Abstract
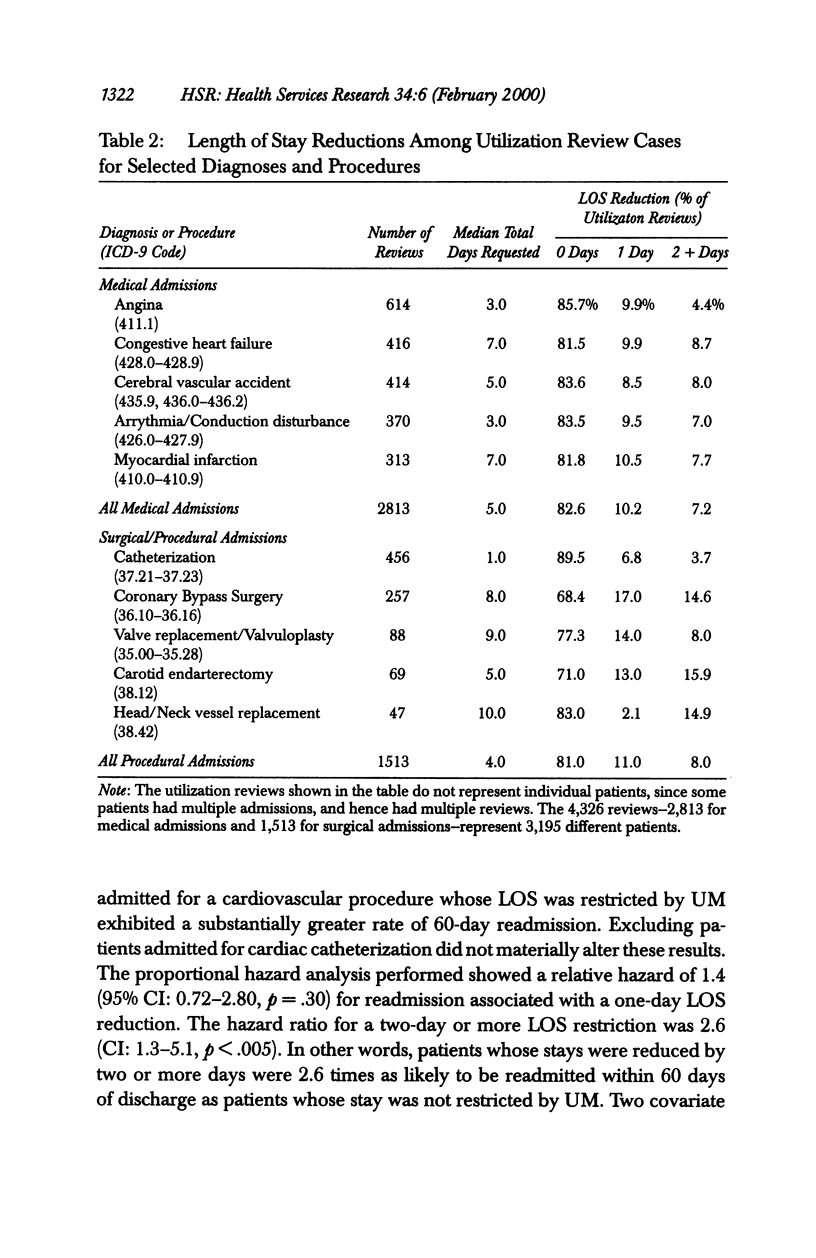
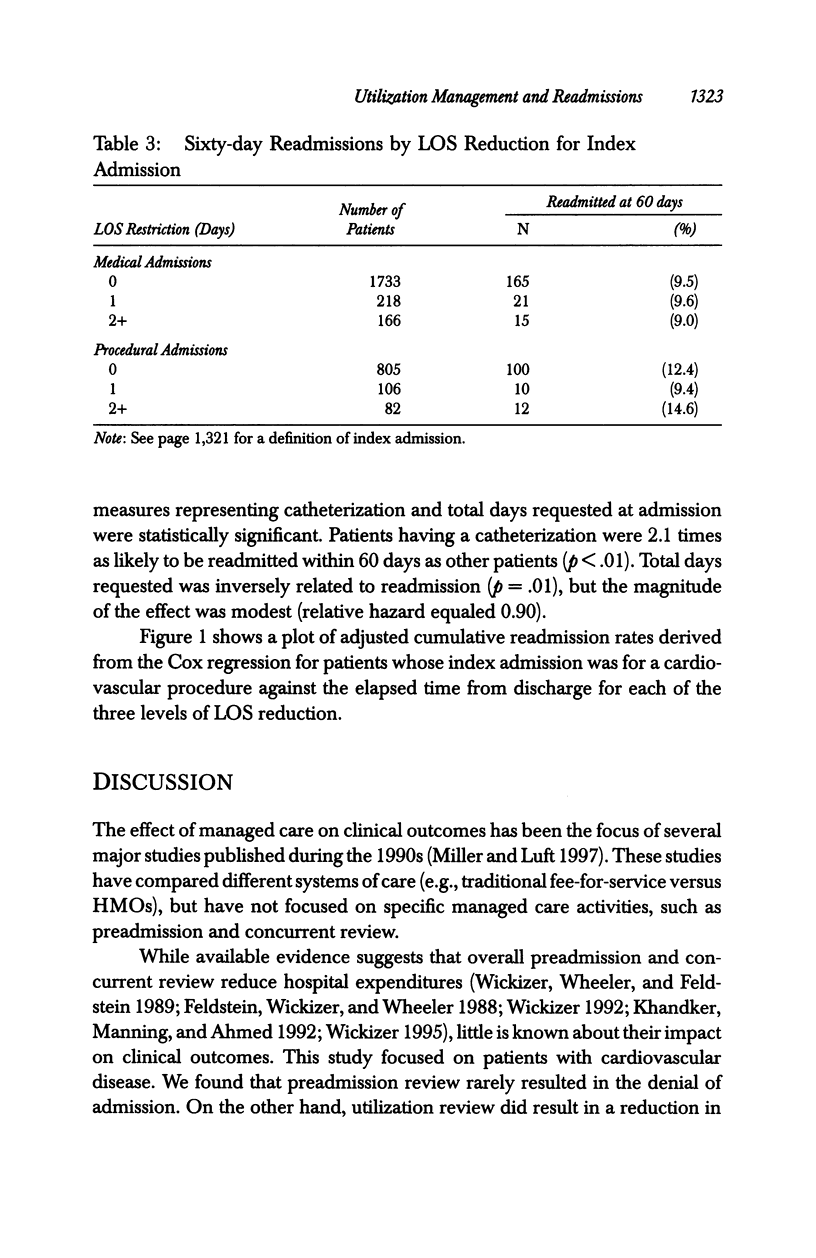
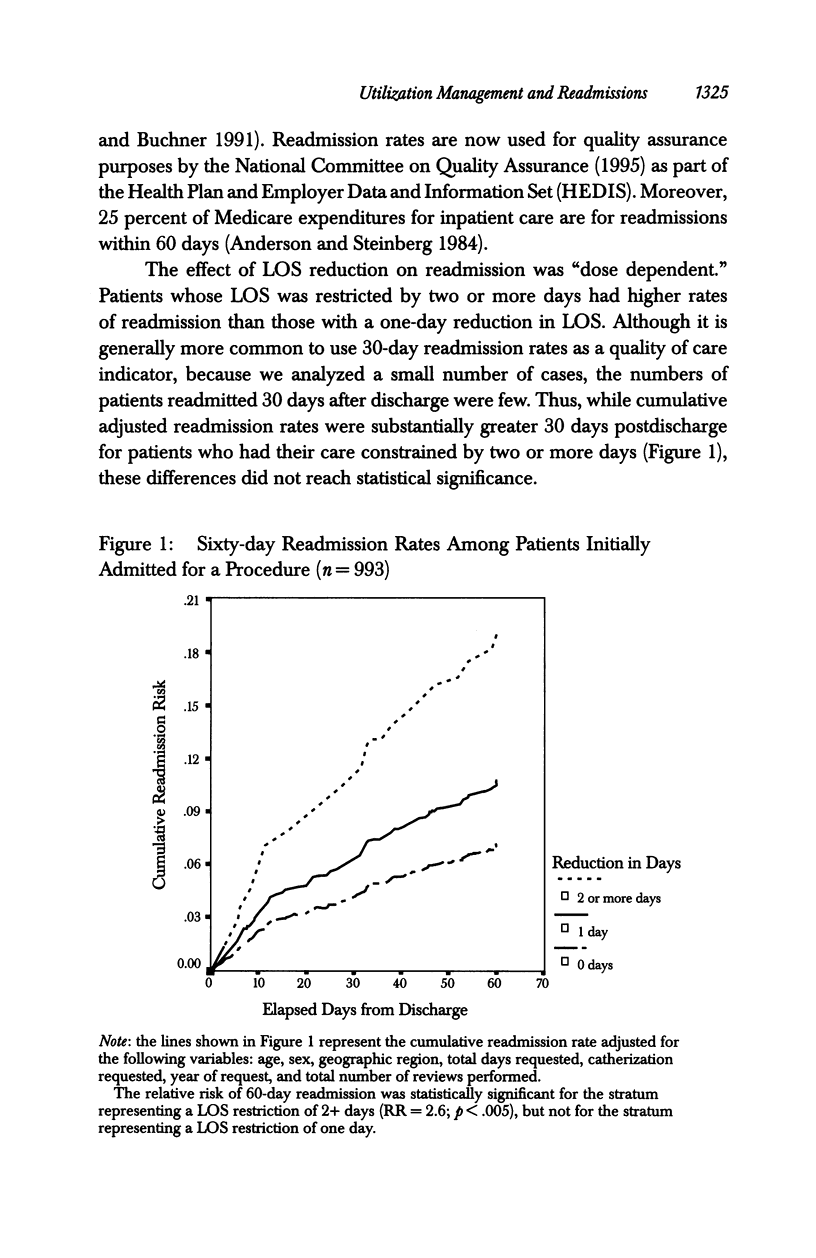
OBJECTIVE: To determine if prospective utilization reviews that lead to reduced hospital length of stay (LOS) relative to days requested by an attending physician affect the likelihood of readmission for privately insured patients with cardiovascular disease. DATA SOURCES: Data obtained from a private insurance company on utilization management decisions from 1989 through 1993. During this five-year period, 39,117 inpatient reviews were conducted, 4,326 (11.1 percent) on patients with cardiovascular disease. We selected for analysis all 4,326 reviews performed on patients with cardiovascular disease. STUDY DESIGN: We used proportional hazard analysis (Cox regression) to investigate the relationship between LOS reductions relative to days requested by a patient's attending physician and the likelihood of readmission within 60 days of discharge. Separate analyses were performed for medical and procedural admissions. PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: There were 2,813 requests for medical admission, and 1,513 requests for procedural admission. Requests for admission were rarely denied. Length of stay was reduced relative to that requested by the treating physician for 17 percent and 19 percent of medical and procedural admissions, respectively. Cumulative 60-day readmission rates were 9.5 percent for medical admissions and 12.3 percent for procedural admissions. We found no relationship between LOS reduction and the likelihood of readmission for medical admissions. However, patients admitted for procedures who had their length of stay reduced by two or more days were 2.6 times as likely to be readmitted within 60 days as those who had no reduction in their length of stay (95% CI: 1.3-5.1; p < .005). CONCLUSIONS: Utilization management (UM) rarely denies requests for inpatient treatment of cardiovascular disease. The association between LOS reduction and the likelihood of readmission for patients admitted for cardiovascular procedures raises concern that UM may adversely affect clinical outcome for some patients. Further research is needed to definitively elucidate any relationship that might exist between utilization review decisions and quality of care.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. F., Steinberg E. P. Hospital readmissions in the Medicare population. N Engl J Med. 1984 Nov 22;311(21):1349–1353. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198411223112105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton C. M., Del Junco D. J., Souchek J., Wray N. P., Mansyur C. L. The association between the quality of inpatient care and early readmission: a meta-analysis of the evidence. Med Care. 1997 Oct;35(10):1044–1059. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199710000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashton C. M., Kuykendall D. H., Johnson M. L., Wray N. P., Wu L. The association between the quality of inpatient care and early readmission. Ann Intern Med. 1995 Mar 15;122(6):415–421. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-122-6-199503150-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailit H. L., Sennett C. Utilization management as a cost-containment strategy. Health Care Financ Rev Annu Suppl. 1991:87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. J., Hilborne L. H., Leape L. L., Fiske M. E., Park R. E., Kamberg C. J., Brook R. H. The appropriateness of use of coronary angiography in New York State. JAMA. 1993 Feb 10;269(6):766–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brook R. H., Lohr K. N. Monitoring quality of care in the Medicare program. Two proposed systems. JAMA. 1987 Dec 4;258(21):3138–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassin M. R., Brook R. H., Park R. E., Keesey J., Fink A., Kosecoff J., Kahn K., Merrick N., Solomon D. H. Variations in the use of medical and surgical services by the Medicare population. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jan 30;314(5):285–290. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198601303140505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassin M. R., Kosecoff J., Park R. E., Winslow C. M., Kahn K. L., Merrick N. J., Keesey J., Fink A., Solomon D. H., Brook R. H. Does inappropriate use explain geographic variations in the use of health care services? A study of three procedures. JAMA. 1987 Nov 13;258(18):2533–2537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesHarnais S., McMahon L. F., Jr, Wroblewski R. Measuring outcomes of hospital care using multiple risk-adjusted indexes. Health Serv Res. 1991 Oct;26(4):425–445. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ermann D. Hospital utilization review: past experience, future directions. J Health Polit Policy Law. 1988 Winter;13(4):683–704. doi: 10.1215/03616878-13-4-683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldstein P. J., Wickizer T. M., Wheeler J. R. Private cost containment. The effects of utilization review programs on health care use and expenditures. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1310–1314. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Hurley R., Lake T., Ensor T., Berenson R. A national survey of the arrangements managed-care plans make with physicians. N Engl J Med. 1995 Dec 21;333(25):1678–1683. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199512213332505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graboys T. B., Biegelsen B., Lampert S., Blatt C. M., Lown B. Results of a second-opinion trial among patients recommended for coronary angiography. JAMA. 1992 Nov 11;268(18):2537–2540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guadagnoli E., Hauptman P. J., Ayanian J. Z., Pashos C. L., McNeil B. J., Cleary P. D. Variation in the use of cardiac procedures after acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1995 Aug 31;333(9):573–578. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199508313330908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway J. J., Thomas J. W. Factors influencing readmission risk: implications for quality monitoring. Health Care Financ Rev. 1989 Winter;11(2):19–32. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper K. J. Medically inappropriate hospital use in a pediatric population. N Engl J Med. 1988 Apr 21;318(16):1033–1037. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198804213181605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandker R. K., Manning W. G., Ahmed T. Utilization review savings at the micro level. Med Care. 1992 Nov;30(11):1043–1052. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199211000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman L. C., Boyd E. A., Heritage J. C. Adherence to prescribed explicit criteria during utilization review. An analysis of communications between attending and reviewing physicians. JAMA. 1997 Aug 13;278(6):497–501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludke R. L., Booth B. M., Lewis-Beck J. A. Relationship between early readmission and hospital quality of care indicators. Inquiry. 1993 Spring;30(1):95–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Luft H. S. Does managed care lead to better or worse quality of care? Health Aff (Millwood) 1997 Sep-Oct;16(5):7–25. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.16.5.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilote L., Califf R. M., Sapp S., Miller D. P., Mark D. B., Weaver W. D., Gore J. M., Armstrong P. W., Ohman E. M., Topol E. J. Regional variation across the United States in the management of acute myocardial infarction. GUSTO-1 Investigators. Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activator for Occluded Coronary Arteries. N Engl J Med. 1995 Aug 31;333(9):565–572. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199508313330907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. L., Pearlman R. A., Buchner D. M. Risk factors for early unplanned hospital readmission in the elderly. J Gen Intern Med. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):223–228. doi: 10.1007/BF02598964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restuccia J. D., Kreger B. E., Payne S. M., Gertman P. M., Dayno S. J., Lenhart G. M. Factors affecting appropriateness of hospital use in Massachusetts. Health Care Financ Rev. 1986 Fall;8(1):47–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice T. Containing health care costs in the United States. Med Care Rev. 1992 Spring;49(1):19–65. doi: 10.1177/002570879204900103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. N., Allen D. R., Handte J. S., Jackson T. C., Leto L., Rodstein B. M., Stratton S. D., Westfall G., Yasser R. Effect of utilization review in a fee-for-service health insurance plan. N Engl J Med. 1995 Nov 16;333(20):1326–1330. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511163332006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler R. M., Sullivan S. D., Ko T. H. The impact of Blue Cross and Blue Shield Plan utilization management programs, 1980-1988. Inquiry. 1991 Fall;28(3):263–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu A. L., Sonnenberg F. A., Manning W. G., Goldberg G. A., Bloomfield E. S., Newhouse J. P., Brook R. H. Inappropriate use of hospitals in a randomized trial of health insurance plans. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 13;315(20):1259–1266. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611133152005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan C. B., Miller M., Feldman R., Dowd B. Employer-sponsored health insurance in 1991. Health Aff (Millwood) 1992 Winter;11(4):172–185. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.11.4.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. W., Holloway J. J. Investigating early readmission as an indicator for quality of care studies. Med Care. 1991 Apr;29(4):377–394. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199104000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wennberg J., Gittelsohn A. Variations in medical care among small areas. Sci Am. 1982 Apr;246(4):120–134. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0482-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickizer T. M. Controlling outpatient medical equipment costs through utilization management. Med Care. 1995 Apr;33(4):383–391. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199504000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickizer T. M., Lessler D., Boyd-Wickizer J. Effects of health care cost-containment programs on patterns of care and readmissions among children and adolescents. Am J Public Health. 1999 Sep;89(9):1353–1358. doi: 10.2105/ajph.89.9.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickizer T. M., Lessler D. Do treatment restrictions imposed by utilization management increase the likelihood of readmission for psychiatric patients? Med Care. 1998 Jun;36(6):844–850. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199806000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickizer T. M., Lessler D., Franklin G. Controlling workers' compensation medical care use and costs through utilization management. J Occup Environ Med. 1999 Aug;41(8):625–631. doi: 10.1097/00043764-199908000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickizer T. M., Lessler D., Travis K. M. Controlling inpatient psychiatric utilization through managed care. Am J Psychiatry. 1996 Mar;153(3):339–345. doi: 10.1176/ajp.153.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickizer T. M., Wheeler J. R., Feldstein P. J. Does utilization review reduce unnecessary hospital care and contain costs? Med Care. 1989 Jun;27(6):632–647. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198906000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P., Tedeschi P. Community correlates of hospital use. Health Serv Res. 1984 Aug;19(3):333–355. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer J. G. Length of stay and hospital bed misutilization. Med Care. 1974 May;12(5):453–462. doi: 10.1097/00005650-197405000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


