Abstract
Anterior cruciate ligament rupture is a common orthopaedic injury, with reconstruction the treatment of choice for active individuals. Graft selection is an important consideration for surgical planning. Achilles tendon allograft is a graft choice most likely used in cases of revision anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. This technical note discusses an approach to Achilles tendon allograft preparation that respects and follows the rotation of the fibers of the Achilles tendon. Key considerations in the use of this technique include (1) identifying the rotational fiber tracks, (2) performing careful dissection along the identified tracks of the fibers, and (3) ensuring an appropriate graft width based on patient size, all of which are crucial for the success of this unique technique. The preservation of the rotational fibers provided by this technique may have the potential to result in increased tensile strength and better clinical outcomes.
Technique Video
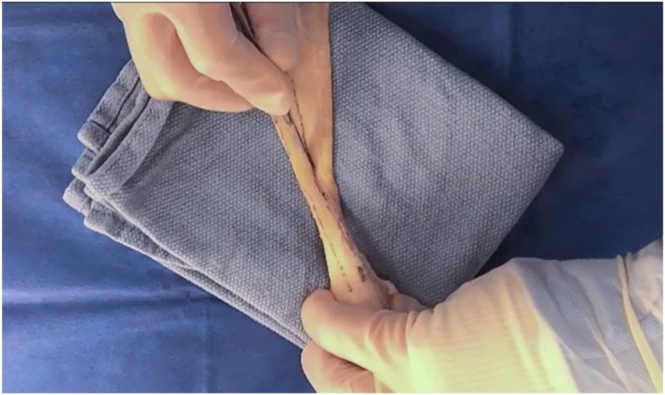
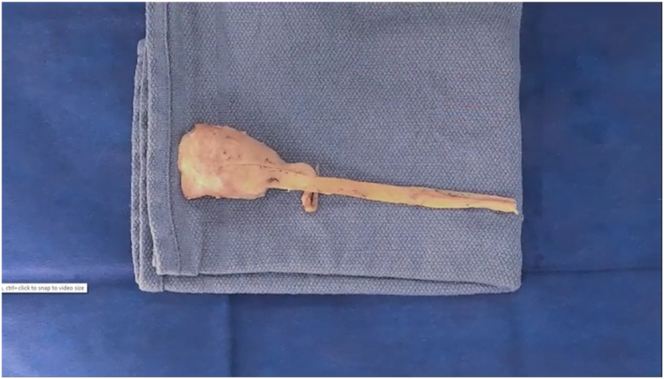
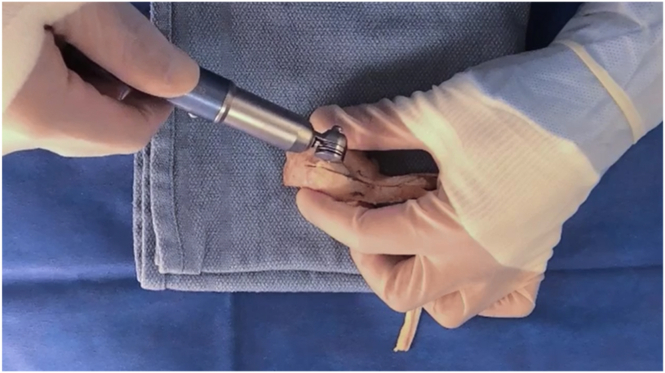
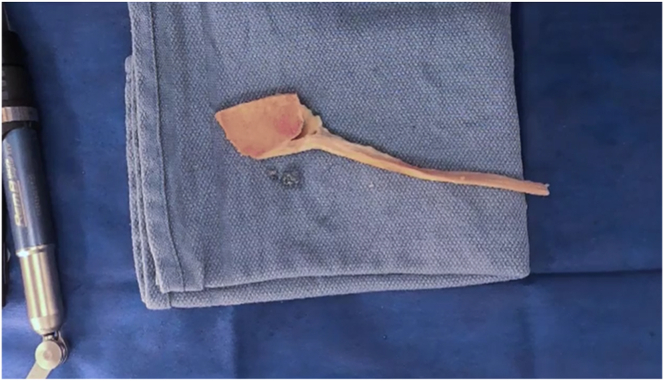
Preparation of Achilles allograft fiber track graft for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. The sterile, fresh-frozen Achilles allograft is delivered to the surgical suite and inspected. The specimen is examined with special attention to the fiber track. With the general fiber track noted, a line is drawn with a sterile, latex-free–tip surgical marker that follows 1 selected fiber track. A second line is drawn 10 mm from the initial line, establishing the surgical parameters of the allograft. Careful dissection using a scalpel is performed following the 2 previously drawn lines, resulting in excess tendon removal. Once complete, an oscillating bone saw is used to trim the bone block following the previously established cuts to the tendinous aspect of the graft, resulting in a 10-mm width of bone block. The final measurement is now made to result in a bone block with a 10-mm depth, followed by an appropriate cut. Any remnant tissue is removed from the graft. The graft is marked to a depth of 10 mm for the bone block, and a cut with an oscillating saw is made. The bone block is further shaped using a rongeur to finalize the size and shape of the graft for the corresponding tunnel in the patient.
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture is a common orthopaedic injury experienced by many patients each year.1 When injured, the ACL is often treated via ACL reconstruction (ACLR). There are a host of factors that influence the success of ACLR, such as tunnel positioning, graft selection, and patient characteristics.2, 3, 4 On the basis of the chosen graft, preparation techniques may influence the strength of the graft. Any ACL graft, whether an autograft or allograft, should have sufficient length and width to accommodate proper positioning in the graft placement process to foster the best patient outcomes.5,6
In recent years, the use of allografts for ACLR has risen exponentially.7 Allografts provide several advantages in the operating room, such as the absence of harvest-site morbidity, a predictable graft size, and decreased operative times.7,8 It should be noted, however, that allografts are associated with a few disadvantages, including increased costs and the potential for delayed healing.8 The Achilles tendon has become an increasingly popular allograft for ACLR in recent years, with positive outcomes of both primary ACLR and revision ACLR in several studies.9, 10, 11 The Achilles tendon provides several advantages, such as sufficient graft length, sufficient graft width, a bone block, and the ability to use the excess allograft tendon for additional ligament reconstruction.12, 13, 14 Additionally, it can be used to combat rotatory instability, which is a common cause of primary reconstruction failure.15
Many techniques have been described regarding Achilles tendon allograft preparation and use in ACLR. However, none to our knowledge give attention to the 90° rotational fiber track (Fig 1) that the Achilles tendon is known to possess.16,17 This technical note describes a fiber track harvest method that may allow for additional graft stability and strength (Video 1).
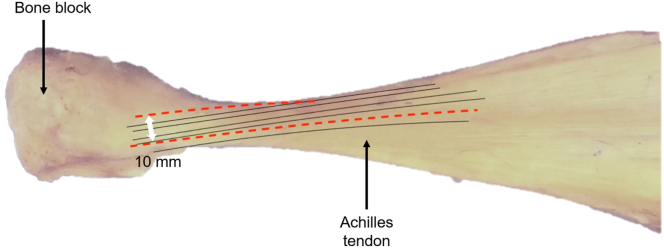
Fig 1.
Achilles allograft sample: superior view, with bone block positioned on left side and Achilles tendon extending to right side. The fiber track path of the tendon is indicated by solid black lines. The red dashed lines indicate possible incision locations to maintain and follow the general fiber track path. The white double arrow indicates that the width between the 2 incisions should be 10 mm.
Surgical Technique
The fresh-frozen Achilles allograft is delivered to the surgical suite. On arrival, the sterile sealed envelope is opened and inspected. The Achilles allograft is then placed in a warm 0.9% saline solution bath on the back table to defrost (Fig 2). The back table has been previously set up with the necessary instruments to prepare the allograft for use (Table 1). After the allograft has finished thawing, it is examined with special attention to the fiber track (Fig 3). Once the general fiber track is decided, the initial line is drawn with a sterile, latex-free–tip surgical marker (Fig 4). During this process, careful attention is paid so that this line follows 1 fiber track and so that the fiber chosen will allow for enough room for the 10-mm width requirement. After the initial line is drawn, careful measurement is performed, and a second line is drawn to result in a 10-mm width (Fig 5). Careful dissection using a scalpel is now performed following the 2 previously drawn lines (Fig 6). This will result in excess tendon removal (Fig 7). At this point, the same longitudinal lines are followed to result in a bone block with the same width (10 mm). An oscillating bone saw is used to trim the bone block along these lines (Figs 8 and 9). The final measurement is now made to result in a bone block with a 10-mm depth (Fig 10), followed by an appropriate cut (Fig 11). At this point, the graft is cleaned of any remaining extra tissue (Fig 12). The bone block is further shaped using a rongeur to ensure easy passage of the graft through the planned bone tunnel (Fig 13). A graft-sizing block is then used to assess the size and shape of the graft for the corresponding tunnel in the patient (Fig 14).
Fig 2.
A sterile, sealed envelope containing the fresh-frozen Achilles allograft is opened and inspected in the surgical suite. The Achilles allograft is then placed in a warm 0.9% saline solution bath on the back table to defrost. After thawing, the allograft specimen is examined to identify the fiber track.
Table 1.
Instruments Required for Achilles Allograft Preparation
| Oscillating saw |
| Graft-sizing block |
| Sterile marker |
| Millimeter latex-free ruler |
| Scalpel |
| Scissors |
| Forceps |
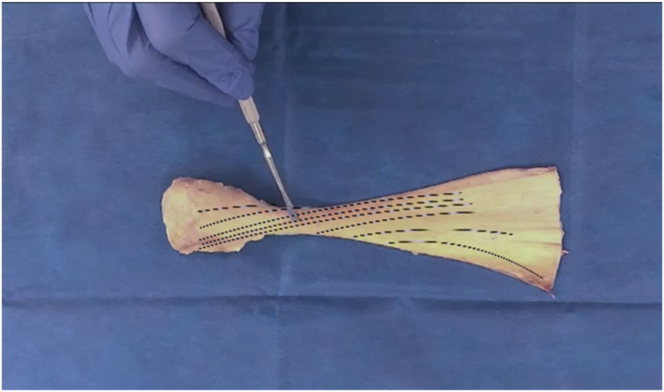
Fig 3.
Superior view of allograft, with bone block positioned on left side and Achilles tendon extending to right side. The fiber track path of the Achilles allograft is identified and indicated by the black dotted and dashed lines.
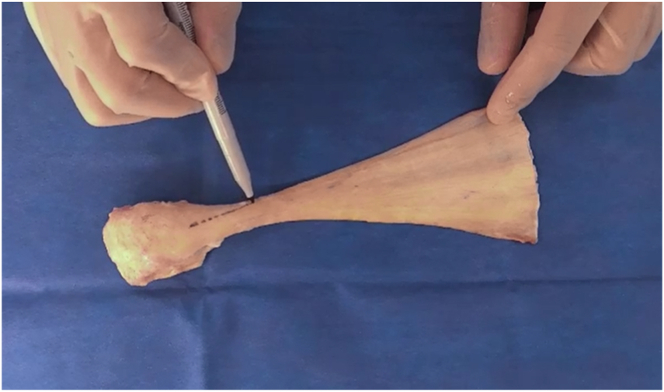
Fig 4.
Superior view of allograft, with bone block positioned on left side and Achilles tendon extending to right side. An initial line is drawn to mark the fiber track using a sterile, latex-free–tip surgical marker. During this process, careful attention is paid so that this line follows 1 fiber track and so that the fiber chosen will allow for enough room for the 10-mm width requirement.
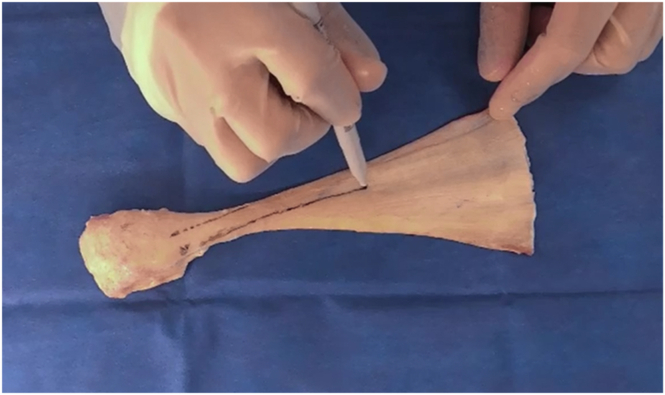
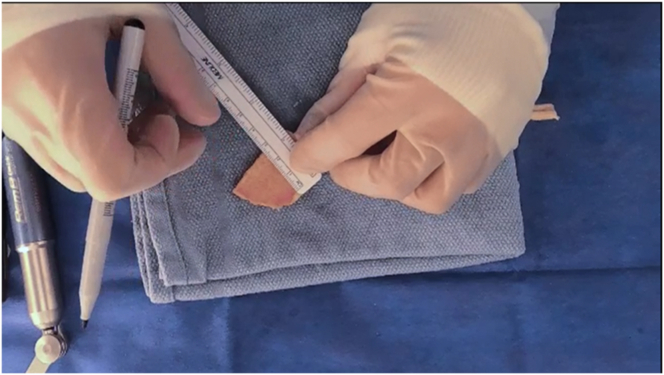
Fig 5.
Superior view of allograft, with bone block positioned on left side and Achilles tendon extending to right side. After the initial line is drawn, a sterile ruler (not shown) is used to measure a 10-mm width to accommodate the graft. A second line is drawn to denote the outer boundary of the graft.
Fig 6.
Superior view of allograft, with bone block positioned at bottom right and Achilles tendon extending toward top. Careful dissection using a scalpel is performed following the 2 previously drawn lines. This will result in excess tendon removal.
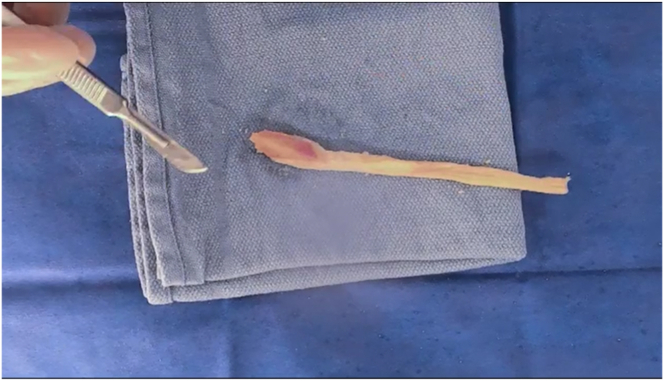
Fig 7.
Allograft with excess tendon removed. The bone block is positioned on the left side, and the Achilles tendon is extending to the right side.
Fig 8.
Superior view of allograft, with bone block positioned between surgeon's thumb and index finger. An oscillating bone saw is used to create the bone block. To maintain the 10-mm width, the same longitudinal lines used to establish the tendinous portion of the allograft are followed to result in a bone block with the same width (10 mm).
Fig 9.
Allograft with remnant bone tissue removed.
Fig 10.
Allograft and bone block. A final measurement is made with a sterile ruler to result in a bone block with a 10-mm depth.
Fig 11.
A final cut with the oscillating saw is made to create a bone block with a 10-mm depth.
Fig 12.
Allograft with bone block of correct size.
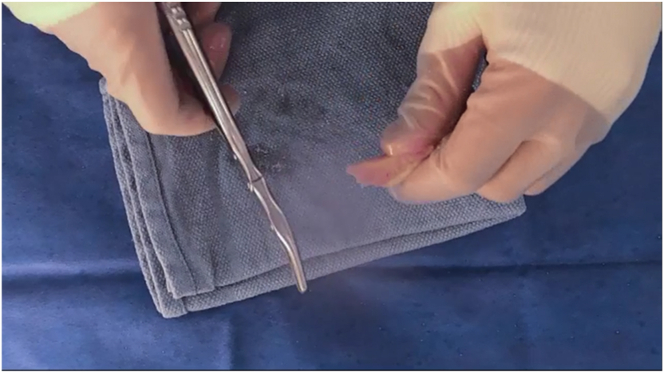
Fig 13.
The bone block is trimmed to a bullet shape with a rongeur to establish its final shape.
Fig 14.
Final specimen.
Discussion
ACL injuries remain a common orthopaedic injury, with ACLR as one of the mainstays of treatment.1 Graft selection in primary and revision ACLR remains a large factor of consideration regarding surgical treatments and outcomes.3 Allograft use for ACLR has risen in recent years,7,8 particularly among patients of older age9 and among young athletes.11 Achilles tendon allografts remain one of the most popular allograft choices of surgeons. A variety of Achilles tendon allograft techniques have been described; however, no studies have used or evaluated the fiber track preservation approach.
There are several key considerations regarding the use of the fiber track preparation technique (Table 2). The first, most important step for successful graft preparation in this harvest procedure is the careful examination of the graft to identify the rotational fibers of the Achilles tendon. Without proper identification of these rotational fibers, excessive rotational fibers are at risk of being destroyed during the preparation process. The second step for successful graft preparation is careful dissection following the track of the rotational fibers to minimize excess fiber disturbance. The final step is ensuring that there is a 10-mm width of graft and bone block because this size will help to ensure a stronger graft. This 10-mm width restores the average human ACL midsubstance width8; however, this is not unique to this harvest procedure. Smaller graft widths used for other grafts have been shown to have higher failure rates.18,19 Ensuring that the 3 aforementioned steps are undertaken is critical for the success of this procedure involving an innovative fiber track harvest method of graft preparation.
Table 2.
Pearls and Pitfalls of Rotational Fiber Track
| Pearls | Pitfalls |
|---|---|
| The natural Achilles tendon fiber track should be carefully identified. | The surgeon should avoid not taking the time to carefully identify the fiber track. |
| A marker should be used to note the fiber track path and where cuts will be made. | Not drawing out the fiber track may cause the surgeon to lose the fiber track. |
| During cutting, time should be taken to ensure that the fiber track is followed. | There is a risk of not following the fibers during cutting. |
As with any reconstructive surgical procedure, there are advantages and disadvantages to known surgical approaches. The same consideration must be made with this allograft preparation technique, especially considering that it proposes use of the rotational fiber track (Table 3). Potential advantages of using the rotational fibers for allograft preparation include maintaining the natural fiber track of the Achilles tendon, which has the potential for increased tensile strength of the graft. To date, the strength of the rotational fibers has not been well characterized, but there is potential for improved surgical outcomes should the rotational fibers prove to be of increased strength. Disadvantages of this preparation technique include a slightly increased operative time to identify the fibers, decreased opportunity for error when making the graft cut, and finally, a lack of current evidence showing improved surgical outcomes.
Table 3.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rotational Fiber Track
| Advantages |
| Maintains natural fiber track of Achilles tendon |
| Potential for increased tensile strength of graft |
| Potential for improved surgical outcomes |
| Disadvantages |
| Slightly increased operative time to identify fibers |
| No current evidence of improved surgical outcomes |
| Less room for error when making graft cut |
This study provides an Achilles tendon allograft preparation technique with special attention to the rotational fiber track within the Achilles tendon. This graft preparation technique may have the potential to result in additional tensile strength owing to the extension and preservation of the rotational fibers. Further investigations should be conducted to assess the tensile strength and clinical patient outcomes with this graft preparation method.
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in the authorship and publication of this article. Full ICMJE author disclosure forms are available for this article online, as supplementary material.
Supplementary Data
Preparation of Achilles allograft fiber track graft for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. The sterile, fresh-frozen Achilles allograft is delivered to the surgical suite and inspected. The specimen is examined with special attention to the fiber track. With the general fiber track noted, a line is drawn with a sterile, latex-free–tip surgical marker that follows 1 selected fiber track. A second line is drawn 10 mm from the initial line, establishing the surgical parameters of the allograft. Careful dissection using a scalpel is performed following the 2 previously drawn lines, resulting in excess tendon removal. Once complete, an oscillating bone saw is used to trim the bone block following the previously established cuts to the tendinous aspect of the graft, resulting in a 10-mm width of bone block. The final measurement is now made to result in a bone block with a 10-mm depth, followed by an appropriate cut. Any remnant tissue is removed from the graft. The graft is marked to a depth of 10 mm for the bone block, and a cut with an oscillating saw is made. The bone block is further shaped using a rongeur to finalize the size and shape of the graft for the corresponding tunnel in the patient.
References
- 1.Longo U.G., Nagai K., Salvatore G., et al. Epidemiology of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery in Italy: A 15-year nationwide registry study. J Clin Med. 2021;10:223. doi: 10.3390/jcm10020223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rayan F., Nanjayan S.K., Quah C., Ramoutar D., Konan S., Haddad F.S. Review of evolution of tunnel position in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. World J Orthop. 2015;6:252–262. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i2.252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Baawa-Ameyaw J., Plastow R., Begum F.A., Kayani B., Jeddy H., Haddad F. Current concepts in graft selection for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. EFORT Open Rev. 2021;6:808–815. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.6.210023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.van der List J.P., Hagemans F.J.A., Hofstee D.J., Jonkers F.J. The role of patient characteristics in the success of nonoperative treatment of anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48:1657–1664. doi: 10.1177/0363546520917386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kyung H.S. Graft considerations for successful anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2019;31:1. doi: 10.1186/s43019-019-0003-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Paschos N.K., Howell S.M. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: Principles of treatment. EFORT Open Rev. 2016;1:398–408. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.1.160032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hulet C., Sonnery-Cottet B., Stevenson C., et al. The use of allograft tendons in primary ACL reconstruction. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27:1754–1770. doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Buerba R.A., Boden S.A., Lesniak B. Graft selection in contemporary anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021;5 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chehab E.L., Flik K.R., Vidal A.F., et al. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using Achilles tendon allograft: An assessment of outcome for patients age 30 years and older. HSS J. 2011;7:44–51. doi: 10.1007/s11420-010-9183-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shah A.A., McCulloch P.C., Lowe W.R. Failure rate of Achilles tendon allograft in primary anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthroscopy. 2010;26:667–674. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2010.02.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zaffagnini S., Grassi A., Marcheggiani Muccioli G.M., et al. Anterior cruciate ligament revision with Achilles tendon allograft in young athletes. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2018;104:209–215. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2017.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zamorano H., Yáñez-Diaz R., Vergara F., et al. Achilles tendon allograft preparation technique for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A technical note. Arthrosc Tech. 2021;10:e2143–e2150. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2021.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee C.S., Han S.B., Jang K.M. Combined anterior cruciate ligament and anterolateral ligament reconstruction using a single Achilles tendon allograft: A technical note. Medicina (Kaunas) 2022;58:929. doi: 10.3390/medicina58070929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Espejo-Reina A., Espejo-Reina M.J., Lombardo-Torre M., Sevillano-Pérez E., Llanos-Rodríguez Á., Espejo-Baena A. Anterior cruciate ligament revision surgery associated to lateral collateral and anterolateral ligaments reconstruction with single Achilles tendon allograft and single femoral tunnel. Arthrosc Tech. 2022;11:e1769–e1777. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2022.06.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zsidai B., Engler I.D., Pujol O., et al. Over-the-top technique for revision ACL reconstruction with Achilles allograft and associated lateral extra-articular tenodesis. Arthrosc Tech. 2022;11:e1633–e1640. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2022.05.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kayce J. Gross anatomy: Achilles tendon. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2022;39:405–410. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2022.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moore K.L., Agur A.M.R., Dalley A.F. Ed 4. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2011. Essential clinical anatomy. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Figueroa F., Figueroa D., Espregueira-Mendes J. Hamstring autograft size importance in anterior cruciate ligament repair surgery. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3:93–97. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.3.170038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fritsch B., Figueroa F., Semay B. Graft preparation technique to optimize hamstring graft diameter for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arthrosc Tech. 2017;6:e2169–e2175. doi: 10.1016/j.eats.2017.08.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Preparation of Achilles allograft fiber track graft for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. The sterile, fresh-frozen Achilles allograft is delivered to the surgical suite and inspected. The specimen is examined with special attention to the fiber track. With the general fiber track noted, a line is drawn with a sterile, latex-free–tip surgical marker that follows 1 selected fiber track. A second line is drawn 10 mm from the initial line, establishing the surgical parameters of the allograft. Careful dissection using a scalpel is performed following the 2 previously drawn lines, resulting in excess tendon removal. Once complete, an oscillating bone saw is used to trim the bone block following the previously established cuts to the tendinous aspect of the graft, resulting in a 10-mm width of bone block. The final measurement is now made to result in a bone block with a 10-mm depth, followed by an appropriate cut. Any remnant tissue is removed from the graft. The graft is marked to a depth of 10 mm for the bone block, and a cut with an oscillating saw is made. The bone block is further shaped using a rongeur to finalize the size and shape of the graft for the corresponding tunnel in the patient.
Preparation of Achilles allograft fiber track graft for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. The sterile, fresh-frozen Achilles allograft is delivered to the surgical suite and inspected. The specimen is examined with special attention to the fiber track. With the general fiber track noted, a line is drawn with a sterile, latex-free–tip surgical marker that follows 1 selected fiber track. A second line is drawn 10 mm from the initial line, establishing the surgical parameters of the allograft. Careful dissection using a scalpel is performed following the 2 previously drawn lines, resulting in excess tendon removal. Once complete, an oscillating bone saw is used to trim the bone block following the previously established cuts to the tendinous aspect of the graft, resulting in a 10-mm width of bone block. The final measurement is now made to result in a bone block with a 10-mm depth, followed by an appropriate cut. Any remnant tissue is removed from the graft. The graft is marked to a depth of 10 mm for the bone block, and a cut with an oscillating saw is made. The bone block is further shaped using a rongeur to finalize the size and shape of the graft for the corresponding tunnel in the patient.