Abstract
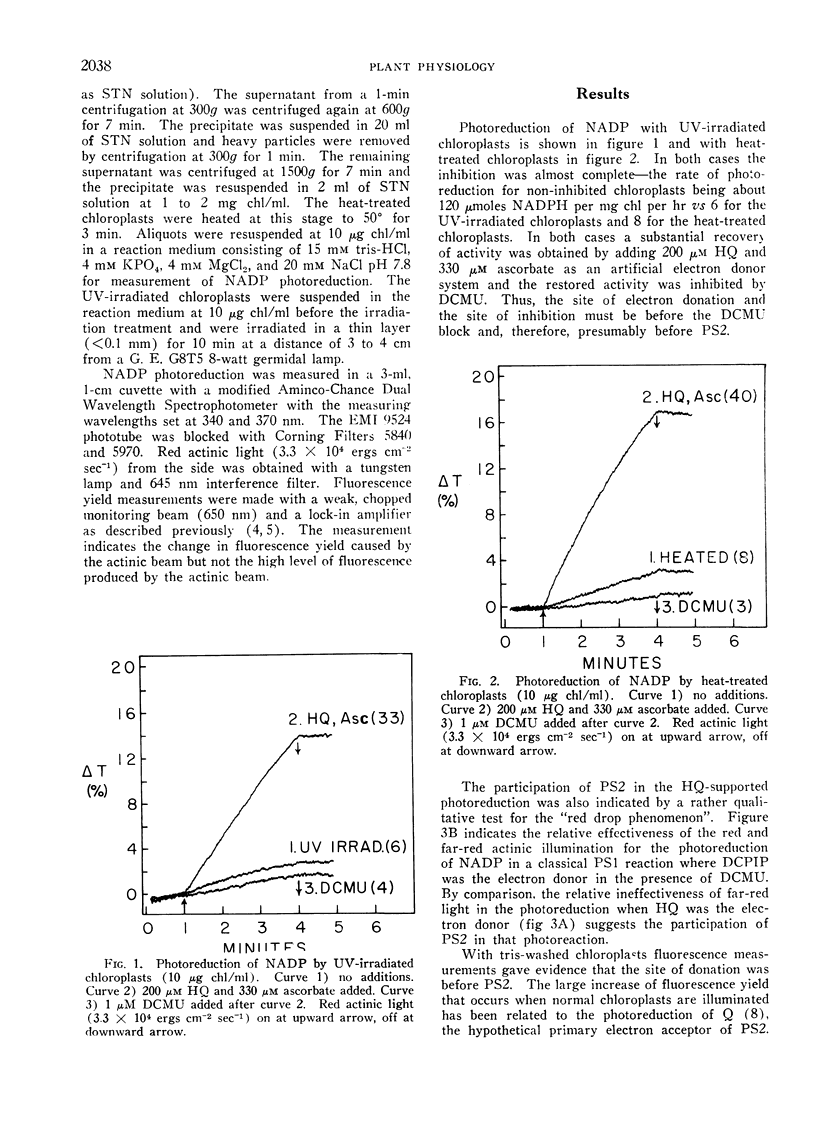
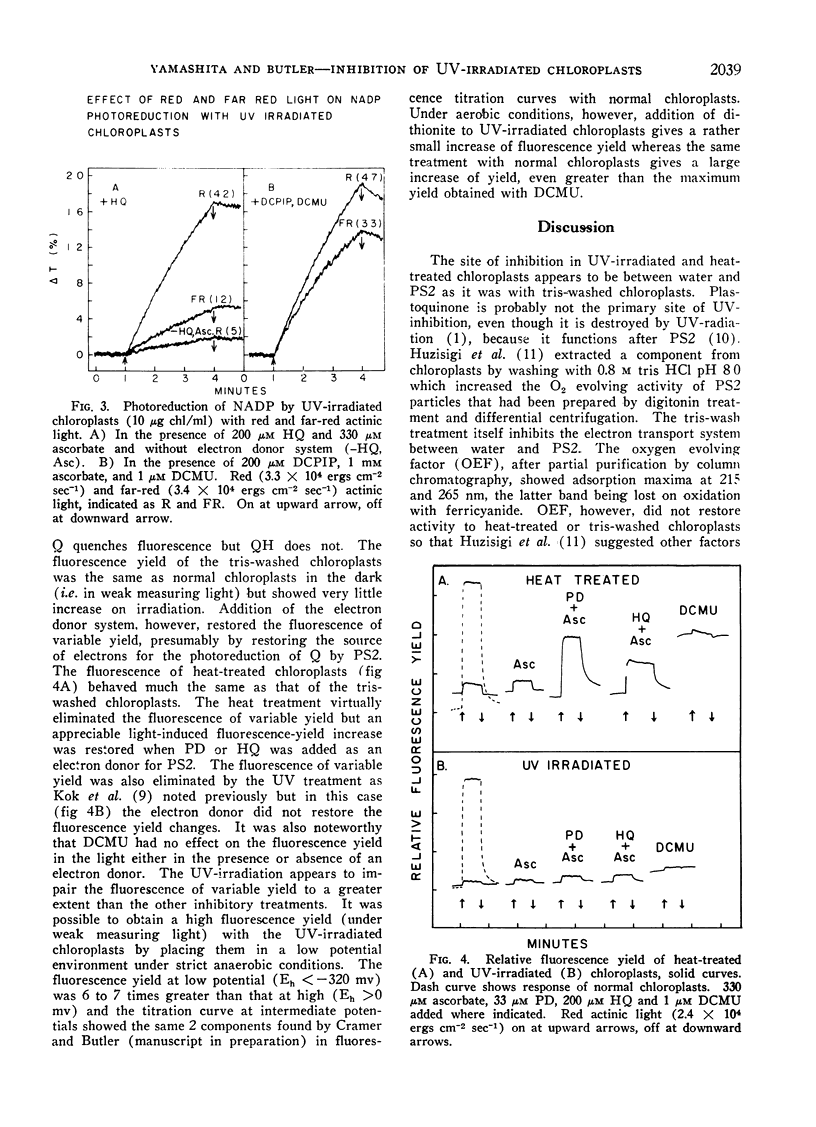
The site of inhibition in UV-irradiated and heat-treated chloroplasts was examined by using artificial electron donor compounds such as p-phenylenediamine and hydroquinone which donated electrons specifically to photosystem II. In both cases the electron donors restored the photoreduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and the restored activity was inhibited by 3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,1-dimethyl urea. The fluorescence of variable yield was eliminated by both inhibitory treatments and was partially restored by the electron donors in the heat-treated but not the UV-irradiated chloroplasts. The results suggest that the sites of inhibition of UV-radiation and heat treatment are in the photosynthetic electron transport chain between water and photosystem II.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMESZ J. SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC EVIDENCE FOR THE PARTICIPATION OF A QUINONE IN PHOTOSYNTHESIS OF INTACT BLUE-GREEN ALGAE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Mar 30;79:257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. W., Kok B. Photoinhibition of Chloroplast Reactions. II. Multiple Effects. Plant Physiol. 1966 Jun;41(6):1044–1049. doi: 10.1104/pp.41.6.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh S., San Pietro A. Ascorbate-supported NADP photoreduction by heated Euglena chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Oct;122(1):144–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kok B., Gassner E. B., Rurainski H. J. Photoinhibition of chloroplast reactions. Photochem Photobiol. 1966 Mar;4(2):215–227. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1965.tb05739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHAVIT N., AVRON M. The effect of ultraviolet light on photophosphorylation and the Hill reaction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Mar 19;66:187–195. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


