Abstract
Background
In September 2012, a comprehensive survey of Pico Island was conducted along an elevational transect, starting at Manhenha (10 m a.s.l.) and culminating at the Pico Mountain caldera (2200 m a.s.l.). The primary objective was to systematically inventory the bryophytes inhabiting the best-preserved areas of native vegetation environments. Twelve sites were selected, each spaced at 200 m elevation intervals. Within each site, two 10 m x 10 m plots were established in close proximity (10-15 m apart). Within these plots, three 2 m x 2 m quadrats were randomly selected and sampled for bryophytes using microplots measuring 10 cm x 5 cm, which were then collected into paper bags. Six substrates were surveyed in each quadrat: rock, soil, humus, organic matter, tree bark and leaves/fronds. Three replicates were obtained from all substrates available and colonised by bryophytes, resulting in a maximum of 18 microplots per quadrat, 54 microplots per plot, 108 microplots per site, and a total of 1296 microplots across the 12 sites on Pico Island.
New information
Two-thirds of the maximum expected number of microplots (n = 878; 67.75%) were successfully collected, yielding a total of 4896 specimens. The vast majority (n = 4869) were identified at the species/subspecies level. The study identified a total of 70 moss and 71 liverwort species or subspecies. Elevation levels between 600-1000 m a.s.l., particularly in the native forest plots, exhibited both a higher number of microplots and greater species richness. This research significantly enhanced our understanding of Azorean bryophyte diversity and distribution, contributing valuable insights at both local and regional scales. Notably, two new taxa for the Azores were documented during the MOVECLIM study, namely the pleurocarpous mosses Antitrichiacurtipendula and Isotheciuminterludens.
Keywords: Azores, Bryoflora, BRYOLAT methodology, elevational gradient, GIMS - Global Island Monitoring Scheme, liverworts, mosses, Pico Island, substrates
Introduction
Bryophytes are ancient terrestrial plants (Laenen et al. 2014), exhibiting different morphological and physiological adaptations that account for their evolutionary success. These plants are characterised by the dominance of the gametophyte over the sporophyte and lack of vascular tissues in the sporophyte. These organisms are taxonomically classified in three Divisions: Bryophyta (mosses), Marchantiophyta (liverworts) and Anthocerotophyta (hornworts) (Goffinet and Shaw 2009). Ecologically, bryophytes occupy a wide range of habitats, from the Poles to the Equator and from sea-level to high mountains, presenting higher diversity in the tropics (Goffinet and Shaw 2009).
As they are small and rootless, bryophytes are very dependent of their immediate context, responding to different environmental changes, namely, substrate composition and acidity, rainfall, temperature, salinity and pollution (e.g. Hodgetts et al. (2019)). Bryophytes maintain a number of ecosystems services, positively influencing the water cycle (Coelho et al. 2023a, Coelho et al. 2023b) and the decomposition of organic material, creating a favourable environment for the development of other non-pioneer organisms (Goffinet and Shaw 2009).
Globally, bryophytes represent the second largest group of plants - with over 20000 species: 13000 mosses, 8000 liverworts and 250 hornworts (Goffinet and Shaw 2009). In Europe, there are 1892 species of bryophytes (1390 mosses; 494 liverworts; 8 hornworts) (Hodgetts et al. 2020), while about a quarter of those are found in the Azores (308 mosses; 162 liverworts; 5 hornworts) (Gabriel et al. 2010), although this archipelago represents only 0.06% of the European territory (Borges et al. 2023). Bryophytes are, thus, one of the main biological groups for maintaining biodiversity (Sérgio et al. 2012), with different taxonomic groups responding differently to environmental pressure and gradients (e.g. Henriques et al. (2016)) and including a number of conservation concern species (Hodgetts et al. 2019).
The distribution of bryophyte species in the nine Azorean islands is uneven, but this fact is not completely explained by area or elevation. For instance, Pico Island, the highest and second largest (2350 m a.s.l.; 445 km2), has similar richness of bryophytes (283 species) to the much smaller Faial Island (1043 m a.s.l.; 173 km2) (286 species) (Forjaz 2004, Gabriel et al. 2010). This may be related to the sampling effort amongst different islands. Indeed, the work of many collectors and authors contributed to the current knowledge of the distribution of Azorean bryophytes. A list of publications mentioning bryophytes collected in Pico Island may be seen in Suppl. material 1. It comprises 96 references, published from 1862 to 2023, including mostly journal articles (65), but also other types of references, such as books and book chapters, theses and dissertations, scientific reports, Herbaria records and expert's documents. Erik Sjögren stands out as the major source of distribution information, with more than 3000 records on Pico Island; however, the publications of Herman Persson, Jan-Peter Frahm, Pierre and Valentine Allorge, Tutin and Warburg and Juana González-Mancebo, are also noteworthy, having added more than 100 records each to the bryoflora distribution of the Island.
The 292 bryophyte species known to Pico Island (162 mosses; 126 liverworts; 4 hornworts) (Gabriel et al. 2010, Ellis et al. 2016, Hanusch et al. 2020, Sérgio et al. 2022, Sérgio 2023, Sérgio in press), represent ca. 60% of the richness found in the Azores (Borges et al. 2010) and include five Azorean endemics, such as the endangered moss, Echinodiumrenauldii (Cardot) Broth. (Coelho et al. 2014b, Gabriel et al. 2018). The composition of the bryoflora in Pico Island is related to the altitudinal gradient, with species richness and abundance responding to elevation, rainfall and substrate diversity (Coelho et al. 2021).
Since 2012, an effort has been made to update the information regarding bryophytes in the Azores, namely under the 'MOVECLIM project – Montane Vegetation as Listening Posts for Climate Change’ (Coelho et al. 2014a, Gabriel et al. 2014, Borges et al. 2018). One of the purposes of this project was to characterise the poorly known, but highly diverse, bryophyte flora of different archipelagos, including the Azores, the Canary Islands and the Mascarene Islands. In the Azores, it was possible to survey seven islands using an adaptation of the BRYOLAT protocol (Gabriel et al. 2014): Pico and Terceira Islands were surveyed in 2012; Flores and São Miguel Islands in 2013; São Jorge and Faial Islands in 2014 and Santa Maria Island in 2019. Graciosa and Corvo Islands, the smallest and devoid of native forest, were not surveyed under this protocol.
Thus, the objective of this study was to inventory bryophyte species in different altitudinal gradients (between 10 m and 2200 m a.s.l.) and substrates (rupicolous, terricolous, humicolous, lignicolous, epiphytic, epiphyllous) in the Island of Pico sampled in a stratified way.
General description
Purpose
The main objective of this work was to inventory the bryoflora present in the Pico Natural Park, including Municipalities of Lajes do Pico, São Roque do Pico and Madalena. Sampling was carried out on different altitudinal levels (between 10 m and 2200 m) and substrates (rupicolous, terricolous, humicolous, lignicolous, epiphytic, epiphyllous), with the aim of expanding the database of bryophyte species (mosses, liverworts, hornworts) known to Pico Island.
Project description
Title
Inventory of bryoflora present in different altitudinal gradients of Pico Island (Azores).
Personnel
The bryoflora inventory of Pico Island was carried out during the month of September 2012, within the dates 5-10, under the responsibility of Rosalina Gabriel (RG) and Claudine Ah-Peng (CAP), with the participation of Márcia C.M. Coelho (MC), Débora Henriques (DH), Silvia Calvo Aranda (SCA) and Fernando Pereira (FP). Species growing on organic matter, tree trunks and leaves were identified by MC supervised by RG, while Helena Hespanhol (HH) identified species growing on rock and soil. Challenging specimens were confirmed by Cecília Sérgio (CS) and Manuela Sim-Sim (MSS). In 2023, the species of the genus Frullania were reviewed by Leila N. Morgado (LNM) and RG and were later confirmed by MSS.
Study area description
The Azores Archipelago is a Portuguese autonomous region and comprises nine islands of volcanic origin. It is located in the North Atlantic Ocean (Fig. 1), about 1500 km from the western coast of mainland Europe and approximately 3900 km from the North America coasts. The shortest distance to European Portuguese coast is about 1400 km (Forjaz 2004).
Figure 1.
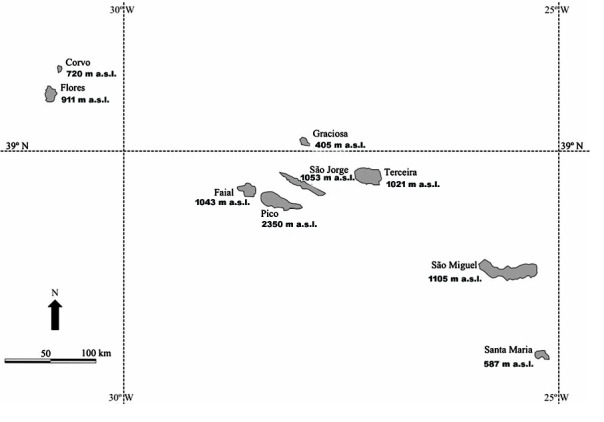
Location and maximum elevation of each island of the Azores Archipelago. Source: Section of Management and Environmental Planning, University of the Azores; Elevation values follow Forjaz (2004).
Given its oceanic location, the Azores have a typically maritime climate, which translates into mild temperatures, with a small temperature range, high relative humidity (%) and high rainfall (mm) in autumn and winter. The average annual temperature varies between 12°C and 23°C, the average annual rainfall varies between 1000 and 1600 mm at sea level and the relative humidity is usually quite high, largely exceeding 80% in all seasons (Forjaz 2004, IPMA 2022).
The Laurissilva Forest of Macaronesia was recognised as a World Natural Heritage site by UNESCO in 1999 (CONSLEG (1992L0043) 2014). Together with the Juniperus-Ilex montane cloud forests, these formations present the highest number of endemisms and other indigenous species (Nunes et al. 2015, Schäfer 2021, Elias et al. 2022). In fact, there are approximately 452 endemic species amongst land and freshwater organisms in the Azores (Borges et al. 2010) and vascular plants stand out with 73 Azorean endemic species and subspecies, a value surpassed only by phylum Arthropoda (266 taxa) (Borges et al. 2010). Native vegetation also includes a high number and cover of bryophytes (Gabriel and Bates 2005, Homem and Gabriel 2008, Couto 2010, Gabriel et al. 2011, Elias et al. 2022), some of which rare and endangered (Esquivel et al. 2008, Hodgetts et al. 2019).
Pico Island (38º33'57" and 38º33'44" N and 28º01'39" and 28º32'33" W), belongs to the central group of the Azores Archipelago (Portugal) in the North Atlantic Ocean. This Island is the second largest (445 km2), the highest (2350 m a.s.l.) and the youngest (0.27 MY) of the Azores (Forjaz 2004) and its forest incorporates the highest contribution of endemic (44%) and native (38%) taxa, compared to the Islands of São Miguel and Terceira (Borges Silva et al. 2022).
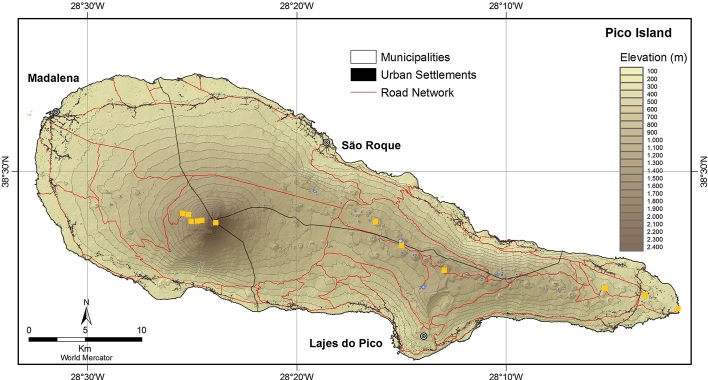
The sampling location and coordinates are listed in Table 1 and Fig. 2.
Table 1.
Bryophyte sampling plots in the different altitudinal gradients (10-2200 m), location name, elevation (in metres) and coordinates (in decimals) (Pico Island, Azores).
| Plot code | Locality | Elevation (m a.s.l.) | Latitude | Longitude |
| PIC_0010_P1 | Pico, Lajes do Pico, 0010 m, Manhenha - Farol. | 17 | 38.413750 | -28.029806 |
| PIC_0010_P2 | 14 | 38.413750 | -28.029944 | |
| PIC_0200_P1 | Pico, Lajes do Pico, 0200 m, Cabeço da Hera. | 224 | 38.418190 | -28.053940 |
| PIC_0200_P2 | 226 | 38.418167 | -28.053639 | |
| PIC_0400_P1 | Pico, Lajes do Pico, 0400 m, Piedade - Fetais. | 365 | 38.425778 | -28.087639 |
| PIC_0400_P2 | 364 | 38.425917 | -28.087361 | |
| PIC_0600_P1 | Pico, São Roque do Pico, 0600 m, Caminho dos Burros - Chão Verde. | 621 | 38.468847 | -28.276194 |
| PIC_0600_P2 | 623 | 38.468814 | -28.275944 | |
| PIC_0800_P1 | Pico, São Roque do Pico, 0800 m, Caiado. | 809 | 38.455778 | -28.257278 |
| PIC_0800_P2 | 813 | 38.455667 | -28.257250 | |
| PIC_1000_P1 | Pico, Lajes do Pico, 1000 m, Caveiro. | 952 | 38.437167 | -28.213028 |
| PIC_1000_P2 | 947 | 38.437167 | -28.212806 | |
| PIC_1200_P1 | Pico, Madalena, 1200 m, Trilho da Montanha. | 1261 | 38.470361 | -28.425250 |
| PIC_1200_P2 | 1261 | 38.470639 | -28.425028 | |
| PIC_1400_P1 | Pico, Madalena, 1400 m, Trilho da Montanha. | 1418 | 38.469583 | -28.421361 |
| PIC_1400_P2 | 1407 | 38.469306 | -28.421250 | |
| PIC_1600_P1 | Pico, Madalena, 1600 m, Trilho da Montanha. | 1601 | 38.465972 | -28.416528 |
| PIC_1600_P2 | 1588 | 38.465472 | -28.416583 | |
| PIC_1800_P1 | Pico, Madalena, 1800 m, Trilho da Montanha. | 1805 | 38.466083 | -28.412556 |
| PIC_1800_P2 | 1802 | 38.465944 | -28.412500 | |
| PIC_2000_P1 | Pico, Madalena, 2000 m, Trilho da Montanha. | 2003 | 38.465722 | -28.408333 |
| PIC_2000_P2 | 2009 | 38.465583 | -28.408111 | |
| PIC_2200_P1 | Pico, Madalena, 2200 m, Trilho da Montanha, Cratera antes do Piquinho. | 2239 | 38.466361 | -28.399222 |
| PIC_2200_P2 | 2242 | 38.466722 | -28.399417 |
Figure 2.
Map of Pico Island with indications of sampling points (yellow squares) (Source: Gil et al. 2017, with modifications).
Design description
The sampling was performed in 2012, during 5-10 September, along a longitudinal elevational transect (east to west) in the Pico Natural Park, including the best-preserved areas of native vegetation. The samples were collected in different altitudinal gradients (10 - 2200 m) and substrates (rupicolous, terricolous, humicolous, lignicolous, epiphytic, epiphyllous).
Funding
This study was financed by ERANET BIOME MOVECLIM – ‘Montane vegetation as listening posts for climate change’ of the regional government of the Azores, grant number M2.1.2/F/04/2011/NET.
MCMC was funded by the FUNDO REGIONAL PARA A CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA (FRCT) of the Regional Government of the Azores, grant number M3.1.2/F/007/2012.
RG, LN and PAVB are currently funded by FCT-UIDB/00329/2020-2024 (Thematic Line 1–integrated ecological assessment of environmental change on biodiversity) and Azores DRCT Pluriannual Funding (M1.1.A/FUNC.UI&D/010/2021-2024).
Sampling methods
Study extent
Pico Island has the highest plant diversity compared to the other islands in the Archipelago, mainly due to a higher number of altitudinal vegetation areas (Dias et al. 2005). The soils are relatively young, mostly composed of basaltic rock debris (i.e. leptosols), presenting lower values of carbon accumulation (Borges Silva et al. 2022). This study was carried out in the Pico National Park (Azores), which has a large protected area (156 km2 - terrestrial, 79 km2 - maritime), including the mountain (the central volcanic formation that reaches 2351 m elevation), native forests and woodlands, lagoons and the coastal zones.
Sampling description
The field study was carried out according to the BRYOLAT methodology (Ah-Peng et al. 2012), with some modifications according to the conditions and knowledge of the Azores flora (Gabriel et al. 2014). In each plot, three quadrats (2 m x 2 m) were randomly selected and bryophytes were sampled in a total of three microplots (5 cm x 10 cm) in each different substrate (rupicolous, terricolous, humicolous, lignicolous, epiphytic, epiphyllous) and altitudinal gradients (between 10 m and 2200 m). This methodology consists of sampling the bryoflora according to the diagram (Fig. 3, Gabriel et al. (2014)). In the laboratory, the abundance and sociability of the bryophyte species were identified and estimated.
Figure 3.

Altitudinal sampling model on Pico Island (Ah-Peng et al. 2012 and Gabriel et al. 2014): (a) 200 m elevation steps, two plots (black squares, 10 m x 10 m) are placed within 10 m to 15 m from each other; (b) each plot is divided into 25 quadrats (grey squares, 2 m x 2 m), from which three are sampled; (c) and (d) – each quadrat is thoroughly examined for different substrata and three microplots (red rectangular shapes, 5 cm x 10 cm) are collected on every microhabitat, except on trees, where nine replicates are made, at three different height levels. (Source: Gabriel et al. (2014)).
Quality control
FIELD: An initial visit of Pico Island was made by PAVB and RG in July 2012 to prospect the most suitable sampling sites. Plots were placed within homogeneous areas of representative native vegetation found at each sampled elevation. Sampling was made by experienced bryologists, who ensured the samples were properly collected, while avoiding the excessive removal of material. STORAGE: After the collection of the microplots in paper bags, these were left open and separated in a darkened room until complete dehydration. After identification, every sample was transferred to herbarium envelopes properly identified. All these envelopes were stored in the Herbarium of the University of the Azores (AZU), Section Bryophytes, under the name “MOVECLIM – AZORES project: Bryophytes from Pico Island (2012)”. TAXONOMY: All efforts were made to achieve an accurate identification of the specimens: (i) the most updated keys and floras were used by/under the supervision of experienced bryologists; (ii) challenging samples were sent to specialists for confirmation/identification; (iii) identification of extremely small or etiolated specimens was not pursued to the species level. Mosses were identified mainly using the floras of Smith (2004) and Casas et al. (2006), whereas liverworts were identified mainly using the floras written by Paton (1999) and Casas et al. (2009) and the taxonomic key of Schumacker and Vána (2005). Visual guides (e.g. Atherton et al. (2010), Lüth (2019)) were also consulted, as well as the BBS Field Guide online pages, the Bildatlas der Moose Deutschlands for morphological and ecological data. Nomenclature follows Gabriel et al. (2010) and updates available on the Azorean Biodiversity Portal (Hodgetts et al. 2020, Borges et al. 2023). Species identification was performed by Márcia Catarina Mendes Coelho, under the supervision of Rosalina Gabriel and by Helena Hespanhol. In 2023, all the Frullania specimens were reviewed by Leila Nunes Morgado under the supervision of Rosalina Gabriel. The identification of some challenging specimens was performed by Manuela Sim-Sim and Cecília Sérgio. REPRESENTATION OF THE PICO BRYOFLORA: Species accumulation curves were generated, based on a presence–absence microplot-scale matrix using Chao 2 estimator. Sampling completeness was high both for liverworts (87.5%) and mosses (94.5%) (Coelho et al. 2021).
Geographic coverage
Description
The study was carried out in Pico Island (Azores Archipelago, Portugal). The 12 sampling sites were distributed amongst the three municipalities of the island: Lajes do Pico, São Roque do Pico and Madalena; the coordinates range between the following values:
Coordinates
38.41375 and 38.47064 Latitude; -28.0298 and -28.42525 Longitude.
Taxonomic coverage
Description
Bryophytes, including specimen from Division Bryophyta (mosses) and Division Marchantiophyta (liverworts). No elements from Division Anthocerotophyta were collected during this survey.
Temporal coverage
Notes
The sampling was performed in 2012, 5-10 September.
Usage licence
Usage licence
Creative Commons Public Domain Waiver (CC-Zero)
IP rights notes
Additional information on this study may also be requested from the corresponding author.
Data resources
Data package title
The MOVECLIM – AZORES project: Bryophytes from Pico Island (2012).
Resource link
https://www.gbif.org/dataset/88d3beab-eb7c-4a3a-927e-7b8bf6d35ef6
Alternative identifiers
Number of data sets
2
Data set 1.
Data set name
Event table
Data format
Darwin Core Archive
Character set
UTF-8
Download URL
Data format version
1.4
Description
The dataset was published in the Global Biodiversity Information Facility platform, GBIF (Gabriel et al. 2023). The following data table includes all the records for which a taxonomic identification of the species was possible. The dataset submitted to GBIF is structured as a sample event dataset that has been published as a Darwin Core Archive (DwCA), which is a standardised format for sharing biodiversity data as a set of one or more data tables. The core data file contains 878 records (eventID). This GBIF IPT (Integrated Publishing Toolkit, Version 2.5.6) archives the data and, thus, serves as the data repository. The data and resource metadata are available for download in the Portuguese GBIF Portal IPT (Gabriel et al. 2023).
Data set 1.
| Column label | Column description |
|---|---|
| id | Identifier of the events, unique for the dataset. |
| type | Type of the record, as defined by the Dublin Core Standard. |
| datasetName | Name of the dataset that in current projects is "MOVECLIM-AZO-PIC_2012_Bryophytes from Pico Island". |
| eventID | Identifier of the events, unique for the dataset. |
| samplingProtocol | The sampling protocol used to capture the species. Detailed description of the sampling methodology in the field. Two plots of 10 m × 10 m (P1, P2), were set out at the best-preserved areas of native vegetation sites, every 200 m elevation, across an elevation gradient from coastal areas to Pico summit. Each plot was subdivided into 25 quadrats (2 m × 2 m), from which three were randomly selected for the collection of bryophyte species. Within each quadrat, bryophytes were collected in small sampling units (microplots of 10 cm × 5 cm), obtaining, whenever possible, three replicates per surveyed substrate (RU, rock, TE, soil, HU, humus, LI, dead wood, T, bark at three heights from the tree [a, 1-50 cm; b, 51-100 cm; c, 101-200 cm], LF, leaves/fronds). |
| minimumElevationInMetres | The lower limit of the range of elevation (altitude above sea level) of the Location. |
| eventDate | The date-time or interval during which an Event occurred. For occurrences, this is the date-time when the event was recorded. |
| year | Year the sample was collected (2012). |
| habitat | The habitat for an Event. |
| continent | The name of the continent in which the Location occurs (Europe). |
| islandGroup | The name of the island group in which the Location occurs (Azores). |
| island | The name of the island on or near which the Location occurs (Pico Island). |
| country | The name of the country or major administrative unit in which the Location occurs (Portugal). |
| countryCode | The standard code for the country in which the Location occurs (PT). |
| municipality | The full, unabbreviated name of the next smaller administrative region than county (city, municipality etc.) in which the Location occurs. |
| locality | The specific description of the place. |
| verbatimCoordinates | Original coordinates recorded. |
| decimalLatitude | Approximate centre point decimal latitude of the field site in GPS coordinates. |
| decimalLongitude | Approximate centre point decimal longitude of the field site in GPS coordinates. |
| geodeticDatum | Standard Global Positioning System coordinate reference for the location of the sample collection points. |
| coordinateUncertaintyInMetres | Uncertain value of coordinate metrics. |
| coordinatePrecision | Value in decimal degrees to a precision of five decimal places. |
| georeferenceSources | Navigation system used to record the location of sample collections. |
Data set 2.
Data set name
Occurrence Table
Data format
Darwin Core Archive
Character set
UTF-8
Download URL
Data format version
1.4
Description
The dataset was published in the Global Biodiversity Information Facility platform, GBIF (Gabriel et al. 2023). The following data table includes all the records for which a taxonomic identification of the species was possible. The dataset submitted to GBIF is structured as an occurrence table that has been published as a Darwin Core Archive (DwCA), which is a standardised format for sharing biodiversity data as a set of one or more data tables. The core data file contains 4896 records (occurrenceID). This GBIF IPT (Integrated Publishing Toolkit, Version 2.5.6) archives the data and, thus, serves as the data repository. The data and resource metadata are available for download in the Portuguese GBIF Portal IPT (Gabriel et al. 2023).
Data set 2.
| Column label | Column description |
|---|---|
| eventID | Identifier of the events, unique for the dataset. |
| licence | Reference to the licence under which the record is published. |
| institutionID | The identity of the institution publishing the data. |
| institutionCode | The code of the institution publishing the data. |
| collectionCode | The code of the collection where the specimens are conserved. |
| datasetName | Project reference. |
| type | Characteristics of the object of study. |
| basisOfRecord | The nature of the data record. |
| dynamicProperties | A list of additional measurements, facts, characteristics or assertions about the record, including IUCN categories (Endangered, Vulnerable, Near Threatened, Least Concern, Not Evaluated) and colonisation status of taxa following the standard notation used for bryophytes (Azorean endemic, Macaronesian endemic, Ibero-Macaronesian endemic, European endemic, non-endemic). |
| occurrenceID | Identifier of the record, coded as a global unique identifier. |
| recordNumber | An identifier given to the Occurrence at the time it was recorded. |
| recordedBy | A list (concatenated and separated) of names of people, groups or organisations responsible for recording the original Occurrence. |
| identifiedBy | A list (concatenated and separated) of names of people, who made the identification. |
| disposition | The current state of a specimen with respect to the collection identified in collectionCode or collectionID. |
| taxonRank | Lowest taxonomic rank of the record. |
| kingdom | Kingdom name. |
| phylum | Phylum name. |
| class | Class name. |
| order | Order name. |
| family | Family name. |
| genus | Genus name. |
| specificEpithet | Specific epithet. |
| infraspecificEpithet | Infraspecific epithet at subspecies level. |
| scientificNameAuthorship | The authorship information for the scientificName formatted according to the conventions of the applicable nomenclaturalCode. |
| scientificName | Complete scientific name including author. |
| organismQuantity | A number or enumeration value for the quantity of organisms (i, solitary specimen - one or few individuals; p, occasional and less than 5% cover; 1, less than 5% cover of total area; 2, 5%-25% of total area; 3, 25%-50% of total area; 4, 50%-75% of total area; 5, 75%-100% of total area). |
| organismQuantityType | Braun-Blanquet Scale. |
| establishmentMeans | The process of establishment of the species in the location, using a controlled vocabulary: 'native non-endemic', 'introduced', 'endemic'. |
| occurrenceRemarks | Remarks on the occurrence substrate from where the specimens were captured. |
Additional information
The 878 events yielded a grand total of 4896 specimens, with the majority (n = 4869; 99.45%) being successfully identified down to the species/subspecies level. Division Bryophyta is represented by 70 species, belonging to three classes (Bryopsida, Polytrichopsida and Sphagnopsida), 10 orders, 28 families and 45 genera, while Division Marchantiophyta is represented by 71 species, including three subspecies, organised in two classes (Jungermanniopsida and Marchantiopsida), six orders, 24 families and 43 genera (see Occurrence Table at Gabriel et al. (2023)). Both the number of species (Fig. 4) and the number of records (Fig. 5) show a peak from 600 m to 1000 m altitude, which correspond to the sites with more complex vegetation (Coelho et al. 2014a, Coelho et al. 2014b, Coelho et al. 2021).
Figure 4.
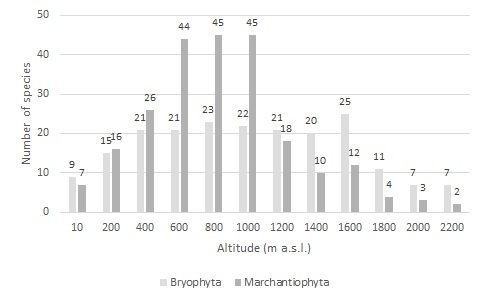
The richness of species of mosses (Division Bryophyta) and liverworts (Division Marchantiophyta) along Pico Island’s elevational gradient.
Figure 5.
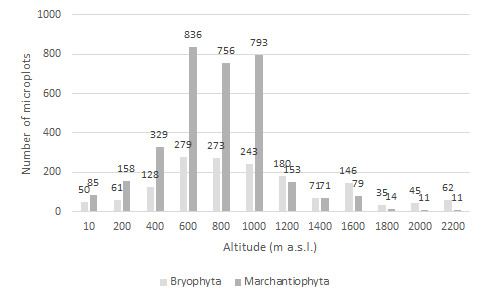
The number of presences in 50 cm2 microplots of species of mosses (Division Bryophyta) and liverworts (Division Marchantiophyta) along Pico Island’s elevational gradient.
Considering the colonisation status, all the taxa can be considered native, but four are Azoren endemics, the liverworts Bazzaniaazorica H.Buch & Perss. and Leptoscyphusporphyriussubsp.azoricus (H.Buch & Perss.) Vanderp. & Heirichs and the pleurocarpic mosses Echinodiumrenauldii (Cardot) Broth. and Rhynchostegiellaazorica Hedenäs & Vanderp.; besides, a total of nine species are Macaronesian endemics, three are Iberian-Macaronesian endemics and seven are European endemics (see Table 2).
Table 2.
List of sampled species and subspecies in each of the colonisation status categories (AZ, Azorean; MAC, Macaronesian; IB-MAC, Ibero-Macaronesian; EUR, European).
| Colonization status | Scientific Name |
| Division: Bryophyta | |
| Azorean endemic | Echinodiumrenauldii (Cardot) Broth. |
| Rhynchostegiellaazorica Hedenäs & Vanderp. | |
| Macaronesian endemic | Alophosiaazorica (Renauld & Cardot) Cardot |
| Andoaberthelotiana (Mont.) Ochyra | |
| Isotheciumprolixum (Mitt.) M.Stech, Sim-Sim, Tangney & D.Quandt | |
| Thamnobryummaderense (Kindb.) Hedenäs | |
| Ibero-Macaronesian endemic | Tetrastichiumfontanum (Mitt.) Cardot |
| Tetrastichiumvirens (Cardot) S.P.Churchill | |
| European endemic | Hypnumuncinulatum Jur. |
| Pseudotaxiphyllumlaetevirens (Dixon & Luisier ex F.Koppe & Düll) Hedenäs | |
| Ulotacalvescens Wilson | |
| Native | Antitrichiacurtipendula (Hedw.) Brid. |
| Brachytheciastrumvelutinum (Hedw.) Ignatov & Huttunen | |
| Brachytheciummildeanum (Schimp.) Schimp. | |
| Campylopusflexuosus (Hedw.) Brid. | |
| Campylopusfragilis (Brid.) Bruch & Schimp. | |
| Campylopuspilifer Brid. | |
| Campylopuspyriformis (Schultz) Brid. | |
| Campylopusshawii Wilson | |
| Cyclodictyonlaetevirens (Hook. & Taylor) Mitt. | |
| Daltonialindigiana Hampe | |
| Dicranellaheteromalla (Hedw.) Schimp. | |
| Dicranumflagellare Hedw. | |
| Dicranumscottianum Turner | |
| Diphysciumfoliosum (Hedw.) D.Mohr | |
| Ditrichumsubulatum Hampe | |
| Fissidensbryoides Hedw. | |
| Fissidensdubius P.Beauv. | |
| Fissidensserrulatus Brid. | |
| Fissidenstaxifolius Hedw. | |
| Fissidensviridulus (Sw.) Wahlenb. | |
| Grimmiaelongata Kaulf. | |
| Heterocladiumheteropterum (Brid.) Schimp. | |
| Heterocladiumwulfsbergii I.Hagen | |
| Hylocomiumsplendens (Hedw.) Schimp. | |
| Hymenolomacrispulum (Hedw.) Ochyra | |
| Hypnumcupressiforme Hedw. | |
| Isotheciuminterludens Stirt. | |
| Isotheciummyosuroides Brid. | |
| Kiaeriablyttii (Bruch & Schimp.) Broth. | |
| Leucobryumglaucum (Hedw.) Ångstr. | |
| Leucobryumjuniperoideum (Brid.) Müll.Hal. | |
| Mniumhornum Hedw. | |
| Myuriumhochstetteri (Schimp.) Kindb. | |
| Plagiomniumundulatum (Hedw.) T.J.Kop. | |
| Polytrichumcommune Hedw. | |
| Polytrichumformosum Hedw. | |
| Polytrichumjuniperinum Hedw. | |
| Polytrichumpiliferum Hedw. | |
| Pseudorhynchostegielladuriaei (Mont.) Ignatov & Vanderp. | |
| Pseudoscleropodiumpurum (Hedw.) M.Fleisch. | |
| Ptychostomumtorquescens (Bruch & Schimp.) Ros & Mazimpaka | |
| Racomitriumaffine (F.Weber & D.Mohr) Lindb. | |
| Racomitriumfasciculare (Hedw.) Brid. | |
| Racomitriumheterostichum (Hedw.) Brid. | |
| Racomitriumlanuginosum (Hedw.) Brid. | |
| Rhynchostegiumconfertum (Dicks.) Schimp. | |
| Rhytidiadelphusloreus (Hedw.) Warnst. | |
| Rhytidiadelphussquarrosus (Hedw.) Warnst. | |
| Sciuro-hypnum plumosum (Hedw.) Ignatov & Huttunen | |
| Sematophyllumsubstrumulosum (Hampe) E.Britton | |
| Serpoleskeaconfervoides (Brid.) Schimp. | |
| Sphagnumpalustre L. | |
| Thamnobryumalopecurum (Hedw.) Gangulee | |
| Thuidiumtamariscinum (Hedw.) Schimp. | |
| Tortellaflavovirens (Bruch) Broth. | |
| Trichostomumbrachydontium Bruch | |
| Ulotacrispa (Hedw.) Brid. | |
| Zygodonconoideus (Dicks.) Hook. & Taylor | |
| Zygodonviridissimus (Dicks.) Brid. | |
| Division: Marchantiophyta | |
| Azorean endemic | Bazzaniaazorica H.Buch & Perss. |
| Leptoscyphusporphyriussubsp.azoricus (H.Buch & Perss.) Vanderp. & Heirichs | |
| Macaronesian endemic | Calypogeiaazorica Bischl. |
| Cheilolejeuneacedercreutzii (H.Buch & Perss.) Grolle | |
| Heteroscyphusdenticulatus (Mitt.) Schiffn. | |
| Radulawichurae Steph. | |
| Telaraneaazorica (H.Buch & Perss.) Pócs | |
| Ibero-Macaronesian endemic | Frullaniaazorica Sim-Sim, Sérgio, Mues & Kraut |
| European endemic | Frullaniamicrophylla (Gottsche) Pearson |
| Lejeuneahibernica Bischl., H.A.Mill. & Bonner ex Grolle | |
| Radulaholtii Spruce | |
| Saccogynaviticulosa (L.) Dumort. | |
| Native | Acrobolbusazoricus (Grolle & Perss.) Briscoe |
| Aneurapinguis (L.) Dumort. | |
| Blepharostomatrichophyllum (L.) Dumort. | |
| Calypogeiaarguta Nees & Mont. | |
| Calypogeiafissa (L.) Raddi | |
| Calypogeiamuelleriana (Schiffn.) Müll.Frib. | |
| Calypogeiasphagnicola (Arnell & J.Perss.) Warnst. & Loeske | |
| Cephaloziabicuspidata (L.) Dumort. | |
| Cololejeuneaazorica V.Allorge & Jovet-Ast | |
| Cololejeuneamicroscopica (Taylor) Schiffn. | |
| Cololejeuneasintenisii (Steph.) Pócs | |
| Coluracalyptrifolia (Hook.) Dumort. | |
| Diplophyllumalbicans (L.) Dumort. | |
| Drepanolejeuneahamatifolia (Hook.) Schiffn. | |
| Frullaniaacicularis Hentschel & von Konrat | |
| Frullaniateneriffae (F.Weber) Nees | |
| Fuscocephaloziopsiscrassifolia (Lindenb. & Gottsche) Váňa & L.Söderstr. | |
| Geocalyxgraveolens (Schrad.) Nees | |
| Gymnomitrionadustum Nees | |
| Harpalejeuneamolleri (Steph.) Grolle | |
| Herbertusazoricus (Steph.) P.W.Richards | |
| Herbertusborealis Crundw. | |
| Lejeuneaeckloniana Lindenb. | |
| Lejeuneaflavasubsp.moorei (Lindb.) R.M.Schust. | |
| Lejeunealamacerina (Steph.) Schiffn. | |
| Lejeuneapatens Lindb. | |
| Lepidoziacupressina (Sw.) Lindenb. subsp. cupressina | |
| Lepidoziareptans (L.) Dumort. | |
| Lophocoleacoadunata (Sw.) Mont. | |
| Lophocoleafragrans (Moris & De Not.) Gottsche, Lindenb. & Nees | |
| Lophocoleaheterophylla (Schrad.) Dumort. | |
| Marchantiapolymorpha L. | |
| Marchesiniamackaii (Hook.) Gray | |
| Marsupellasparsifolia (Lindb.) Dumort. | |
| Metzgeriafurcata (L.) Corda | |
| Mniolomafuscum (Lehm.) R.M.Schust. | |
| Myriocoleopsisminutissima (Sm.) R.L.Zhu, Y.Yu & Pócs | |
| Nardiascalaris Gray | |
| Nowelliacurvifolia (Dicks.) Mitt. | |
| Odontoschismadenudatum (Mart.) Dumort. | |
| Pallavicinialyellii (Hook.) Gray | |
| Pelliaepiphylla (L.) Corda | |
| Plagiochilabifaria (Sw.) Lindenb. | |
| Plagiochilaexigua (Taylor) Taylor | |
| Plagiochilapunctata (Taylor) Taylor | |
| Plagiochilaretrorsa Gottsche | |
| Porellacanariensis (F.Weber) Underw. | |
| Porellaobtusata (Taylor) Trevis. | |
| Pseudomarsupidiumdecipiens (Hook.) Grolle | |
| Radulaaquilegia (Hook.f. & Taylor) Gottsche, Lindenb. & Nees | |
| Radulacarringtonii J.B.Jack | |
| Radulacomplanata (L.) Dumort. | |
| Rebouliahemisphaerica (L.) Raddi | |
| Riccardiachamedryfolia (With.) Grolle | |
| Riccardiamultifida (L.) Gray | |
| Scapaniagracilis Lindb. | |
| Scapaniascandica (Arnell & H.Buch) Macvicar | |
| Telaraneaeuropaea J.J.Engel & G.L.Merr. | |
| Jubulahutchinsiae(Hook.)Dumort.subsp.hutchinsiae | |
Almost two-thirds of the bryophytes were collected in three of the 12 elevation levels: at 600 m a.s.l. (22.90%), 800 m (21.13%) and 1000 m (21.28%); that proportion is much higher for liverworts than mosses (72.36% vs. 50.54%) (Figs 4, 5).
Supplementary Material
List of publications mentioning bryophytes in Pico Island (Azores) - 1862-2023
Rosalina Gabriel
Data type
Table
Brief description
List of references mentioning the distribution of bryophytes - mosses, liverworts and hornworts - in Pico Island (Azores, Portugal). Each reference includes also information on the year of publication and type.
File: oo_958534.txt
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by ERANET BIOME MOVECLIM – ‘Montane vegetation as listening posts for climate change’ of the regional government of the Azores, grant number M2.1.2/F/04/2011/NET. M.C.M.C. was funded by the FUNDO REGIONAL PARA A CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA (FRCT) of the regional government of the Azores, grant number M3.1.2/F/007/2012.
RG and PAVB were also supported by the projects Azores DRCT Pluriannual Funding (M1.1.A/FUNC.UI&D/010/2021-2024) and FCT-UIDB/00329/2020-2024 (Thematic Line 1 – integrated ecological assessment of environmental change on biodiversity). The project FCT-UIDB/00329/2020-2024 supported the Open Access of this manuscript.
Funding Statement
This study was financed by ERANET BIOME MOVECLIM – ‘Montane vegetation as listening posts for climate change’ of the regional government of the Azores, grant number M2.1.2/F/04/2011/NET. M.C.M.C. was funded by the FUNDO REGIONAL PARA A CIÊNCIA E TECNOLOGIA (FRCT) of the regional government of the Azores, grant number M3.1.2/F/007/2012. R.G. is currently funded by FCT-UIDB/00329/2020-2024 (Thematic Line 1–integrated ecological assessment of environmental change on biodiversity) and Azores DRCT Pluriannual Funding (M1.1.A/FUNC.UI&D/010/2021-2024).
Author contributions
RG: Conceptualisation; Methodology; Research (field and laboratory work); Resources; Data Curation; Darwin Core dataset preparation; Formal analysis and interpretation; Manuscript writing.
LNM: Formal analysis and interpretation; Research (laboratory work); Manuscript writing.
MCMC: Research (field and laboratory work).
CAP, DSGH, FP, SCA: Research (field work).
CS, HH, MSS: Research (laboratory work).
PAVB: Darwin Core dataset revision, GBIF IPT management.
All the authors participated in data interpretation and manuscript revision.
References
- Ah-Peng Claudine, Wilding Nicholas, Kluge Juergen, Descamps-Julien Blandine, Bardat Jacques, Chuah-Petiot Min, Strasberg Dominique, Hedderson T. A. J. Bryophyte diversity and range size distribution along two altitudinal gradients: Continent vs. island. Acta Oecologica. 2012;42:58–65. doi: 10.1016/j.actao.2012.04.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton I., Bosanquet S., Lawley M., editors. Mosses and liverworts of Britain and Ireland: a field guide. British Bryological Society; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Borges P. A. V., Costa A., Cunha R., Gabriel R., Gonçalves V., Gonçalves V., Martins A., Melo I., Parente M., Raposeiro P., Rodrigues P., et al. A list of the terrestrial and marine biota from the Azores. 1ª. Princípia Editora, Lda.; Cascais: 2010. 429. [Google Scholar]
- Borges P. A. V., Cardoso Pedro, Kreft Holger, Whittaker R. J., Fattorini Simone, Emerson B. C., Gil Artur, Gillespie R. G., Matthews T. J., Santos A. M. C., Steinbauer M. J., Thébaud Christophe, Ah-Peng Claudine, Amorim I. R., Aranda Silvia Calvo, Arroz A. M., Azevedo J. M. N., Boieiro Mário, Borda-de-Água Luís, Carvalho J. C., Elias R. B., Fernández-Palacios J. M., Florencio Margarita, González-Mancebo J. M., Heaney L. R., Hortal Joaquín, Kueffer Christoph, Lequette Benoit, Martín-Esquivel J . L., López Heriberto, Lamelas-López Lucas, Marcelino José, Nunes Rui, Oromí Pedro, Patiño Jairo, Pérez A. J., Rego Carla, Ribeiro S. P., Rigal François, Rodrigues Pedro, Rominger A. J., Santos-Reis Margarida, Schaefer Hanno, Sérgio Cecília, Serrano A. R. M., Sim-Sim Manuela, Stephenson P. J., Soares A. O., Strasberg Dominique, Vanderporten Alain, Vieira Virgílio, Gabriel Rosalina. Global Island Monitoring Scheme (GIMS): a proposal for the long-term coordinated survey and monitoring of native island forest biota. Biodiversity and Conservation. 2018;27(10):2567–2586. doi: 10.1007/s10531-018-1553-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Borges Paulo Alexandre Vieira, Gabriel Rosalina, Soares António Onofre, Silva Luís, Gonçalves João M., editors. Portal da Biodiversidade dos Açores. https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/ [2023-09-06T00:00:00+03:00]. https://azoresbioportal.uac.pt/
- Borges Silva Lurdes C., Pavão Diogo C., Elias Rui B., Moura Mónica, Ventura Maria A., Silva Luís. Taxonomic, structural diversity and carbon stocks in a gradient of island forests. Scientific Reports. 2022;12(1) doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05045-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casas C., Brugués M., Cros R. M., Sérgio C. Handbook of mosses of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands: illustrated keys to genera and species. Institut d'Estudis Catalans; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Casas C., Brugués M., Cros R. M., Sérgio C., Infante M. Handbook of liverworts and hornworts of the Iberian Peninsula and the Balearic Islands: illustrated keys to genera and species. Institut d'estudis Catalans; 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho Márcia Catarina Mendes, Gabriel Rosalina, Henriques Débora Sofia Gouveia, Ah-Peng Claudine. Espécies raras de briófitos ao longo do gradiente altitudinal de floresta nativa na ilha do Pico (Açores): o caso de Echinodium renauldii (Cardot) Broth.. In: Azevedo José Neto, Rocha Gilberta Nunes, Simões Nelson José de Oliveira, Borges Paulo Alexandre Vieira, Santos Ricardo Serrão, Raposeiro Pedro Miguel Valente Mendes., editors. Ciência nos Açores - que futuro?; Jornadas da Ciência nos Açores; Ponta Delgada. 07-08 June 2013; Ponta Delgada: SRECC - Secretaria Regional da Educação, Ciência e Cultura; 2014. 318. Portuguese. [Google Scholar]
- Coelho Márcia Catarina Mendes, Gabriel Rosalina, Henriques Débora Sofia Gouveia, Ah-Peng Claudine. Espécies raras de briófitos ao longo do gradiente altitudinal de floresta nativa na ilha do Pico (Açores): o caso de Echinodium renauldii (Cardot) Broth.. In: , editor. Livro de Actas das Jornadas ‘Ciência nos Açores: Que futuro?’; Ciência nos Açores: Que futuro?; Ponta Delgada. 07-08 June; Ponta Delgada: SREEC - Secretaria Regional da Educação, Ciência e Cultura; 2014. 318 [Google Scholar]
- Coelho Márcia Catarina Mendes, Gabriel Rosalina, Hespanhol Helena, Borges Paulo Alexandre Vieira, Ah-Peng Claudine. Bryophyte diversity along an elevational gradient on Pico Island (Azores, Portugal) Diversity. 2021;13(4):162. doi: 10.3390/d13040162. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho Márcia Catarina Mendes, Gabriel Rosalina, Ah-Peng Claudine. Characterizing and quantifying water content in 14 Species of bryophytes present in Azorean Native Vegetation. Diversity. 2023;15(2) doi: 10.3390/d15020295. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho Márcia Catarina Mendes, Gabriel Rosalina, Ah-Peng Claudine. Seasonal hydration status of common bryophyte species in Azorean native vegetation. Plants. 2023;12(16) doi: 10.3390/plants12162931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (1992L0043) CONSLEG. Consolidated text produced by the CONSLEG system of the Office for Official Publications of the European Communities. http://www.icnf.pt/portal/naturaclas/rn2000/resource/docs/ diret-habit http://www.icnf.pt/portal/naturaclas/rn2000/resource/docs/ diret-habit
- Couto A. B. Padrões de distribuição dos briófitos dos Açores em diferentes escalas: contributo para a conservação de espécies ameaçadas. Repository - UAC; Angra do Heroísm: 2010. 51. [Google Scholar]
- Dias E., Mendes C., Melo C., Pereira D., Elias R. Azores Central Islands vegetation and flora field guide. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/228973592_Azores_Central_Islands_vegetation_and_ flora_field_guide Quercetea. 2005;7:123–173. [Google Scholar]
- Elias Rui Bento, Rodrigues António Félix Flores, Gabriel Rosalina. Guia prático da flora nativa dos Açores / Field Guide of Azorean Native Flora. 1st Edition. Vol. 1. IAC - Instituto Açoriano de Cultura; Angra do Heroísmo: 2022. 519. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L. T., Ah-Peng C., Aranda S. C., Bednarek-Ochyra H., Borovichev E. A., Cykowska-Marzencka B., Duarte M. C., Enroth J., Erzberger P., Fedosov V., Fojcik B., Gabriel R., Coelho M. C. M., Henriques D. S. G., Ilina O. V., Gil-Novoa J. E., Morales-Puentes M. E., Gradstein S. R., Gupta R., Nath V., Asthana A. K., Koczur A., Lebouvier M., Mesterházy A., Mogro F., Mežaka A., Németh Cs., Orgaz J. D., Sakamoto Y., Paiva J., Sales F., Pande N., Sabovljević M. S., Pantivić J., Sabovljević A. D., Pérez-Haase A., da Costa D. Pinheiro, Plášek V., Sawicki J., Szczecińska M., Chmielewski J., Potemkin A., Schäfer-Verwimp A., Schofield W. B., Sérgio C., Sim-Sim M., Sjögren S., Spitale D., Stebel A., Ştefănuţ S., Suárez G. M., Flores J. R., Thouvenot L., Váňa J., Yoon Y. - J., Kim J. H., Zubel R. New national and regional bryophyte records, 45. Journal of Bryology. 2016;37(4):308–329. doi: 10.1179/1743282015y.0000000035. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Esquivel J. L.M., Hernandez M. A., Borges Paulo Alexandre Vieira, Faria B. F., editors. Top 100. Las 100 especies amenazadas prioritariasde gestión en la región europea biogeográfica de la Macaronesia. Consejería de Medio Ambiente yOrdenación Territorial, Gobierno de Canarias; Canarias: 2008. 500. [Google Scholar]
- Forjaz V. H. Atlas básico dos Açores. OVGA; Ponta Delgada: 2004. 108. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel R., Bates J. W. Bryophyte community composition and habitat specificity in the natural forests of Terceira, Azores. Plant Ecology. 2005;177(1):125–144. doi: 10.1007/s11258-005-2243-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel R., Sjögren E., Schumacker R., Sérgio C., Aranda S. C., Claro D., Claro D., Homem N., Martins B. In: A list of the terrestrial and marine fungi, flora and fauna from the Azores. Borges Paulo Alexandre Vieira, Costa A., Cunha R., Gabriel R., Gonçalves V., Martins A. F., Melo I., Parente M., Raposeiro P., Rodrigues P., Santos R. S., Silva L., Vieira P., Vieira V., editors. Princípia Editora Lda; Cascais: 2010. List of bryophytes (Anthocerotophyta, Marchantiophyta, Bryophyta).99-115. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel R., Homem N., Couto A., Aranda S., Borges P. A. V. Azorean bryophytes: a preleminary review of rarity pattern. http://hdl.handle.net/10400.3/2059 Açoreana. 2011;7:149–206. [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel R., Coelho Márcia Catarina Mendes, Henriques Débora Sofia Gouveia, Borges Paulo Alexandre Vieira, Elias Rui Bento, Kluge J., Ah-Peng C. Long-term monitoring across elevational gradients to assess ecological hypothesis: a description of standardized sampling methods in oceanic islands and first results. https://repositorio.uac.pt/bitstream/10400.3/3296/1/LMSpp45-67_Gabriel_etal_N31.pdf Arquipelago - Life and Marine Sciences. 2014;(0873-4704):45–67.
- Gabriel Rosalina, Sim-Sim Maria Manuela, González-Mancebo Juana María. Conservation concern’ bryophytes find refuge on cave entrances in the Azores. ARPHA Conference Abstracts. 2018;1 doi: 10.3897/aca.1.e29395. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel R., Morgado L., Coelho Márcia Catarina Mendes, Aranda Silvia Calvo, Henriques Débora Sofia Gouveia, Pereira F., Borges P. A. V., Hespanhol Helena, Sérgio C., Sim-Sim M., Ah-Peng C. Universidade dos Açores. Dataset/Samplingevent; 2023. [2023-12-27T00:00:00+02:00]. The MOVECLIM – AZORES project: Bryophytes from Pico Island (2012) 1.4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil Artur, Fonseca Catarina, Benedicto‐Royuela José. Land cover trade‐offs in small oceanic islands: A temporal analysis of Pico Island, Azores. Land Degradation & Development. 2017;29(2):349–360. doi: 10.1002/ldr.2770. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Goffinet B., Shaw A. J., editors. Bryophyte Biology. Cambridge University Press; 2009. 565. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hanusch Maximilian, Ortiz Edgardo M., Patiño Jairo, Schaefer Hanno. Biogeography and integrative taxonomy of Epipterygium (Mniaceae, Bryophyta) TAXON. 2020;69(6):1150–1171. doi: 10.1002/tax.12324. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Henriques Débora Sofia Gouveia, Borges Paulo Alexandre Vieira, Ah-Peng Claudine, Gabriel Rosalina. Mosses and liverworts show contrasting elevational distribution patterns in an oceanic island (Terceira, Azores): the influence of climate and space. Journal of Bryology. 2016;38(3):183–194. doi: 10.1080/03736687.2016.1156360. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgetts Nick, Cálix Marta, Englefield Eve, Fettes Nicholas, García Criado Mariana, Patin Lea, et al. A miniature world in decline: European Red List of mosses, liverworts and hornworts. 1st Edition. Vol. 1. IUCN, International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources; Brussels, Belgium: 2019. 100. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgetts N. G., Söderström L., Blockeel T. L., Caspari S., Ignatov M. S., Konstantinova N. A., Lockhart N., Papp B., Schröck C., Sim-Sim M., Bell D., Bell N. E., Blom H. H., Bruggeman-Nannenga M. A., Brugués M., Enroth J., Flatberg K. I., Garilleti R., Hedenäs L., Holyoak D. T., Hugonnot V., Kariyawasam I., Köckinger H., Kučera J., Lara F., Porley R. D. An annotated checklist of bryophytes of Europe, Macaronesia and Cyprus. Journal of Bryology. 2020;42(1):1–116. doi: 10.1080/03736687.2019.1694329. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Homem Nídia, Gabriel Rosalina. Briófitos raros dos Açores / Azorean rare bryophytes. 1st Edition. Vol. 1. Princípia Editora, Lda.; Estoril: 2008. 96. [Google Scholar]
- IPMA Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera. https://www.ipma.pt/pt/index.html https://www.ipma.pt/pt/index.html
- Laenen B., Shaw B., Schneider H., Goffinet B., Paradis E., Désamoré A., Heinrichs J., Villarreal J. C., Gradstein S. R., McDaniel S. F., Long D. G., Forrest L. L., Hollingsworth M. L., Crandall-Stotler B., Davis E. C., Engel J., Von Konrat M., Cooper E. D., Patiño J., Cox C. J., Vanderpoorten A., Shaw A. J. Extant diversity of bryophytes emerged from successive post-Mesozoic diversification bursts. Nature Communications. 2014;5(1) doi: 10.1038/ncomms6134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüth M. Mosses of Europe - A Photographic Flora. Freiburg, Germany; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes R., Gabriel R., Elias R., Rigal F., Soares A. S., Cardoso P., Borges P. A. V. Arthropods and other Biota associated with Azorean Trees and Shrubs, Juniperusbrevifolia. Arquipelago - Life and Marine Sciences. 2015;32:19–48. [Google Scholar]
- Paton J. A. The liverwort flora of the British Isles. Harley Books; 1999. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer H. Flora of the Azores – A field guide. 3ª. Margraf Publishers GmbH; 2021. 445. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacker R., Vána J. Identification keys to the liverworts and hornworts of Europe and Macaronesia. 2ª. Station Scientifique des Hautes-Fagnes; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sérgio C., Garcia C. A., Sim-Sim M., C. Vieira, Hespanhol H., Stow S. BryoAtlas - Portugal (Atlas of threatened bryophytes of Portugal) MNHNC/CBA; Lisboa: 2012. 422. [Google Scholar]
- Sérgio Cecília, Garcia César A., Porley Ron D. Observations on the Taxonomy and Distribution of Epipterygiumatlanticum Hanusch and E. tozeri (Grev.) Lindb. (Mniaceae Schwägr.) in Mainland Portugal. Cryptogamie, Bryologie. 2022;43(13):195–200. doi: 10.5252/cryptogamie-bryologie2022v43a13. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sérgio C. Notes on some newly recorded bryophytes in human or anthropogenic habitats from Azores. Arquipelago. Life and Marine Sciences. 2023;38:51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Sérgio C. New National and Regional bryophyte records: Tortellafasciculata (Culm.) Culm. Journal of Bryology. in press
- Smith A. J.E. The moss flora of Britain and Ireland. Cambridge university press; 2004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
List of publications mentioning bryophytes in Pico Island (Azores) - 1862-2023
Rosalina Gabriel
Data type
Table
Brief description
List of references mentioning the distribution of bryophytes - mosses, liverworts and hornworts - in Pico Island (Azores, Portugal). Each reference includes also information on the year of publication and type.
File: oo_958534.txt