Abstract
The d-glyceraldehyde 3-P dehydrogenases of spinach leaf, pea seed, and pea shoot were purified. The NADP and NAD-linked enzymes of either spinach leaves and pea shoots could not be separated. Changes in the ratio of NADP- to NAD-linked activity of the spinach leaf and pea shoot enzymes were observed during both purification and storage of crude extracts. The spinach leaf, pea shoot, and pea seed enzymes differ electrophoretically from each other and from the rabbit muscle enzyme.
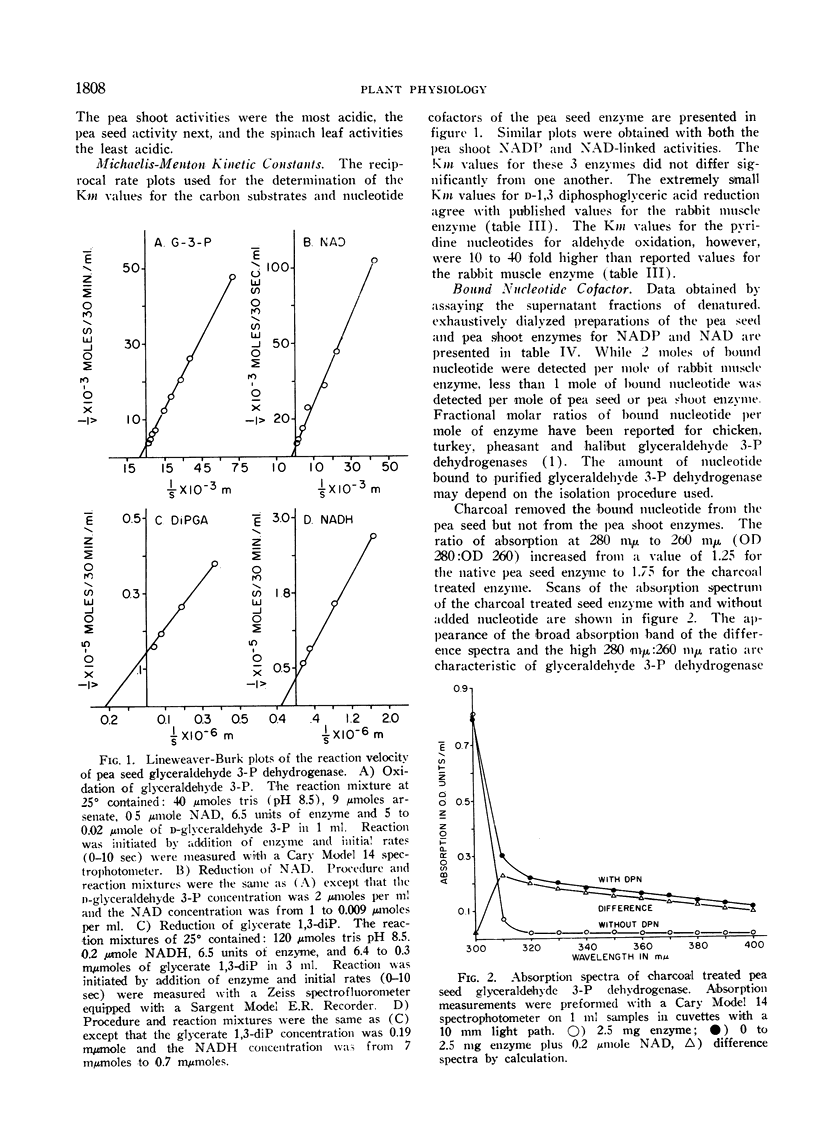
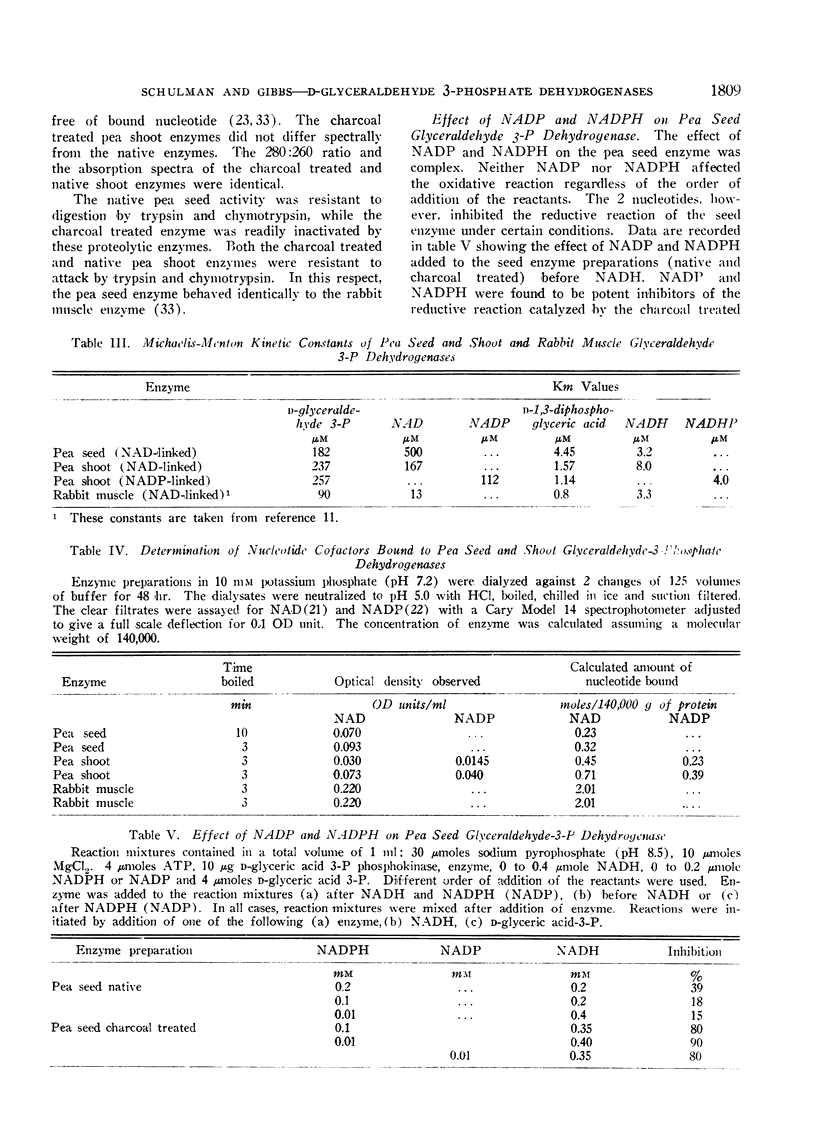
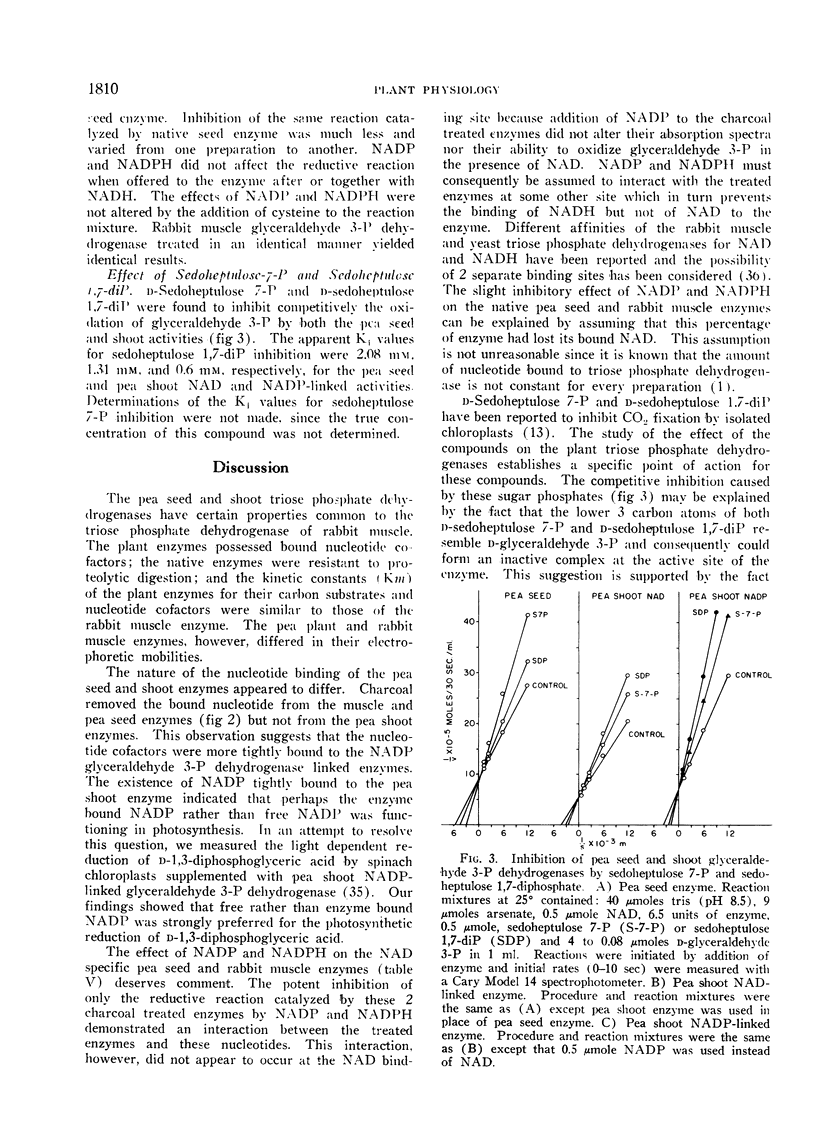
The pea seed and shoot enzymes contain bound nucleotide cofactor, resist proteolytic attack, have similar Michaelis-Menton kinetic constants and are competitively inhibited by d-sedoheptulose-7-phosphate and d-sedoheptulose 1,7-diphosphate. Charcoal removes the bound nucleotide from the pea seed enzyme but not from the pea shoot enzymes. NADP and NADPH were found to inhibit the reductive but not oxidative reaction catalyzed by the charcoal treated seed enzyme. The function of the pea shoot NADP and NAD-linked enzymes in chloroplast metabolism is discussed in regard to their location and catalytic properties. Although the NADP-linked activity can be assigned a primary, if not exclusive function in photosynthesis, the assignment of a distinct metabolic function to the NAD-linked activity cannot be made at present.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLISON W. S., KAPLAN N. O. THE COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY OF TRIOSEPHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jul;239:2140–2152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENNEMAN F. N., VOLK W. A. Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase activity with triphosphopyridine nucleotide and with diphosphopyridine nucleotide. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2443–2447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURFINE C. S., VELICK S. F. THE ACYL-ENZYME INTERMEDIATE AND THE KINETIC MECHANISM OF THE GLYCERALDEHYDE 3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE REACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:844–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. C., Gibbs M. Intracellular and Phylogenetic Distribution of Ribulose 1,5-Diphosphate Carboxylase and D-Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenases. Plant Physiol. 1959 May;34(3):324–329. doi: 10.1104/pp.34.3.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBS M. Triosephosphate dehydrogenase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in the pea plant. Nature. 1952 Jul 26;170(4317):164–165. doi: 10.1038/170164a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEMAN R. H., ARNON D. I. Changes in glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase during the life cycle of a green plant. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Aug;57(2):421–436. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90304-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAGEMAN R. H., ARNON D. I. The isolation of triosephosphate dehydrogenase from pea seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1955 Mar;55(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(55)90554-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVIR E. A., GIBBS M. STUDIES ON THE REDUCTIVE PENTOSE PHOSPHATE CYCLE IN INTACT AND RECONSTITUTED CHLOROPLAST SYSTEMS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Oct;238:3183–3187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hageman R. H., Waygood E. R. Methods for the Extraction of Enzymes from Cereal Leaves with Especial Reference to the Triosephosphate Dehydrogenases. Plant Physiol. 1959 Jul;34(4):396–400. doi: 10.1104/pp.34.4.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood W., Carr N. G. A single glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase active with NAD and NADP in Anabaena variabilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 12;146(1):309–311. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIMSKY I., RACKER E. Approaches to the mechanism of action of double-headed enzymes. Fed Proc. 1958 Dec;17(4):1135–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortwerth B. J., Koeppe O. J. Light dependent increase of triosephosphate dehydrogenase in pea leaves. Plant Physiol. 1966 Sep;41(7):1213–1217. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.7.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen J. M., Lane M. D. Spinach ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2350–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E., KRIMSKY I. The mechanism of oxidation of aldehydes by glyceralde-hyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Oct;198(2):731–743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIN M., ARNON D. I. ENZYMIC MECHANISMS OF PYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE REDUCTION IN CHLOROPLASTS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1405–1411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER J. F., BLACK C. C., GIBBS M. Studies on photosynthetic processes. I. The effect of light intensity on triphosphopyridine nucleotide reduction, adenosine triphosphate formation, and carbon dioxide assimilation in spinach chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:577–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. A. LOCATION OF GLYCERALDEHYDE-3-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE IN STARCH-GELS. Nature. 1964 Sep 5;203:1070–1071. doi: 10.1038/2031070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WU R., RACKER E. Regulatory mechanisms in carbohydrate metabolism. III. Limiting factors in glycolysis of ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1959 May;234(5):1029–1035. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


