Abstract
The role of ABCC4, an ATP-binding cassette transporter, in the process of platelet formation, megakaryopoiesis, is unknown. Here, we show that ABCC4 is highly expressed in megakaryocytes (MKs). Mining of public genomic data (ATAC-seq and genome wide chromatin interactions, Hi-C) revealed that key megakaryopoiesis transcription factors (TFs) interacted with ABCC4 regulatory elements and likely accounted for high ABCC4 expression in MKs. Importantly these genomic interactions for ABCC4 ranked higher than for genes with known roles in megakaryopoiesis suggesting a role for ABCC4 in megakaryopoiesis. We then demonstrate that ABCC4 is required for optimal platelet formation as in vitro differentiation of fetal liver derived MKs from Abcc4−/− mice exhibited impaired proplatelet formation and polyploidization, features required for optimal megakaryopoiesis. Likewise, a human megakaryoblastic cell line, MEG-01 showed that acute ABCC4 inhibition markedly suppressed key processes in megakaryopoiesis and that these effects were related to reduced cAMP export and enhanced dissociation of a negative regulator of megakaryopoiesis, protein kinase A (PKA) from ABCC4. PKA activity concomitantly increased after ABCC4 inhibition which was coupled with significantly reduced GATA-1 expression, a TF needed for optimal megakaryopoiesis. Further, ABCC4 protected MKs from 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP) as Abcc4−/− mice show a profound reduction in MKs after 6-MP treatment. In total, our studies show that ABCC4 not only protects the MKs but is also required for maximal platelet production from MKs, suggesting modulation of ABCC4 function might be a potential therapeutic strategy to regulate platelet production.
Keywords: megakaryocytes, platelets, megakaryopoiesis, ABCC4 protein, cyclic AMP, PKA (protein kinase A), 6-Mercaptopurine resistance, thrombocytosis, thrombocytopenia
1. Introduction
Production of platelets by their progenitors, the megakaryocytes (MKs) is referred to as megakaryopoiesis. Megakaryocyte production of platelets is intimately connected with its unique cell cycle where MKs bypass cytokinesis, in a process referred to as endomitosis1. This capability of MKs to bypass cytokinesis yields massive cells (some with diameters up to 160 μm) with polyploid nuclei.1,2 The modal polyploid state of murine and human MKs is 16N during megakaryopoiesis, but can increase up to 128N.3,4 Polyploid MKs re-organize their cytoplasm into morphologically discernible networks of demarcated membranes to enable formation of proplatelets.5 MKs produce up to 1011 platelets that are released into the blood to aid in the repair of vascular injuries. MK polyploidization and maturation are regulated by both internal and extracellular cues, but the factors that facilitate megakaryopoiesis are incompletely understood. Importantly, it is not completely understood how protein kinase A (PKA) impairs megakaryopoiesis and affects polyploidization.6,7
We identified the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) ABCC4, as the first mammalian nucleotide exporting ABC transporter because it conferred cellular resistance to nucleotide analog antiretroviral drugs.8 Many studies have now shown that ABCC4 can also export various endogenous nucleotides (cAMP, cGMP) and diverse drugs (chemotherapeutics like 6-mercaptopurine nucleotides, methotrexate and topotecan).9,10 Recent ABCC4 cryo-EM structures have provided a structural basis for the recognition and transport of multiple structurally diverse drug substrates by ABCC4.11 We and others have also shown that ABCC4 regulates platelet function.12–14 However, a role for ABCC4 in megakaryopoiesis has not been determined despite a GWAS study that showed that ABCC4 was among over 60 other candidate genes with the potential to regulate platelet number.15 Other ABC transporters have been implicated in megakaryopoiesis.16 For instance the lipid transporter, ABCA1 was linked to megakaryopoiesis because its mRNA expression increased during MK differentiation.17,18 Additionally, the lipid transporter ABCG4, when ablated in mice, showed enhanced MK progenitor proliferation and increased platelet production.19 To date, the vast majority of studies describe ABCC4’s role in platelet function12,20,21. It is unknown if ABCC4 has a role in megakaryopoiesis.
ABCC4 is capable of transporting the nucleotide forms of the chemotherapeutic and immunosuppressant drug, 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP)9,22–24. High ABCC4 expression in some acute myeloid leukemias (AML) promotes resistance to 6-MP due to the efflux of its nucleotide metabolites, 6-thioguanine (6-TGN).25 Some AML patients treated with 6-MP suffer from severe hematopoietic toxicity and thrombocytopenia as side effects, which require dose reduction or discontinuation of the drug. We have previously shown that Abcc4−/− mice suffered dose-dependent hematopoietic toxicity due to hematopoietic cell accumulation of 6-TGN; these findings paralleled the identification of a non-functional variant in humans of Asian descent that seemed to explain sensitivity to mercaptopurines.22 However, it is unknown if ABCC4 protects MKs against cytotoxic ABCC4 substrates. Elucidation of this may account for the variability of thrombocytopenic events among AML patients receiving chemotherapy with ABCC4 substrates.
In the present study, we show that ABCC4 is needed for optimal megakaryopoiesis. We also show that the strong expression of ABCC4 in MKs is protective as Abcc4−/− mice showed a marked reduction in megakaryocytes after treatment with 6-mercaptopurine. This study is the first to report ABCC4’s role in megakaryopoiesis and provides novel insight into how ABCC4 inhibition could modulate platelet formation.
2. Methods
2.1. Platelet isolation from mouse blood
Abcc4−/− mice were maintained on a C57/BL6 background. Animal studies were conducted following the protocols approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. Murine blood was collected in a tube containing sodium citrate buffer (0.109 M, 3.2%) and centrifuged for 20 minutes at 350g at room temperature (RT). This separated the blood into an upper yellow layer of platelet rich plasma (PRP) and a lower dense layer of red blood cells. The PRP layer was carefully removed and centrifuged for 10 minutes at 2000g at RT, which separated into pale-yellow supernatant containing platelet poor plasma (PPP) and a platelet pellet.
2.2. MKs culture from fetal liver
MKs culture from the fetal liver was performed as described previously.26 Briefly, fetal liver cells were isolated from 13.5 to 15.5 days embryos. The liver tissues were gently homogenized and cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% FBS and 2mM L-Glutamine in presence of thrombopoietin (50 ng/ml) for 4 days to induce differentiation. The MKs and megakaryocyte progenitors (MKPs) were isolated by 1.5%/3% BSA density gradient separation.26
2.3. Isolation of hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) from bone marrow
Bone marrow cells were collected from the femur and tibia of mice. Isolated cells were stained with R-Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated primary antibodies (CD4 # 553049, CD8 # 553033, NK-1.1 # 553165, B220 # 553090, Mac-1 # 553311, Gr-1 # 553128 and Ter119 # 553673, BD Pharmingen) and magnetically labelled with microbeads conjugated to monoclonal PE-antibodies (isotype: mouse IGg1). The cell suspension was passed through a MACs column (Miltenyi Biotec) and the negative fraction containing lineage negative HPCs was collected.
2.4. Culture of MEG-01 cells
MEG-01 cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI, Gibco) media supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 2mM glutamine in a humidified incubator at 37°C supplied with 5% CO2.27
2.5. Flow cytometry
The number of platelets in murine blood was measured by counting CD41 and CD61 double positive cells. Blood diluted in PBS was stained with fluorophore-conjugated antibodies (CD61 #553347; CD41 #558040, BD Sciences) and analyzed by using BD Biosciences Fortessa flow cytometer. Bone marrow derived cells were stained with fluorophore conjugated CD150 (#115931, BioLegend), CD48 (#103403, BioLegend), CD41 and CD61 to isolate MKs and MKPs. All antibodies were used at 1:100 dilutions. To determine the ploidy, MKs were stained with propidium iodide (PI, 50μg/ml) for 30 minutes at RT and analyzed by flow cytometry. Differentiating MEG-01 cells were initially fixed with 70% ethanol before staining with PI. Data analysis was performed using either BD FACS or FlowJo software version 10.7.1.
2.6. Quantitative- real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
RNA extraction was performed using RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen) following the manufacturer’s protocol. RNA concentration and purity were assessed by using Nanodrop 1000 spectrophotometer. cDNA synthesis was performed using iScript Reverse Transcription Supermix reagent from Bio-Rad. The cDNA was amplified using SYBR GreenER qPCR Supermix (Life Technologies) in a ABI prism PCR System (Applied Biosystems). Primer sequences used for human GATA1 and GAPDH are listed in Suppl Table 4. mRNA fold expression of the genes was calculated using 2−ΔΔCt method and GAPDH as a normalization control.
2.7. RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq)
Paired-end sequencing was performed using Novaseq Illumina sequencer with read length capacity of 100 bps. The read alignment to the reference genome, hg38 (for human samples) and mm10 (for murine samples), was performed using STAR software (version 2.7) and gene level quantification was determined using RSEM (version 1.3.1). Mapping QC matrix and principal component analysis was performed for all the samples to evaluate the coverage depth and quality of RNA-seq. The cutoffs of p-value<0.05, FDR<0.05, and/or absolute log2FC>1 was used to define differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The pathway analysis of the DEGs was done using Enrichr database.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 8. The significance of difference (p-value< 0.05) was determined using either Student’s t test, one or two-way analysis of variance where applicable.
3. Results
3.1. High ABCC4 expression in megakaryocyte (MK) lineage
Interrogation of the publicly available BloodSpot database (https://servers.binf.ku.dk/bloodspot/?gene=ABCC4%20&dataset=BLUEPRINT_Normals) showed higher ABCC4 mRNA expression in MKs (log2FC=9.65) compared to other hematopoietic cells (Fig 1 A).28 However, ABCC4 expression in the megakaryocyte erythrocyte progenitors (MEPs) was lower (log2FC=5.14) than in the MKs. Consistent with these findings, murine models showed higher Abcc4 mRNA expression in MKs compared to MKPs (Fig 1 B and Suppl Fig 1, Geodata profile: GDS1316/1443870). Among the various ABC transporters (ABCG2, ABCB1, ABCC1) and A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAP1, AKAP10, AKAP11, AKAP12) expressed in MKs, ABCC4 mRNA expression was the highest (Suppl Fig 2 A) whereas in MEPs, ABCC4 mRNA expression was similar to other ABC transporters and AKAPs (Suppl Fig 2 B). The human megakaryoblastic cell line, CHRF-288–11 when differentiated to MK with Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) time-dependently upregulated ABCC4 mRNA during megakaryocytic differentiation (Fig 1 C, Geodata Profile: GDS2926/1683).29 ABCC4 protein expression also increased in PMA treated MEG-01 cells (human megakaryoblastic cell line) (Fig 1 D).
Figure 1. ABCC4 is highly expressed in Megakaryocytes (MKs).
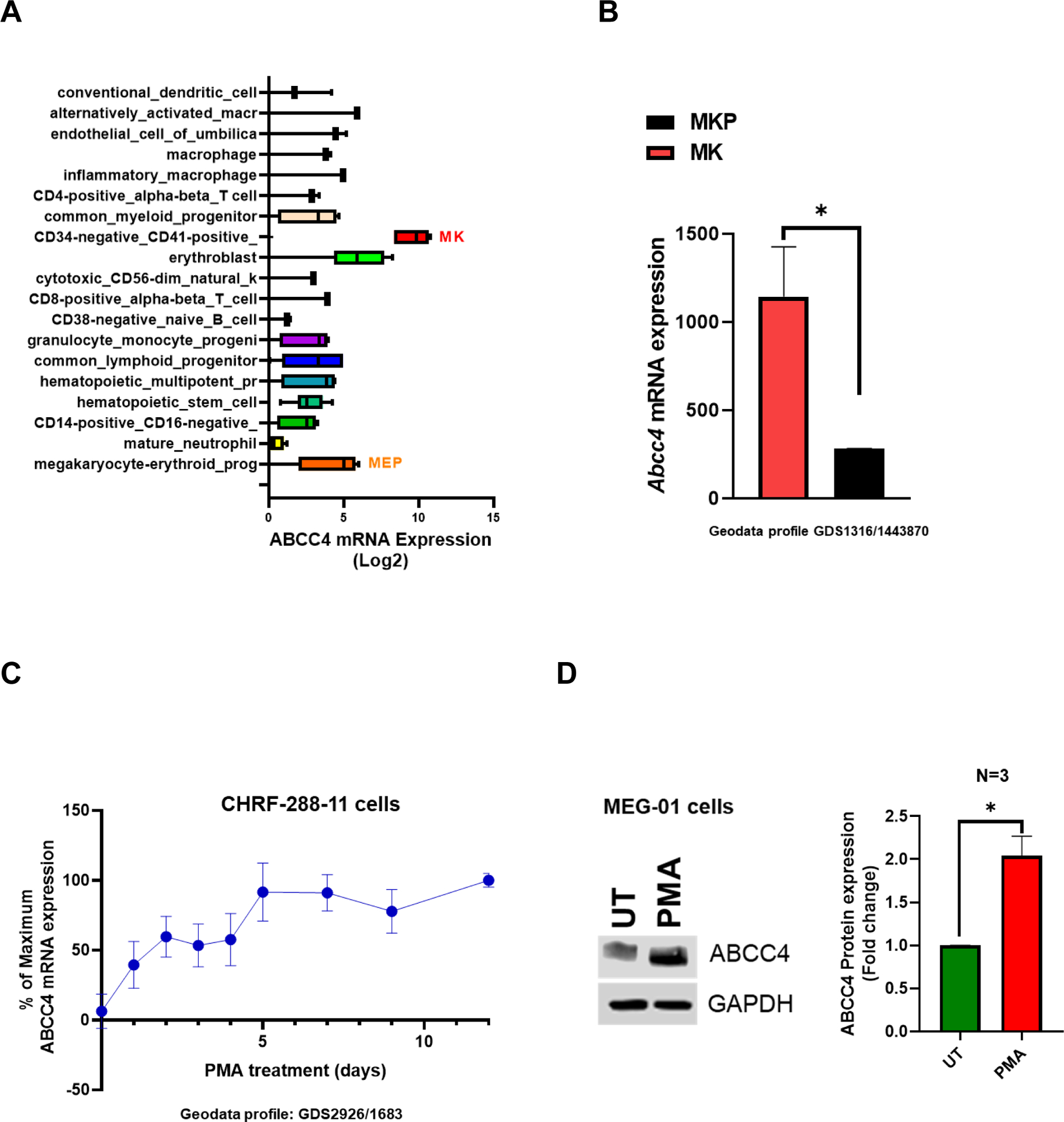
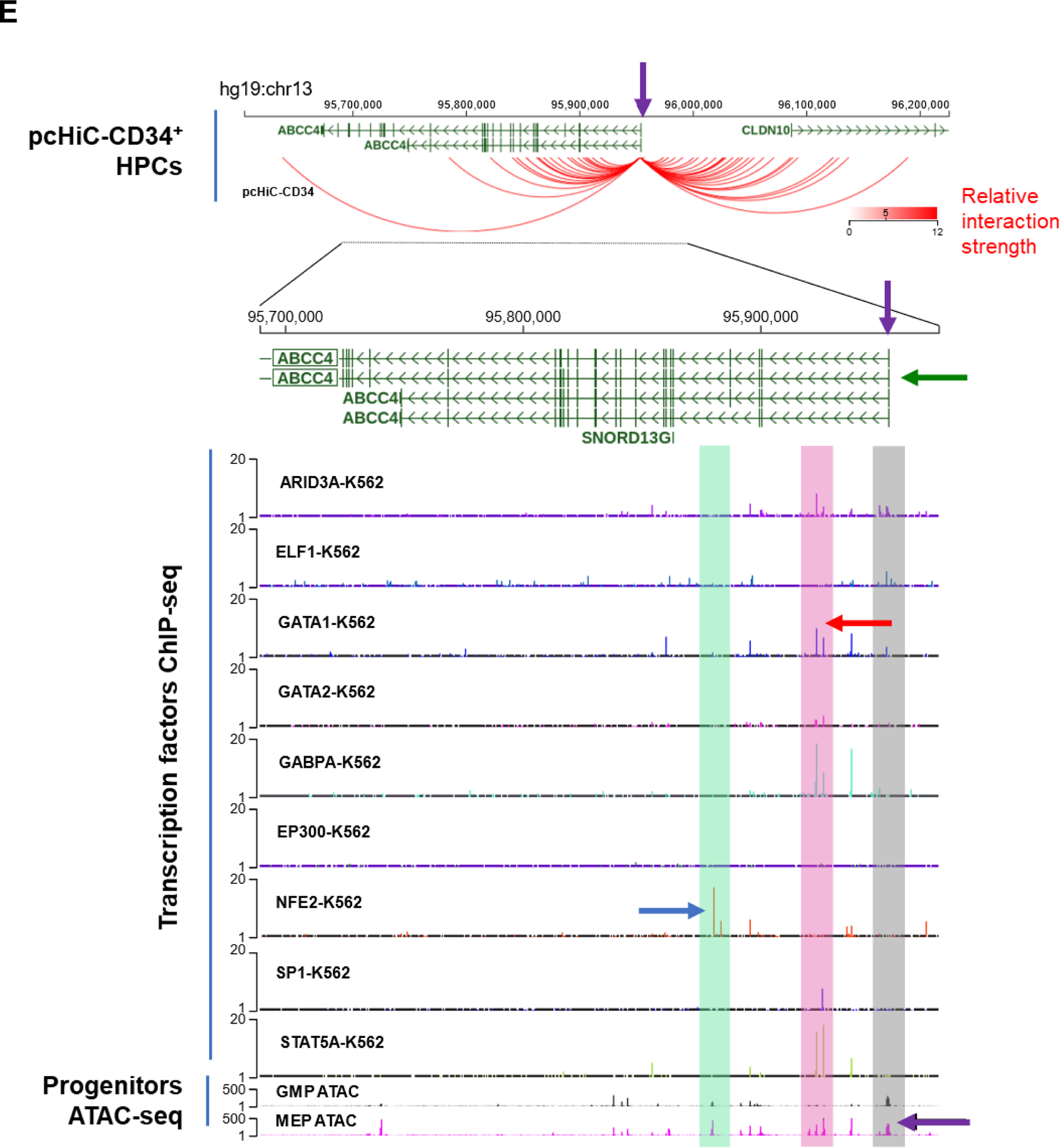
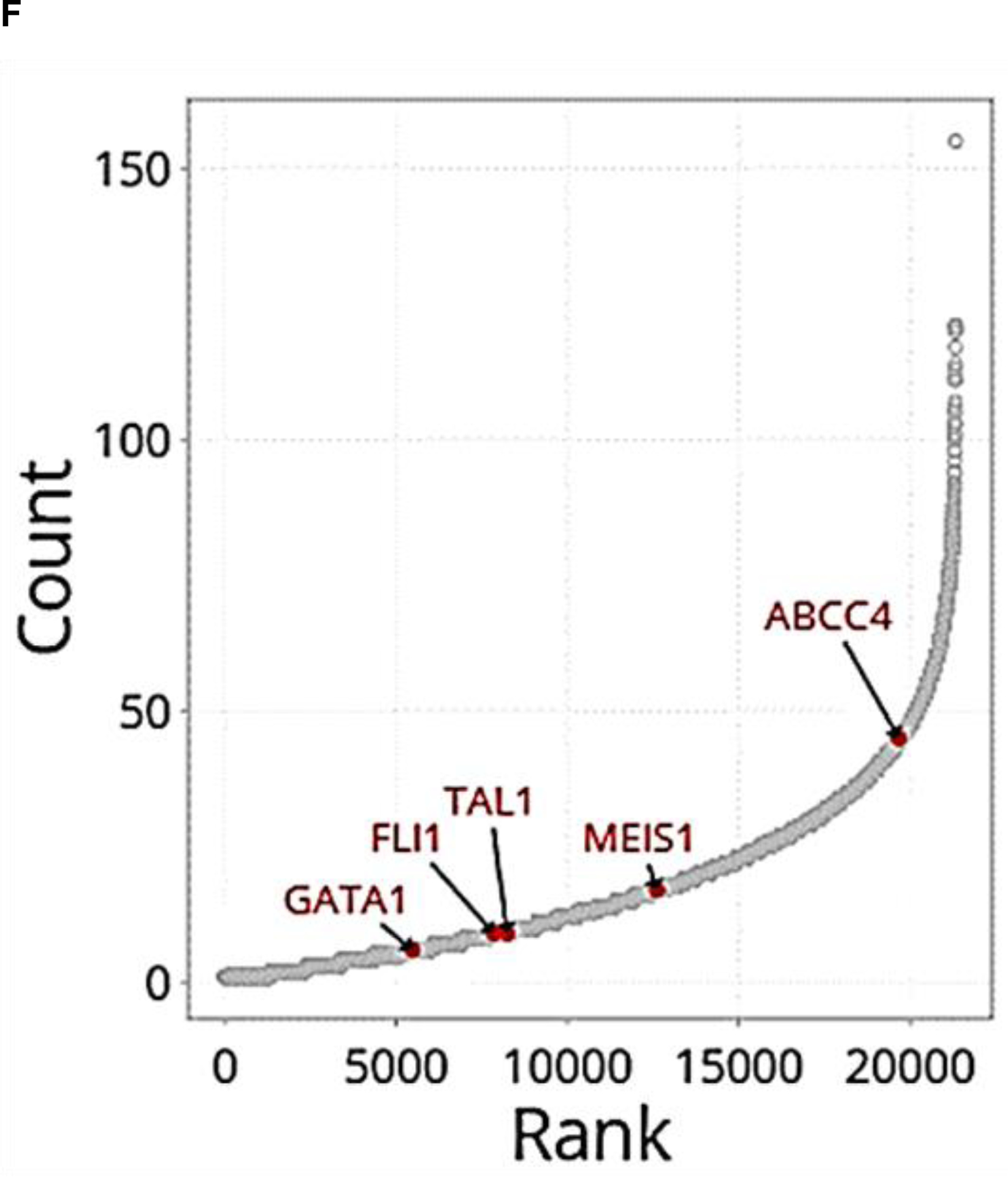
A. ABCC4 expression is highest in MKs and MK erythroid progenitors (MEPs) among various normal hematopoietic cells derived from human cord blood (BloodSpot database: https://servers.binf.ku.dk/bloodspot/?gene=ABCC4%20&dataset=BLUEPRINT_Normals) B. Abcc4 expression in MKs and MKPs derived from murine fetal liver using microarray (geodata profile GDS1316/1443870), N=20, *p-value<0.05, Student’s t test. C. ABCC4 expression in CHRF-288–11 cells during 10 days of differentiation with PMA (10 ng/ml) (GDS2926/1683). D. ABCC4 expression in MEG-01 cells after treatment with/without PMA (100 nM) for 2 days. Densitometric quantification of the blots (N=3 independent experiments) were performed using Image Studio Lite version 5.2. Bars represent means (± SEM) of ABCC4 expression normalized with GAPDH (*p-value<0.05, Student’s t test). E. Differential ATAC-seq peaks were observed between granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMPs) and MEPs at multiple regions (green and pink) of ABCC4 gene locus in a study.30 Transcription factors (TFs) binding to those ATAC peaks were identified using TF ChIP-seq clusters from ENCODE (Human GRch37/hg19 Assembly). Grey bar highlights that ABCC4 promoter region (purple arrow) is accessible to regulatory elements in both the MEP and GMP. The blue and red arrows point to the prominent peaks for NFE2 and GATA1 respectively, indicating them as possible TFs regulating ABCC4. The promoter capture Hi-C data from CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPCs) show multiple loops in ABCC4 gene loci, indicating multiple TF interactions between the promoter of ABCC4 and adjacent regions. Green arrow points to the dominant ABCC4 isoform (ENST00000645237.2). F. Promoter Hi-C data of all the genes in CD34+ HPCs ranked in order of the number of interactions (counts) to their promoters.
Analysis of public ATAC-seq and ChIP-seq datasets from human granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMPs) and MEPs showed that the ABCC4 gene locus had multiple regions that were in an open conformation and bound by key megakaryopoiesis TFs.30 The ATAC-seq data also showed that ABCC4 promoter’s regulatory region is accessible in both MEP and GMP. Notably, NFE2 as well as GATA-1 signals were strong in MEPs suggesting that ABCC4 is regulated by these key TFs (Fig 1 E). Given these binding sites and open chromatin regions did not directly bind to the ABCC4 promoter, we sought evidence for global genomic interactions with enhancers that loop to ABCC4 promoter. Indeed, we interrogated genome-wide interactions using public Hi-C data obtained from CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors (Fig 1 E, F). This data showed these TFs prominently interacted with ABCC4’s promoter through enhancers.30 Importantly, ranking the genes by their total contact number with their promoter showed that ABCC4 ranked higher than genes with known established roles in megakaryopoiesis (GATA1, FLI1, TAL1 and MEIS1) (Fig 1 F). Consistent with these findings, we also noticed in a murine model that Abcc4 expression in MKs, but not MKPs, was dependent upon Gata1 as Abcc4 expression was markedly reduced after Gata1 deletion (Suppl Fig. 1, Geodata profile: GDS1316/1443870).31
3.2. ABCC4 selectively protects MKs from 6-MP toxicity
We previously reported that ABCC4 conferred resistance to 6-MP toxicity in myeloid cells by actively effluxing 6-MP metabolites, 6-TGNs.22 Here, we examined if ABCC4 conferred resistance to 6-MP toxicity of additional blood cells by performing a complete blood count analysis of WT and Abcc4−/− mice. After 10 days of 6-MP treatment, platelets derived from Abcc4−/− mice were profoundly reduced to ~5% of the normal mean platelet number compared to ~50% in the WT (Fig 2 A). Granulocyte, lymphoid and erythroid cells were comparably affected in WT and Abcc4−/− mice (Supp Fig 3 A, B). Microarray data of mouse normal hematopoietic cells obtained from the BloodSpot database (GSE14833 and GSE6506) showed that lymphocytes, monocytes and erythrocytes have very low Abcc4 expression; granulocytes have Abcc4 expression similar to MKPs. (Suppl Fig 3 C). This might account for why Abcc4 did not protect these cells from 6-MP toxicity. In untreated WT and Abcc4−/− mice, flow cytometric quantification of platelets using the surface markers CD41 and CD61 indicated no difference in basal platelets (Suppl Fig 3 D). Given that, the estimated half-life (t1/2) of platelets is about 57 hours (2.4 days) in both WT and Abcc4−/− mice (data not shown), we expect that most of the platelets that accumulated before 6-MP treatment would be eliminated by day 10 (~5-fold t1/2), so the platelets enumerated on day 10 after 6-MP treatment were likely newly formed platelets. The profound reduction in platelet number after 6-MP treatment of Abcc4−/− mice might be due to either platelet apoptosis or impaired platelet production.
Figure 2. ABCC4 protects MKs from 6-Mercaptopurine toxicity.
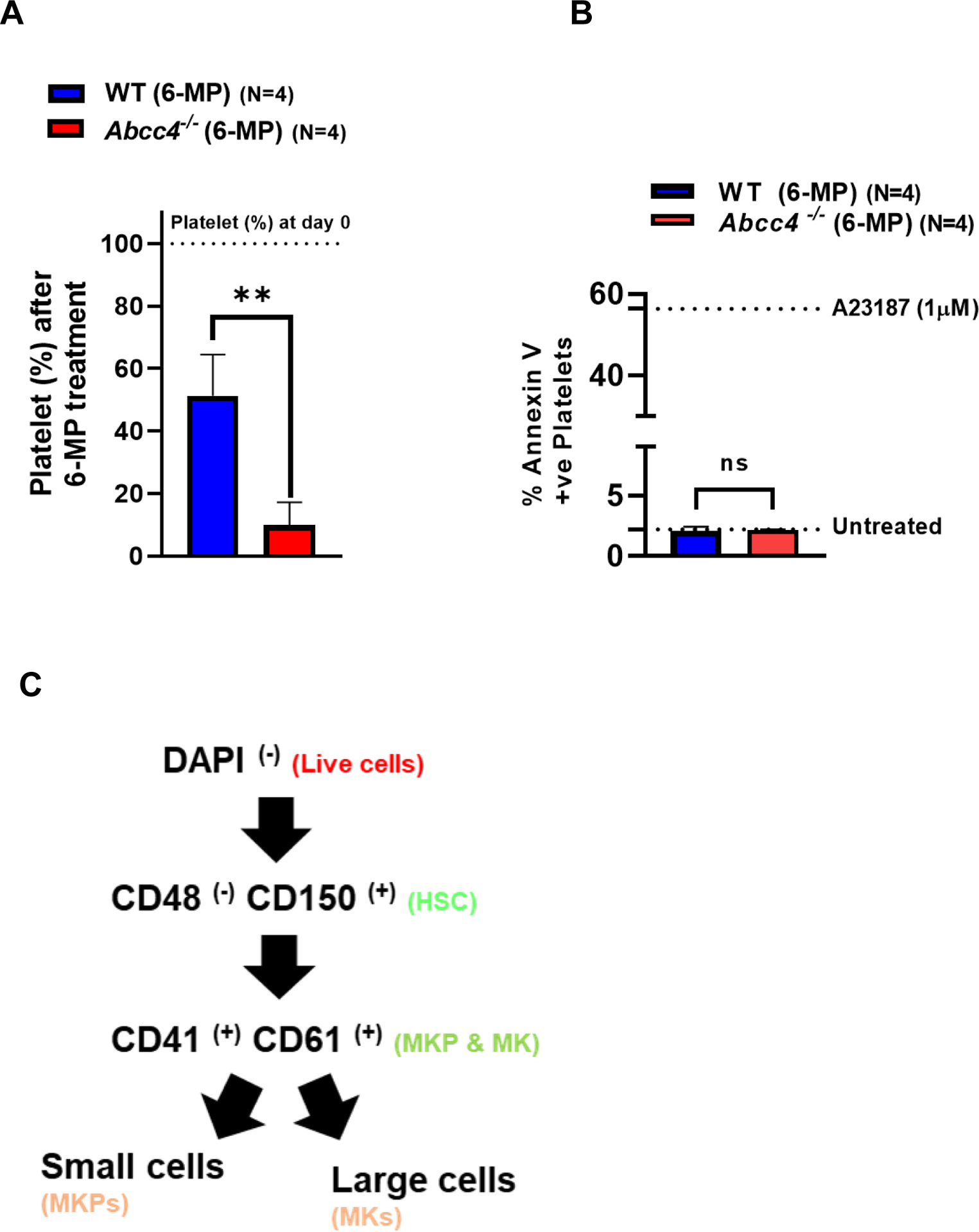
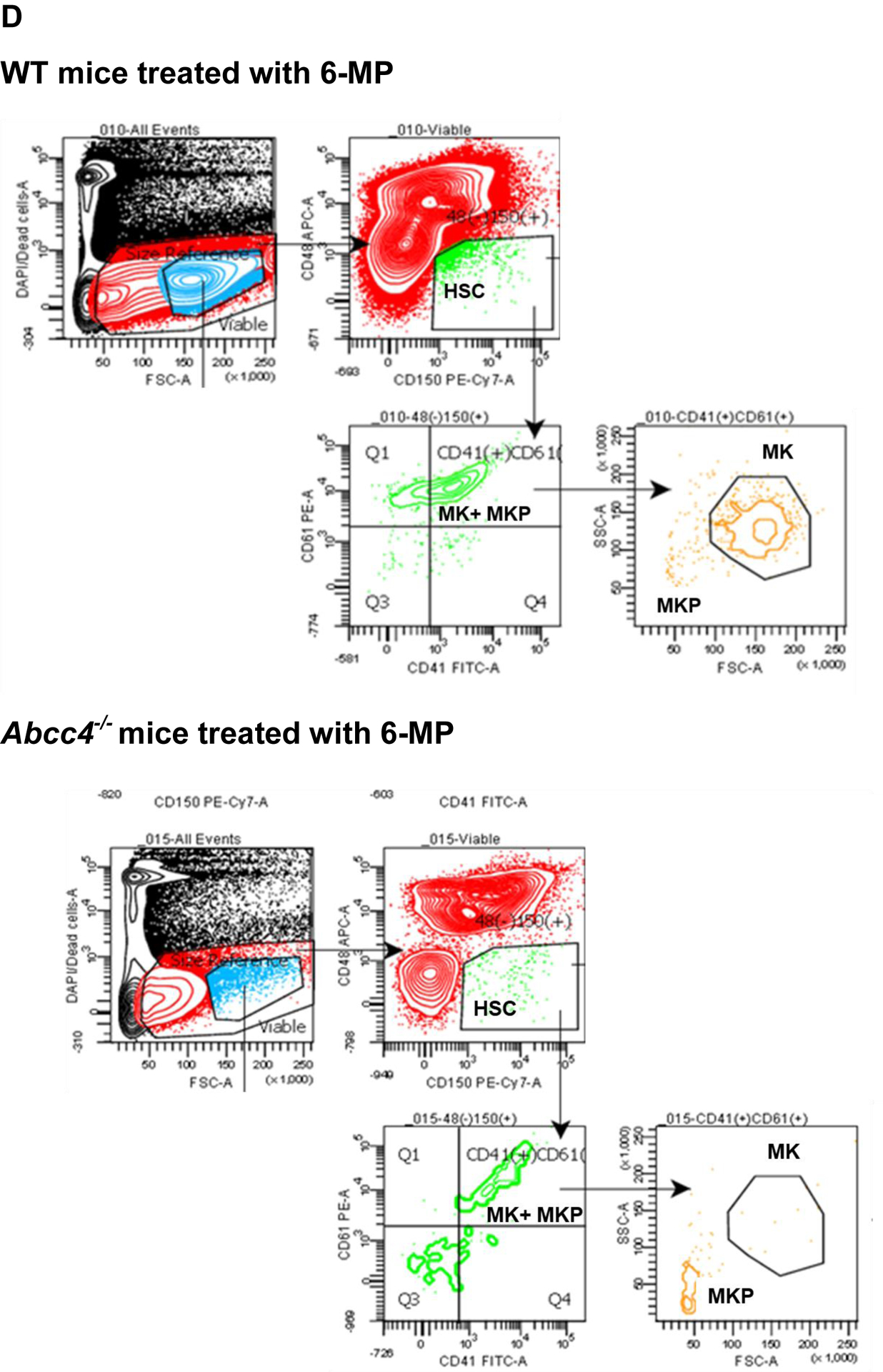
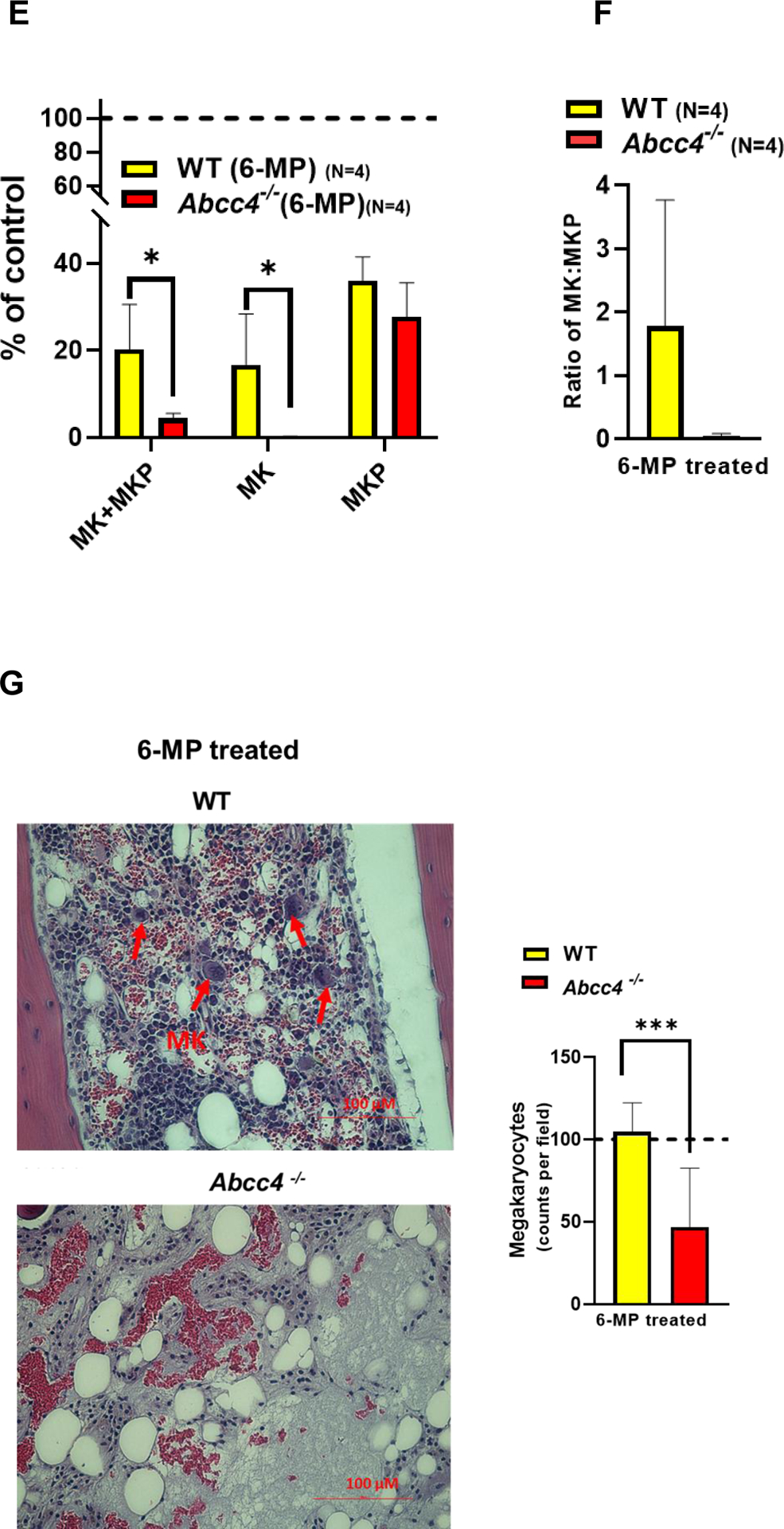
A. Platelet number in WT (N=4) or Abcc4−/− mice (N=4) was counted using automatic hematology analyzer (Forcyte, Gen 10, Oxford Science) on day 0 and day 10 after treatment with 6-Mercaptopurine (6-MP 100mg/kg) daily. Bars represent mean % (± SD) of platelets after 6-MP treatment, calculated as a % of platelets on day 0, ** p-value<0.01, Student’s t test. B. Platelets from WT (N=4) or Abcc4−/− mice (N=4) were treated with 6-MP (6.25–50 μM) for 90 minutes at RT. WT or Abcc4−/− mice (N=1 for each group) were treated with saline or calcium ionophore A23187 (1 μM) as a negative and positive control for apoptosis respectively. Flow cytometric measurement of Annexin V intensity was used to determine apoptosis. C-D. Scheme of gating strategy used for flow cytometric isolation of MKs and MKPs from bone marrow of WT or Abcc4−/− mice after saline or 6-MP treatment. From the pool of live cells, HSC, MKP and MKs were successively isolated using the corresponding antibodies. E. Bars show mean (± SD) MKs or MKPs in WT or Abcc4−/− mice treated with 6-MP (N=4), calculated as a % of control (saline, N=2), *P<0.05, two-way ANOVA. F. Bars represent mean (± SD) ratios of MK: MKPs in WT (N=4) nor Abcc4−/− (N=4) mice treated with 6-MP. G. Bone marrow from 6-MP treated WT or Abcc4−/− mice stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (40X objective, scale bar 100 μm). H. Bars show mean (± SD) number of MKs in bone marrow of WT (number of fields =8) or Abcc4−/− (number of fields =12) mice treated with 6-MP, *** p-value <0.001, Student’s t test.
To determine if platelets of Abcc4−/− mice were more sensitive to 6-MP, platelets of both WT and Abcc4−/− mice were treated ex vivo with 6-MP or the calcium ionophore A23187, an agent known to be lethal to platelets.32 Platelet apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry using Annexin V positivity as an indicator of cell death. Platelets from both genotypes demonstrated a similar low Annexin V signal after 6-MP treatment while treatment with A23187 led to equally high Annexin V signals. This indicates that 6-MP does not directly induce apoptosis in WT and Abcc4−/− platelets and that the similar Annexin V staining after A23287 suggests that ABCC4’s absence does not generally affect platelet apoptosis (Fig 2 B). The Bcl-anti-apoptotic family proteins have an important role in platelet survival.33 We then showed that there was no difference between WT and Abcc4−/− mice in the expression of either pro-survival proteins (Bcl-xL, Bcl2) or the pro-apoptotic protein (Bax) (Suppl Fig 3 E). These results are not surprising because it is unlikely that 6-MP induces apoptosis in platelets due to the lack of DNA.
We hypothesized that ABCC4 affects platelet production by protecting either MKs or MKPs from 6-MP toxicity. We then determined if the number of MKs or MKPs from the bone marrow of either WT or Abcc4−/− mice were affected by 6-MP treatment using the scheme shown in Fig 2 C. Flow cytometric quantification revealed a strong reduction of MKs, but not MKPs, from 6-MP treated Abcc4−/− mice (Fig 2 D, E). The resistance to 6-MP toxicity of WT MK was reflected in the large reduction in the ratio of MK:MKP (Fig 2 F). Further, hematoxylin and eosin staining of the bone marrow from 6-MP treated WT or Abcc4−/− mice affirmed that the MKs from Abcc4−/− mice was significantly more sensitive than WT MKs (Fig 2 G). We also examined the effect of 6-MP on MKs derived from the fetal liver of WT and Abcc4−/− mice. We first confirmed that Abcc4 protein was highly expressed in MKs derived from the fetal liver of WT and that Abcc4 protein was absent in the MKs from Abcc4−/− mice (Suppl Fig 4 A). Importantly, MK differentiation (proplatelets) was reduced in MKs derived from Abcc4−/− fetal liver culture compared to the WT (Suppl Fig 4 B). Notably, while 6-MP treatment was cytotoxic to both the WT and Abcc4−/− cultured MK, the Abcc4−/− MKs appeared more severely affected (Suppl Fig 4 C). Treatment of these same cultures with Etoposide, a topoisomerase II inhibitor known to cause apoptosis, revealed similar lethality in both cultures regardless of genotype indicating Abcc4−/− MKs are not generally more sensitive to death stimuli (Suppl Fig 4 D).
3.3. Defective proplatelet formation and polyploidization in Abcc4−/− fetal liver derived MKPs
MKs account for a small % (approximately 0.05 to 1%) of the total nucleated murine bone marrow cells. Thus, the limited number of MKs in mouse represent an ethical challenge to obtain enough material for biochemical analyses (e.g., measurement of cAMP).34 Therefore as a proxy for MKs, we isolated the much more abundant hematopoietic progenitors (HPCs) from WT and Abcc4−/− bone marrow. cAMP levels were markedly higher in HPCs from Abcc4−/− mice than the WT regardless of gender (Fig 3 A). Excessive intracellular cAMP inhibits megakaryopoiesis6,7,35–37. It is unknown if ABCC4 function affects megakaryopoiesis.
Figure 3. Loss of Abcc4 causes defective proplatelet formation and delayed platelet genesis.
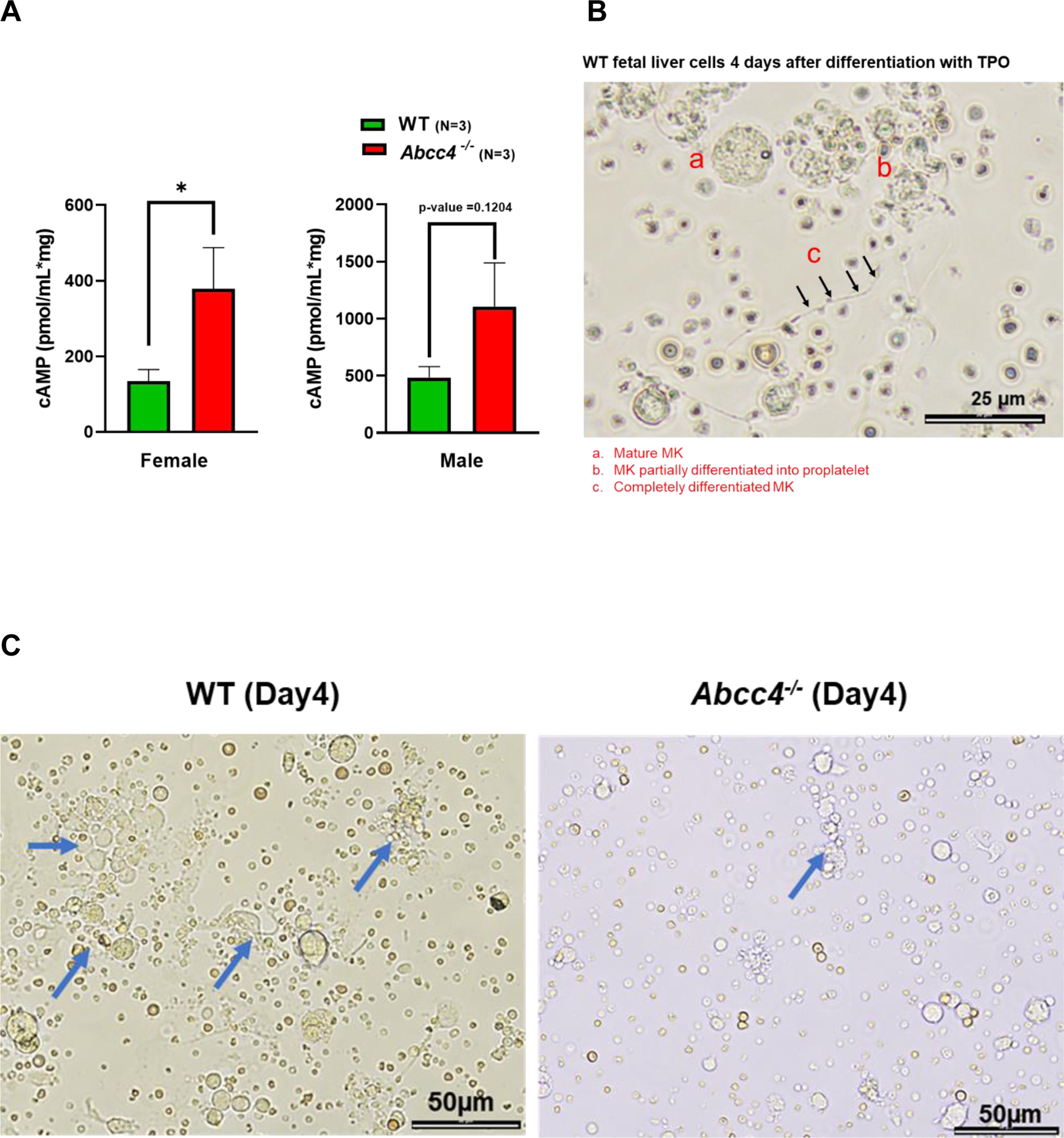
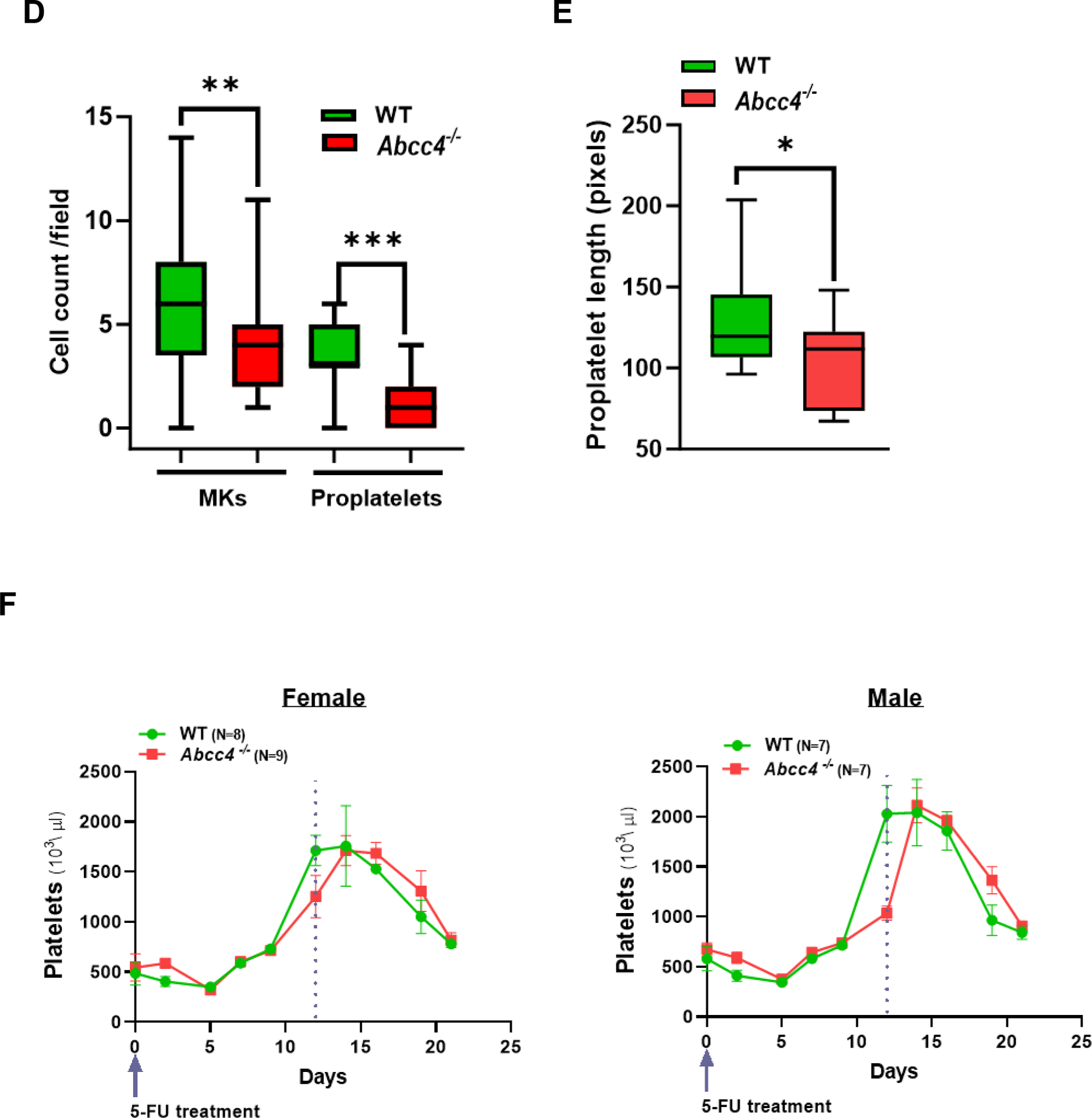
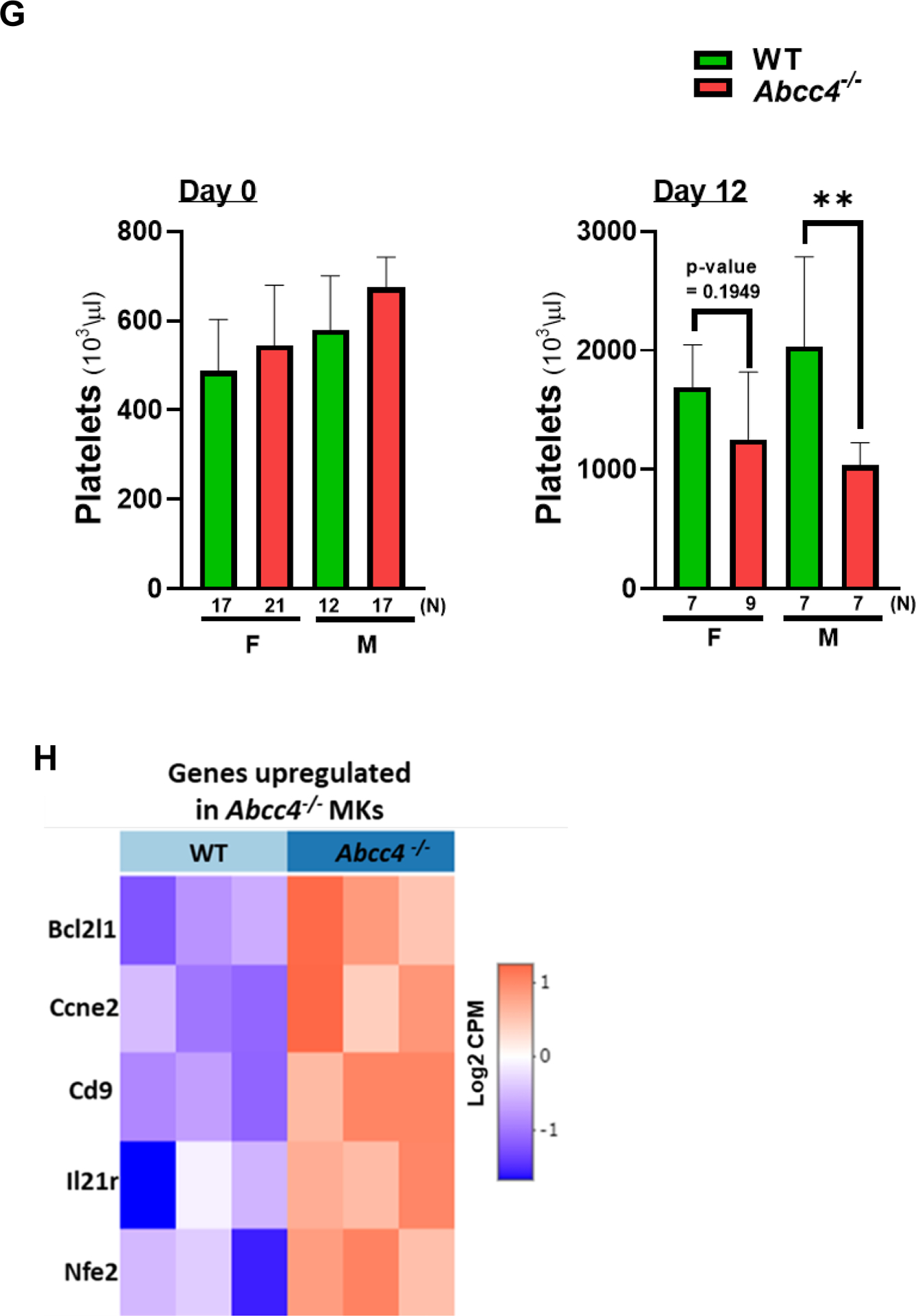
A. HPCs were isolated from the bone marrow of WT or Abcc4−/− mice (male and female) by collecting lineage negative cells through MACS cell separation. Intracellular cAMP level in HPCs was measured using cAMP ELISA assay. Bars represent mean (± SEM) calculated from N=3 mice for each group, *p-value<0.05, Student’s t test. B. Fetal liver cells derived from WT mice after 4 days of differentiation with thrombopoietin (TPO, 50 ng/ml), showing (a) mature MK (b) MK differentiated partially into proplatelet and (c) completely differentiated proplatelet (40x objective, scale bar 25 μm). Images are from N=2 independent experiments, where liver from at least 6 fetuses were pooled for each experiment. C. WT and Abcc4−/− fetal liver culture 4 days after TPO treatment (20x objective, scale bar 50 μm), showing defect in proplatelet formation. Blue arrows show proplatelets formed. D. Bars show mean (± SD) number of MKs and proplatelets (PP) per field (number of fields = at least 25) and ratio of MK:PP. The figure shows representative result from N=2 independent experiments, where liver from at least 6 fetuses were pooled for each experiment (** p-value<0.01, *** p-value<0.001 and ns non-significant, one-way ANOVA). Proplatelet number was determined by considering each cluster of proplatelet as one. E. Bars represent mean proplatelet length (± SEM), *p-value<0.05, Student’s t test. The longest diameter of the proplatelet was considered while measuring the proplatelet length. F. Single dose of 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU, 50mg/kg) was administered to WT or Abcc4−/− mice (female or male, N=8 for each group) and platelets counts were monitored from day 0 to day 21. Graphs showing peak platelet formation in WT mice on day 12, which is delayed in Abcc4−/− mice. G. Bars shows no difference in mean platelet count between WT (female N=17, male N=12) and Abcc4−/− mice (female N=21, male N=17) at day 0. At day 12, there were marked differences in platelet count between WT (female N=7, male N=7) and Abcc4−/− mice (female N=9, male N=7); bars represent mean (± SD), **p-value< 0.01, F: female, M: male, one-way ANOVA. H. RNA-seq was performed in MKs derived from the WT and Abcc4−/− murine bone marrow. MKs were isolated from the murine bone marrow by flow cytometric sorting of CD41+ cells. Heatmap obtained from RNA-seq of MKs derived from the bone marrow of WT and Abcc4−/− mice (N=3) shows genes regulating megakaryopoiesis were significantly enriched in Abcc4−/− mice (p-value<0.05, FDR<0.05).
To determine if ABCC4 absence affects megakaryopoiesis, we isolated the fetal liver cells and cultured them in vitro in presence of thrombopoietin (TPO). TPO promoted MK differentiation in WT fetal liver cells as observed by the extensive proplatelet formation (Fig 3 B, C). In contrast, MKs derived from Abcc4−/− mice displayed markedly impaired proplatelet formation, with both the number of proplatelets as well as MKs per field being significantly lower in the Abcc4−/− fetal liver culture (Fig 3 C, D). The proplatelet length was also significantly reduced in Abcc4−/− fetal liver culture compared to the WT (Fig 3 E). As MKs mature, polyploid nuclei are generated because cytokinesis is skipped to increase DNA content.38 We determined the ploidy of differentiating MKs from WT and Abcc4−/− fetal liver culture. Ploidy analysis indicated a strong reduction in polyploidy at the 32N-128N level in Abcc4−/− MKs, but for unknown reasons ploidy was similar at <8N (Suppl Fig 5).
3.4. Delayed platelet genesis in Abcc4−/− mice is related to MK gene compensation
The similar basal platelet number in WT and Abcc4−/− mice is puzzling given our in vitro results (in fetal liver derived MKs) and suggests that compensation for platelet formation occurs in vivo in Abcc4−/− mice (Fig 3 G - Day 0). To determine if Abcc4 absence impacts de novo megakaryopoiesis in vivo, WT or Abcc4−/− mice were treated with a single dose of 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU). This treatment destroys all cycling cells and drives quiescent HPCs (including MKs) to differentiate.39 Platelet and peripheral red blood cell levels were monitored after a single 5-FU treatment to assess in vivo megakaryopoiesis and erythropoiesis. The nadir in red blood cells and the subsequent production of red blood cells (erythropoiesis) was unaffected by Abcc4’s absence (Suppl Fig 6). The nadir in platelet level after 5-FU treatment was similar in WT and Abcc4−/− mice suggesting no difference in platelet turnover. However, achieving maximal platelet number (day 12 in WT) was significantly delayed in both genders of Abcc4−/− mice (Fig 3 F, G- Day 12). This minimal defect in maximal platelet production in Abcc4−/− mice in vivo (compared to significant reduction in vitro MK differentiation in fetal liver culture derived from Abcc4−/− mice, Fig 3 C–E) suggests that Abcc4−/− MKs may compensate for Abcc4’s absence in vivo.
To determine if Abcc4−/− MKs compensate for Abcc4’s absence, RNA-seq analysis of MKs purified from the bone marrow of untreated adult WT and Abcc4−/− mice was performed. The heatmap of the RNA-seq data shows that in Abcc4−/− MKs, multiple genes that promote megakaryopoiesis (Bcl2l1, Ccne2, Cd9, Il21r, Nfe2, Fig 3 H, Suppl Table 1) were upregulated, supporting the proposal that Abcc4−/− MKs compensate for Abcc4’s absence in vivo, thus accounting for near normal level of platelets in vivo in Abcc4−/− mice and minimal defect in megakaryopoiesis in vivo after 5-FU treatment.
3.5. ABCC4 interacts with PKA and its inhibition promotes intracellular cAMP elevation and dissociation of PKA subunits
To extend the study of ABCC4’s role in megakaryopoiesis to a human model and also assess if acute short-term ABCC4 inhibition affected megakaryopoiesis, we used MEG-01 cells which are derived from megakaryoblasts.27 MEG-01 cells differentiate when the cells are treated with PMA.27 PMA-treated MEG-01 cells strongly increased ABCC4 protein expression (Fig 4 A). Co-treatment with ceefourin 2 (Cee2), a specific ABCC4 inhibitor40 for 2 days, did not affect the PMA induced increase in ABCC4 protein level (Fig 4 A). However, ABCC4 inhibition strongly increased intracellular cAMP and decreased the extracellular cAMP level, consistent with inhibition of ABCC4 mediated cAMP export (Fig 4 B).
Figure 4. ABCC4 interacts with PKA and its inhibition promotes intracellular cAMP elevation and PKA dissociation.
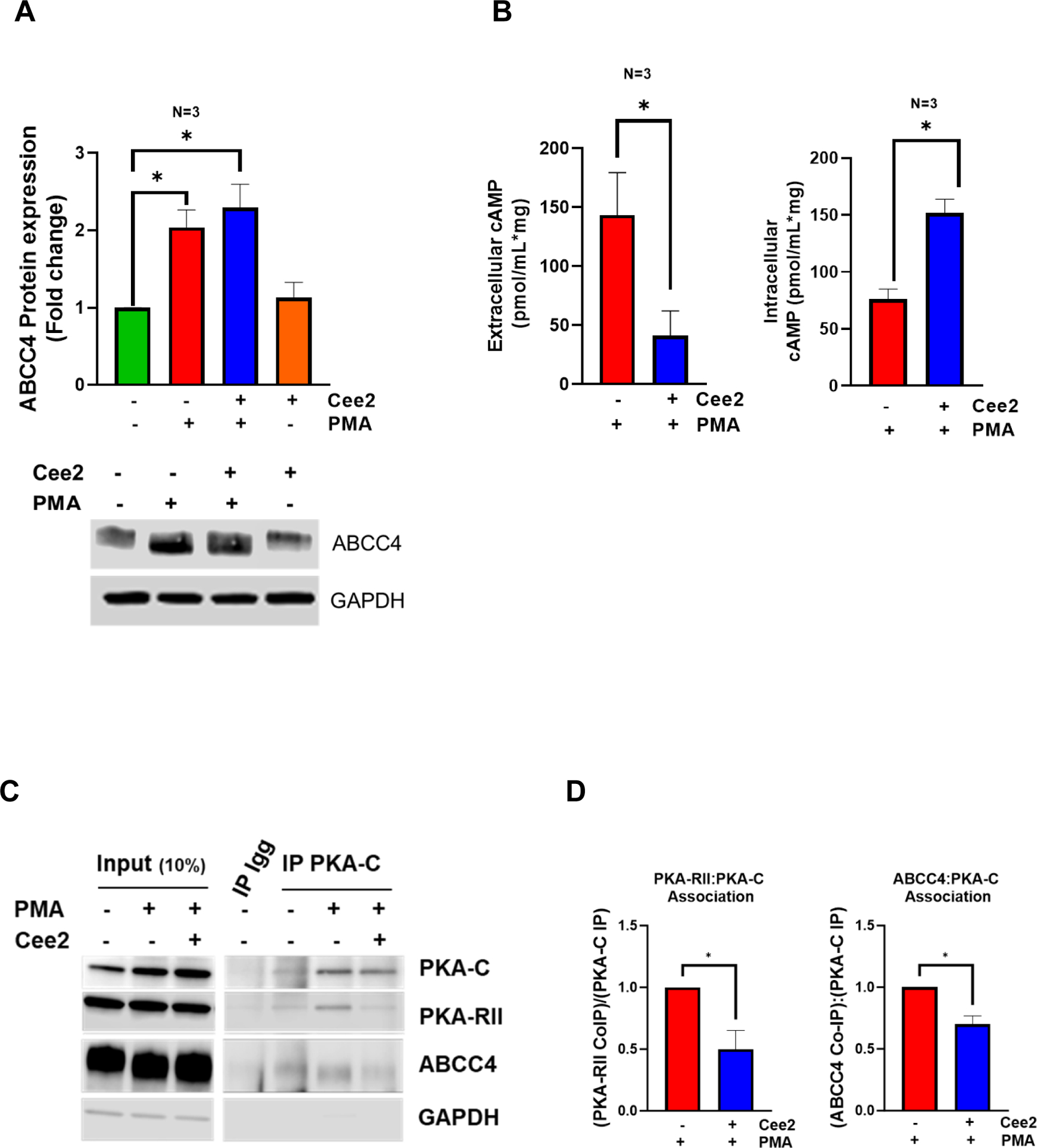
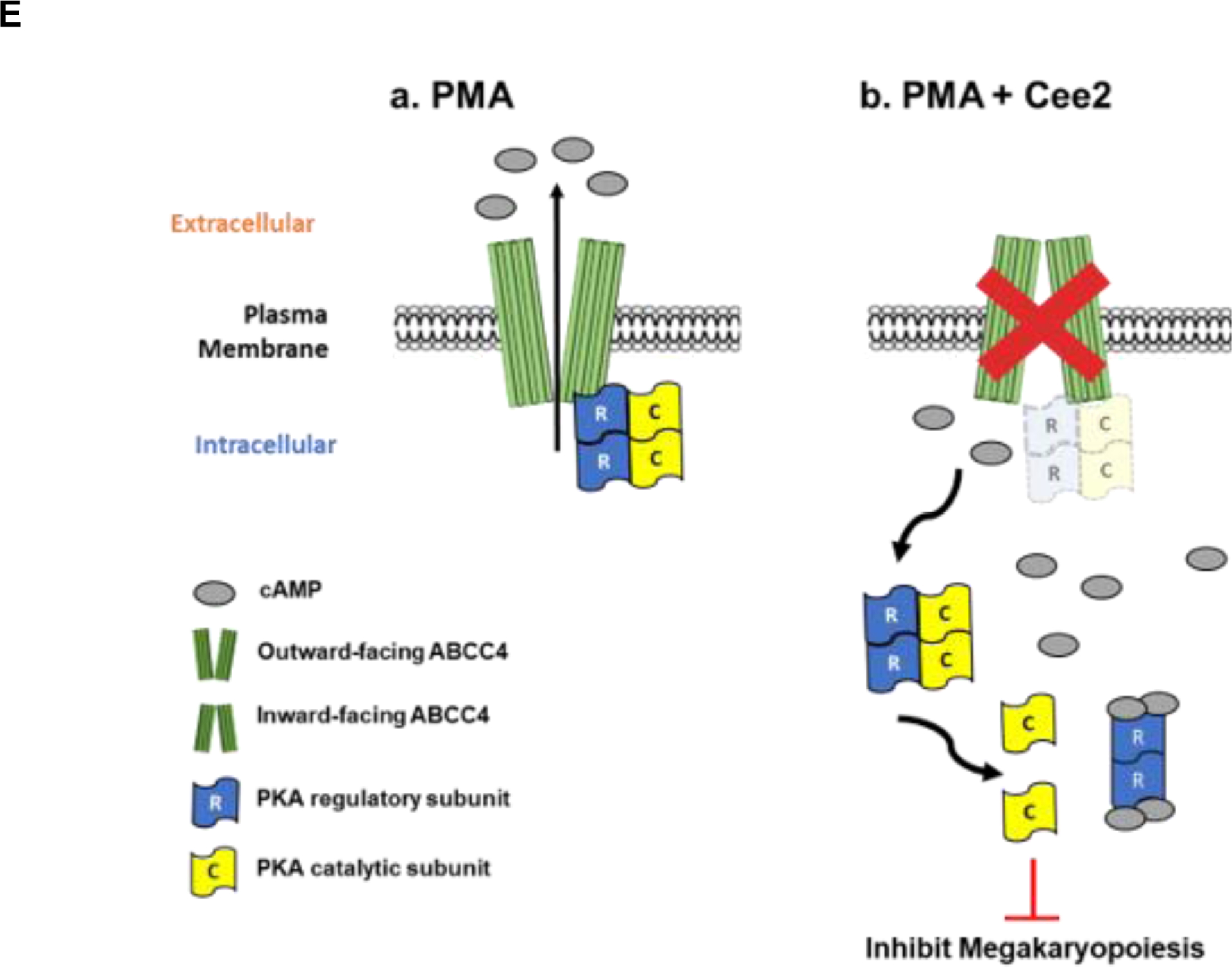
A. ABCC4 expression in MEG-01 cells treated with PMA (100 nM) with/without Ceefourin 2 (Cee2, 20 μM) for 2 days. Bars show mean (± SEM) of the densitometric quantification of ABCC4 expression from N=3 independent experiments (*p-value<0.05, one-way ANOVA). B. Bars show the mean (± SEM) intracellular and extracellular cAMP levels in differentiating cells treated with/without Cee2, after deduction of basal cAMP at untreated and Cee2-treated conditions (N=3 independent experiments, *p-value<0.05, Student’s t test). C. Co-immunoprecipitation was performed to examine PKA-C interaction with PKA-R or ABCC4 in differentiating MEG-01 cells in presence or absence of Cee2. Representative immunoblots show PKA-RII subunit and ABCC4 interacts with PKA-C under basal conditions and during PMA mediated differentiation. The interactions of PKA-RII or ABCC4 with PKA-C reduce after Cee2 treatment in differentiating cells. D. Bars show mean (± SD) ratios of co-immunoprecipitated (co-IP) PKA-RII: IP-ed PKA-C and ratio of co-IP ABCC4: IP-ed PKA-C, normalized to the ratio at PMA-treated conditions (N=2 independent experiments, *p-value<0.05, one-way ANOVA). E. Model showing the role of ABCC4 as a scaffold protein for PKA that controls its activity. (a) During PMA differentiation, ABCC4 scaffolds portions of PKA at the membrane, (b) ABCC4 inhibition in PMA-differentiated cells elevates the intracellular cAMP levels, that promote PKA release from ABCC4 and dissociation of PKA-C from PKA-R, which increases PKA activity and inhibits megakaryopoiesis.
cAMP binding to the PKA regulatory subunits (PKA-R) promotes PKA activity by enhancing the dissociation of its catalytic subunits (PKA-C).41 To determine if ABCC4 affects PKA signaling, we immunoprecipitated PKA-C and assessed the ratio of co-immunoprecipitated PKA-RII to the PKA-C. The ratio of PKA-RII: PKA-C was markedly lower in PMA and Cee2-treated cells compared to the PMA-treated cells (Fig 4 C, D), consistent with the increased intracellular cAMP binding that promoted dissociation of the catalytic subunit, PKA-C, from the PKA-R regulatory subunit after ABCC4 inhibition. This suggests greater abundance of free PKA-C after ABCC4 inhibition. Immunoprecipitation of PKA-C revealed an association between ABCC4 and PKA-C. This association between PKA-C and ABCC4 persisted with PMA differentiation but was strongly reduced after ABCC4 inhibition (Fig 4 C, D). We developed a model (Fig 4 E) which depicts that, in PMA-differentiated cells cAMP levels are low that allows ABCC4 to sequester portions of PKA at the plasma membrane. ABCC4 inhibition elevates cAMP to promote PKA-C dissociation from ABCC4 as well as PKA-R, to increase PKA activity. This suggests that ABCC4 serves as a PKA scaffold that appears to restrain PKA activity.
3.6. ABCC4 inhibition in differentiating MEG-01 cells impairs polyploidization
ABCC4 inhibition in PMA-differentiated MEG-01 cells significantly decreased polyploidy (Fig 5 A). The polyploidy of N<4 was unaffected by ABCC4 inhibition (data not shown). One pathway PMA induces polyploidization in MKs is through PKC activation of MEK/ERK signaling.42 ABCC4 inhibition increases PKA activity, which might affect PMA-induced polyploidization by interfering with either PKC or its downstream effectors, MEK/ERK. Treatment of Alisertib, an Aurora A kinase inhibitor, induces polyploidization in MEG-01 cells.43 ABCC4 inhibition did not affect Alisertib-induced polyploidization indicating ABCC4’s role in MK differentiation is independent of Aurora Kinase A signaling (Fig 5 B, C).
Figure 5. ABCC4 inhibition impairs polyploidization and causes morphological changes in differentiating MEG-01 cells, possibly through reduced expression of GATA1 target genes.
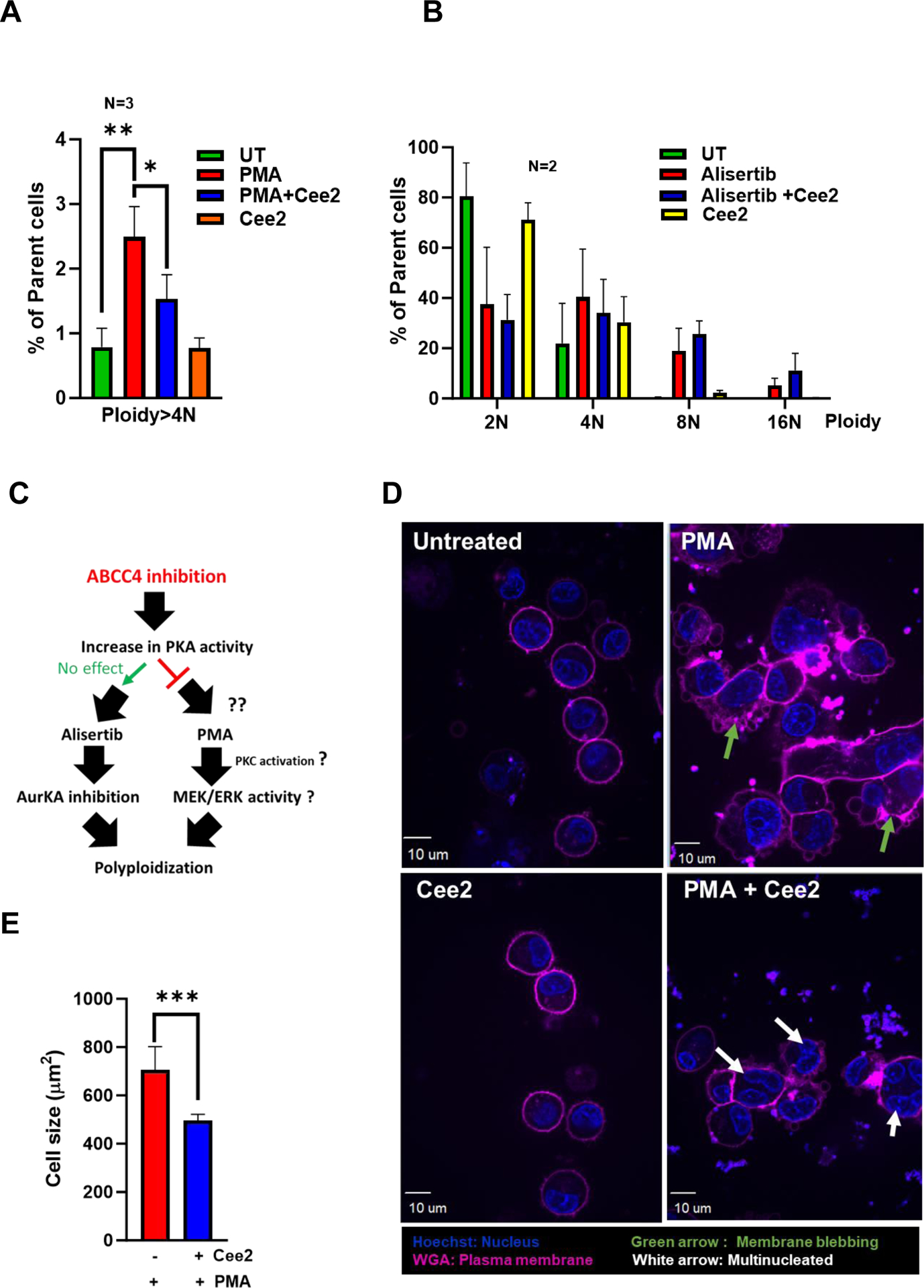
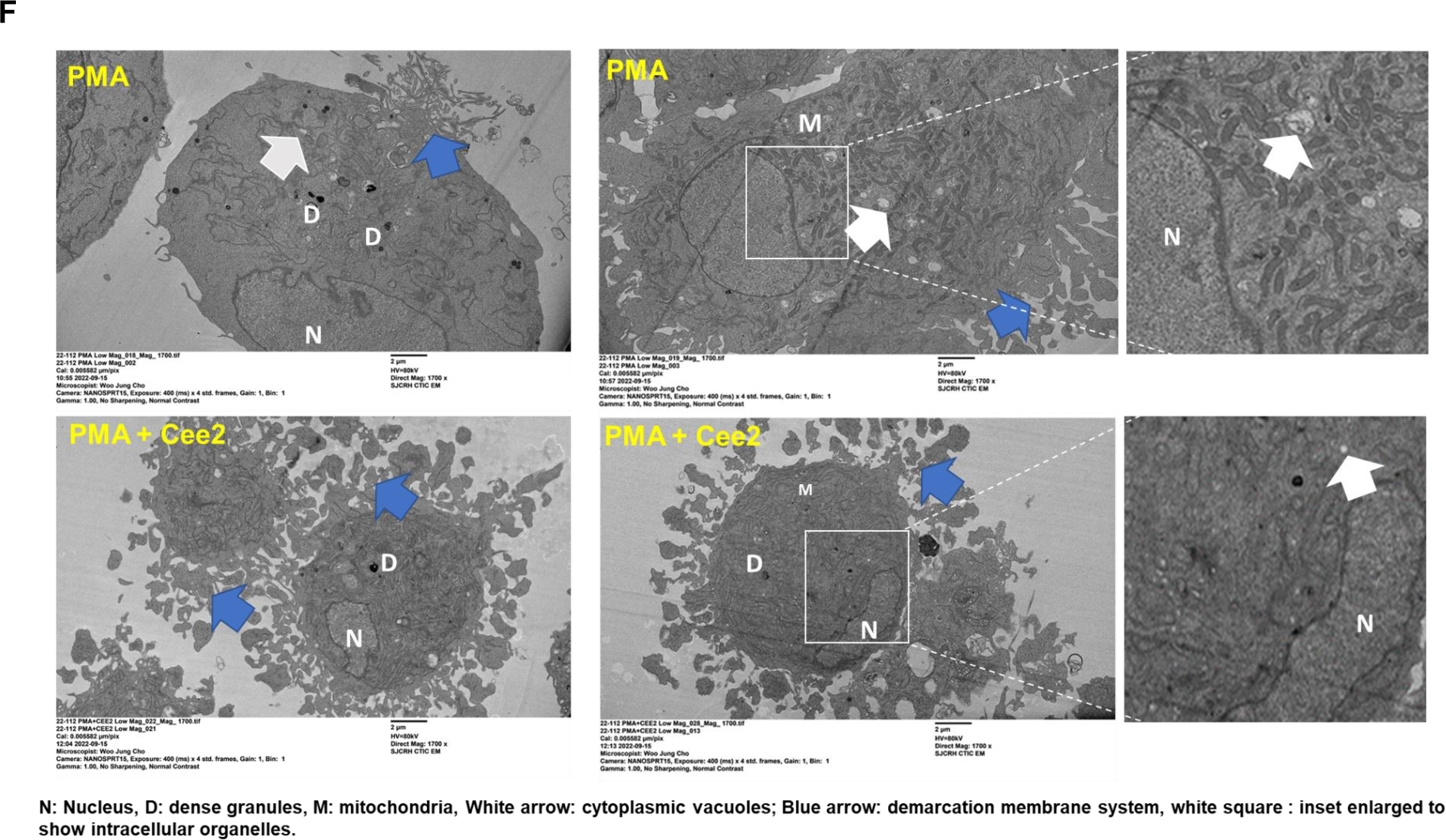
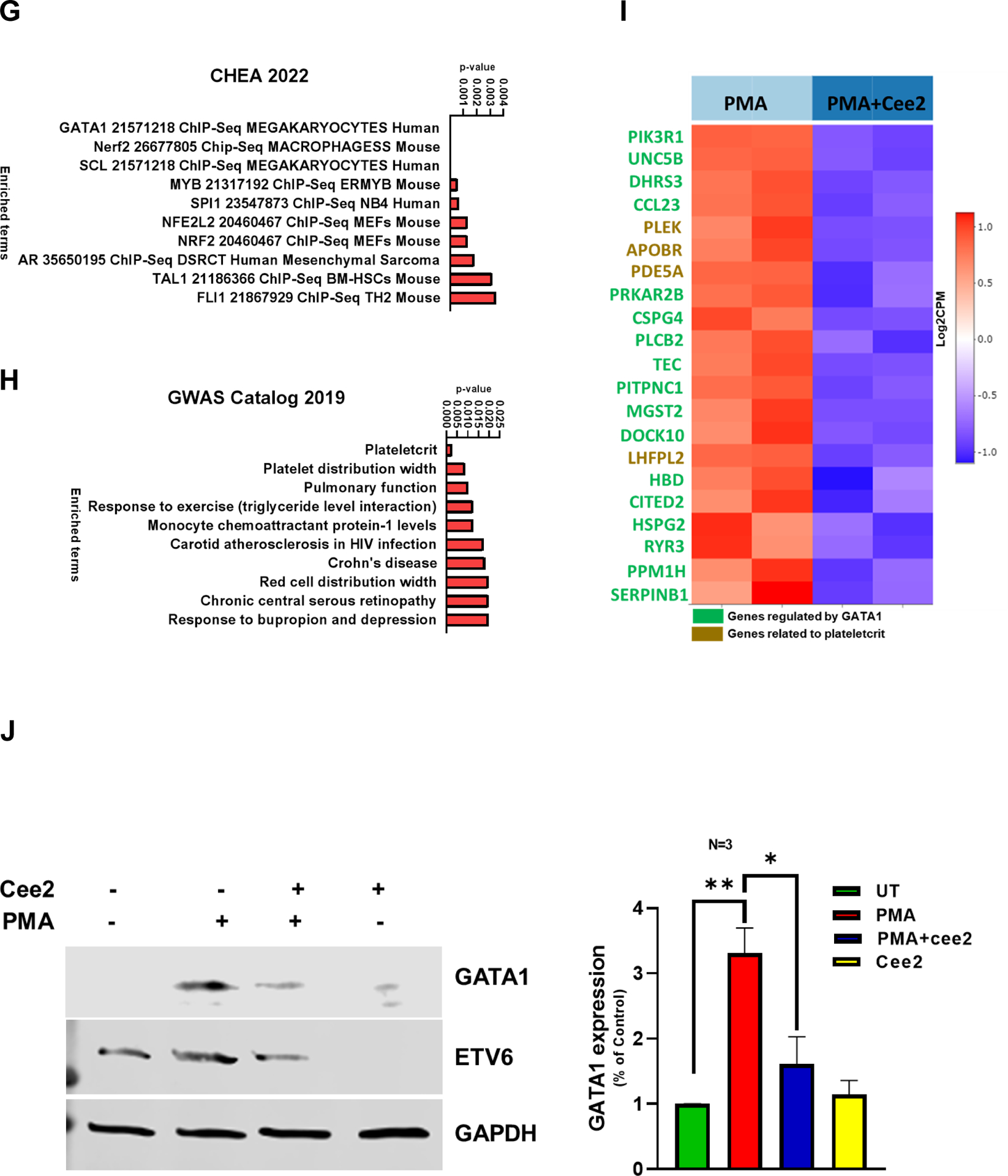
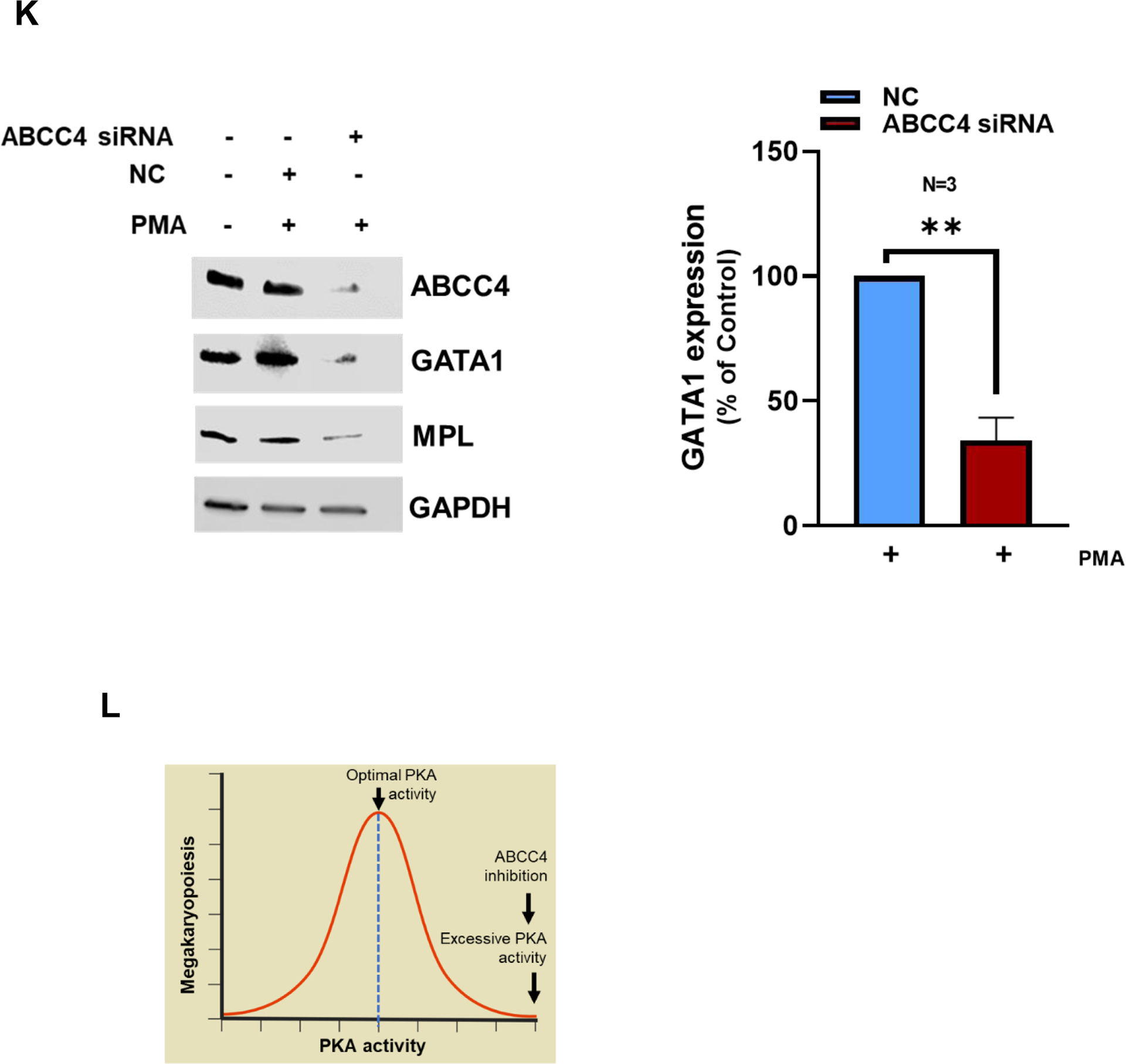
A. Ploidy analysis of PMA differentiated MEG-01 cells treated with/without Cee2 (20μM) for 2 days was assessed by flow cytometric measurement of propidium iodide intensity. ABCC4 inhibition in differentiated cells shows significant reduction in ploidy at >4N level. Bar represents mean (± SEM), N=3 independent experiments, *p-value<0.05, **p-value<0.01, one-way ANOVA. B. Ploidy of MEG-01 cells treated with Alisertib (1μM) with/without Cee2 (20μM). Inhibition of ABCC4 did not affect the Alisertib induced polyploidization (at 2N-16N level). Bar represents mean (± SEM), N=2 independent experiments. C. Model showing that ABCC4 inhibition causes polyploidization defect in PMA-differentiated cells independent of Aurora Kinase signaling. ABCC4 inhibition increases PKA activity which might block either PKC or its downstream effectors, possibly MEK/ERK activity which regulate PMA-induced polyploidization. D. Representative confocal image (63X objective, scale bar, 10 μm) showing untreated, PMA-treated, Cee2-treated and PMA+Cee2-treated MEG-01 cells. PMA-treated cells are larger and have greater cytoplasmic: nuclear ratio, and numerous membrane blebbing (green arrow) than the PMA+Cee2-treated cells. PMA-treated cells have single large lobulated nucleus, whereas PMA+Cee2-treated cells have multiple small nuclei (white arrow). Wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) and Hoechst 33342 dyes were used to stain the plasma membrane and the nucleus respectively. E. Bars show mean (± SEM) size of cells treated with PMA with/without Cee2, *** p-value <0.001, Student’s t test). F. Representative transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images of PMA-differentiated MEG-01 cells with or without ABCC4 inhibition. PMA treated cells are bigger in size with highly developed cytoplasm, vacuoles (white arrow) and demarcation membrane system (blue arrow), bigger nucleus (N), larger number of dense granules (D), mitochondria (M) and form longer and thicker proplatelets than the PMA+Cee2-treated cells (1700X objective, scale bar, 2 μm). G-H. RNA-seq analysis of PMA-differentiated cells with/without ABCC4 inhibition was performed (N=2 independent experiments). Pathway analysis of the top 50 upregulated differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in PMA treated cells, showed that GATA1 target genes (using CHEA 2022 and Enrichr) and plateletcrit genes (using Catalog 2019 analysis using Enrichr) were significantly downregulated in PMA-differentiated cells after ABCC4 inhibition. I. Heatmap showing GATA1 target genes (green) and genes related to plateletcrit (brown) were significantly downregulated after ABCC4 inhibition. A p-value<0.05, FDR<0.05, and/or absolute log2(FC) >1 was used to define DEGs. The top DEGs were defined by the cutoff of FDR<0.05 and ranked by log2(FC) in descending order. J. Representative immunoblots showing expression of GATA1 and its target, ETV6 after ABCC4 inhibition. Bars show mean (± SEM) from N=3 independent experiments, *p-value<0.05, , **p-value<0.01, one-way ANOVA. K. MEG-01 cells were transfected with 25 nM of negative control (NC) and ABCC4 siRNA for 24 hours before differentiating with PMA (100 nM). Representative immunoblots from N=3 independent experiments, showing expression of GATA1 and its target MPL after ABCC4 siRNA knockdown in differentiating MEG-01 cells. Bars show mean (± SEM) from N=3 independent experiments, **p-value<0.01, Student’s t test. L. Model showing that balanced PKA activity is important for optimal megakaryopoiesis. Megakaryopoiesis is inhibited by either very low or very high PKA activity. Inhibition of ABCC4 causes elevated cAMP/PKA signaling that inhibits megakaryopoiesis.
3.7. ABCC4 inhibition in differentiating MEG-01 cells is associated with morphological changes during MEG-01 differentiation
Reduction in size is a hallmark of impaired megakaryoblast differentiation.44,45 ABCC4 inhibition with Cee2 significantly reduced the size of the PMA-treated MEG-01 cells by 1.4-fold (Fig 5 D, E). ABCC4 inhibited cells displayed smaller and less lobulated nuclei compared to PMA-treated cells (Fig 5 D), consistent with defective polyploidization. These cells also exhibited less membrane blebbing, and limited demarcation membrane formation. We used transmission electron microscopy to further assess the ultrastructural morphology. PMA and Cee2-treated cells were smaller in size with smaller nuclei and had a reduced cytoplasmic to nuclear ratio compared to the PMA-treated cells (Fig 5 F). Defective endomitosis and cytoplasmic maturation likely account for this. Further, the vacuolar network in the cytoplasm was less prominent with a poorly formed demarcation membrane system (DMS) within the cytoplasm. Moreover, mitochondria and dense granules were fewer which signifies reduced cellular energy production and protein synthesis. These morphological and organelle changes indicate that ABCC4 inhibition impairs the cytoplasmic maturation of differentiating MKs.
3.8. Acute ABCC4 inhibition alters expression of GATA1 target genes and genes related to platelet number
The morphological differences produced by acute ABCC4 inhibition during MEG-01 differentiation led us to hypothesize that ABCC4 inhibition might be related to underlying alterations in the gene expression program required for optimal MEG-01 differentiation. RNA-seq analysis of MEG-01 cells treated with either PMA or PMA and Cee2 showed that genes related to megakaryopoiesis were significantly upregulated after PMA treatment in MEG-01 cells (Suppl Fig 7, Suppl Table 2 A). Pathway analysis of the top 50 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in PMA-treated compared to PMA and Cee2-treated cells (using Enrichr and CHEA 2022 database), suggested that GATA1 target genes were significantly downregulated after ABCC4 inhibition (Fig 5 G, Suppl Table 2 B). GATA1 target genes were identified using the human megakaryocyte GATA1 21571218 Chip-Seq dataset.46 In addition, Genes related to the platelet formation (plateletcrit : a measure of total platelet mass) were also significantly downregulated after ABCC4 inhibition (using Enrichr and GWAS catalog 2019, Fig 5 H, Suppl Table 2 C). Genes related to polyploidization namely, PLEK, MK maturation, FYB1 and proplatelet maturation, PPBP were also significantly downregulated in PMA and Cee2-treated cells compared to PMA-treated cells (Suppl Table 2 B, D). When intracellular cAMP levels are highly elevated, cells undergo a negative feedback mechanism to maintain the cAMP homeostasis, for instance, by increasing the phosphodiesterases47. The expression of the majority of phosphodiesterases were either downregulated or did not change after ABCC4 inhibition (Suppl Table 2 E).
3.9. ABCC4 knockdown or inhibition in differentiated MEG-01 cells reduced GATA1 expression
To investigate if the reduced expression of GATA1 target genes after ABCC4 inhibition was related to GATA1 expression, we determined GATA1 protein expression. GATA1 protein expression increased after PMA-induced differentiation in MEG-01 cells. ABCC4 inhibition in these cells drastically reduced protein expression of GATA1 and its known target ETS variant transcription factor 6 (ETV6) (Fig 5 J). siRNA knockdown of ABCC4 in MEG-01 cells reduced GATA1 protein expression (Fig 5 K). Expression of Myeloproliferative Leukemia Virus Oncogene (MPL) Protein, a known GATA1 target, was also reduced after siRNA knockdown of ABCC4. These results suggest that either ABCC4 absence or loss of function reduces GATA-1 expression in differentiating MEG-01 cells which is consistent with the reduction in GATA-1 target gene expression in these cells, after ABCC4 inhibition. However, siRNA knockdown of ABCC4 did not affect GATA1 mRNA expression (Suppl Fig 8). Treatment with 8Br-cAMP, a synthetic cAMP analog, also reduced GATA-1 expression (Suppl Fig 9). These results suggest that a balance of cAMP/PKA signaling is important for optimal megakaryopoiesis, which is displayed in a model in Fig 5 L.
4. Discussion
To our knowledge, the contribution of ABCC4 to the process of platelet production from megakaryocytes was unknown prior to these studies. A GWAS study had hinted at a role for ABCC4, but it was among 69 genomic loci that reportedly contributed to regulation of platelet number, but not megakaryopoiesis.15 Our finding that ABCC4 was highly expressed in MKs and the genomic data showing that important megakaryocytic transcription factors interacted with regulatory regions in ABCC4 provided the impetus for our studies. We demonstrated that optimal MK differentiation in vitro requires ABCC4. Our data also show that high ABCC4 expression in MKs protects them against the cytotoxicity induced by chemotherapeutics which are ABCC4 substrates, like 6-MP metabolites.
Previously, we demonstrated that myeloid cells derived from WT mice were more resistant to 6-MP toxicity than those from Abcc4−/− mice because Abcc4 prevented the accumulation of cytotoxic 6-MP nucleotide metabolites, 6-TGNs.22 In the current study, we found that ABCC4 conferred resistance to 6-MP toxicity in MKs but not MKPs. ABCC4 expression is higher in MKs than MKPs, which likely contributes to their resistance to 6-MP toxicity. Further the kinetics of reduction in platelets in 6-MP treated Abcc4−/− mice allowed us to infer that the 6MP reduction in platelets was due to an impairment in platelet production. Platelets were unaffected by 6-MP’s cytotoxic effect which is consistent with its absence of a nucleus. The high expression of ABCC4 in MKs suggested it might protect MKs from 6-MP cytotoxicity which is unlikely in the progenitors for granulocytes, lymphocytes and erythrocytes which have low ABCC4 expression. The effect of ABCC4 on the MK lineage suggests the possibility that other chemotherapeutic drugs that are cytotoxic and ABCC4 substrates, might induce thrombocytopenia especially in patients with impaired ABCC4 function. It is notable that many ABCC4 substrates in the adverse drug event database that display a risk of thrombocytopenia are ABCC4 substrates (Suppl Table 5). Chou et al. showed that the ABC transporter expression in some hematopoietic lineages determines the capability of these cells to be protected from some chemotherapy.48 They showed that the neutropenia in patients taking Aurora Kinase inhibitors was related to developmental patterns of ABC transporter expression neutrophil differentiation.
ABCC4 contributes to megakaryopoiesis as MKs derived from Abcc4−/− mice fetal liver cells exhibit defective polyploidization and proplatelet formation, key processes in MK differentiation and platelet formation. However, the in vivo delay in platelet formation in Abcc4−/− mice was puzzling because it was less profound than the strong in vitro differentiation defect exhibited in MKs from Abcc4−/− mice. This suggested that compensation occurred in vivo in Abcc4−/− mice. This proposition was then supported by two findings: 1) unchallenged Abcc4−/− have normal platelet counts and 2) Abcc4−/− mice challenged toward megakaryopoiesis by 5-FU treatment exhibited only a minor delay in maximal megakaryopoiesis. An analysis of MKs gene expression from Abcc4−/− mice supports the idea of compensation for Abcc4’s absence because of the enrichment in expression of genes like, Nfe249, Cd950, Bcl2l151 and Il21r52 in Abcc4−/− MKs. In aggregate these findings support the proposition that in MKs from Abcc4−/− mice compensate for ABCC4 absence by upregulating expression of genes with key roles in megakaryopoiesis. Furthermore, our studies with human megakaryoblastic cell line MEG-01, showed that simple acute ABCC4 inhibition with Ceefourin 2, a specific ABCC4 inhibitor40, impaired processes related to platelet formation (i.e., polyploidization and cytoplasmic maturation).
Acute inhibition of ABCC4 using Ceefourin 2 promoted elevation of intracellular cAMP as well as the PKA-C subunit dissociation from ABCC4 in PMA-differentiated MEG-01 cells, suggesting that ABCC4 modulates megakaryopoiesis by regulating PKA activity. The role of ABCC4 in effluxing its substrate cAMP is well known.10,12 Our study covered an novel interaction between ABCC4 and PKA-C, which likely means that ABCC4 facilitates PKA compartmentalization by sequestering it at the membrane. Here, ABCC4 seems to act as a scaffold analogous to A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs) which contribute to compartmentalization of PKA activity.52 Elevation of cAMP level due to ABCC4 inhibition further stimulates PKA activity within the compartment (Fig 4 E).
PKA activity needs restraint to promote optimal megakaryopoiesis as excessive PKA activity impairs it (Fig 5 L). Studies have shown that excessive PKA activity can repress the E2A-CDKN1A transcriptional axis in megakaryopoiesis.6 In addition, the drug that combats formation of too many platelets (thrombocytosis), Anagrelide, elevates cAMP to hyperactivate PKA activity which impair proplatelet formation.53 In accord with these findings, our results showed that excessive PKA activity due to ABCC4 absence or inhibition negatively impacted megakaryopoiesis. ABCC4 inhibition reduced protein levels of GATA1 and its target, MPL, because GATA1 is a major TF regulating megakaryopoiesis54. Furthermore, downregulation of GATA1 regulated genes, after ABCC4 inhibition, is consistent with the phenotypic defects in polyploidization and cytoplasmic maturation we observed. Moreover, 8-Br cAMP, a synthetic analog of cAMP known to activate PKA signaling55, reduced GATA1 protein, but not mRNA suggesting a post-translational effect. This result is also consistent with a previous report by Zhang et. al.56 that showed elevated cAMP significantly reduced GATA1 expression.
ABCC4 inhibition compromised polyploidization during MEG-01 differentiation possibly through PKA induced reduction of GATA1 expression. Polyploidization in PMA-differentiation of MKs is also regulated by MEK/ERK signaling through PKC activation. We did not know if excessive PKA activity due to ABCC4 inhibition impacted PKC-MEK/ERK signaling arm of MK differentiation. Inhibition of Aurora A Kinase by Alisertib induces megakaryopoiesis.57 We showed that ABCC4 inhibition did not affect the polyploidization induced by Alisertib in MEG-01 cells which suggests that the effect of ABCC4 inhibition on megakaryopoiesis in MEG-01 is independent of Aurora A kinase. Further investigation may be needed to provide a more detailed relationship between these processes.
Our studies highlight a dual role for ABCC4 as both a protector of MK and as a regulator of megakaryopoiesis. The regulation of PKA activity by ABCC4 is novel and likely contributes to PKA compartmentalization. Loss of either ABCC4 or its function caused excessive accumulation of cAMP and inhibited megakaryopoiesis. This study has clinical relevance as patients with reduced ABCC4 function (or absence of functional ABCC4, like in the recently described PEL blood group)13 might be more susceptible to drug induced thrombocytopenia. We have previously demonstrated that patients, especially those of Asian descent, have a single-nucleotide polymorphism in human ABCC4 (rs3765534), which results in reduced ABCC4 function due to impaired localization in the plasma membrane.22 These patients may have a greater likelihood of severe 6-MP induced thrombocytopenia than those patients with normal ABCC4 function. This underscored the need to identify ABCC4 genetic variants before administrating chemotherapeutics that are ABCC4 substrates which can cause thrombocytopenia. For instance, dasatinib, a chemotherapeutic used for chronic myelogenous leukemia, is also an ABCC4 substrate58 which affects megakaryopoiesis, but also inhibits platelet formation.59 Caution might need to be taken while concurrently administrating chemotherapeutics that are ABCC4 substrates (e.g., 6-MP) and drugs that inhibit ABCC4 function (e.g., nelfinavir, ibuprofen)60 as it might exacerbate the chemotherapeutic drug induced thrombocytopenia.
Supplementary Material
Key Points.
The ABC transporter, ABCC4, protects megakaryocytes against 6-Mercaptopurine toxicity.
ABCC4 impacts megakaryopoiesis by regulating intracellular cAMP level and PKA activity.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Animal Resources Center, Cell and Tissue Imaging Center, Hartwell Center Genome Sequencing Facility, Center for Applied Bioinformatics and Flow Cytometry & Cell Sorting Shared Resources, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, for the assistance with animal studies, confocal and transmission electron microscopy, RNA sequencing, bioinformatic analysis and flow cytometry respectively. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants R01 CA194057, CA194206, P30 CA21745, CA21865, 5R01DK080834, NCI P30 CA021765, CA96832, and by ALSAC.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest Disclosures
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Data Sharing
RNA-seq data from WT and Abcc4−/− mice and MEG-01 cells are available at GEO under GSE234629 (reviewer’s token is adwlowumthszxgn).
References
- 1.Mazzi S, Lordier L, Debili N, Raslova H, Vainchenker W. Megakaryocyte and polyploidization. Exp Hematol. 2018;57:1–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Michelson AD, Cattaneo M, Frelinger A, Newman P. Platelets. Academic press; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tomer A, Friese P, Conklin R, et al. Flow cytometric analysis of megakaryocytes from patients with abnormal platelet counts. Blood. 1989;74(2):594–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Heazlewood SY, Ahmad T, Cao B, et al. High ploidy large cytoplasmic megakaryocytes are hematopoietic stem cells regulators and essential for platelet production. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):2099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Machlus KR, Italiano JE Jr. The incredible journey: From megakaryocyte development to platelet formation. J Cell Biol. 2013;201(6):785–796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rubinstein JD, Elagib KE, Goldfarb AN. Cyclic AMP signaling inhibits megakaryocytic differentiation by targeting transcription factor 3 (E2A) cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A) transcriptional axis. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(23):19207–19215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Begonja AJ, Gambaryan S, Schulze H, et al. Differential roles of cAMP and cGMP in megakaryocyte maturation and platelet biogenesis. Exp Hematol. 2013;41(1):91–101 e104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Schuetz JD, Connelly MC, Sun D, et al. MRP4: A previously unidentified factor in resistance to nucleoside-based antiviral drugs. Nat Med. 1999;5(9):1048–1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen ZS, Lee K, Kruh GD. Transport of cyclic nucleotides and estradiol 17-beta-D-glucuronide by multidrug resistance protein 4. Resistance to 6-mercaptopurine and 6-thioguanine. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(36):33747–33754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.van Aubel R, Smeets PHE, Peters JGP, Bindels RJM, Russel FGM. The MRP4/ABCC4 gene encodes a novel apical organic anion transporter in human kidney proximal tubules: putative efflux pump for urinary cAMP and cGMP. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13(3):595–603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen Y, Wang L, Hou W-T, et al. Structural insights into human ABCC4-mediated transport of platelet agonist and antagonist. Nature Cardiovascular Research. 2023;2(7):693–701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cheepala SB, Pitre A, Fukuda Y, et al. The ABCC4 membrane transporter modulates platelet aggregation. Blood. 2015;126(20):2307–2319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Azouzi S, Mikdar M, Hermand P, et al. Lack of the multidrug transporter MRP4/ABCC4 defines the PEL-negative blood group and impairs platelet aggregation. Blood. 2020;135(6):441–448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guarino ML, Massimi I, Alemanno L, Conti L, Angiolillo DJ, Pulcinelli FM. MRP4 over-expression has a role on both reducing nitric oxide-dependent antiplatelet effect and enhancing ADP induced platelet activation. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021;51(3):625–632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gieger C, Radhakrishnan A, Cvejic A, et al. New gene functions in megakaryopoiesis and platelet formation. Nature. 2011;480(7376):201–208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang W, Buitrago L, Wang Y. ABC transporters in megakaryopoiesis and platelet activity. Thromb Res. 2017;156:126–133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Barlage S, Boettcher D, Boettcher A, Dada A, Schmitz G. High density lipoprotein modulates platelet function. Cytometry A. 2006;69(3):196–199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nofer JR, Herminghaus G, Brodde M, et al. Impaired platelet activation in familial high density lipoprotein deficiency (Tangier disease). J Biol Chem. 2004;279(32):34032–34037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Murphy AJ, Bijl N, Yvan-Charvet L, et al. Cholesterol efflux in megakaryocyte progenitors suppresses platelet production and thrombocytosis. Nat Med. 2013;19(5):586–594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schmitz G, Schambeck CM. Molecular defects in the ABCA1 pathway affect platelet function. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb. 2006;35(1–2):166–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jedlitschky G, Greinacher A, Kroemer HK. Transporters in human platelets: physiologic function and impact for pharmacotherapy. Blood. 2012;119(15):3394–3402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Krishnamurthy P, Schwab M, Takenaka K, et al. Transporter-mediated protection against thiopurine-induced hematopoietic toxicity. Cancer Res. 2008;68(13):4983–4989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tanaka Y, Manabe A, Fukushima H, et al. Multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4) polymorphisms impact the 6-mercaptopurine dose tolerance during maintenance therapy in Japanese childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenomics J. 2015;15(4):380–384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wijnholds J, Mol CA, van Deemter L, et al. Multidrug-resistance protein 5 is a multispecific organic anion transporter able to transport nucleotide analogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(13):7476–7481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pitre A, Ge Y, Lin W, et al. An unexpected protein interaction promotes drug resistance in leukemia. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Vijey P, Posorske B, Machlus KR. In vitro culture of murine megakaryocytes from fetal liver-derived hematopoietic stem cells. Platelets. 2018;29(6):583–588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ogura M, Morishima Y, Ohno R, et al. Establishment of a novel human megakaryoblastic leukemia cell line, MEG-01, with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1985;66(6):1384–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bagger FO, Kinalis S, Rapin N. BloodSpot: a database of healthy and malignant haematopoiesis updated with purified and single cell mRNA sequencing profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1):D881–D885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Fuhrken PG, Chen C, Miller WM, Papoutsakis ET. Comparative, genome-scale transcriptional analysis of CHRF-288–11 and primary human megakaryocytic cell cultures provides novel insights into lineage-specific differentiation. Exp Hematol. 2007;35(3):476–489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Corces MR, Buenrostro JD, Wu B, et al. Lineage-specific and single-cell chromatin accessibility charts human hematopoiesis and leukemia evolution. Nat Genet. 2016;48(10):1193–1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li Z, Godinho FJ, Klusmann JH, Garriga-Canut M, Yu C, Orkin SH. Developmental stage-selective effect of somatically mutated leukemogenic transcription factor GATA1. Nat Genet. 2005;37(6):613–619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Li Y, Yan Y, Liu F, Wang L, Feng F, Xiao Y. Effects of calpain inhibitor on the apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells induced by calcium ionophore A23187. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(2):1685–1693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhang H, Nimmer PM, Tahir SK, et al. Bcl-2 family proteins are essential for platelet survival. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(5):943–951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kimmerlin Q, Tavian M, Gachet C, Lanza F, Brouard N. Isolation of Mouse Megakaryocyte Progenitors. J Vis Exp. 2021(171). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Freson K, Peeters K, De Vos R, et al. PACAP and its receptor VPAC1 regulate megakaryocyte maturation: therapeutic implications. Blood. 2008;111(4):1885–1893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lane WJ, Hattori K, Dias S, et al. Anagrelide metabolite induces thrombocytopenia in mice by inhibiting megakaryocyte maturation without inducing platelet aggregation. Exp Hematol. 2001;29(12):1417–1424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Vittet D, Duperray C, Chevillard C. Cyclic-AMP inhibits cell growth and negatively interacts with platelet membrane glycoprotein expression on the Dami human megakaryoblastic cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1995;163(3):645–655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lordier L, Jalil A, Aurade F, et al. Megakaryocyte endomitosis is a failure of late cytokinesis related to defects in the contractile ring and Rho/Rock signaling. Blood. 2008;112(8):3164–3174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schoedel KB, Morcos MNF, Zerjatke T, et al. The bulk of the hematopoietic stem cell population is dispensable for murine steady-state and stress hematopoiesis. Blood. 2016;128(19):2285–2296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cheung L, Flemming CL, Watt F, et al. High-throughput screening identifies Ceefourin 1 and Ceefourin 2 as highly selective inhibitors of multidrug resistance protein 4 (MRP4). Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;91(1):97–108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jackson PK. cAMP Signaling in Nanodomains. Cell. 2020;182(6):1379–1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Herrera R, Hubbell S, Decker S, Petruzzelli L. A role for the MEK/MAPK pathway in PMA-induced cell cycle arrest: modulation of megakaryocytic differentiation of K562 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1998;238(2):407–414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wen Q, Goldenson B, Silver SJ, et al. Identification of regulators of polyploidization presents therapeutic targets for treatment of AMKL. Cell. 2012;150(3):575–589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Noetzli LJ, French SL, Machlus KR. New Insights Into the Differentiation of Megakaryocytes From Hematopoietic Progenitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(7):1288–1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Su CH, Liao WJ, Ke WC, Yang RB, Tarn WY. The Y14-p53 regulatory circuit in megakaryocyte differentiation and thrombocytopenia. iScience. 2021;24(11):103368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tijssen MR, Cvejic A, Joshi A, et al. Genome-wide analysis of simultaneous GATA1/2, RUNX1, FLI1, and SCL binding in megakaryocytes identifies hematopoietic regulators. Dev Cell. 2011;20(5):597–609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rochais F, Vandecasteele G, Lefebvre F, et al. Negative feedback exerted by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and cAMP phosphodiesterase on subsarcolemmal cAMP signals in intact cardiac myocytes: an in vivo study using adenovirus-mediated expression of CNG channels. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(50):52095–52105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chou DB, Furlong BA, Posey RR, et al. Differential ABC transporter expression during hematopoiesis contributes to neutrophil-biased toxicity of Aurora kinase inhibitors. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):6021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lecine P, Villeval JL, Vyas P, Swencki B, Xu Y, Shivdasani RA. Mice lacking transcription factor NF-E2 provide in vivo validation of the proplatelet model of thrombocytopoiesis and show a platelet production defect that is intrinsic to megakaryocytes. Blood. 1998;92(5):1608–1616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Nakamura-Ishizu A, Matsumura T, Stumpf PS, et al. Thrombopoietin Metabolically Primes Hematopoietic Stem Cells to Megakaryocyte-Lineage Differentiation. Cell Rep. 2018;25(7):1772–1785 e1776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kozuma Y, Kojima H, Yuki S, Suzuki H, Nagasawa T. Continuous expression of Bcl-xL protein during megakaryopoiesis is post-translationally regulated by thrombopoietin-mediated Akt activation, which prevents the cleavage of Bcl-xL. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(6):1274–1282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Benbarche S, Strassel C, Angenieux C, et al. Dual role of IL-21 in megakaryopoiesis and platelet homeostasis. Haematologica. 2017;102(4):637–646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Miyashita N, Onozawa M, Yokoyama S, et al. Anagrelide Modulates Proplatelet Formation Resulting in Decreased Number and Increased Size of Platelets. Hemasphere. 2019;3(4):e268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Shivdasani RA, Fujiwara Y, McDevitt MA, Orkin SH. A lineage-selective knockout establishes the critical role of transcription factor GATA-1 in megakaryocyte growth and platelet development. EMBO J. 1997;16(13):3965–3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Branski P, Palucha A, Szewczyk B, Wieronska JM, Pilc A, Nowak G. Antidepressant-like activity of 8-Br-cAMP, a PKA activator, in the forced swim test. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2008;115(6):829–830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zhang Z, Wu AZ, Feng ZM, Mruk D, Cheng CY, Chen CL. Gonadotropins, via cAMP, negatively regulate GATA-1 gene expression in testicular cells. Endocrinology. 2002;143(3):829–836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ding YH, Zhou ZW, Ha CF, et al. Alisertib, an Aurora kinase A inhibitor, induces apoptosis and autophagy but inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015;9:425–464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Furmanski BD, Hu S, Fujita KI, et al. Contribution of ABCC4-mediated gastric transport to the absorption and efficacy of dasatinib. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(16):4359–4370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Mazharian A, Ghevaert C, Zhang L, Massberg S, Watson SP. Dasatinib enhances megakaryocyte differentiation but inhibits platelet formation. Blood. 2011;117(19):5198–5206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Fukuda Y, Takenaka K, Sparreboom A, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors interact with ATP binding cassette transporter 4/multidrug resistance protein 4: a basis for unanticipated enhanced cytotoxicity. Mol Pharmacol. 2013;84(3):361–371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Luo Y, Hitz BC, Gabdank I, et al. New developments on the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) data portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(D1):D882–D889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Hansen KD, Irizarry RA, Wu Z. Removing technical variability in RNA-seq data using conditional quantile normalization. Biostatistics. 2012;13(2):204–216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Mifsud B, Tavares-Cadete F, Young AN, et al. Mapping long-range promoter contacts in human cells with high-resolution capture Hi-C. Nat Genet. 2015;47(6):598–606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
RNA-seq data from WT and Abcc4−/− mice and MEG-01 cells are available at GEO under GSE234629 (reviewer’s token is adwlowumthszxgn).


