Figure 5.
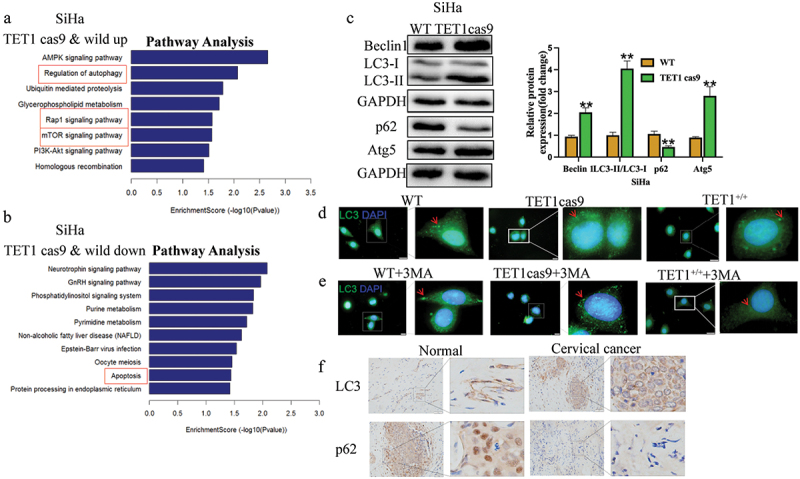
Effect of TET1 on the biological functions of cervical cancer cells.
(a) KEGG analysis revealed the signalling pathways associated with the upregulated activity of TET1 knockdown in SiHa cells when compared with that in wild-type cells; (b) KEGG analysis was performed to identify the signalling pathways associated with the downregulated activity of TET1 in SiHa cells when compared with that in wild-type cells. (c) Western blotting was performed to detect the autophagy indexes of SiHa cells after TET1 knockdown; (d,e) Immunofluorescence also showed that there were more autophagosomes in the TET1 cas9 group than in the WT group, while the TET1+/+ group had the least number of autophagosomes. Furthermore, immunofluorescence results show that knockdown of TET1 can attenuate the inhibitory effect of 3 MA on autophagy, while overexpression of TET1 can continue to inhibit autophagy in the presence of 3 MA; (f) Immunohistochemical detection of LC3 and P62 expression in cervical cancer and adjacent tissues.
