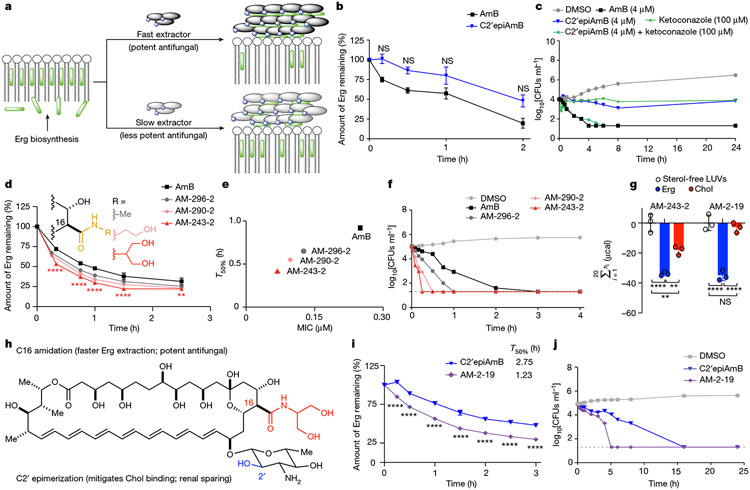
Fig. 3 ∣. Kinetics of Erg extraction enabling tuning of antifungal efficacy.
a, Competitive kinetics model of sterol encapsulation for AmB analogues. b, C2′epiAmB extracts Erg more slowly than AmB from C. albicans SN250 at 5 μM (n = 4 for 0.167 and 0.5 h and n = 3 for 1.0 and 2.0 h time points). Pairwise comparison with AmB at each time point using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. c, Cotreatment of C. albicans SN250 with the Erg biosynthesis inhibitor ketoconazole promotes faster killing and restores potency for C2′epiAmB. CFUs, colony-forming units. d, At 5 μM, hyper potent AmB amides extract Erg more quickly than the parent AmB (n = 3 per time point) from C. albicans SN250. Pairwise comparison with AmB at each time point using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test; **P = 0.0064, ****P < 0.0001. e, Kinetics versus efficacy for C. albicans SN250, showing T50% (time required for 50% Erg extraction) versus observed MIC. f, Rate of cell killing at 4 μM (n = 2 per sample per time point) for C. albicans SN250. g, ITC data showing retained Chol binding for AM-243-2 and selectivity for Erg over Chol for AM-2-19 (n = 3). Pairwise comparison using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test; **P = 0.0012, **P = 0.0038, ****P < 0.0001. h, The hybrid design strategy combines the renal-sparing nature of C2′ epimerization and potency-promoting C41 amidation in AM-2-19. i, AM-2-19 extracts Erg more quickly than C2′epiAmB (5 μM; n = 3 per time point) from C. albicans SN250. Pairwise comparison with C2′epiAmB at each time point using two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test; ****P < 0.0001. j, AM-2-19 kills C. albicans SN250 more quickly than C2′epiAmB (4 μM). Results are means ± s.d. For c,f,j a nominal value of 20 CFUs ml−1 was assigned on the basis of the dilution factor for plates with no fungal growth.