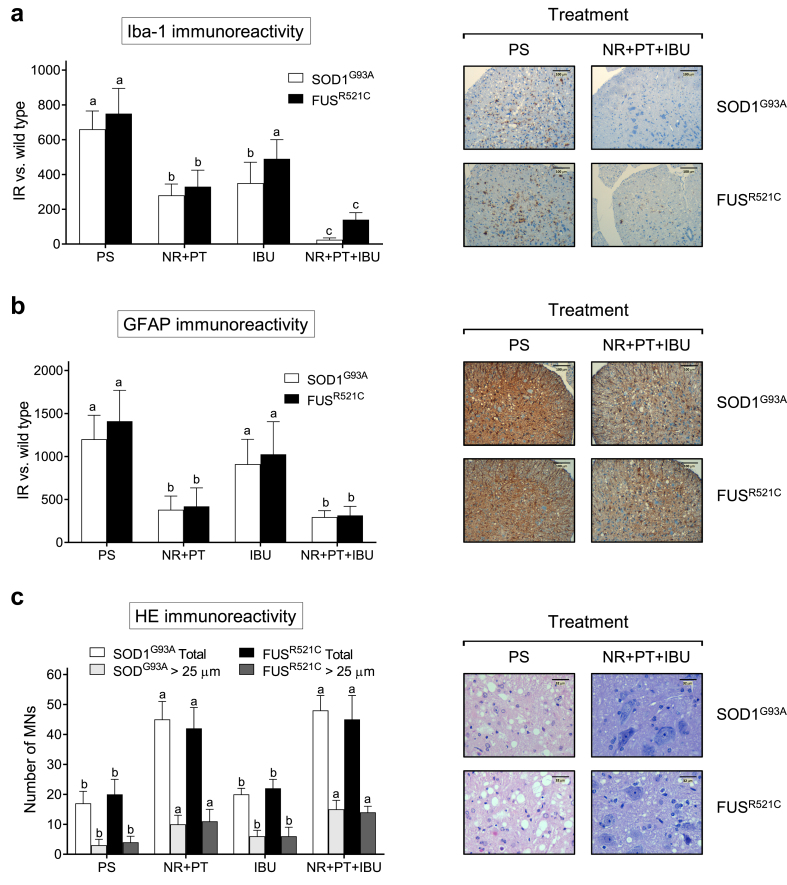
Fig. 2.
NR + PT + IBU reduces motor neuron degeneration and neuroinflammation in the medulla. (a) Iba1 staining and immunoreactivity. (b) GFAP staining and immunoreactivity. (c) Number of MNs/section and HE staining. Tissue samples were obtained (at postnatal week 18/advanced state of progression) from SOD1 G93A and FUSR521C 1C mice (see Fig. 1). Mice were treated with physiological saline (PS), NR + PT, IBU or NR + PT + IBU as in Fig. 1. All the mice were subjected to the tests and training indicated in Fig. 1. Representative images of microglia (Iba1) staining (a), astroglia (GFAP) staining (b) and hematoxylin and eosin staining (c) of the anterior horns of the thoracic spinal cord are shown, comparing mice treated with PS or NR + PT + IBU. a, b Glia quantification (IR, immunoreactivity). Reactive glia is quantified based on the immunostaining signal (arbitrary units), where the data obtained with the different treatments in ALS mice are subtracted from the data obtained in WT mice treated with PS. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to make comparisons among the different treatments. Different letters indicate statistical differences, P < 0.05 (a and b, n = 7; c, n = 14).