Abstract
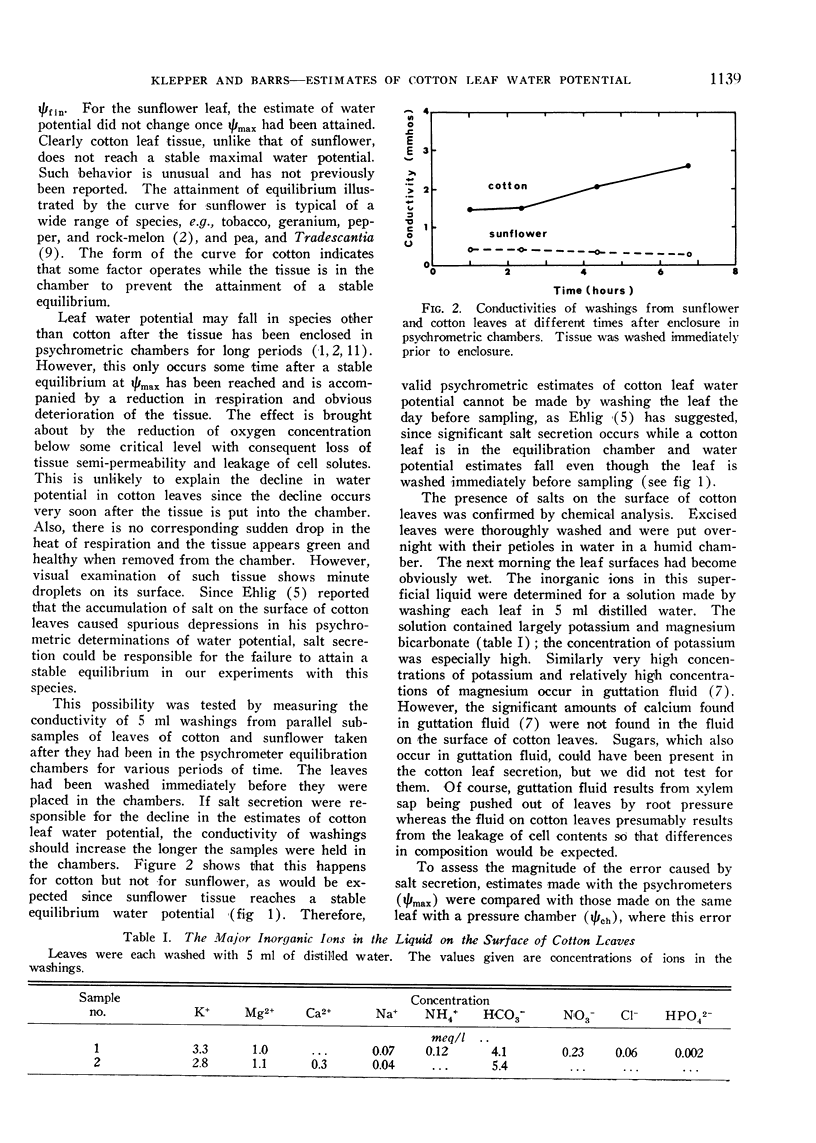
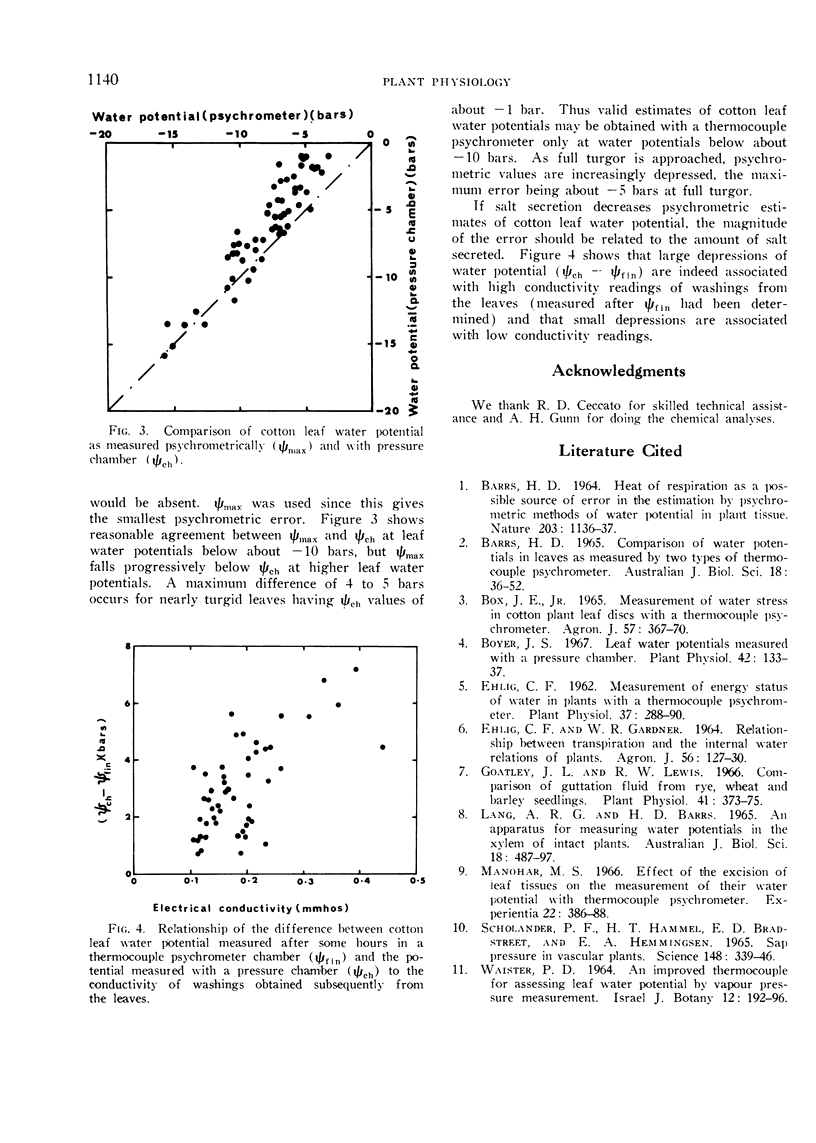
Thermocouple psychrometers gave lower estimates of water potential of cotton leaves than did a pressure chamber. This difference was considerable for turgid leaves, but progressively decreased for leaves with lower water potentials and fell to zero at water potentials below about −10 bars. The conductivity of washings from cotton leaves removed from the psychrometric equilibration chambers was related to the magnitude of this discrepancy in water potential, indicating that the discrepancy is due to salts on the leaf surface which make the psychrometric estimates too low. This error, which may be as great as 400 to 500%, cannot be eliminated by washing the leaves because salts may be secreted during the equilibration period. Therefore, a thermocouple psychrometer is not suitable for measuring the water potential of cotton leaves when it is above about −10 bars.
Full text
PDF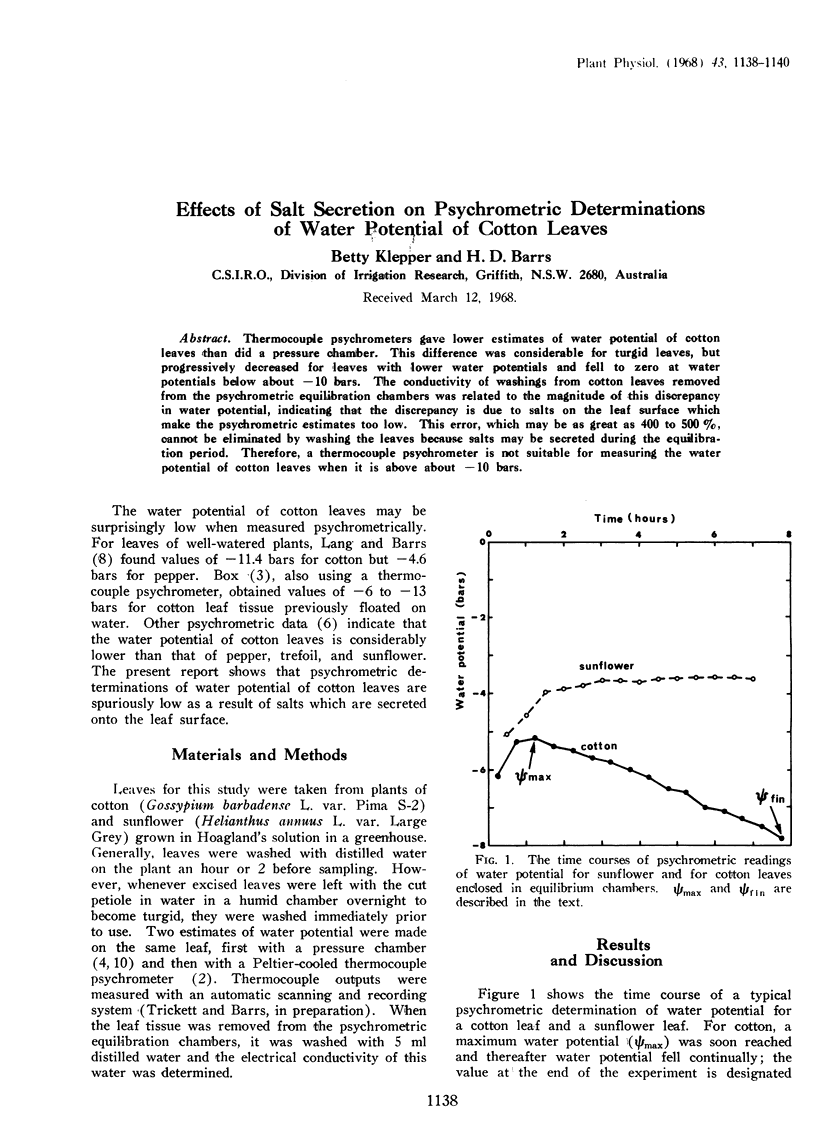
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer J. S. Leaf water potentials measured with a pressure chamber. Plant Physiol. 1967 Jan;42(1):133–137. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholander P. F., Bradstreet E. D., Hemmingsen E. A., Hammel H. T. Sap Pressure in Vascular Plants: Negative hydrostatic pressure can be measured in plants. Science. 1965 Apr 16;148(3668):339–346. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3668.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


