Abstract
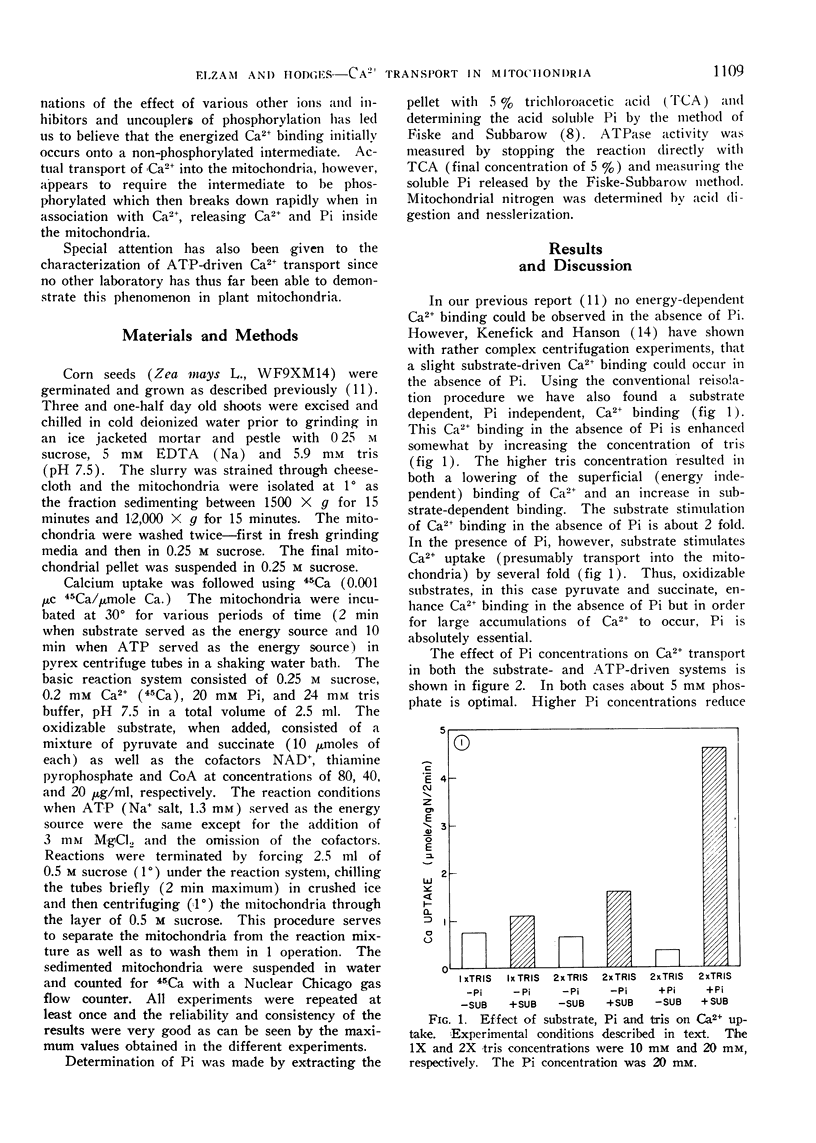
Experimental conditions which optimize both substrate- and ATP-dependent Ca2+ transport in corn (Zea mays) mitochondria have been determined. It has been found that a substrate (pyruvate + succinate) dependent, Pi independent, binding of Ca2+ occurs. This reaction is very rapid and complete in less than 30 seconds. For massive accumulation of calcium, Pi is essential. Phosphate is accumulated along with the calcium and the ratio of Ca:Pi accumulated is about 1.6:1 indicating the precipitation of hydroxyapatite inside the mitochondria.
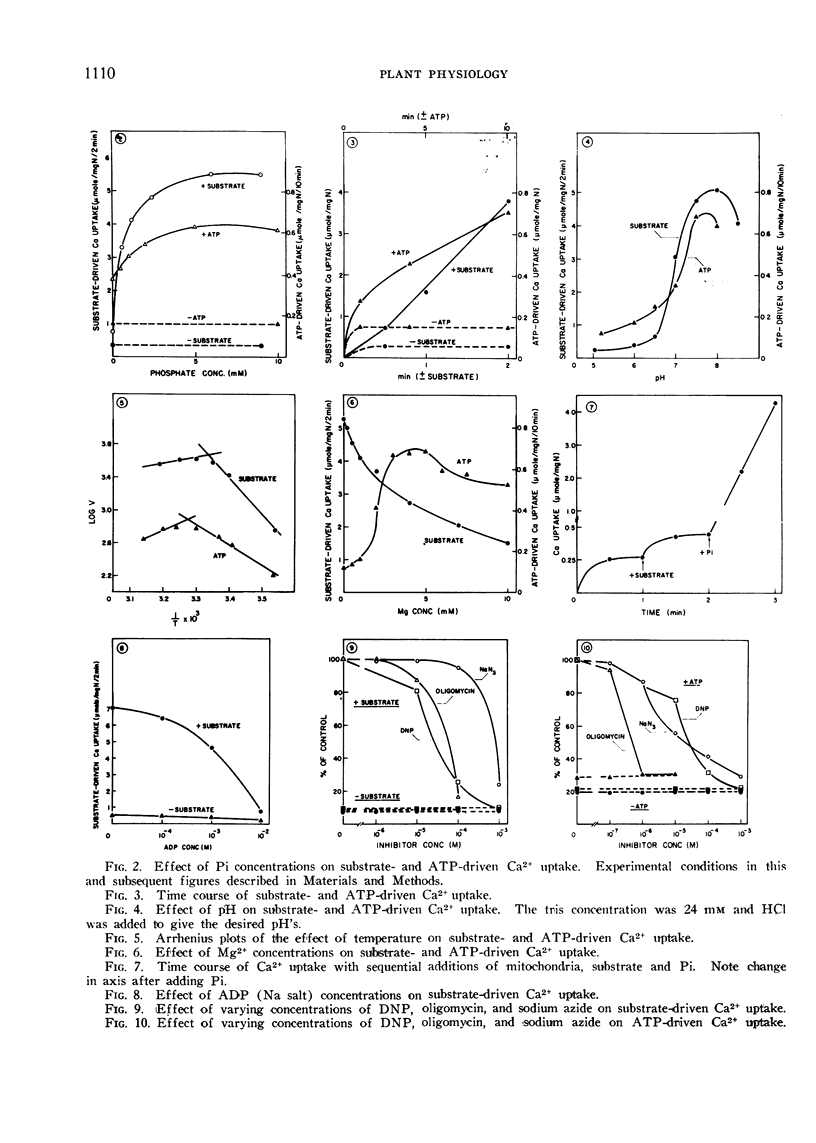
The activation energies and Michaelis constants for both the substrate- and ATP-driven reactions have been determined. It has also been shown that the substrate-driven system is more efficient in Ca2+ accumulation than the ATP-driven system. This is partially due to the fact that Mg2+ is essential for the ATP-driven system but not for the substrate-driven system and that Mg2+ acts as a strong competitor of Ca2+ transport. The effect of other inorganic ions on Ca2+ transport energized by both substrate and ATP were examined.
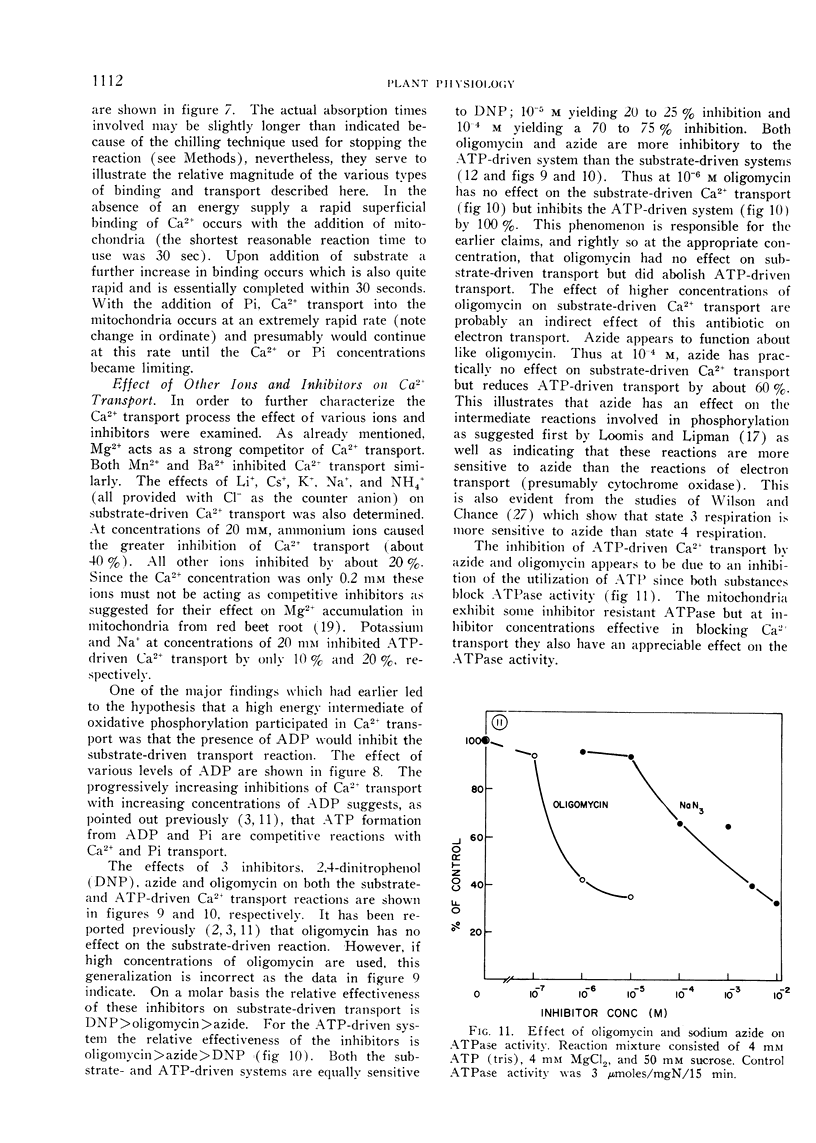
The results lend support to the hypothesis that high energy intermediates of oxidative phosphorylation participate directly in Ca2+ binding and transport in plant mitochondria.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRIERLEY G. P., BACHMANN E., GREEN D. E. Active transport of inorganic phosphate and magnesium ions by beef heart mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Nov 15;48:1928–1935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.11.1928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIERLEY G. P., MURER E., BACHMANN E. STUDIES ON ION TRANSPORT. III. THE ACCUMULATION OF CALCIUM AND INORGANIC PHOSPHATE BY HEART MITOCHONDRIA. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Apr;105:89–102. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90239-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bielawski J., Lehninger A. L. Stoichiometric relationships in mitochondrial accumulation of calcium and phosphate supported by hydrolysis of adenosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4316–4322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANCE B. THE ENERGY-LINKED REACTION OF CALCIUM WITH MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2729–2748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockrell R. S., Harris E. J., Pressman B. C. Energetics of potassium transport in mitochondria induced by valinomycin. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2326–2335. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh I. K., Wiskich J. T. Ion uptake by carrot tissue and mitochondria. Aust J Biol Sci. 1967 Jun;20(3):553–564. doi: 10.1071/bi9670553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson J. B., Miller R. J. Evidence for active phosphate transport in maize mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):727–734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Elzam O. E. Effect of azide and oligomycin on the transport of calcium ions in corn mitochondria. Nature. 1967 Aug 26;215(5104):970–972. doi: 10.1038/215970a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges T. K., Hanson J. B. Calcium Accumulation by Maize Mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1965 Jan;40(1):101–109. doi: 10.1104/pp.40.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenefick D. G., Hanson J. B. Contracted state as an energy source for ca binding and ca + inorganic phosphate accumulation by corn mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1966 Dec;41(10):1601–1609. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.10.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenefick D. G., Hanson J. B. The site of oligomycin action in corn mitochondria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):899–902. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI C. S., LEHNINGER A. L. STOICHIOMETRY OF RESPIRATORY STIMULATION, ACCUMULATION OF CA++ AND PHOSPHATE, AND OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN RAT LIVER MITOCHONDRIA. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3971–3980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Chance B., Ogata E. A mechanism for the reactions of calcium with mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1069–1076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H. Mitochondrial ion transport: mechanism and physiological significance. Fed Proc. 1966 May-Jun;25(3):903–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A. K. The permeability of the human erythrocyte to sodium and potassium. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;36(1):57–110. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. F., Chance B. Reversal of azide inhibition by uncouplers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):751–756. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


