/BF02135318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HECHTER O., LESTER G. Cell permeability and hormone action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1960;16:139–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. M., Daly O. Regulation of betacyanin efflux from beet root by poly-L-lysine, ca-ion and other substances. Plant Physiol. 1966 Nov;41(9):1429–1434. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.9.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. M., Halpern L. A. Effects of peroxides on permeability and their modification by indoles, vitamin E, and other substances. Plant Physiol. 1965 Sep;40(5):792–796. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.5.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEPPERMAN J., TEPPERMAN H. M. Some effects of hormones on cells and cell constituents. Pharmacol Rev. 1960 Sep;12:301–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


