Abstract
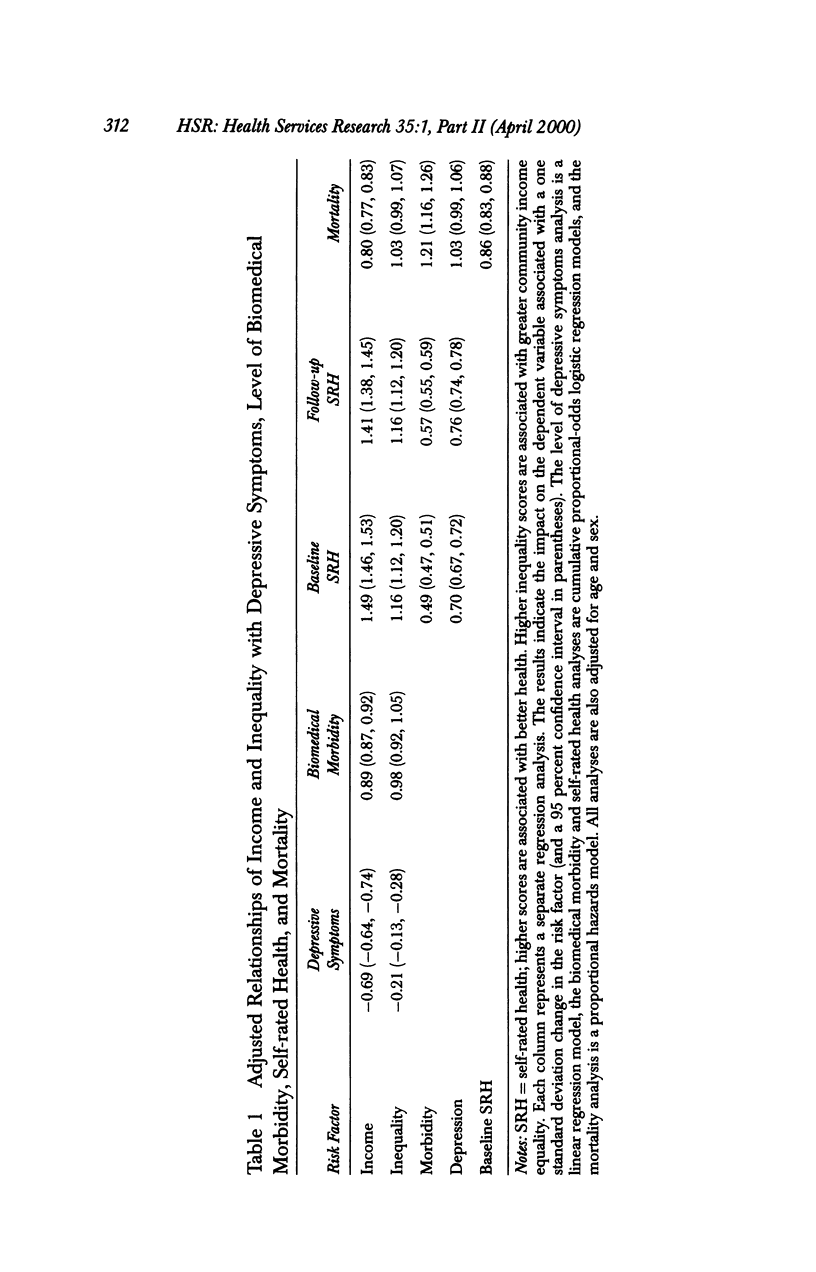
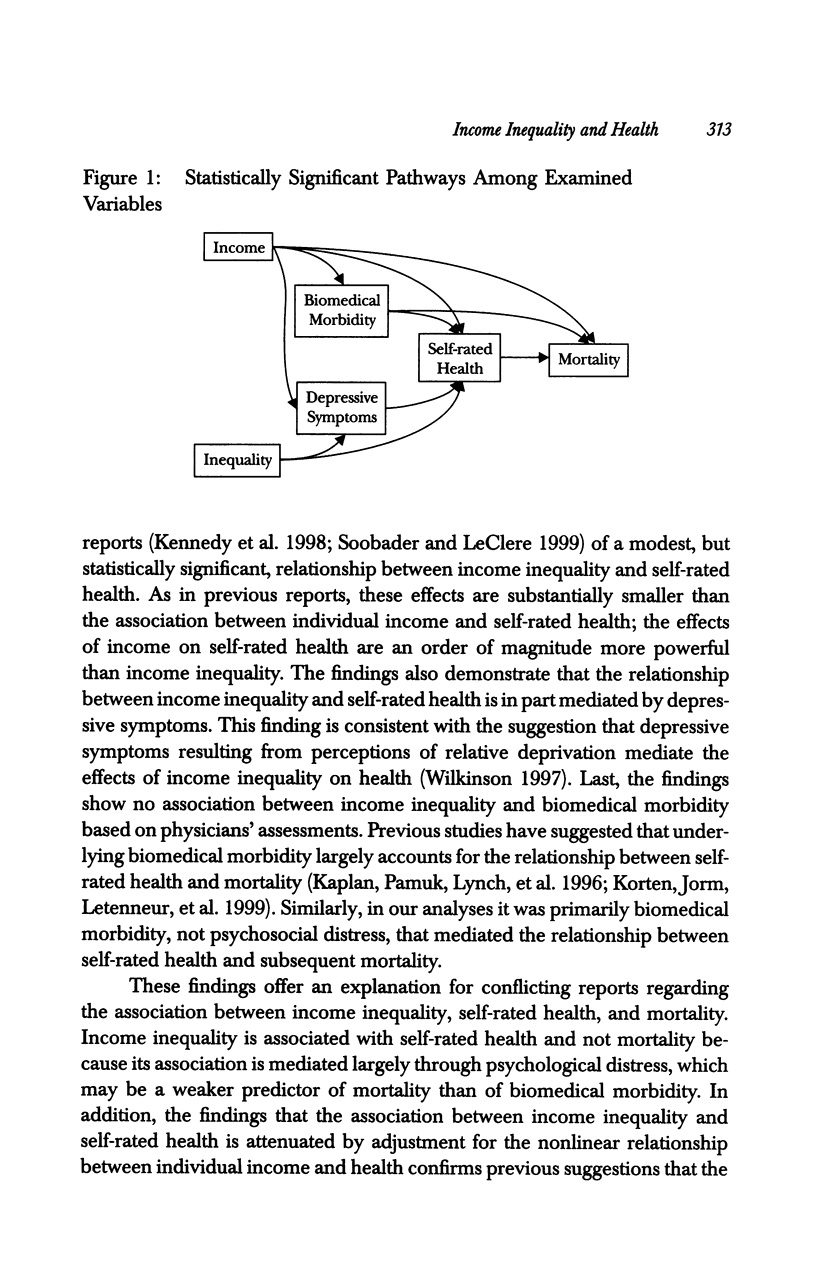
OBJECTIVE: To examine the pathways between income inequality, self-rated health, and mortality in the United States. DATA SOURCE: The first National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey and Epidemiologic Follow-up Study. DESIGN: This was a longitudinal, multilevel study. DATA COLLECTION: Baseline data were collected on county income inequality, individual income, age, sex, self-rated health, level of depressive symptoms, and severity of biomedical morbidity from physical examination. Follow-up data included self-rated health assessed in 1982 through 1984 and mortality through 1987. PRINCIPAL FINDINGS: After adjustment for age and sex, income inequality had a modest independent effect on the level of depressive symptoms, and on baseline and follow-up self-rated health, but no independent effect on biomedical morbidity or subsequent mortality. Individual income had a larger effect on severity of biomedical morbidity, level of depressive symptoms, baseline and follow-up self-rated health, and mortality. CONCLUSION: Income inequality appears to have a small effect on self-rated health but not mortality; the effect is mediated in part by psychological, but not biomedical pathways. Individual income has a much larger effect on all of the health pathways.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anda R., Williamson D., Jones D., Macera C., Eaker E., Glassman A., Marks J. Depressed affect, hopelessness, and the risk of ischemic heart disease in a cohort of U.S. adults. Epidemiology. 1993 Jul;4(4):285–294. doi: 10.1097/00001648-199307000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Shlomo Y., White I. R., Marmot M. Does the variation in the socioeconomic characteristics of an area affect mortality? BMJ. 1996 Apr 20;312(7037):1013–1014. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7037.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosma H., van de Mheen H. D., Mackenbach J. P. Social class in childhood and general health in adulthood: questionnaire study of contribution of psychological attributes. BMJ. 1999 Jan 2;318(7175):18–22. doi: 10.1136/bmj.318.7175.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly M. C., Duncan G. J., Kaplan G. A., Lynch J. W. Macro-to-micro links in the relation between income inequality and mortality. Milbank Q. 1998;76(3):315-39, 303-4. doi: 10.1111/1468-0009.00094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everson S. A., Goldberg D. E., Kaplan G. A., Cohen R. D., Pukkala E., Tuomilehto J., Salonen J. T. Hopelessness and risk of mortality and incidence of myocardial infarction and cancer. Psychosom Med. 1996 Mar-Apr;58(2):113–121. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199603000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio A. F. A concurrent validational study of the NCHS General Well-Being Schedule. Vital Health Stat 2. 1977 Sep;(73):1–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiscella K., Franks P. Poverty or income inequality as predictor of mortality: longitudinal cohort study. BMJ. 1997 Jun 14;314(7096):1724–1727. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7096.1724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasure-Smith N., Lespérance F., Talajic M. Depression following myocardial infarction. Impact on 6-month survival. JAMA. 1993 Oct 20;270(15):1819–1825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravelle H. How much of the relation between population mortality and unequal distribution of income is a statistical artefact? BMJ. 1998 Jan 31;316(7128):382–385. doi: 10.1136/bmj.316.7128.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idler E. L., Benyamini Y. Self-rated health and mortality: a review of twenty-seven community studies. J Health Soc Behav. 1997 Mar;38(1):21–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G. A., Goldberg D. E., Everson S. A., Cohen R. D., Salonen R., Tuomilehto J., Salonen J. Perceived health status and morbidity and mortality: evidence from the Kuopio ischaemic heart disease risk factor study. Int J Epidemiol. 1996 Apr;25(2):259–265. doi: 10.1093/ije/25.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G. A., Pamuk E. R., Lynch J. W., Cohen R. D., Balfour J. L. Inequality in income and mortality in the United States: analysis of mortality and potential pathways. BMJ. 1996 Apr 20;312(7037):999–1003. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7037.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B. P., Kawachi I., Glass R., Prothrow-Stith D. Income distribution, socioeconomic status, and self rated health in the United States: multilevel analysis. BMJ. 1998 Oct 3;317(7163):917–921. doi: 10.1136/bmj.317.7163.917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy B. P., Kawachi I., Prothrow-Stith D. Income distribution and mortality: cross sectional ecological study of the Robin Hood index in the United States. BMJ. 1996 Apr 20;312(7037):1004–1007. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7037.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korten A. E., Jorm A. F., Jiao Z., Letenneur L., Jacomb P. A., Henderson A. S., Christensen H., Rodgers B. Health, cognitive, and psychosocial factors as predictors of mortality in an elderly community sample. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1999 Feb;53(2):83–88. doi: 10.1136/jech.53.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz P. M., House J. S., Lepkowski J. M., Williams D. R., Mero R. P., Chen J. Socioeconomic factors, health behaviors, and mortality: results from a nationally representative prospective study of US adults. JAMA. 1998 Jun 3;279(21):1703–1708. doi: 10.1001/jama.279.21.1703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. W., Kaplan G. A., Pamuk E. R., Cohen R. D., Heck K. E., Balfour J. L., Yen I. H. Income inequality and mortality in metropolitan areas of the United States. Am J Public Health. 1998 Jul;88(7):1074–1080. doi: 10.2105/ajph.88.7.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madans J. H., Cox C. S., Kleinman J. C., Makuc D., Feldman J. J., Finucane F. F., Barbano H. E., Cornoni-Huntley J. 10 years after NHANES I: mortality experience at initial followup, 1982-84. Public Health Rep. 1986 Sep-Oct;101(5):474–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern H. Ecologic studies in epidemiology: concepts, principles, and methods. Annu Rev Public Health. 1995;16:61–81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pu.16.050195.000425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D. Income inequality and mortality: why are they related? BMJ. 1996 Apr 20;312(7037):987–988. doi: 10.1136/bmj.312.7037.987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soobader M. J., LeClere F. B. Aggregation and the measurement of income inequality: effects on morbidity. Soc Sci Med. 1999 Mar;48(6):733–744. doi: 10.1016/s0277-9536(98)00401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorlie P. D., Backlund E., Keller J. B. US mortality by economic, demographic, and social characteristics: the National Longitudinal Mortality Study. Am J Public Health. 1995 Jul;85(7):949–956. doi: 10.2105/ajph.85.7.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. E., Jr The status of health assessment 1994. Annu Rev Public Health. 1995;16:327–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pu.16.050195.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson R. G. Commentary: income inequality summarises the health burden of individual relative deprivation. BMJ. 1997 Jun 14;314(7096):1727–1728. doi: 10.1136/bmj.314.7096.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


