Fig. 4 |. Conformational changes in membrane-bound S-OPA1 result in the dissociation of the membrane-embedded fusion loop from the outer leaflet.
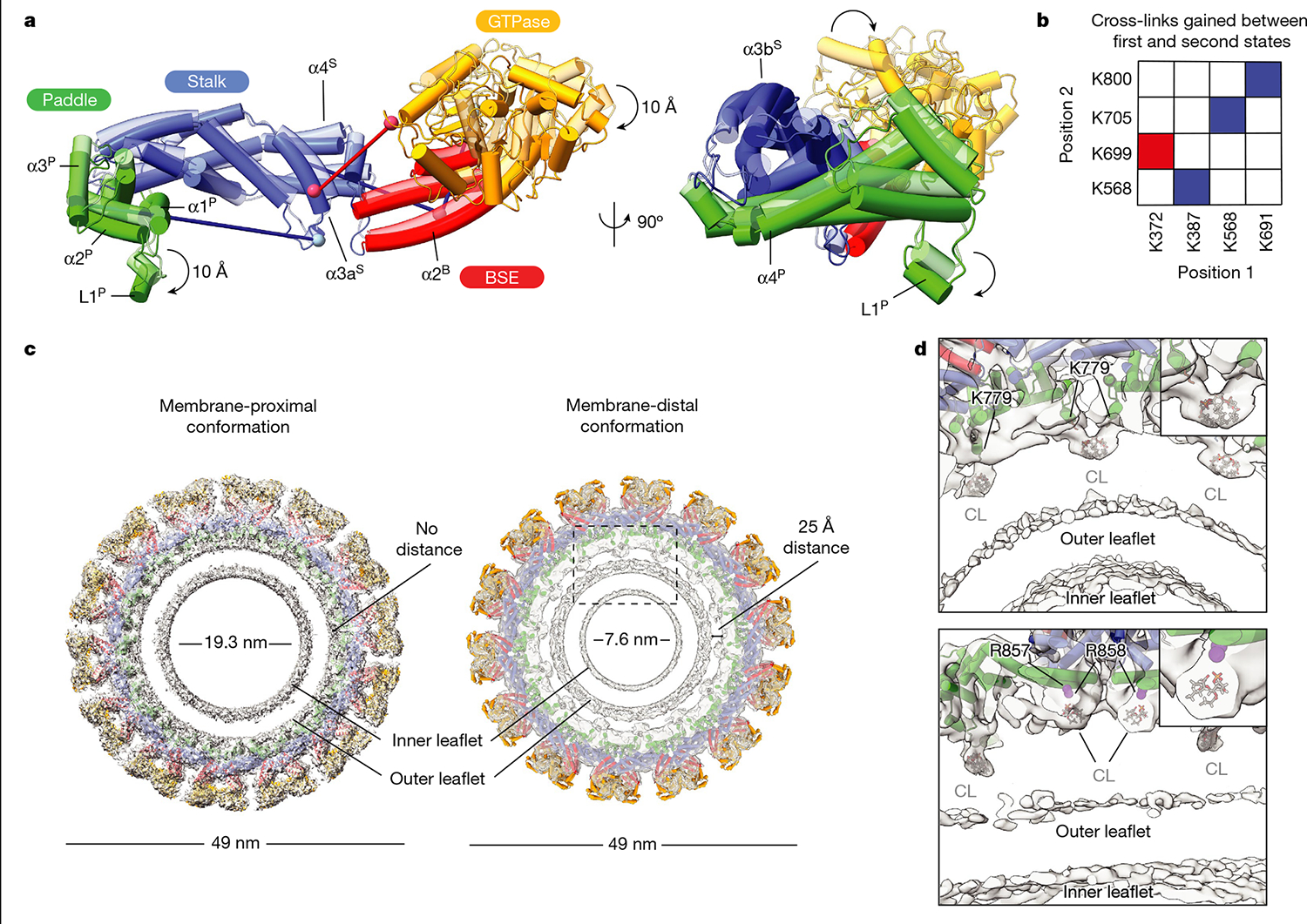
a, A comparison of membrane-proximal (transparent) and membrane-distal conformations (opaque) of S-OPA1 shows an approximately 20 Å shift in the GTPase domain towards a neighbouring GTPase domain density and an approximately 10 Å rotation of the PD L1P MIL towards the membrane. Additional conformational changes are also apparent for BSE and stalk domains. b, Cross-links that are only satisfied in membrane-proximal (blue) and membrane-distal (red) conformations of membrane-bound S-OPA1. Identified cross-link pairs are mapped on the S-OPA1 subunits and described as positions 1 and 2. c, Structural comparison of the membrane-proximal and membrane-distal conformations of the S-OPA1 polymer. The cryo-EM structures have the models placed in the density. In membrane-distal conformation, the PD is moved away from the outer leaflet creating a gap of about 25 Å between the membrane-facing surface of the PD and the lipid bilayer. The area indicated by a box is a magnified in d. d, Magnified views of the PD–membrane interface in membrane-distal conformation. The top view of the central slices indicates the positions of lipid-binding sites. Bound lipids at the protein–membrane contact sites are identified as CL, and the acyl tails are truncated according to the map density. CL molecules flanking PDs are shown in grey. The PD residues associated with lipids include two arginine residues (Arg857, Arg858) and one lysine residue (Lys779) and are numbered accordingly.
