Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its more severe form, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), can promote the development of cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes. Similarly, type 2 diabetes confers the greatest risk for the development of NASH, especially when associated with obesity. Although lifestyle changes are critical to success, early implementation of pharmacological treatments for obesity and type 2 diabetes are essential to treat NASH and avoid disease progression. This article reviews current guidance regarding the use of pharmacological agents such as pioglitazone, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists, and sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in the setting of NAFLD and NASH. It also reviews the latest information on new drugs currently being investigated for the treatment of NASH.
A healthy lifestyle is the cornerstone of management for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), as reviewed elsewhere in this article collection (1) and in recent guidelines on optimal lifestyle strategies for people with NAFLD (2–5). However, lifestyle changes frequently are insufficient to reach the weight loss threshold needed to significantly reverse nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and avoid cirrhosis. Weight regain is also fairly common (6). Given that obesity and type 2 diabetes are so often associated with NASH and both worsen disease progression and outcomes (7,8), treatments for NASH must include careful management of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
The prevalence of NAFLD is rapidly increasing, with the highest prevalence in people who have both type 2 diabetes and obesity (7,9). Type 2 diabetes is associated with NAFLD and poses the highest risk for its progression to NASH with advanced hepatic fibrosis. The severity of fibrosis is the most significant predictor of adverse liver outcomes (10). In the United States, the prevalence in people with type 2 diabetes of clinically significant fibrosis (defined on liver histology as having moderate or more severe fibrosis [stage ≥F2]), is estimated to be ∼15–25% (11–14). This estimate is consistent with prevalence rates reported in European (15–17) and worldwide (9). Furthermore, patients with NAFLD have a two- to threefold increased risk of progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes (18,19).
For these reasons, it is important that clinicians following patients at high risk for NAFLD become aware of the problem and implement early screening and management strategies (20). Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent or delay liver disease progression, optimize management of early cirrhosis when present, and reduce the risk of developing diabetes or cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Obesity, NAFLD, and type 2 diabetes share underlying altered pathophysiological mechanisms, including insulin resistance (8), so it is not unexpected that some treatments for type 2 diabetes (e.g., pioglitazone and glucagon-like peptide 1 [GLP-1] receptor agonists) have demonstrated benefits in NASH (21). Treatment should follow a dual goal of treating hyperglycemia and obesity, as well as targeting liver disease in individuals with NASH, as recommended in current guidelines (2–5). Treatments that offer cardiovascular protection also should be considered, given that CVD is the leading cause of mortality of patients with NAFLD (22).
To summarize, the reasons to recommend pharmacological treatment for NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes include the following:
Patients with type 2 diabetes, in particular when obesity is present, have a high prevalence of significant liver fibrosis and thus a higher risk of developing cirrhosis and even hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Type 2 diabetes is likely to accelerate steatohepatitis progression to cirrhosis.
Some treatments for type 2 diabetes (e.g., pioglitazone and GLP-1 receptor agonists) are effective to treat NASH and may reduce cardiovascular risk.
Early intervention and treatment may prevent cirrhosis (23).
Increased awareness about these risks should encourage physicians and all caregivers to educate patients about healthy lifestyle modifications and to prescribe pharmacological treatment with established benefits for NASH as needed.
This article reviews pharmacological approaches to type 2 diabetes and obesity for people who have NAFLD or NASH and provides a brief description of agents currently in phase 3 development for the treatment of NASH itself.
Pharmacological Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes With Benefits in NAFLD
Among the many pharmacological treatments for type 2 diabetes, agents from two drug classes have been demonstrated to improve NASH: the thiazolidinedione (TZD) pioglitazone and the GLP-1 receptor agonists (Table 1). Metformin has not been shown to improve steatohepatitis in controlled, paired biopsy studies (8,21). Other drug classes such as sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and insulin may improve hepatic steatosis, but at present lack evidence of promoting histological improvement of steatohepatitis or fibrosis. The sections below summarize the most recent evidence on the safety and efficacy of available glucose-lowering drugs for the treatment of NAFLD. The effects of these drugs in NAFLD are shown in Figure 1.
Table 1.
Summary: Effects in RCTs of Pharmacological Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes in Patients With NAFLD
| Drug/Drug Class | Steatosis | Steatohepatitis | Fibrosis | Cardiovascular Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioglitazone | Improves | Improves | Reduces progression | Benefit |
| GLP-1 receptor agonists | Improves | Improves | Reduces progression | Benefit |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | Improves | Unknown | Unknown | Benefit |
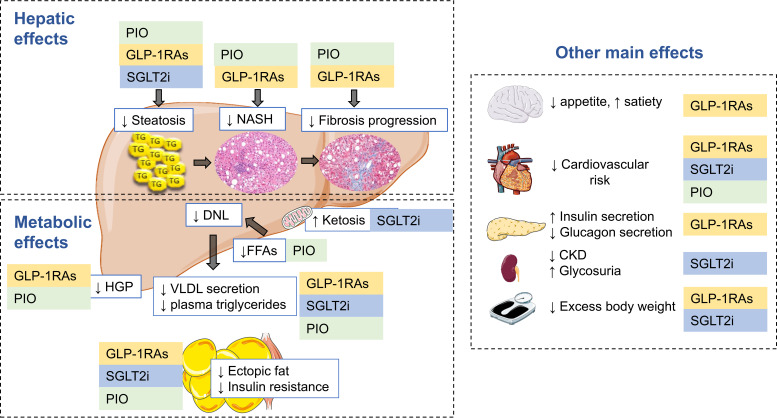
Figure 1.
Hepatic and metabolic effects of pioglitazone, GLP-1 receptor agonist, and SGLT2 inhibitor therapy in NAFLD. People with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD share common pathophysiological mechanisms, among which insulin resistance plays a central role. Excess energy intake and sedentarism promote weight gain that exacerbates potential genetic traits for insulin resistance. Dysfunctional, insulin-resistant adipose tissue promotes excess lipolysis and flow of FFA flux to the liver, increasing de novo lipogenesis (DNL) and intrahepatic triglyceride accumulation (simple steatosis), which, by a number of mechanisms, may progress over time to NASH, fibrosis, and eventually cirrhosis. Hepatic insulin resistance leads to excess hepatic glucose production (HGP), which, with dysfunctional pancreatic β-cell function, will lead to hyperlgycemia. Pioglitazone (PIO), GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) and SGLT2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) are effective in treating hyperglycemia, reducing cardiovascular risk, and conferring multiple hepatic benefits in NAFLD. Pioglitazone is also a potent insulin sensitizer that restores the normal biology of adipose tissue and its response to insulin, which translates into increases in plasma adiponectin and reduction in FFA flux to the liver. GLP-1 receptor agonists reduce appetite, promote glucose-dependent insulin secretion, restore normal glucagon secretion, and have many pleiotropic metabolic and vascular effects. Both pioglitazone and GLP-1 receptor agonists decrease hepatic glucose production and improve plasma lipid metabolism. SGLT2 inhibitors promote glycosuria and a state of ketosis that induces moderate weight loss with metabolic improvement and cardiorenal protection. CKD, chronic kidney disease; TG, triglycerides; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. This figure includes pictures from Servier Medical Art used under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0).
Pioglitazone
Mechanism of action and systemic effects
Pioglitazone, a TZD derivative, is a peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor (PPAR) γ agonist used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes (24). It improves insulin sensitivity and glucose and lipid metabolism, restoring plasma free fatty acid levels (21,25) and reversing atherogenic dyslipidemia by lowering plasma triglycerides and small, dense LDL cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol (26). Pioglitazone increases plasma adiponectin, which, together with a reduction in visceral fat and improvement in insulin sensitivity, contributes to reversing steatohepatitis (27).
Pioglitazone may cause a dose-dependent weight gain (1–2% with 15 mg/day and 3–5% with 45 mg/day) (28); therefore, nutritional counseling is of particular importance (8). Complete medical histories and physical exams are needed in individuals taking TZDs because some patients may experience weight gain from fluid retention, which will be evident as lower-extremity edema. Of note, the improvement in steatohepatitis with pioglitazone has been reported with doses of 30–45 mg/day (29–34). Because lower pioglitazone doses (15 mg/day) can improve glucose and lipid metabolism with minimal weight gain (8,9), it is currently also being investigated for the treatment of NASH (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT04501406).
Pioglitazone decreases the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes (35,36) and reduces CVD in people with (37,38) or without (36) type 2 diabetes. The general perception about this TZD is also changing (8,25,26,39) because it can slow the progression of atherosclerosis (40), improve left ventricular diastolic function, and reduce epicardial adipose tissue (41). The American Diabetes Association’s Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023 suggest its use to lower the risk of cerebrovascular events and myocardial infarction in patients with a history of stroke who also have prediabetes and insulin resistance (42). However, pioglitazone should be avoided in patients with symptomatic heart failure (HF) and is contraindicated if New York Heart Association class III and IV HF is present because, if treatment causes fluid retention, especially when combined with high-dose insulin therapy (28,43–45), it may exacerbate preexisting HF and lead to clinical decompensation. However, no increase in HF was reported in recent large randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of pioglitazone when patients with HF were excluded (8,39). Should HF be suspected, proper work-up is warranted.
Whether pioglitazone increases the risk of bone fractures is controversial. Some studies have reported no increased risk (46), but others found increased risk with long-term use (47). This outcome may be time- and dose-dependent and more significant in higher-risk groups. In a relatively small 3-year prospective study in individuals with type 2 diabetes and NASH (48), a lower bone density at the level of the spine (but no increase in fractures) was found in patients taking pioglitazone compared with those in the placebo group. It appears that calcium and vitamin D supplementation may prevent bone loss and fractures, although this strategy requires further testing. A baseline level of bone mineral density may be recommended in people with a higher risk of fracture.
There also has been controversy regarding bladder cancer with pioglitazone. Current evidence does not support this relationship (36,49,50); however, because of discrepancies in the literature, guidelines recommend against its use in patients with active bladder cancer (51).
Pioglitazone treatment in patients with NASH
Pioglitazone was the first glucose-lowering agent shown in an RCT to reverse NASH. There have been six RCTs with liver histology as the primary outcome that compared the effect of pioglitazone versus placebo for the treatment of NASH (Table 2). Doses of pioglitazone varied from 30 to 45 mg/day. Improvement in steatohepatitis was first reported in a 6-month proof-of-concept study in people with impaired glucose tolerance or type 2 diabetes (29). This report was followed by additional studies ranging from 6 to 36 months in this population (31,33,34). In the trial of longest duration, Cusi et al. (31) treated 101 patients with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes with pioglitazone or placebo for 18 months. Fifty-one percent of those in the pioglitazone group had resolution of NASH versus 19% in placebo (P <0.001). Pioglitazone treatment led to a reduction in mean fibrosis score, but the proportion of patients with fibrosis improvement fell short of statistical significance (39 vs. 25%, P = 0.130), although fewer individuals exhibited fibrosis progression compared with placebo (12 vs. 28%, P = 0.039).
Table 2.
RCTs Reporting Histological Outcomes in People With NASH Treated With Pioglitazone
| Study | n | Pioglitazone Dose, mg/day | Patients With Type 2 Diabetes, % | Duration, weeks | Patients With NASH Resolution, %* | People With Fibrosis Improvement, %* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belfort et al. (29) | 55 | 45 | 42 | 24 | Not reported† | 13 |
| Aithal et al. (30) | 74 | 30 | 0 | 50 | Not reported† | 9 |
| Sanyal et al. (32) | 247 | 30 | 0 | 96 | 26‡ | 13 |
| Cusi et al. (31) | 101 | 45 | 51 | 72 | 32‡ | 14 |
| Bril et al. (34) | 105 | 45 + vitamin E | 100 | 72 | 31‡ | 22 |
| Huang et al. (33) | 90 | 30 | 23 | 24 | 16 | 1 |
As summarized in Table 2, pioglitazone has also been proven safe and effective to ameliorate steatohepatitis in people without type 2 diabetes (30,32). Benefit has also been reported in an Asian population study (33). In 90 patients with biopsy-proven NASH (only 23% of whom had type 2 diabetes), pioglitazone treatment for 24 weeks improved steatohepatitis (46.7 vs. 11.1% with placebo, P = 0.002), although it fell short of the end point of NASH resolution (26.7 vs. 11.1%, P = 0.1). There was less progression of fibrosis in the pioglitazone group (6.7 vs. 33.3% with placebo, P = 0.02) (33).
More recently, to assess the additive effect of vitamin E plus pioglitazone, Bril et al. (34) compared vitamin E and vitamin E plus pioglitazone versus placebo in 105 patients with type 2 diabetes and NASH. Pioglitazone added to vitamin E (but not vitamin E alone) reached the primary end point of a reduction of ≥2 points in the NAFLD activity score (from two different liver histological parameters) without worsening fibrosis and achieved resolution of NASH in 43% of patients (vs. 12% with placebo) (P <0.001 for both).
A meta-analysis (52) of eight RCTs with TZD treatment in patients with NASH, including five studies with pioglitazone, confirmed that pioglitazone (but not rosiglitazone) induces NASH resolution (odds ratio [OR] 3.65, 95% CI 2.32–5.74, P <0.001) compared with placebo and improves liver fibrosis at any stage (OR 1.77, 95% CI 1.15–2.72, P = 0.009). More recently, a meta-analysis focusing on the effect of pioglitazone in individuals with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes and NAFLD (53) reported improvement in steatosis and in resolution of steatohepatitis (OR 1.78, 95% CI 1.05–3.04, P = 0.03) but not of fibrosis. In contrast to pioglitazone, rosiglitazone does not improve steatohepatititis (54).
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Dual Agonists
Mechanism of action and systemic effects
In recent years, GLP-1 receptor agonists have become a powerful tool for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity, improving glycemic control, inducing weight loss, and reducing CVD (55,56). They induce glucose-dependent insulin secretion, improve dysregulated glucagon secretion, and increase satiety. GLP-1 receptor agonists also reduce hepatic de novo lipogenesis, hepatic glucose production, and very-low-density lipoprotein and triglyceride secretion (57). They have an excellent safety profile; gastrointestinal side effects are the most common barrier to long-term adoption but are usually dose-dependent and transitory (58).
In addition, many dual agonists are being developed. Tirzepatide, a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide/GLP-1 receptor agonist, has been approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and of obesity, providing significant benefits in terms of glycemic and weight control (59).
GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment in patients with NASH
The beneficial effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists on the liver are mediated by multiple pathways, but apparently not by direct effects on hepatocytes, which lack GLP-1 receptors (60). As summarized in Table 3, several RCTs have reported that GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment yielded reductions in hepatic triglycerides on imaging (61–65). However, few RCTs have included paired liver biopsy histological outcomes. In an early RCT pilot study (66), liraglutide treatment for 48 weeks yielded histological improvement in people with or without type 2 diabetes (39% resolution of NASH vs. 9% in the placebo group, P = 0.019). In a landmark study by Newsome et al. (67), treatment for 72 weeks with semaglutide yielded more patients with NASH resolution compared with placebo (59% at the higher semaglutide dose vs. 17% with placebo, P <0.001). Although neither study demonstrated an improvement in liver fibrosis, fewer patients had a worsening of fibrosis compared with placebo.
Table 3.
RCTs With GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in People With NAFLD
| Studies Showing Relative Reduction in Liver Fat on Imaging (MRI-Based Methods Only) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Agent | n | Duration, weeks | Patient With Type 2 Diabetes, % | Weight Loss, % | Reduction of Steatosis, % |
| Vanderheiden et al. (61) | Liraglutide | 71 | 24 | 100 | 2 | −30* |
| Frøssing et al. (62) | Liraglutide | 72 | 26 | 0 | 6 | −32* |
| Guo et al. (63)† | Liraglutide | 96 | 26 | 100 | 5 | −24* |
| Bizino et al. (65) | Liraglutide | 49 | 26 | 100 | 5 | −12 |
| Flint et al. (64) | Semaglutide | 67 | 72 | 73 | 10 | −41* |
| Harreiter et al. (99)‡ | Exenatide | 30 | 24 | 100 | 2 | −4 |
| Studies Showing NASH Resolution in Histology | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | Agent | n | Duration, weeks | Patient With Type 2 Diabetes, % | Weight Loss, % | People With NASH Resolution, % |
| Armstrong et al. (66) | Liraglutide | 52 | 48 | 33 | 5 | 30* |
| Newsome et al. (67) | Semaglutide | 320 | 72 | 62 | 4–12 | 19–42* |
| Loomba et al. (69)§ | Semaglutide | 71 | 48 | 75 | 9 | 13 |
Weight loss, reduction on steatosis, and NASH resolution are rounded, placebo-substracted data.
Significant treatment difference versus placebo.
Compared liraglutide versus placebo; unblinded study.
Compared dapagliflozin + exenatide versus dapagliflozin + placebo.
Only participants with cirrhosis were studied.
Cirrhosis is a condition in which treatment of hyperglycemia is challenging because patients with cirrhosis are prone to hypoglycemia and pharmacological treatment options are limited (68). A recent study by Loomba et al. (69) examined the effect of 48 weeks of semaglutide treatment in 71 patients with obesity and NASH-related compensated cirrhosis. Although there was no significant improvement in liver fibrosis or in resolution of NASH, likely because of the advanced liver disease state and short treatment duration, semaglutide was well tolerated and found to be safe overall, with improved glycemic control, minimal hypoglycemia, weight loss, and other cardiometabolic benefits.
The effects of tirzepatide in NAFLD have also been assessed by MRI-Proton Density Fat Fraction (MRI-PDFF) in an imaging substudy of the SURPASS-3 trial (70), in which 296 patients with type 2 diabetes were randomized to tirzepatide 5, 10, or 15 mg or basal insulin degludec. All doses of tirzepatide significantly reduced liver fat content (relative reduction of 40–47 vs. 11% with insulin, P <0.001).
SGLT2 Inhibitors
Mechanism of action and systemic effects
SGLT2 inhibitors are another important class of agents for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. They are potent and selective inhibitors of SGLT2 glucose transporters in the proximal tubule of the kidney, which is responsible for 90% of the filtered glucose reabsorption, inducing glucose urinary excretion. These agents improve glucose control, lipid levels, and blood pressure; induce weight loss; and—of particular interest—confer cardiorenal protection (71). In fact, in addition to treating type 2 diabetes, SGLT2 inhibitors have been proven effective for the treatment of HF and chronic kidney disease in patients without type 2 diabetes. These agents also increase mitochondrial oxidative capacity and induce higher β-hydroxibutirate levels (72). Their main adverse events are genito-urinary tract infections, osmotic diuresis, and diabetic ketoacidosis (rare in patients with type 2 diabetes) (71).
SGLT2 inhibitor treatment in patients with NASH
There has been significant interest in exploring the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors for the treatment of NAFLD (73). In RCTs using as a primary outcome MRI-measured changes in liver triglyceride content (Table 4), SGLT2 inhibitors have been shown to decrease hepatic steatosis. This result occurred with either dapagliflozin (74), empagliflozin (75–77), or canagliflozin (78). This outcome has been also evaluated in an RCT in which liver steatosis was measured by computed tomography scan (79) in 38 patients with type 2 diabetes who were treated with dapagliflozin (vs. placebo) for 12 weeks and showed improvement in steatosis. A similar trend has been reported in two RCTs with empagliflozin that evaluated liver fat with transient elastography (80,81).
Table 4.
RCTs With SGLT2 Inhibitors in People With Type 2 Diabetes and NAFLD (MRI-Based Methods Only)
| Study | Agent | n | Duration, weeks | Weight Loss, % | Reduction of Steatosis, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bolinder et al. (100) | Dapagliflozin | 80 | 24 | −2 | NS |
| Eriksson et al. (101) | Dapagliflozin | 84 | 12 | −2 | 10 |
| Cusi et al. (78) | Canagliflozin | 56 | 24 | −3 | 18 |
| Latva-Rasku et al. (74) | Dapagliflozin | 32 | 8 | −3 | 13* |
| Kahl et al. (75) | Empagliflozin | 84 | 24 | −3 | 22* |
| Gaborit et al. (76) | Empagliflozin | 56 | 12 | −3 | 25* |
| Elhini et al. (77) | Empagliflozin | 256 | 24 | −7 | 31* |
Weight loss and reduction of steatosis are rounded, placebo-substracted data.
Significant compared with placebo group.
We lack placebo-controlled RCTs assessing liver histology outcomes. However, two open-label trials with ipragliflozin (82) and tofogliflozin (83) evaluated histological outcomes. Takahashi et al. (82) compared ipragliflozin to lifestyle changes during 72 weeks of treatment in 55 patients with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD and found that some features of steatohepatitis improved (specifically, ballooning [52 vs. 24%, P = 0.02] and liver fibrosis [57 vs. 16%, P = 0.01]). Takeshita et al. (83) randomized 40 patients with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD to receive tofogliflozin or glimepiride for 48 weeks but reported no significant differences in histological outcomes between the groups. Larger RCTs with paired biopsies are greatly needed to clarify the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on NASH.
Pharmacological Treatments for Obesity With Benefit in NAFLD
Current guidelines (2–4) recommend weight loss of at least 5%, preferably ≥10%, in people with NAFLD because it can reverse NASH and even liver fibrosis (84) in addition to ameliorating obesity-related comorbidities. However, lifestyle changes do not always achieve this weight loss goal, calling for the use of adjunctive pharmacological treatment.
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
The use of GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with NASH was discussed above. Two of these agents also have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of obesity: liraglutide 3 mg/day and semaglutide 2.4 mg/week. The dual agonist tirzepatide at its highest dose (15 mg) reduced body weight by 20.9% (95% CI 19.9–21.8%) compared with a reduction of 3.1% (95% CI 1.9–4.3%) with placebo (P <0.001) (85) and has been recently approved for the treatment of obesity. Triple agonists are also being investigated for the treatment of obesity; one such treatment, retatrutide, has been associated with significant weight reductions (86).
Other Pharmacological Treatments for Obesity
Other FDA-approved pharmacological treatments for obesity include orlistat, naltrexone/bupropion, and phentermine/topiramate. There are scarce data about the effects of these treatments on NASH (2,87). Orlistat is a lipase inhibitor that induces weight loss by inhibiting the absorption of dietary triglycerides (87). A meta-analysis of three RCTs and four single-arm trials showed improvement in ALT and AST but with no histological effect (88). In a trial with 50 patients randomized to orlistat/diet/vitamin E or diet/vitamin E for 9 months, there was no additive effect of orlistat on hepatic histology; there was only an improvement in histology in relation to weight loss irrespective of treatment group (89). Regarding naltrexone/bupropion, in a post hoc analysis of four phase 3 RCTs with a total of 2,073 subjects, a weight loss–related improvement in ALT was observed (90).
Other Pharmacological Treatments for NASH
Vitamin E
Vitamin E has demonstrated benefit for the treatment of NASH. Sanyal et al. (32) reported on an RCT involving 247 adults without type 2 diabetes with biopsy-proven NASH. Treatment with vitamin E (800 IU/day) for 96 weeks led to resolution of steatohepatitis in 36% of the vitamin E group versus 21% of those taking placebo (P = 0.05). No improvement in fibrosis was observed. A more recent RCT (34) compared the efficacy of vitamin E 800 IU/day, vitamin E 800 UI/day plus pioglitazone 30 mg/day, or placebo for 18 months in 105 patients with type 2 diabetes and NASH. The group taking vitamin E alone did not achieve the primary outcome (reduction of ≥2 points in the NAFLD activity score without worsening of fibrosis) compared with placebo (31 vs. 19%, P = 0.26).
A meta-analysis (91) of RCTs of vitamin E (with and without histologic data) reported some liver histological benefit but did not differentiate patients with or without type 2 diabetes. Thus, there is not enough evidence for the use of vitamin E as a treatment for NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes (34) and should be considered only on a case-by-case basis.
Additional Treatments
As previously mentioned, assessment of cardiovascular risk in patients with NAFLD is mandatory, and treatment of associated risk factors should follow current established management guidelines. Lipid-lowering and antihypertensive treatments should be prescribed in people with NAFLD when needed. There is some concern among clinicians about statin therapy, but statins have been shown to be safe in patients with NAFLD (92,93); however, they should be avoided in those with decompensated cirrhosis (2–5).
Drugs in Advanced Stages of Development for the Treatment of NASH
There are many drugs in development for the treatment of NASH, with a broad spectrum of mechanisms of action and metabolic targets (94). The sections below briefly summarize those in advanced stages of development (i.e., phase 3 clinical trials).
Lanifibranor
Lanifibranor is a pan-PPAR agonist. In a phase 2b RCT (95), 247 patients with NASH (with and without type 2 diabetes) received lanifibranor 1,200 mg/day, lanifibranor 800 mg/day, or placebo for 6 months. Significantly more patients in the group taking lanifibranor 1,200 mg than in the placebo group achieved NASH resolution without worsening fibrosis (49 vs. 22%), and more had improved fibrosis without worsening NASH (48 vs. 29%; relative risk 1.68 [95% CI 1.15–2.46]). These effects are being further assessed in an ongoing phase 3 RCT (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT04849728) with 2,000 participants with NASH and fibrosis (stage F2–F3) receiving either lanifibranor 800 mg/day, lanifibranor 1,200 mg/day, or placebo for 72 weeks.
A recent 24-week RCT examined the mechanism of action of lanifibranor in people with NAFLD and type 2 diabetes and reported a marked improvement in glucose (i.e., reductions in A1C and hepatic and muscle insulin resistance) and lipid metabolism, with an ∼50% reduction in intrahepatic triglyceride content (96).
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Dual Agonists
There is considerable research activity exploring the many metabolic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists, as well as dual- and triple-peptide agonists in people with NAFLD (57). The evidence for semaglutide was discussed earlier. Of note, there is an ongoing paired-biopsy phase 3 clinical trial (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT04822181) in which 1,200 participants with NASH and significant fibrosis (stages F2–F3) are to receive semaglutide 2.4 mg/week or placebo for 72 weeks. A phase 2 paired-biopsy RCT with the dual agonist tirzepatide (also discussed earlier) is also ongoing in people with NASH and fibrosis (stage F2–F3), who are randomized to receive tirzepatide 5, 10, or 15 mg or placebo to assess tirzepatide’s effect on steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT04166773).
Resmetirom
Resmetirom is a selective thyroid hormone receptor β agonist that has been studied for the treatment of NASH. A phase 2 clinical trial (97) evaluated resmetirom 80 mg/day in 125 patients with NASH with fibrosis stage 1–3 for 36 weeks. The researchers found a significant reduction in liver fat (measured by MRI-PDFF) in the resmetirom group compared with placebo (40 vs. 14%). Histologically, 27% of participants in the resmetirom group had resolution of NASH compared with 6% in the placebo group (P = 0.018). Fibrosis improved in 28.8% of the patients treated with resmetirom compared with 23.5% of those taking placebo (P = 0.65).
The resmetirom NASH development program involves four ongoing phase 3 clinical trials: MAESTRO-NASH, MAESTRO-NAFLD-1, MAESTRO-NAFLD-OLE, and MAESTRO-NASH-OUTCOMES. Results were recently reported from the MAESTRO-NASH (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT03900429) trial in ∼1,000 participants with NASH and fibrosis who were randomized to resmetirom 80 mg/day (n = 316), resmetirom 100 mg/day (n = 321), or placebo (n = 318), with a second biopsy performed after 52 weeks of treatment. The investigators reported significant benefit in the primary outcomes of NASH resolution (without worsening of fibrosis) (26–30 vs. 10% with placebo) and improvement in fibrosis without worsening of NAFLD activity score (24–26 vs. 14% with placebo).
Other Drugs in Development
Several fibroblast growth factor 21 analogs are in development for the treatment of NASH (94). Recently, the results of a phase 2b RCT reported on pegozafermin (98). In 222 participants with biopsy-proven NASH and fibrosis (stage F2–F3), there was an improvement in liver fibrosis in 27% of patients in the pegozafermin group compared with 7% with placebo (P = 0.008). NASH resolution was also more frequent with pegozafermin (26 vs. 2% with placebo).
Conclusion
There are effective treatments—namely, pioglitazone and GLP-1 receptor agonists—to ameliorate NASH for people with type 2 diabetes, a population at the highest risk of disease progression. Physicians managing these individuals must use these drugs as recommended in recent guidelines (2–5). Early intervention could prevent the development of cirrhosis, progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes, and CVD, which is the main cause of death in people with NAFLD. For cardiorenal protection, SGLT2 inhibitors should also be considered, although their role for the treatment of NASH remains unclear. Novel drugs for steatohepatitis are under intense investigation and will soon become available. Screening individuals at high risk for steatohepatitis and intervening early to prevent hepatic and extrahepatic complications is the responsibility of all caregivers who wish to improve the quality of life of people with obesity, prediabetes, or type 2 diabetes.
Article Information
Duality of Interest
K.C. has received research support toward the University of Florida as a principal investigator from Echosens, Inventiva, LabCorp, and Nordic Bioscience. He is also a consultant for Aligos, Arrowhead, AstraZeneca, BMS, Boehringer Ingelheim, Covance, Eli Lilly, GSK, Madrigal, Novo Nordisk, Prosciento, Sagimet, and Siemens. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed to writing, reviewing, and editing the manuscript. K.C. is the guarantor of this work and, as such, had full access to all materials and takes responsibility for the accuracy and integrity of the content.
References
- 1. Zelber-Sagi S, Moore BJ. Practical lifestyle management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease for busy clinicians. Diabetes Spectr 2024;37:39–47 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Cusi K, Isaacs S, Barb D, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in primary care and endocrinology clinical settings: co-sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Endocr Pract 2022;28:528–562 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al.; American Diabetes Association . 4. Comprehensive medical evaluation and assessment of comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023;46(Suppl. 1):S49–S67 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Rinella ME, Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Siddiqui MS, et al. AASLD practice guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2023;77:1797–1835 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kanwal F, Shubrook JH, Adams LA, et al. Clinical care pathway for the risk stratification and management of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2021;161:1657–1669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Machado AM, Guimarães NS, Bocardi VB, et al. Understanding weight regain after a nutritional weight loss intervention: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr ESPEN 2022;49:138–153 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Younossi ZM, Golabi P, Paik JM, Henry A, Van Dongen C, Henry L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): a systematic review. Hepatology 2023;77:1335–1347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Gastaldelli A, Cusi K. From NASH to diabetes and from diabetes to NASH: mechanisms and treatment options. JHEP Rep 2019;1:312–328 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Stefan N, Cusi K. A global view of the interplay between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022;10:284–296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Sanyal AJ, Van Natta ML, Clark J, et al. Prospective study of outcomes in adults with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med 2021;385:1559–1569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Barb D, Repetto EM, Stokes ME, Shankar SS, Cusi K. Type 2 diabetes mellitus increases the risk of hepatic fibrosis in individuals with obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2021;29:1950–1960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Ciardullo S, Monti T, Perseghin G. High prevalence of advanced liver fibrosis assessed by transient elastography among U.S. adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021;44:519–525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Harrison SA, Gawrieh S, Roberts K, et al. Prospective evaluation of the prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis in a large middle-aged US cohort. J Hepatol 2021;75:284–291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lomonaco R, Godinez Leiva E, Bril F, et al. Advanced liver fibrosis is common in patients with type 2 diabetes followed in the outpatient setting: the need for systematic screening. Diabetes Care 2021;44:399–406 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Julián MT, Pera G, Soldevila B, et al. Atherogenic dyslipidemia, but not hyperglycemia, is an independent factor associated with liver fibrosis in subjects with type 2 diabetes and NAFLD: a population-based study. Eur J Endocrinol 2021;184:587–596 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Sporea I, Mare R, Popescu A, et al. Screening for liver fibrosis and steatosis in a large cohort of patients with type 2 diabetes using vibration controlled transient elastography and controlled attenuation parameter in a single-center real-life experience. J Clin Med 2020;9:1032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Koehler EM, Plompen EP, Schouten JN, et al. Presence of diabetes mellitus and steatosis is associated with liver stiffness in a general population: the Rotterdam Study. Hepatology 2016;63:138–147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Kim Y, Chang Y, Ryu S, Wild SH, Byrne CD. NAFLD improves risk prediction of type 2 diabetes: with effect modification by sex and menopausal status. Hepatology 2022;76:1755–1765 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Cusi K. Time to include nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the management of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020;43:275–279 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Kanwal F, Shubrook JH, Younossi Z, et al. Preparing for the NASH epidemic: a call to action. Diabetes Care 2021;44:2162–2172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Budd J, Cusi K. Role of agents for the treatment of diabetes in the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Diab Rep 2020;20:59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Lazarus JV, Mark HE, Anstee QM, et al. Advancing the global public health agenda for NAFLD: a consensus statement. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022;19:60–78 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Belfort-DeAguiar R, Lomonaco R, Cusi K. Approach to the patient with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2023;108:483–495 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Davies MJ, Aroda VR, Collins BS, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022: a consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2022;45:2753–2786 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. DeFronzo RA, Inzucchi S, Abdul-Ghani M, Nissen SE. Pioglitazone: the forgotten, cost-effective cardioprotective drug for type 2 diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis Res 2019;16:133–143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Lebovitz HE. Thiazolidinediones: the forgotten diabetes medications. Curr Diab Rep 2019;19:151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Gastaldelli A, Sabatini S, Carli F, et al. PPAR-γ-induced changes in visceral fat and adiponectin levels are associated with improvement of steatohepatitis in patients with NASH. Liver Int 2021;41:2659–2670 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Aronoff S, Rosenblatt S, Braithwaite S, Egan JW, Mathisen AL, Schneider RL. Pioglitazone hydrochloride monotherapy improves glycemic control in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes: a 6-month randomized placebo-controlled dose-response study: the Pioglitazone 001 Study Group. Diabetes Care 2000;23:1605–1611 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Belfort R, Harrison SA, Brown K, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 2006;355:2297–2307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Aithal GP, Thomas JA, Kaye PV, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of pioglitazone in nondiabetic subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2008;135:1176–1184 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Cusi K, Orsak B, Bril F, et al. Long-term pioglitazone treatment for patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2016;165:305–315 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Sanyal AJ, Chalasani N, Kowdley KV, et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1675–1685 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Huang JF, Dai CY, Huang CF, et al. First-in-Asian double-blind randomized trial to assess the efficacy and safety of insulin sensitizer in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis patients. Hepatol Int 2021;15:1136–1147 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Bril F, Biernacki DM, Kalavalapalli S, et al. Role of vitamin E for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2019;42:1481–1488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. DeFronzo RA, Tripathy D, Schwenke DC, et al. Pioglitazone for diabetes prevention in impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 2011;364:1104–1115 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Kernan WN, Viscoli CM, Furie KL, et al. Pioglitazone after ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack. N Engl J Med 2016;374:1321–1331 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Zhou Y, Huang Y, Ji X, Wang X, Shen L, Wang Y. Pioglitazone for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with or at high risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2020;105:dgz252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Dormandy JA, Charbonnel B, Eckland DJ, et al. Secondary prevention of macrovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes in the PROactive study (PROspective pioglitAzone Clinical Trial In macroVascular Events): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005;366:1279–1289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Nesti L, Tricò D, Mengozzi A, Natali A. Rethinking pioglitazone as a cardioprotective agent: a new perspective on an overlooked drug. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2021;20:109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Nissen SE, Nicholls SJ, Wolski K, et al. Comparison of pioglitazone vs glimepiride on progression of coronary atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: the PERISCOPE randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2008;299:1561–1573 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Moody AJ, Molina-Wilkins M, Clarke GD, et al. Pioglitazone reduces epicardial fat and improves diastolic function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2023;25:426–434 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, et al.; American Diabetes Association . 3. Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes and associated comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023;46(Suppl. 1):S41–S48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Mudaliar S, Chang AR, Henry RR. Thiazolidinediones, peripheral edema, and type 2 diabetes: incidence, pathophysiology, and clinical implications. Endocr Pract 2003;9:406–416 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Nesto RW, Bell D, Bonow RO, et al. Thiazolidinedione use, fluid retention, and congestive heart failure: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2004;27:256–263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Jain R, Osei K, Kupfer S, Perez AT, Zhang J. Long-term safety of pioglitazone versus glyburide in patients with recently diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacotherapy 2006;26:1388–1395 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Pavlova V, Filipova E, Uzunova K, Kalinov K, Vekov T. Pioglitazone therapy and fractures: systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2018;18:502–507 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Viscoli CM, Inzucchi SE, Young LH, et al. Pioglitazone and risk for bone fracture: safety data from a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017;102:914–922 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Portillo-Sanchez P, Bril F, Lomonaco R, et al. Effect of pioglitazone on bone mineral density in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a 36-month clinical trial. J Diabetes 2019;11:223–231 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Lewis JD, Habel LA, Quesenberry CP, et al. Pioglitazone use and risk of bladder cancer and other common cancers in persons with diabetes. JAMA 2015;314:265–277 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Vaccaro O, Masulli M, Nicolucci A, et al. Effects on the incidence of cardiovascular events of the addition of pioglitazone versus sulfonylureas in patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin (TOSCA.IT): a randomised, multicentre trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2017;5:887–897 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Hampp C, Pippins J. Pioglitazone and bladder cancer: FDA’s assessment. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 2017;26:117–118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Musso G, Cassader M, Paschetta E, Gambino R. Thiazolidinediones and advanced liver fibrosis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a meta-analysis. JAMA Intern Med 2017;177:633–640 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Lian J, Fu J. Pioglitazone for NAFLD patients with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021;12:615409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Ratziu V, Giral P, Jacqueminet S, et al. Rosiglitazone for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: one-year results of the randomized placebo-controlled Fatty Liver Improvement with Rosiglitazone Therapy (FLIRT). Gastroenterology 2008;135:100–110 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Marx N, Husain M, Lehrke M, Verma S, Sattar N. GLP-1 receptor agonists for the reduction of atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Circulation 2022;146:1882–1894 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Lincoff AM, Brown-Frandsen K, Colhoun HM, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in obesity without diabetes. N Engl J Med 2023;389:2221–2232 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Yabut JM, Drucker DJ. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor-based therapeutics for metabolic liver disease. Endocr Rev 2023;44:14–32 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Patel Chavez C, Cusi K, Kadiyala S. The emerging role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for the management of NAFLD. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2022;107:29–38 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Lingvay I, Cheng AY, Levine JA, et al. Achievement of glycaemic targets with weight loss and without hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes with the once-weekly glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide: a post hoc analysis of the SURPASS-1 to -5 studies. Diabetes Obes Metab 2023;25:965–974 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Pyke C, Heller RS, Kirk RK, et al. GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology 2014;155:1280–1290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Vanderheiden A, Harrison LB, Warshauer JT, et al. Mechanisms of action of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with high-dose insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2016;101:1798–1806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Frøssing S, Nylander M, Chabanova E, et al. Effect of liraglutide on ectopic fat in polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018;20:215–218 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Guo W, Tian W, Lin L, Xu X. Liraglutide or insulin glargine treatments improves hepatic fat in obese patients with type 2 diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in twenty-six weeks: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2020;170:108487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Flint A, Andersen G, Hockings P, et al. Randomised clinical trial: semaglutide versus placebo reduced liver steatosis but not liver stiffness in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2021;54:1150–1161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Bizino MB, Jazet IM, de Heer P, et al. Placebo-controlled randomised trial with liraglutide on magnetic resonance endpoints in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a pre-specified secondary study on ectopic fat accumulation. Diabetologia 2020;63:65–74 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Armstrong MJ, Gaunt P, Aithal GP, et al. Liraglutide safety and efficacy in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (LEAN): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet 2016;387:679–690 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Newsome PN, Buchholtz K, Cusi K, et al. A placebo-controlled trial of subcutaneous semaglutide in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 2021;384:1113–1124 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Castera L, Cusi K. Diabetes and cirrhosis: current concepts on diagnosis and management. Hepatology 2023;77:2128–2146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Loomba R, Abdelmalek MF, Armstrong MJ, et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once weekly in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-related cirrhosis: a randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol 2023;8:511–522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Gastaldelli A, Cusi K, Fernández Landó L, Bray R, Brouwers B, Rodríguez Á. Effect of tirzepatide versus insulin degludec on liver fat content and abdominal adipose tissue in people with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3 MRI): a substudy of the randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 SURPASS-3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022;10:393–406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Xu B, Li S, Kang B, Zhou J. The current role of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes mellitus management. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2022;21:83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Veelen A, Andriessen C, Op den Kamp Y, et al. Effects of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on substrte metabolism in prediabetic insulin resistant individuals: a randomized, double-blind crossover trial. Metabolism 2023;140:155396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Androutsakos T, Nasiri-Ansari N, Bakasis AD, et al. SGLT-2 inhibitors in NAFLD: expanding their role beyond diabetes and cardioprotection. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Latva-Rasku A, Honka MJ, Kullberg J, et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin reduces liver fat but does not affect tissue insulin sensitivity: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with 8-week treatment in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Care 2019;42:931–937 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Kahl S, Gancheva S, Straßburger K, et al. Empagliflozin effectively lowers liver fat content in well-controlled type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, phase 4, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2020;43:298–305 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Gaborit B, Ancel P, Abdullah AE, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on ectopic fat stores and myocardial energetics in type 2 diabetes: the EMPACEF study. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2021;20:57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Elhini SH, Wahsh EA, Elberry AA, et al. The impact of an SGLT2 inhibitor versus ursodeoxycholic acid on liver steatosis in diabetic patients. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022;15:1516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Cusi K, Bril F, Barb D, et al. Effect of canagliflozin treatment on hepatic triglyceride content and glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2019;21:812–821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Phrueksotsai S, Pinyopornpanish K, Euathrongchit J, et al. The effects of dapagliflozin on hepatic and visceral fat in type 2 diabetes patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;36:2952–2959 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Taheri H, Malek M, Ismail-Beigi F, et al. Effect of empagliflozin on liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease without diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Adv Ther 2020;37:4697–4708 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Chehrehgosha H, Sohrabi MR, Ismail-Beigi F, et al. Empagliflozin improves liver steatosis and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Diabetes Ther 2021;12:843–861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Takahashi H, Kessoku T, Kawanaka M, et al. Ipragliflozin improves the hepatic outcomes of patients with diabetes with NAFLD. Hepatol Commun 2022;6:120–132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Takeshita Y, Honda M, Harada K, et al. Comparison of tofogliflozin and glimepiride effects on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in participants with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, 48-week, open-label, active-controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2022;45:2064–2075 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Vilar-Gomez E, Martinez-Perez Y, Calzadilla-Bertot L, et al. Weight loss through lifestyle modification significantly reduces features of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2015;149:367–378.e5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med 2022;387:205–216 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Jastreboff AM, Kaplan LM, Frías JP, et al. Triple-hormone-receptor agonist retatrutide for obesity: a phase 2 trial. N Engl J Med 2023;389:514–526 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Polyzos SA, Goulis DG, Giouleme O, Germanidis GS, Goulas A. Anti-obesity medications for the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr Obes Rep 2022;11:166–179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Wang H, Wang L, Cheng Y, Xia Z, Liao Y, Cao J. Efficacy of orlistat in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Rep 2018;9:90–96 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Harrison SA, Fecht W, Brunt EM, Neuschwander-Tetri BA. Orlistat for overweight subjects with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a randomized, prospective trial. Hepatology 2009;49:80–86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Bajaj HS, Burrows M, Blavignac J, et al. Extended-release naltrexone/bupropion and liver health: pooled, post hoc analysis from four randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes Metab 2021;23:861–865 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Vadarlis A, Antza C, Bakaloudi DR, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effect of vitamin E supplementation in adult patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2021;36:311–319 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Torres-Peña JD, Martín-Piedra L, Fuentes-Jiménez F. Statins in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Front Cardiovasc Med 2021;8:777131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Bril F, Portillo Sanchez P, Lomonaco R, et al. Liver safety of statins in prediabetes or T2DM and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: post hoc analysis of a randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2017;102:2950–2961 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Dufour JF, Anstee QM, Bugianesi E, et al. Current therapies and new developments in NASH. Gut 2022;71:2123–2134 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Francque SM, Bedossa P, Ratziu V, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of the pan-PPAR agonist lanifibranor in NASH. N Engl J Med 2021;385:1547–1558 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Barb D, Kalavalapalli S, Godinez Leiva E, et al. Lanifibranor reverses insulin resistance and improves glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) [Abstract 5035C]. In AASLD The Liver Meeting November 10–14, 2023 Late-Breaking Abstracts. Alexandria, VA, American Association for the Study of Liver Disease; 2023, p. 31–32 [Google Scholar]
- 97. Harrison SA, Bashir MR, Guy CD, et al. Resmetirom (MGL-3196) for the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2019;394:2012–2024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Loomba R, Sanyal AJ, Kowdley KV, et al. Randomized, controlled trial of the FGF21 analogue pegozafermin in NASH. N Engl J Med 2023;389:998–1008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Harreiter J, Just I, Leutner M, et al. Combined exenatide and dapagliflozin has no additive effects on reduction of hepatocellular lipids despite better glycaemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin: EXENDA, a 24-week, prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled pilot trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 2021;23:1129–1139 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Bolinder J, Ljunggren Ö, Kullberg J, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin on body weight, total fat mass, and regional adipose tissue distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with inadequate glycemic control on metformin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012;97:1020–1031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Eriksson JW, Lundkvist P, Jansson PA, et al. Effects of dapagliflozin and n-3 carboxylic acids on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in people with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind randomised placebo-controlled study. Diabetologia 2018;61:1923–1934 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]