Abstract
Enhancing nanoparticles’ anti-cancer capabilities as drug carriers requires the careful adjustment of formulation parameters, including loading efficiency, drug/carrier ratio, and synthesis method. Small adjustments to these parameters can significantly influence the drug-loading efficiency of nanoparticles. Our study explored how chitosan and polyethylene glycol (PEG) coatings affect the structural properties, drug-loading efficiency, and anti-cancer efficacy of Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs). The loading efficiency of the NPs was determined using FTIR spectrometry and XRD. The quantity of chrysin incorporated into the coated NPs was examined using UV–Vis spectrometry. The effect of the NPs on cell viability and apoptosis was determined by employing the HCT 116 human colon carcinoma cell line. We showed that a two-fold increase in drug concentration did not impact the loading efficiency of Fe3O4 NPs coated with PEG. However, there was a 33 Å difference in the crystallite sizes obtained from chitosan-coated Fe3O4 NPs and drug concentrations of 1:0.5 and 1:2, resulting in decreased system stability. In conclusion, PEG coating exhibited a higher loading efficiency of Fe3O4 NPs compared to chitosan, resulting in enhanced anti-tumor effects. Furthermore, variations in the loaded amount of chrysin did not impact the crystallinity of PEG-coated NPs, emphasizing the stability and regularity of the system.
Keywords: magnetite nanoparticles, coating agents, loading efficiency, drug concentration, colon cancer
1. Introduction
Resistance to chemotherapy is a major challenge in the effective treatment of various cancers, including colorectal cancers. Nanoparticles (NPs) are gaining attention as a powerful tool for preventing chemoresistance due to their improved stability, biocompatibility, enhanced permeability, and precise targeting [1]. The advantages of NPs include sustained drug release over time, the maintenance of therapeutic concentrations in the tumor, and the potential overcoming of resistance associated with the rapid excretion of free drugs [2]. Novel functionalized magnetic NPs play a critical role in the delivery of various drugs and drug candidates, including promising therapeutic biomacromolecules, specific cell types, individual cells, or specific intracellular compartments, such as the nucleus and mitochondria [3]. Currently, nanosized iron oxide particles are widely employed in oncological studies as drug carriers. This is due to their low toxicity, stability in aqueous solutions, biocompatibility, and ability to facilitate the magnetic hyperthermia of tumor cells [4,5,6].
However, the success rate that leads to nanoparticles being used on a large scale as clinical products is low [7]. The first cancer nanomedicine, Doxil®, was the first FDA-approved liposomal nanoparticle formulation for the treatment of certain cancers [8]. Iron oxide nanoparticles, such as Feridex, Combidex, Feraheme, and NanoTherm are some of the FDA-approved agents for both cancer imaging and therapy applications [9]. Despite the advantages of iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery and diagnostics, numerous animal experiments have confirmed their toxicity to organs, such as the nervous system, heart, lungs, thyroid, liver, and lymph nodes [10,11]. Therefore, it became an important task to develop strategies to prevent the opsonization of nanoparticles to extend their circulation, enhance their carrier capacity, and improve targeted delivery. A recently reported innovative approach using magnetic biohybrid microrobot multimers (BMMs) based on chlorella demonstrated significant promise for targeted drug delivery [12]. Reduced toxicity may be achieved by improving iron oxide nanoparticles’ carrier capacity and introducing them in smaller, more potent doses.
The major disadvantage of unmodified NPs is their nonspecific interactions with cells, leading to accumulation outside target organs [13]. Moreover, unmodified NPs have high toxicity and low colloidal stability in physiological media [14]. The careful surface modification of NPs, i.e., functionalization with biocompatible agents, can mitigate these challenges and enable the maintenance of both magnetic characteristics and the optimization of drug carrier capability [15,16,17]. Colloid modification can be achieved through the use of monomeric stabilizers (such as carboxylates, phosphates, and sulfates) or polymeric stabilizers (such as polyacrylic acid, polyethyleneimine, and polyethylene glycol) [18,19,20,21,22,23]. Polymers are widely used as a shell covering the surfaces of nanomaterials. They can prevent NP oxidation and provide nanoparticles with collateral stability [24]. Moreover, the polymer coating can improve NP biocompatibility and reduce their toxicity [25]. In addition, coating with polymers can be arranged to respond to specific triggers, such as changes in temperature, pH, NPs, and polymer concentration ratios, allowing for substance-controlled release [26].
Selecting the coating agent and method for NPs is critical to ensure their efficiency as drug carriers [27,28]. It is imperative that the chosen coating preserves the loading capacity of the NPs, facilitating the effective encapsulation of therapeutic agents while maintaining the stability of the drug carrier [13]. The coating method is the most frequently employed surface modification approach to conjugate organic and inorganic materials onto the surface of magnetic NPs [22]. In this case, modification can be performed according to the encapsulation strategy or through the formation of a self-assembled monolayer onto the particles’ surfaces [29]. Coating with polymers is widely used to modify the surface of NPs to prevent aggregation and produce stable suspensions [30]. Our current study focuses on the synthesis and characterization of iron oxide NPs modified by coating their surfaces with various polymer materials at different concentrations. These NPs were further loaded with the natural anti-cancer bioflavonoid chrysin to achieve increased anticancer efficacy. Chrysin, also known as 5,7-dihydroxyflavone or 5,7-dihydroxy-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-4-one, has demonstrated significant anti-carcinogenic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-oxidant properties [31]. Magnetite NPs (Fe3O4, diameter ~20–25 nm) were chosen as a nucleus due to their previously demonstrated low toxicity and biodegradability. PEG and chitosan were employed for designing the polymeric shell of the NPs because of their biocompatibility and non-toxic characteristics. The anti-cancer efficacy of the NPs was studied using HCT-116 human colon cancer cells in in vitro conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Iron (III) chloride tetrahydrate (FeCl2·4H2O), iron (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O), polyethylene glycol (PEG, MW6000), chitosan (degree of deacetylation <90%, MW177.20), ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH, 23–25%), acetic acid (CH3COOH, 99%), chrysin (C15H10O4, 97%), and N, N-dimethylformamide (HCON(CH3)2, ≥99%) were purchased from KarmaLab (Izmir, Turkey). All of the used chemicals were of analytical grade.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of PEG and Chitosan-Coated Nanoparticles
The synthesis of the magnetite NPs involved the chemical co-precipitation of ferric and ferrous salts under the presence of nitrogen gas [32]. FeCl3·6H2O and FeCl2·4H2O with a 2:1 mole ratio were dissolved in 100 mL of deionized water. The solution was heated under vigorous stirring until 70 °C was reached for 30 min. For the PEG coating, an appropriate amount of polymer was slowly added to the solution. After stirring for 60 min, chemical precipitation was achieved at a stirring rate of 400 rpm by adding 10–15 mL of NH4OH (23–25%) drop-wise until the pH reached 10, and then the temperature was raised to 90 °C. After the system was cooled to room temperature, the precipitate was separated with a NdFeB magnet and washed with deionized water and ethanol in the ratio of 2:1, respectively, several times until the pH was neutral. This step was required for the NPs’ further characterization. Finally, the PEG-coated magnetite NPs were dried in an oven at 80 °C for 4 h. Coating with chitosan was implemented by first preparing the chitosan solution. For this, 0.25 g of fine chitosan powder was dissolved in a mixture of 25 mL of deionized water and 1.25 mL of acetic acid. The chitosan-coated magnetite NPs were obtained using a previously described method [33].
The loading of chrysin into the PEG-magnetite NP system was performed using the adsorption method. Briefly, a solution of the anti-cancer drug dissolved in N, N-dimethylformamide, was added to the PEG-magnetic iron oxide NP powder, and the mixture was stirred with a mechanical stirrer at 700 rpm for 6 h at 25 °C. At the end of the procedure, free drug molecules were removed via magnetic cleaning. The resulting samples, PEG-magnetite NPs-chrysin, were then washed three times and dried in an oven at 40 °C for 4 h. The chrysin-loaded chitosan-stabilized magnetite NPs were synthesized using the same protocol.
In this research, the influence of drug concentration and coating agent type on drug-loading efficiency was investigated. To achieve this, the chrysin concentration was varied between 250 mg, 500 mg, and 1000 mg (Table 1).
Table 1.
The composition of Fe3O4 NPs. While preparing the samples, the quantity of Fe3O4 NPs coated with PEG and chitosan remained constant at 500 mg, while the amount of chrysin loaded into the NPs was varied at three different ratios: 1:0.5, 1:1, and 1:2.
| Sample | Fe3O4 NPs (mg) |
Coating Agent | Chrysin (mg) |
Ratio of Fe3O4 and Chrysin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@PEG250 | 500 | PEG | 250 | 1:0.5 |
| Fe3O4@PEG500 | 500 | PEG | 500 | 1:1 |
| Fe3O4@PEG1000 | 500 | PEG | 1000 | 1:2 |
| Fe3O4@Chitosan250 | 500 | Chitosan | 250 | 1:0.5 |
| Fe3O4@Chitosan500 | 500 | Chitosan | 500 | 1:1 |
| Fe3O4@Chitosan1000 | 500 | Chitosan | 1000 | 1:2 |
2.2.2. Characterization of Coated and Drug-Loaded Magnetite Nanoparticles
The structure and drug-loading efficiency of the iron oxide NPs coated with various polymers were investigated using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and visible ultraviolet (UV–Vis) spectroscopy. To evaluate the crystalline nature and size characterization of the samples, XRD analysis was conducted using a Rigaku Mini Flex 600 X-ray diffractometer with high-intensity Cu–Kα radiation and 2θ ranging from 10° to 80°. Regarding the structure of the magnetite NPs with various coating agents, a FTIR spectrometer Varian 3600 with KBr pellets was used. In this case, the spectrum was observed from 4000–4500 cm−1. Additionally, the drug-loading efficiency for all the samples was investigated using a Specord 250 PLUS UV/Vis spectrometer.
2.2.3. Calculation of Drug-Loading Efficiency (LE)
The suspensions of the drug-loaded Fe3O4 polymer-coated samples were centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 20 min. The loading efficiency (LE) for the samples was determined by quantifying the absorption of the clear supernatant using UV–Vis spectroscopy. The absorbance values of chrysin were measured on a UV–Vis spectrum at a wavelength of 276.4 nm. The percentage of the LE of chrysin in the PEG and chitosan-coated magnetite NPs was determined using the following equation, respectively, as reported earlier [20]:
where Dt is the total amount of chrysin and Df is the amount of free chrysin in the supernatant after centrifugation.
2.2.4. Cell Culture and MTT Assay
The anti-cancer efficacy of selected Fe3O4 NPs was studied using HCT 116 human colon cancer cells. HCT 116 cells were maintained in DMEM medium containing 10% FBS and 1% PSN under a humidified atmosphere (5% CO2) at 37 °C. Once 75–80% confluence was achieved, the cells were re-equilibrated with trypsin (0.25%) and EDTA (0.52 mM) in PBS and harvested at the appropriate density for 24 h before the cell viability assessment. In this assay, the HCT 116 cells were treated with chrysin-loaded Fe3O4 NPs coated with both PEG and chitosan at different concentrations (0–40 µg/mL) for 24 h. After treatment, the cells were rinsed with PBS, and MTT solution was added to form formazan salt. Subsequently, the media were replaced with DMSO (200 mL) to dissolve the formed formazan crystals in each well. The viability of the cells was spectrophotometrically determined at 570 nm using an ELISA reader (Emax, Molecular Devices, San Jose, CA, USA) to identify the number of viable cells, and the percentage of viability was calculated using the following equation: (1 − [ODt/ODc]) × 100%, where ODt is the mean optical density of wells treated with the tested sample and ODc is the mean optical density of untreated cells. All the treatment experiments were performed in triplicates.
2.2.5. Apoptosis Assay
Early and late apoptotic cells were analyzed using the Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit I (BD Biosciences Pharmingen, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), following the recommended instructions. The cells were seeded in a 25 cm2 tissue culture flask (1 × 106 cells). After overnight incubation, the cells were exposed to 5 μg/mL of Fe3O4@PEG500 and Fe3O4@Chtiosan500 in a 1:1 PEG-chrysin and chitosan-chrysin ratio. A positive control was included consisting of 5 μg/mL of chrysin, a concentration previously validated for its efficacy against HCT 116 cells [34,35]. The cells were trypsinized and rinsed twice with phosphate-buffered saline-1% bovine serum albumin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, then resuspended in 100 μL of 1× binding buffer. Subsequently, an aliquot of 2.5 μL of propidium iodide (PI) and 0.5 μL of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) were added, and this was allowed to react for 15 min. Lastly, the fluorescence of the cells was measured after adding 100 μL of 1× binding buffer before being evaluated using BD FACSCanto™ II flow cytometers (BD Biosciences, New York, NY, USA, by Maxwell Becton and Fairleigh S. Dickinson) with FlowJo™ Software version 10.10 (Ashland, OR, USA: Becton, Dickinson & Company, 2017).
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were conducted using JMP software version 16 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA). The differences among multiple groups were analyzed using a one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s method for post-hoc comparisons. Differences with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
2.2.7. Declaration of Generative AI in Writing This Manuscript
We declare that the manuscript creation process did not involve the use of any AI tools to develop ideas, generate text, or improve the overall quality of content. During the writing process, conventional writing and proofreading tools such as Grammarly were involved to ensure grammatical accuracy and language refinement.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization and Structural Properties
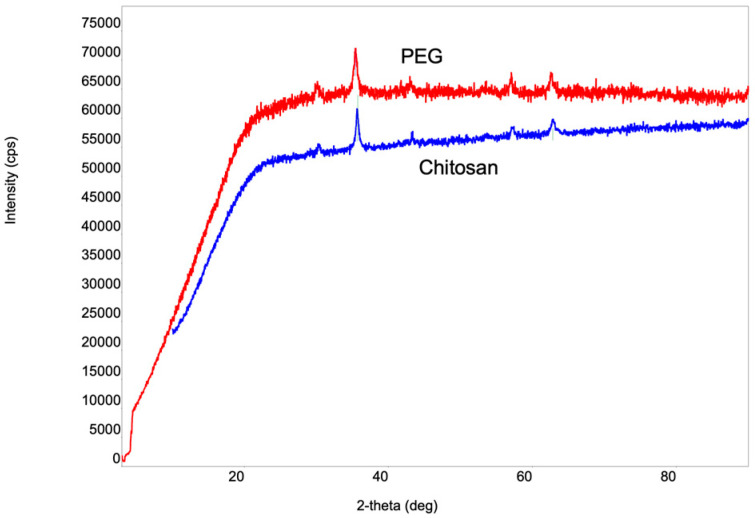
Examining the phase arrangement of the synthesized NPs holds significance in establishing correlations with various physicochemical properties. For phase identification, we employed XRD analysis. The selection of this method was based on its simplicity and its non-destructive impact on the samples. Figure 1 shows the X-ray structural images of the Fe3O4 NPs coated with various stabilizers.
Figure 1.
X-ray diffractogram of Fe3O4 NPs coated with PEG and chitosan. The crystal structure of the magnetite (Fe3O4) NPs synthesized via chemical co-precipitation and coated with PEG and chitosan was analyzed. Characteristic X-ray lines of magnetite NPs were observed in both samples. Therefore, the d-spacing values of the significant peaks match well (ICDD DB card number 01-073-9877).
The values of the 2-theta angle and crystallite size for the iron oxide NPs coated with PEG and chitosan are presented in Table 2. The values of the 2-theta angles obtained for both cases correspond to spinal-structured Fe3O4 particles with a cubic crystal lattice. Table 2 shows that the values of the 2-theta angles for the chitosan-coated nanoparticles shift to relatively larger angles compared to PEG-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles, which is manifested by the relative decrease in nanoparticle size.
Table 2.
The 2-theta angle values and crystallite sizes of iron oxide NPs coated with surface PEG and chitosan. The average crystallite sizes of magnetite NPs with different coatings were calculated according to Scherrer’s equation.
| Samples | 2-Theta Angle Values | Crystallite Size | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@PEG | 30.30° | 35.66° | 43.29° | 57.17° | 62.81° | 25.30 nm |
| Fe3O4@Chitosan | 30.37° | 35.74° | 43.45° | 57.5° | 62.83° | 25.10 nm |
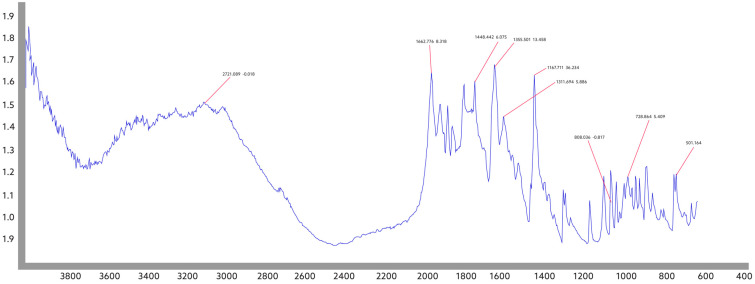
FTIR spectral analysis was conducted to determine the presence of functional groups in the samples. In addition to the synthesized samples, an FTIR spectrum was recorded for pure chrysin (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
FTIR spectrum of pure chrysin. FTIR spectrum for pure chrysin allows the evaluation of its molecular state.
The absorption band at 3012 cm−1 observed in the FTIR spectrum of chrysin corresponds to OH groups, the absorption band at 2926 cm−1 corresponds to CH groups, and the absorption band at 1652 cm−1 corresponds to the C=O carbonyl group. Additionally, the bands at 1610 cm−1, 1355 cm−1, 1245 cm−1, and 1167 cm−1 demonstrate the chain vibrations of C-C, C-OH, C=C, and C-O-C groups.
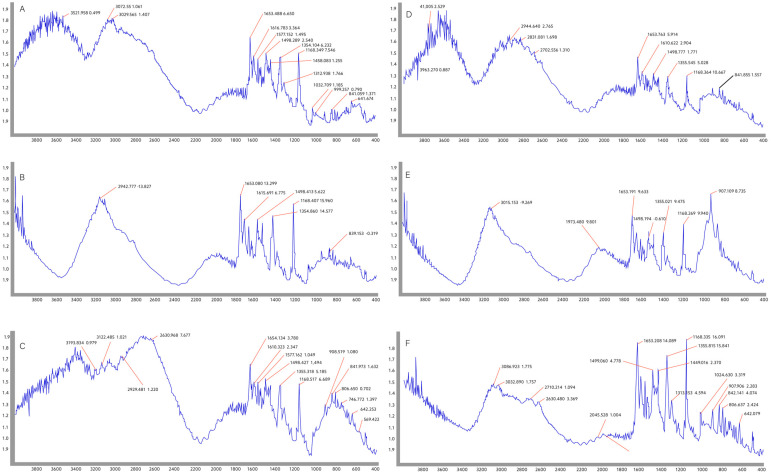
The FTIR spectrum of the samples obtained after attaching different amounts of chrysin on PEG and chitosan-coated magnetite NPs was comparatively studied (Figure 3A,B).
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of the samples obtained after attaching chrysin on Fe3O4@PEG and Fe3O4@chitosan in different ratios: (A) Fe3O4@PEG250 with a 1:0.5 PEG-chrysin ratio; (B) Fe3O4@PEG500 with a 1:1 PEG-chrysin ratio; (C) Fe3O4@PEG1000 with a 1:2 PEG-chrysin ratio; (D) Fe3O4@Chitosan250 with a 1:0.5 chitosan-chrysin ratio; (E) Fe3O4@Chitosan500 with a 1:1 chitosan-chrysin ratio; (F) Fe3O4@Chitosan1000 with a 1:2 chitosan-chrysin ratio. The characteristic peaks in the spectra indicate that PEG and chitosan-coated magnetite NPs were successfully synthesized, and the chrysin drug was loaded into them.
All chrysin-specific absorption bands were observed in the chrysin-loaded Fe3O4@PEG/samples (Figure 3A–C). The absorption bands at 1633 cm−1 and 1724 cm−1 observed in all the samples belong to PEG [35], and the changes observed in the range of 400–600 cm−1 belong to the Fe3O4 NPs [36]. There was no significant difference in the FTIR spectra of the chrysin Fe3O4@PEG system when varying the amount of the drug. For these samples, a slight change in the loading efficiency was determined depending on the initial amount of the drug (Table 3), which was confirmed by the almost unchanged structure in the FTIR spectra.
Table 3.
Results obtained from the UV–Vis and XRD analyses.
| Sample | Crystallite Size (XRD) | Loading Efficiency (UV–Vis) |
|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4@PEG250 | 164 Å | 92% |
| Fe3O4@PEG500 | 168 Å | 96% |
| Fe3O4@PEG1000 | 153 Å | 97% |
| Fe3O4@Chtiosan250 | 208 Å | 45% |
| Fe3O4@Chtiosan500 | 192 Å | 50% |
| Fe3O4@Chtiosan1000 | 175 Å | 58% |
In the FTIR spectrum of the chrysin-loaded Fe3O4@Chitosan system (Figure 3D–F), all absorption bands belonging to chrysin were observed. In the spectrum, the bands corresponding to 2921 cm−1 and 2877 cm−1 correspond to chitosan, and the peaks in the range of 400–600 cm−1 coincide with the absorption bands of Fe3O4. The intensity of the chitosan absorption bands, which is clearly visible in the spectrum at a 1:0.5 concentration of Fe3O4 and the drug substance, is weakened at the 1:1 and 1:2 concentrations. This shows that the amount of chrysin in the system increased (Table 3).
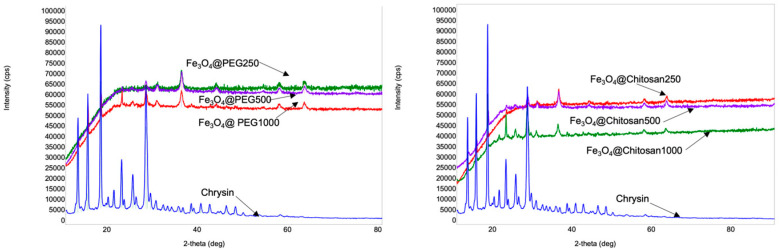
The comparative studies of the X-ray diffractograms were conducted on the samples obtained from magnetite NPs with different coating agents and loaded with various amounts of chrysin (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
X-ray diffractograms of the obtained samples based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with different polymers and loaded with various amounts of chrysin and pure chrysin. Fe3O4@PEG250, Fe3O4@PEG500 and Fe3O4@PEG1000 accordingly correspond to the Fe3O4@PEG and chrysin ratios of 1:0.5, 1:1, and 1:2. Fe3O4@Chtiosan250, Fe3O4@Chitosan500, and Fe3O4@Chitosan1000 accordingly correspond to Fe3O4@Chitosan and chrysin ratios of 1:0.5, 1:1, and 1:2.
The results obtained from the UV–Vis and XRD analyses are presented in a comparative manner in Table 3. The average crystallite sizes of the magnetite NPs with different coatings were calculated using Scherrer’s equation according to the diffraction peak at 35.4° [37]. Chrysin was detected at 276.4 nm. The drug-loading efficiency was determined as follows: LE = (The total amount of chrysin-the amount of free chrysin/the total amount of chrysin) × 100%.
A decrease in the size of the crystallites was observed in the chitosan-coated iron oxide NPs, with an increase in the amount of loaded chrysin in the NPs. In contrast, for PEG-stabilized NPs, no such regularity was observed between the drug concentration and crystallite size. There was a slight difference between the drug-loading efficiency values in Fe3O4@PEG500 and Fe3O4@PEG1000. There was a two-fold increase in the amount of drug compared to the amount of magnetite NPs, which did not lead to a significant increase in the loading efficiency. When chitosan was used as a coating material, the difference between the chrysin loading efficiency (Fe3O4@Chitosan500 and Fe3O4@Chitosan1000) values increased to 8%. While the variation of the drug amount depending on the amount of PEG-coated magnetite NPs had no significant effect on the loading efficiency, this was not observed in the case of chitosan-coated magnetite NPs. At the same time, when we look at the X-ray spectrum of pure chrysin, we see intense X-ray lines at 12.7°, 15°, 17.8°, and 27.8° values of 2-theta angles, which shows that chrysin has a highly crystalline nature. After loading chrysin on the surface of the nanoparticles, although the position of the characteristic peaks of chrysin was retained for all samples, their intensity decreased dramatically, and some of them completely disappeared. In the X-ray spectra of the samples coated with chitosan, although the intensities of the characteristic chrysin lines were reduced, they can be observed (Fe3O4@Chitosan250, Fe3O4@Chitosan500, and Fe3O4@Chitosan1000). In contrast, for the samples coated with PEG on the surface, only characteristic curve lines were partially observed for the Fe3O4@PEG1000 sample, where the amount of drug was twice the amount of nanoparticle. For the other samples (Fe3O4@PEG250 and Fe3O4@PEG500), most of the characteristic chrysin lines were overlapped by polymer noise. The available data suggest that this change in the X-ray spectrum of a drug with a high degree of crystallinity confirms its coverage on the nanoparticle surface [38,39,40]. Our X-ray studies show that drug-loading was more effective in PEG-coated nanoparticles. These results are in agreement with the results obtained from UV–Vis spectral analysis.
3.2. In-Vitro Cytotoxicity Analysis and Apoptosis Assay
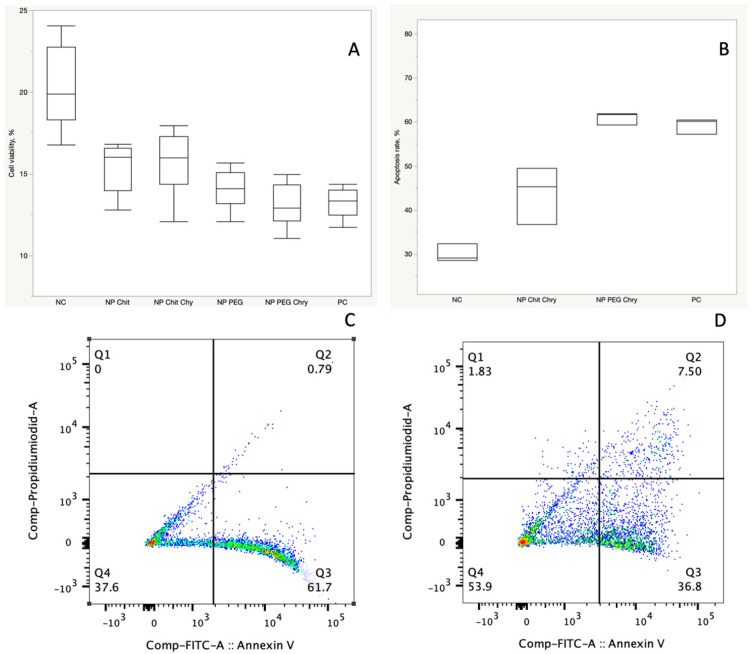
Our study employed the MTT cell viability assay to assess the cytotoxic effects of Fe3O4 NPs coated with PEG and chitosan at a 1:1 nanoparticle (Fe3O4@PEG500 versus Fe3O4@Chitosan500) and drug ratio to explore their anti-cancer activity. The HCT-116 cell lines were treated with concentrations ranging from 1 mg to 25 µg/mL for 24 h with both types of NPs. The inhibitory concentration (IC50) for HCT-116 cells following a 24-h treatment was determined to be 16.68 µg/mL. For subsequent investigations, an optimal concentration of 5 µg/mL was chosen for both the PEG and chitosan-coated Fe3O4 NPs, which was below the IC50 value. The IC50 value indicated that extended treatments for 48 and 72 h exhibited significant toxicity to the cells, leading us to exclusively focus on a 24-h treatment duration. The cell viability studies demonstrated that PEG-coated Fe3O4 NPs (Fe3O4@PEG500) exhibited a significantly higher inhibition of cells compared to their chitosan-coated counterparts at the same concentration (PNP_PEG_Chry vs. NP_Chit_Chry = 0.0033) (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
Cell viability and apoptosis rate under treatment with Fe3O4 NPs coated with PEG and chitosan. (A) Cell viability assessment using the MTT test with a 5 µg/mL treatment of Fe3O4@PEG500 with a 1:1 PEG-chrysin ratio and with 5µg/mL of Fe3O4@Chitosan500 with a 1:1 chitosan-chrysin ratio (PNP_PEG_Chry vs. NP_Chit_Chry = 0.0033). NC = negative control, where no treatment was administered. PC = positive control, where a treatment with 5 μg/mL of pure chrysin was applied. (B) Apoptosis rates following 48 h of treatment with Fe3O4@PEG500 and Fe3O4@Chitosan500 NPs, comparing the effects of coating with PEG versus chitosan. NC = negative control, representing the condition where no treatment was administered, serving as a control group. PC = positive control, representing the positive control group where a treatment of 5 μg/mL of chrysin was applied, serving as a reference for assessing the impact of the treatment with pure chrysin. (C) Representative images from the FACS experiments conducted after 48 h of treatment with Fe3O4@PEG500, inducing apoptosis in 61.7% of cells. (D) Representative images from the FACS experiments conducted after 48 h of treatment with Fe3O4@Chitosan500, inducing apoptosis in 36.8% of cells. Viable cells stain negative for both PI and Annexin V (Q4); early apoptotic cells stain positive for Annexin V and negative for PI (Q3); necrotic cells stain positive for PI only (Q1); and late apoptotic cells stain positive for both Annexin-V and PI (Q2). In order to make the text shorter we decided not include, because the image is self-descriptive.
Interestingly, the cell viability experiments revealed that PEG-coated Fe3O4 NPs without chrysin showed a significantly higher inhibitory effect than chitosan-coated Fe3O4 without chrysin at the same concentration (PNP_PEG vs. NP_Chit = 0.0471). Furthermore, both NPs coated with PEG and chitosan exhibited a suppressive impact on cell viability in the absence of chrysin (PNP_PEG vs. Control < 0.0001 and PNP_Chit vs. Control < 0.0001). The apoptosis assay revealed that following a 48-h treatment at 5 µg/mL, PEG-coated Fe3O4 NPs containing chrysin induced a significantly higher rate of apoptosis compared to chitosan-coated NPs (PNP_PEG_Chry vs. NP_Chit_Chry = 0.0004), whereas 24 h of treatment showed no significant difference. Specifically, the apoptotic response was more pronounced for the 1:1 PEG-chrysin ratio of 5 µg/mL Fe3O4@PEG500 than the 1:1 chitosan-chrysin ratio of 5 µg/mL Fe3O4@Chitosan500. These observations indicate that PEG-coated NPs have a more pronounced inhibitory effect on HCT-116 cells, underscoring their potential as a more effective cytotoxic agent in this context (Figure 5B). These findings contribute valuable insights into the differential cytotoxicity of coated Fe3O4 NPs, providing a basis for further exploration and optimization of nanoparticle formulations for enhanced anti-cancer applications.
4. Discussion
Optimizing nanoparticle coating conditions is essential for developing effective drug delivery systems, as interactions with biological fluids (blood, interstitial fluid, or mucosal secretions) lead to the formation of a protein layer, also known as a protein corona, around the nanoparticles, which can significantly influence their properties [41,42]. The development of strategies to produce nanoparticles with improved biocompatibility and lower immunogenicity is one of the main tasks of current studies, in which surface modifications to minimize protein adsorption and improve overall performance are one of the main directions [43].
Improving the loading efficiency of NPs by modifying their surface properties is a crucial aspect of enhancing the effectiveness of drug delivery systems [44]. Formulation parameters, including coating concentration, drug/carrier ratio, and nanoparticle synthesis method, need to be systematically optimized. Small changes to these parameters can have a significant impact on loading efficiency [45].
The modification of NPs with different coating agents shields the surface from aggregation [46]. Additionally, it alters their surface chemistry [47], reduces opsonization by proteins [48], and decreases phagocytosis by macrophages [49], thereby prolonging their circulation time. Moreover, particle surface modification can significantly influence their cellular uptake and toxicity.
In this study, we used a modified co-precipitation technique for the preparation of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles containing PEG and chitosan as stabilizing polymers and loaded them with the anti-tumor agent chrysin. There are limited studies on the development and characterization of magnetic drug transport systems loaded with chrysin. Nosrati et al. (2018) reported the synthesis of chrysin-loaded iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles coated with L-phenylalanine (chrysin@Phe@IOMNs), demonstrating the potential application of co-polymers with more complex structures in coatings or more than one drug substance as an effective drug carrier [50]. Another study investigated the loading of doxorubicin and chrysin onto magnetite nanoparticles coated with a PCL–PEG–PCL triblock co-polymer [51]. This study explored the factors influencing drug-loading efficiency, revealing positive effects on solubility properties, gradual drug release, and enhanced anti-tumor effects. Notably, the literature lacks studies on chrysin loading and the system characterization of magnetite nanoparticles coated with PEG or chitosan. Therefore, we studied the structure and anti-tumor efficacy of the system by varying the concentration of drug and coating materials to determine their optimal effective proportion that maximizes drug loading while maintaining system stability. In our study, the most efficient loading was observed in the presence of PEG as the coating agent, while a lower percentage of drug loading was noted when the chitosan polymer was used. This discrepancy can be attributed to chitosan’s hydrophobic property [52] creating a non-homogeneous environment in water. The drug was loaded into magnetite NPs using a non-covalent method during sample preparation. It is known that non-covalent interactions are stronger in homogeneous and dispersed environments than in non-homogeneous environments [53].
The change in the size of the crystallites determines the degree of order of the system [54,55]. From this perspective, it can be concluded that the variation in the loaded amount of chrysin does not affect the degree of crystallinity of PEG-coated NPs and, therefore, the regularity of the system. These results align with the UV–Vis results, indicating effective drug loading. Thus, for Fe3O4 NPs coated with PEG, a two-fold increase in drug amount does not practically affect the loading efficiency. However, there is a 33 Å difference in the sizes of crystallites obtained at 1:0.5 (Sample: Fe3O4@Chitosan250) and 1:2 (Sample: Fe3O4@Chtiosan1000) concentrations of chitosan-coated Fe3O4 NPs and drug concentrations. Such a difference in crystallite size for different amounts of loaded drug substance led to a 13% difference in the drug-loading efficiency.
Our cell culture experiments utilizing HCT 116 colon cancer cells validated the superiority of PEG coating over chitosan. Interestingly, both PEG and chitosan-coated NPs exhibited a statistically significant anti-cancer effect, even in the absence of the anti-cancer drug chrysin, when compared to the negative control. The selective cytotoxicity of iron oxide NPs in cancer cells compared to normal cells is a known phenomenon, underscoring the importance of conducting further investigations to achieve a comprehensive understanding of the underlying mechanisms [56]. The mechanisms being studied extensively in this context include the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect and the stimulation of magnetic hyperthermia in tumor tissues [57]. In direct comparison, PEG-coated Fe3O4 NPs demonstrated a stronger anti-cancer effect than their chitosan-coated counterparts. These findings underscore the potential of PEG-coated NPs as a more efficacious option for anti-cancer applications, warranting further exploration and consideration in the development of targeted cancer therapies.
PEG is a platform that provides several advantageous properties [58] within drug delivery, and one of them is ensuring the stability of nanosuspensions over a wide pH range. PEG-based nanostructures were also evaluated for extended circulation times [59]. The polysaccharides most widely used for modifying the surface of magnetic NPs include alginate, pullulan, chitosan, dextran, heparin, and starch [60,61]. Studies have reported that, for instance, the chitosan coating of Fe3O4 NPs leads to the formation of positively charged particles and enhances cellular uptake [62].
In conclusion, our study investigated the impact of coating agents on the structural properties and drug-loading efficiency of Fe3O4 NPs, specifically focusing on chitosan and PEG coatings. The XRD results revealed a notable trend: regardless of the type of coating agent, the presence of chrysin in varying amounts influenced the crystallite sizes. Remarkably, PEG-coated NPs consistently exhibited the smallest crystallite sizes even at the highest drug loading values, suggesting that the addition of chrysin did not disrupt the structural order of the PEG-coated system. This observation aligns with the loading efficiency results, indicating that PEG-coated NPs maintained their structural integrity and loading efficiency even with a two-fold excess of drug. In contrast, chitosan-coated NPs exhibited an increase in crystallite size with a corresponding rise in drug loading. This trend suggests that, unlike PEG, the regularity of the chitosan-coated system was affected by higher drug amounts, potentially impacting loading efficiency. Therefore, the optimal nanoparticle-to-drug ratio, ensuring maximum drug loading while maintaining structural regularity, was determined to be 1:1 for PEG-coated NPs. This finding highlights the robustness of PEG in preserving the order of the NP drug system even under increased drug-loading conditions. On the other hand, chitosan-coated NPs demonstrated a relative increase in loading efficiency with higher drug amounts, albeit at the expense of structural regularity. The potential consequence of reduced structural regularity in chitosan-coated systems was postulated to be an increased likelihood of recognition and removal by living organism cells as “dangerous” particles. This insight underscores the importance of considering not only the loading efficiency but also the structural impact of drug loading on the coated NPs, particularly for applications where the preservation of the nanoparticle structure is critical for therapeutic efficacy and safety. The beneficial role of PEG as a coating agent was emphasized in our cell culture experiments with HCT 116 colon carcinoma cells, wherein PEG-coated NPs exhibited a stronger inhibition of cell viability and a higher apoptosis rate compared to their chitosan-coated counterparts.
In summary, the selection of coating material plays a pivotal role in governing the structural response of drug-loaded NPs, with PEG demonstrating superior structural robustness even under high drug-loading conditions. These findings contribute valuable insights into the design and optimization of nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems for enhanced efficacy and biocompatibility.
Acknowledgments
We thank PAGEL (The Partnerships for the Health Sector in Developing Countries) program of the German Academic Exchange Service for supporting research cooperation between Azerbaijani and German scholars within this project.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K., V.Y. and H.S.; methodology, A.K. and S.H.; validation, S.H. and M.M.Y.; formal analysis, A.K., V.Y. and S.H.; investigation, A.K., S.H., S.N. and L.G.; resources, C.R. and S.B.; writing—V.Y., A.K. and H.S.; writing—review and editing, V.Y. and A.K.; visualization, A.K. and V.Y.; supervision, C.R. and V.Y.; project administration, V.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Funding Statement
This research received no external funding.
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
References
- 1.Yao Y., Zhou Y., Liu L., Xu Y., Chen Q., Wang Y., Wu S., Deng Y., Zhang J., Shao A. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery in cancer therapy and its role in overcoming drug resistance. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020;7:193. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Yagublu V., Karimova A., Hajibabazadeh J., Reissfelder C., Muradov M., Bellucci S., Allahverdiyev A. Overview of physicochemical properties of nanoparticles as drug carriers for targeted cancer therapy. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022;13:196. doi: 10.3390/jfb13040196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Guo X., Wei X., Chen Z., Zhang X., Yang G., Zhou S. Multifunctional nanoplatforms for subcellular delivery of drugs in cancer therapy. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020;107:100599. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2019.100599. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ulbrich K., Hola K., Subr V., Bakandritsos A., Tucek J., Zboril R. Targeted drug delivery with polymers and magnetic nanoparticles: Covalent and noncovalent approaches, release control, and clinical studies. Chem. Rev. 2016;116:5338–5431. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ramazanov M., Karimova A., Shirinova H. Magnetism for drug delivery, MRI and hyperthermia applications: A review. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021;11:8654–8668. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Włodarczyk A., Gorgoń S., Radoń A., Bajdak-Rusinek K. Magnetite nanoparticles in magnetic hyperthermia and cancer therapies: Challenges and perspectives. Nanomaterials. 2022;12:1807. doi: 10.3390/nano12111807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Thapa R.K., Kim J.O. Nanomedicine-based commercial formulations: Current developments and future prospects. J. Pharm. Investig. 2023;53:19–33. doi: 10.1007/s40005-022-00607-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jordan F., Naylor A., Kelly C., Howdle S., Lewis A., Illum L. Sustained release hGH microsphere formulation produced by a novel supercritical fluid technology: In vivo studies. J. Control. Release. 2010;141:153–160. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2009.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhu L., Zhou Z., Mao H., Yang L. Magnetic nanoparticles for precision oncology: Theranostic magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for image-guided and targeted cancer therapy. Nanomedicine. 2017;12:73–87. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2016-0316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chrishtop V.V., Mironov V.A., Prilepskii A.Y., Nikonorova V.G., Vinogradov V.V. Organ-specific toxicity of magnetic iron oxide-based nanoparticles. Nanotoxicology. 2021;15:167–204. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2020.1842934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Malhotra N., Lee J.-S., Liman R.A.D., Ruallo J.M.S., Villaflores O.B., Ger T.-R., Hsiao C.-D. Potential toxicity of iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles: A review. Molecules. 2020;25:3159. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gong D., Celi N., Zhang D., Cai J. Magnetic biohybrid microrobot multimers based on chlorella cells for enhanced targeted drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2022;14:6320–6330. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c16859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chrastina A., Massey K.A., Schnitzer J.E. Overcoming in vivo barriers to targeted nanodelivery. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2011;3:421–437. doi: 10.1002/wnan.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Abbasi R., Shineh G., Mobaraki M., Doughty S., Tayebi L. Structural parameters of nanoparticles affecting their toxicity for biomedical applications: A review. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2023;25:43. doi: 10.1007/s11051-023-05690-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Park Y.C., Smith J.B., Pham T., Whitaker R.D., Sucato C.A., Hamilton J.A., Bartolak-Suki E., Wong J.Y. Effect of PEG molecular weight on stability, T2 contrast, cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces. 2014;119:106–114. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2014.04.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Prabhu S., Mutalik S., Rai S., Udupa N., Rao B.S.S. PEGylation of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle for drug delivery applications with decreased toxicity: An in vivo study. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015;17:412. doi: 10.1007/s11051-015-3216-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dadfar S.M., Roemhild K., Drude N.I., von Stillfried S., Knüchel R., Kiessling F., Lammers T. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Diagnostic, therapeutic and theranostic applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019;138:302–325. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Szekeres M., Tóth I.Y., Illés E., Hajdú A., Zupkó I., Farkas K., Oszlánczi G., Tiszlavicz L., Tombácz E. Chemical and colloidal stability of carboxylated core-shell magnetite nanoparticles designed for biomedical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013;14:14550–14574. doi: 10.3390/ijms140714550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Friedrich B., Auger J.-P., Dutz S., Cicha I., Schreiber E., Band J., Boccacccini A.R., Krönke G., Alexiou C., Tietze R. Hydroxyapatite-coated SPIONs and their influence on cytokine release. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:4143. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tóth I.Y., Illés E., Szekeres M., Zupkó I., Turcu R., Tombácz E. Chondroitin-Sulfate-A-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Testing to Predict Their Colloidal Behavior in Biological Milieu. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:4096. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Giraldo-Villegas M., Urquijo J., Arnache-Olmos O.L., Rojas-López M. Polyacrylic acid-coated iron oxide nanoparticles could be a useful tool for tracking inflammatory monocytes. Future Sci. OA. 2019;5:FSO423. doi: 10.2144/fsoa-2019-0066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schubert J., Chanana M. Coating matters: Review on colloidal stability of nanoparticles with biocompatible coatings in biological media, living cells and organisms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018;25:4553–4586. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180601101859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Thunemann A., Schutt D., Kaufner L., Pison U., Mohwald H. Maghemite nanoparticles protectively coated with poly (ethylene imine) and poly (ethylene oxide)-block-poly (glutamic acid) Langmuir. 2006;22:2351–2357. doi: 10.1021/la052990d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.McBain S.C., Yiu H.H., Dobson J. Magnetic nanoparticles for gene and drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008;3:169–180. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s1608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nathanael A.J., Oh T.H. Biopolymer coatings for biomedical applications. Polymers. 2020;12:3061. doi: 10.3390/polym12123061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chang B., Sha X., Guo J., Jiao Y., Wang C., Yang W. Thermo and pH dual responsive, polymer shell coated, magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release. J. Mater. Chem. 2011;21:9239–9247. doi: 10.1039/c1jm10631g. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Langer R. Drug delivery and targeting. Nature. 1998;392:5–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cao J., Guenther R.H., Sit T.L., Opperman C.H., Lommel S.A., Willoughby J.A. Loading and release mechanism of red clover necrotic mosaic virus derived plant viral nanoparticles for drug delivery of doxorubicin. Small. 2014;10:5126–5136. doi: 10.1002/smll.201400558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wu W. nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. IOP Publ. 2015;16:23501. doi: 10.1088/1468-6996/16/2/023501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xu H., Cheng L., Wang C., Ma X., Li Y., Liu Z. Polymer encapsulated upconversion nanoparticle/iron oxide nanocomposites for multimodal imaging and magnetic targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials. 2011;32:9364–9373. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Talebi M., Talebi M., Farkhondeh T., Simal-Gandara J., Kopustinskiene D.M., Bernatoniene J., Samarghandian S. Emerging cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying anticancer indications of chrysin. Cancer Cell Int. 2021;21:214. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-01906-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Petcharoen K., Sirivat A. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles via the chemical co-precipitation method. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 2012;177:421–427. doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2012.01.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Singh R., Lillard Jr J.W. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009;86:215–223. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2008.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Devi S.V., Prakash T. Kinetics of cisplatin release by in-vitro using poly (D, L-Lactide) coated Fe3O4 Nanocarriers. IEEE Trans. NanoBioscience. 2013;12:60–63. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2012.2230024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wallyn J., Anton N., Vandamme T.F. Synthesis, principles, and properties of magnetite nanoparticles for in vivo imaging applications—A review. Pharmaceutics. 2019;11:601. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11110601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Martínez-Cabanas M., López-García M., Barriada J.L., Herrero R., de Vicente M.E.S. Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. Development of magnetic hybrid materials for efficient As (V) removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2016;301:83–91. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.149. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Antarnusa G., Suharyadi E. A synthesis of polyethylene glycol (PEG)-coated magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their characteristics for enhancement of biosensor. Mater. Res. Express. 2020;7:056103. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab8bef. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sundararajan M., Thomas P.A., Venkadeswaran K., Jeganathan K., Geraldine P. Synthesis and characterization of chrysin-loaded β-cyclodextrin-based nanosponges to enhance in-vitro solubility, photostability, drug release, antioxidant effects and antitumorous efficacy. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017;17:8742–8751. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2017.13911. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gupta N., Rajera R., Nagpal M., Arora S. Primaquine loaded chitosan nanoparticles for liver targeting. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2013;1:35–43. doi: 10.2174/2211738511301010035. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chadha R., Bhalla Y., Nandan A., Chadha K., Karan M. Chrysin cocrystals: Characterization and evaluation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017;134:361–371. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Saptarshi S.R., Duschl A., Lopata A.L. Interaction of nanoparticles with proteins: Relation to bio-reactivity of the nanoparticle. J. Nanobiotechnology. 2013;11:26. doi: 10.1186/1477-3155-11-26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Cedervall T., Lynch I., Foy M., Berggård T., Donnelly S.C., Cagney G., Linse S., Dawson K.A. Detailed identification of plasma proteins adsorbed on copolymer nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007;46:5754–5756. doi: 10.1002/anie.200700465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Malachowski T., Hassel A. Engineering nanoparticles to overcome immunological barriers for enhanced drug delivery. Eng. Regen. 2020;1:35–50. doi: 10.1016/j.engreg.2020.06.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Siafaka P.I., Üstündağ Okur N., Karavas E., Bikiaris D.N. Surface modified multifunctional and stimuli responsive nanoparticles for drug targeting: Current status and uses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016;17:1440. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rafiei P., Haddadi A. A robust systematic design: Optimization and preparation of polymeric nanoparticles of PLGA for docetaxel intravenous delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2019;104:109950. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.109950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bilal M., Iqbal H.M., Adil S.F., Shaik M.R., Abdelgawad A., Hatshan M.R., Khan M. Surface-coated magnetic nanostructured materials for robust bio-catalysis and biomedical applications-A review. J. Adv. Res. 2022;38:157–177. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.09.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yusuf A., Almotairy A.R.Z., Henidi H., Alshehri O.Y., Aldughaim M.S. Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of the implication of nanoparticles’ physicochemical properties on responses in biological systems. Polymers. 2023;15:1596. doi: 10.3390/polym15071596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tavano R., Gabrielli L., Lubian E., Fedeli C., Visentin S., Polverino De Laureto P., Arrigoni G., Geffner-Smith A., Chen F., Simberg D. C1q-mediated complement activation and C3 opsonization trigger recognition of stealth poly (2-methyl-2-oxazoline)-coated silica nanoparticles by human phagocytes. ACS Nano. 2018;12:5834–5847. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b01806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Qie Y., Yuan H., Von Roemeling C.A., Chen Y., Liu X., Shih K.D., Knight J.A., Tun H.W., Wharen R.E., Jiang W. Surface modification of nanoparticles enables selective evasion of phagocytic clearance by distinct macrophage phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:26269. doi: 10.1038/srep26269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Nosrati H., Javani E., Salehiabar M., Manjili H.K., Davaran S., Danafar H. Biocompatibility and anticancer activity of L-phenyl alanine-coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles as potential chrysin delivery system. J. Mater. Res. 2018;33:1602–1611. doi: 10.1557/jmr.2018.148. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Jahangiri S., Amirkhani L., Akbarzadeh A., Hajimohammadi R. Encapsulation of Doxorubicin and Chrysin on magnetic PCLPEG-PCL nanoparticles: Optimization of parameters and drug delivery evaluation. Int. J. Nano Dimens. 2021;12:380–392. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sundaresan V., Menon J.U., Rahimi M., Nguyen K.T., Wadajkar A.S. Dual-responsive polymer-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for drug delivery and imaging applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2014;466:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.03.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hauser A.K., Mathias R., Anderson K.W., Hilt J.Z. The effects of synthesis method on the physical and chemical properties of dextran coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2015;160:177–186. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.04.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Reyes-Ortega F., Delgado Á.V., Schneider E.K., Checa Fernández B., Iglesias G. Magnetic nanoparticles coated with a thermosensitive polymer with hyperthermia properties. Polymers. 2017;10:10. doi: 10.3390/polym10010010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Namikuchi E.A., Gaspar R.D., da Silva D.S., Raimundo I.M., Mazali I.O. PEG size effect and its interaction with Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by solvothermal method: Morphology and effect of pH on the stability. Nano Express. 2021;2:020022. doi: 10.1088/2632-959X/ac0596. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Mohsin M.H., Khashan K.S., Sulaiman G.M., Mohammed H.A., Qureshi K.A., Aspatwar A. A novel facile synthesis of metal nitride@ metal oxide (BN/Gd2O3) nanocomposite and their antibacterial and anticancer activities. Sci. Rep. 2023;13:22749. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49895-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Abu-Huwaij R., Al-Assaf S.F., Mousli F., Kutkut M.S., Al-Bashtawi A. Perceptive review on properties of iron oxide nanoparticles and their antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Syst. Rev. Pharm. 2020;11:418–431. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Suk J.S., Xu Q., Kim N., Hanes J., Ensign L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016;99:28–51. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dunn S.E., Brindley A., Davis S.S., Davies M.C., Illum L. Polystyrene-poly (ethylene glycol)(PS-PEG2000) particles as model systems for site specific drug delivery. 2. The effect of PEG surface density on the in vitro cell interaction and in vivo biodistribution. Pharm. Res. 1994;11:1016–1022. doi: 10.1023/A:1018939521589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Uthaman S., Lee S.J., Cherukula K., Cho C.-S., Park I.-K. Polysaccharide-coated magnetic nanoparticles for imaging and gene therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2015;2015:959175. doi: 10.1155/2015/959175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Doh K.-O., Yeo Y. Application of polysaccharides for surface modification of nanomedicines. Ther. Deliv. 2012;3:1447–1456. doi: 10.4155/tde.12.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Aibani N., Rai R., Patel P., Cuddihy G., Wasan E.K. Chitosan nanoparticles at the biological interface: Implications for drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1686. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within the article.