Abstract
The apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is a glycoprotein which plays a vital role in different inflammatory conditions and in the catabolism of lipids and triglycerides. The aim of this study was to identify and evaluate the top 100 most cited studies on ApoE research. A bibliometric study was conducted. On January 18, 2021, studies published on ApoE were searched in the Web of Science Core Collection database without any limitations. The obtained data were analyzed for a number of attributes using HistCiteTM and VOSviewer software. The search yielded a total of 16,242 results. Of the total retrieved results, the top 100 most cited studies were selected. The top 100 most cited studies on ApoE were published from 1977 to 2017 and were cited 86,181 times. Single study citations ranged from 426 to 6,327. The studies were published in 41 journals authored by 589 authors. The study “Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families” was cited 6,327 times. Mahley RW, Roses AD, and Saunders AM were the most prolific authors who published ten studies each. Most of the studies were published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. A total of 151 institutions were involved, and the USA was the most productive country. Our finding provides valuable insight on ApoE research which may be useful for researchers, academia, and funding agencies to identify new future research domains.
Keywords: Apolipoprotein E, ApoE, bibliometric analysis, Web of Science, VOSviewer
Introduction
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is a glycoprotein with a molecular mass of 34 kDa and consists of 299 amino acids and is mainly synthesized in the liver. ApoE plays a vital role in different inflammatory conditions and the catabolism of cholesterol, lipid, and triglycerides. ApoE is expressed in adipocytes and macrophages [1-2]. ApoE modulates multiple pathways, with emerging knowledge on ApoE presenting new opportunities for Alzheimer's disease therapy [2]. The first study on ApoE, “Isolation and partial characterization of an arginine-rich apolipoprotein from human plasma very-low-density lipoproteins: Apolipoprotein E”, indexed in the Web of Science was published in 1975 and was authored by Utermann G [3]. Furthermore, 737 studies (from 1975 to 1990), 6,261 studies (between 1991 and 2005), and a total of 9,232 studies (from 2006 to 2020) were published on ApoE. As of 19 January 2021, only 12 studies have been published on ApoE. Of the total published studies, 10,087 (62.1%) were original articles, and 372 (2.3%) were published as reviews. In the past two decades, interest in ApoE research has increased significantly, and many scientific journals with high impact factors (IF) and quartile rankings (Q1-4) such as Circulation (IF: 23.6, Q1), Atherosclerosis (IF: 3.9, Q1), and Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis and Vascular Biology (IF: 6.6, Q1) have published at least 500 studies on ApoE.
Neurology (4,236, 26.1%), cardiology (3,907, 24.1%), and molecular biology (2,290, 14.1%) were the top three most studied research areas. Havekes LM was the leading author (192 studies, 1.2%), while Weisgraber KH, Mahley RW, Roses AD, Saunders AM, Holtzman DM, Zhang Y have published at least 100 studies on ApoE. The United States Department of Health Human Services (3,265, 20.1%), and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) (3,264, 20.1%) were the leading funding agencies for ApoE research. Duke University (489, 3.0%), University of California, San Francisco (417, 2.6%), and the University of Washington (304, 1.9%) were the most productive organizations on ApoE research. The United States of America (USA) was the leading country with the greatest number of publications (6,589, 40.6%) in ApoE research. China, Japan, England, Germany, Netherlands, Canada, France, Sweden, Italy, Australia, Spain, Finland, South Korea, Scotland, Belgium, Israel, and Switzerland have published at least 200 studies on ApoE. In light of the above statements, we systematically analyzed the published literature, and key parameters in the ApoE research field. Therefore, the current study was conducted to discern and characterize the top 100 most cited studies on ApoE.
Methods
A bibliometric study was designed. The data used in this study were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection database accessed through the online library of Southeast University, Nanjing, China. The search was performed as of 19 January, 2021. The database was searched using key terms including “Apolipoprotein E” OR “Apolipoprotein-E” OR “ApoE” in the “Title” field without any search limitations. The top 100 most cited studies were selected based on number of citations in descending order. The included studies were characterized by a number of attributes; study title, citation number, authorship, journal name, document type, publication year, institution, and country. The impact factor of journals were queried from 2019 Journal Citation Reports® (Clarivate Analytics 2020). The obtained data were exported to HistCiteTM (https://clarivate.com/) for bibliometric characterization. Visualization network mapping such as co-authorship country, co-occurrences of all keywords, co-citation cited authors, and bibliographic coupling sources were constructed by using VOSviewer software (https://www.vosviewer.com/) for Windows.
Results
Characteristics of studies
The searches retrieved a total of 16,242 results of which the top 100 most cited studies were selected. The top 100 most cited studies were published in 41 journals with 3,780 cited references and were authored by 589 authors. All the studies were published in the English language with a total local citation score (TLCS) of 509 and a total global citation score (TGCS) of 86,181. Individual study citations ranged from 426 to 6,327 citations. The study authored by Corder EH and colleagues “Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families” published in 1993 in Science was cited 6,327 times with an average citation count of 253.1 times per year (Table 1).
Table 1. Top ten most cited studies on ApoE.
| Ranking | Study | LCS | GCS | GCS/t | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Corder et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families | 25 | 6,327 | 253.1 | [4] |
| 2 | Strittmatter et al. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease | 31 | 3416 | 136.6 | [5] |
| 3 | Mahley. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology | 27 | 3394 | 113.1 | [6] |
| 4 | Saunders et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease | 18 | 3065 | 122.6 | [7] |
| 5 | Farrer et al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease | 5 | 2540 | 120.9 | [8] |
| 6 | Hixson and Vernier. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI | 11 | 2470 | 88.2 | [9] |
| 7 | Plump et al. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells | 17 | 1802 | 69.3 | [10] |
| 8 | Davignon et al. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis | 15 | 1789 | 59.6 | [11] |
| 9 | Zhang et al. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E | 15 | 1758 | 67.6 | [12] |
| 10 | Corder et al. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset alzheimer disease | 13 | 1361 | 56.7 | [13] |
LCS: local citation score, GCS: global citation score, GCS/t: global citation score per year
Of the top 100 influential studies analyzed, Mahley RW (studies = 10, citations = 8,856), Roses AD (studies = 10, citations = 18,498), and Saunders AM (studies = 10, citations = 18,548) were the most prolific authors. A further 65 authors published at least two studies, while 521 authors published one study each. The authors with at least five published studies are presented in Table 2. Of all analyzed journals, eight journals published at least five studies (Table 3), nine journals at least two studies, and 24 journals published one study each.
Table 2. Authors with at least five ApoE studies.
| Author | Records | LCS | GCS | GCS/t |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mahley RW | 10 | 85 | 8856 | 323.7 |
| Roses AD | 10 | 137 | 18498 | 747.2 |
| Saunders AM | 10 | 131 | 18548 | 751.9 |
| Holtzman DM | 9 | 29 | 5331 | 1115.6 |
| PericakVance MA | 8 | 92 | 15954 | 662.1 |
| Strittmatter WJ | 8 | 127 | 17537 | 704.5 |
| Weisgraber KH | 7 | 45 | 4530 | 166.3 |
| Breslow JL | 6 | 46 | 5141 | 205.8 |
| Herz J | 5 | 13 | 3204 | 160.4 |
| Plump AS | 5 | 37 | 4614 | 191.5 |
| Schmechel DE | 5 | 67 | 9873 | 397.9 |
LCS: local citation score, GCS: global citation score, GCS/t: global citation score per year
Table 3. Journals that have published at least five ApoE studies.
| Journal | Records | LCS | GCS | GCS/t | IF* | Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America | 12 | 96 | 11640 | 580.8 | 9.41 | Q1 |
| Journal of Clinical Investigation | 7 | 24 | 4080 | 218.6 | 11.86 | Q1 |
| Circulation | 6 | 0 | 3230 | 189.7 | 23.60 | Q1 |
| JAMA-Journal of the American Medical Association | 6 | 13 | 5105 | 261.8 | 45.54 | Q1 |
| Journal of Biological Chemistry | 5 | 19 | 2670 | 132.6 | 4.24 | Q2 |
| Lancet | 5 | 24 | 4152 | 175.2 | 60.39 | Q1 |
| Nature | 5 | 23 | 3187 | 197.5 | 42.78 | Q1 |
| Science | 5 | 70 | 12775 | 570.5 | 41.85 | Q1 |
IF*: impact factor, 2019 Journal Citation Reports® (Clarivate Analytics 2020), LCS: local citation score, GCS: global citation score, GCS/t: global citation score per year, Q: quartile
The majority of studies were published as research articles (n = 81, GCS = 68,236 citations), and only 13 (GCS = 11,959 citations) were published as reviews; four and two documents were notes and letters, respectively. The top 100 most cited studies were published from 1977 to 2017, with total citations ranging from 509 in 2007 to 17,790 in 1993. Most studies were published in 1994 and cited 7,383 times, while studies (n = 8) published in 1993 received the most citations (17,790) (Table 4). A total of 151 institutions were involved in the top 100 most cited ApoE studies. The University of California, San Francisco, Washington University, and Duke University were the leading institutes with at least ten studies, each (Table 5). Five institutions published at least five studies, 32 institutions published two studies, and 111 institutions published only one study each. The USA was the most productive country (n = 78, 71,227 citations). Only four other countries published at least five studies (Table 6).
Table 4. Publication year of analyzed ApoE studies.
| Publication year | Records | LCS | GCS | Publication year | Records | LCS | GCS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1977 | 1 | 7 | 645 | 1998 | 6 | 9 | 3080 |
| 1981 | 1 | 9 | 527 | 1999 | 4 | 6 | 2752 |
| 1982 | 1 | 7 | 636 | 2000 | 6 | 12 | 4168 |
| 1985 | 3 | 22 | 1737 | 2001 | 4 | 0 | 2021 |
| 1986 | 1 | 8 | 533 | 2002 | 6 | 2 | 3459 |
| 1987 | 1 | 8 | 534 | 2003 | 3 | 1 | 1919 |
| 1988 | 2 | 41 | 5183 | 2004 | 2 | 0 | 1242 |
| 1989 | 2 | 12 | 1077 | 2007 | 1 | 0 | 509 |
| 1990 | 1 | 11 | 2470 | 2008 | 2 | 12 | 1049 |
| 1991 | 4 | 33 | 3042 | 2009 | 3 | 7 | 2652 |
| 1992 | 4 | 52 | 5024 | 2010 | 1 | 3 | 539 |
| 1993 | 8 | 129 | 17790 | 2011 | 2 | 3 | 1084 |
| 1994 | 10 | 64 | 7383 | 2012 | 2 | 2 | 1303 |
| 1995 | 4 | 10 | 2039 | 2013 | 1 | 0 | 1225 |
| 1996 | 5 | 16 | 3166 | 2017 | 1 | 0 | 556 |
| 1997 | 8 | 23 | 6837 |
LCS: local citation score, GCS: global citation score
Table 5. Institutions that have published at least five ApoE studies.
| Institution | Country | Records | LCS | GCS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of California San Francisco | USA | 12 | 101 | 10467 |
| Washington University | USA | 12 | 32 | 7254 |
| Duke University | USA | 11 | 136 | 21088 |
| Harvard University | USA | 7 | 23 | 3814 |
| Massachusetts General Hospital | USA | 7 | 63 | 14703 |
| University of California Los Angeles | USA | 6 | 48 | 10053 |
| Rockefeller University | USA | 5 | 22 | 3549 |
| University of Texas | USA | 5 | 15 | 3149 |
LCS: local citation score, GCS: global citation score
Table 6. Countries that have produced the top 100 most cited studies on ApoE.
| Country | Records | LCS | GCS |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States of America | 78 | 443 | 71227 |
| United Kingdom | 7 | 24 | 4631 |
| Canada | 5 | 32 | 5861 |
| Germany | 5 | 9 | 2927 |
| Japan | 5 | 18 | 3684 |
| Austria | 4 | 8 | 2480 |
| France | 3 | 6 | 1973 |
| Sweden | 3 | 1 | 1554 |
| Belgium | 2 | 4 | 1768 |
| Finland | 2 | 1 | 989 |
| Israel | 2 | 1 | 998 |
| Netherlands | 2 | 7 | 3600 |
| Unknown | 2 | 4 | 1116 |
| Denmark | 1 | 0 | 574 |
| Federal Republic of Germany | 1 | 7 | 645 |
| Italy | 1 | 2 | 1105 |
| Peoples Republic of China | 1 | 0 | 1225 |
| Singapore | 1 | 5 | 470 |
| Switzerland | 1 | 1 | 619 |
LCS: local citation score, GCS: global citation score
Co-authorship country
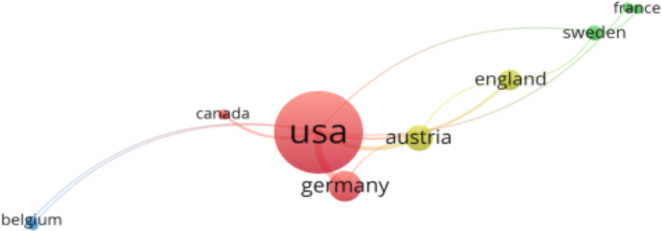
Countries with at least two studies were included in this analysis. Of the 19 countries considered, 14 met the defined thresholds. The USA was the leading country (total link strength (TLS) = 16, studies = 75, citations = 67,561), followed by Germany (TLS = 6, studies = 5, citations = 2,927), Austria (TLS = 5, studies = 4, citations = 2,480), England (TLS = 4, studies = 5, citations = 3,110), and Sweden (TLS = 3, studies = 3, citations = 1,554). Belgium, Canada, France, Japan, and Netherlands had TLS scores of two each, while Germany, Finland, Israel, and Scotland had TLS scores of 0 and were excluded from network visualization mapping. The co-authorship country analysis is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Co-authorship country visualization mapping based on total link strength (TLS). Of the total countries, only 10 countries formed 4 clusters and each color represents different cluster; red represents cluster 1 (Canada, Germany, USA), green color represents cluster 2 (France, Japan, Sweden), blue color represents cluster 2 (Belgium, Netherlands), and yellow color represents cluster 4 (Austria, England).
Co-occurrences all keywords
The minimum occurrence of a keyword was fixed at five. Of the total keywords, only 31 papers met the threshold. Based on TLS, ‘expression’ (TLS = 31, occurrences = 10), and ‘Apolipoprotien-E’ (TLS = 30, occurrences = 11) were the most dominant keywords. The co-occurrences of all keywords are presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2.
Co-occurrence all keywords network visualization mapping based on total link strength (TLS). The 31 keywords made 4 clusters; cluster 1 red color (9 keywords), cluster 2 green color (9 keywords), cluster 3 blue color (8 keywords), and cluster 4 yellow color (5 keywords).
Co-citation cited authors
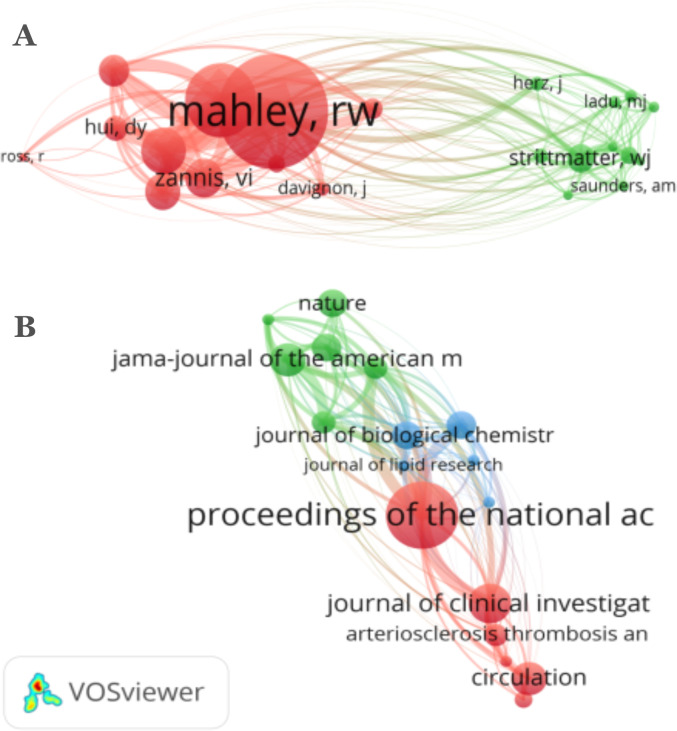
The minimum number of citations of an author was fixed at 20. Of the total authors, only 23 met the defined threshold. The top three authors based on TLS are Mahley RW (TLS = 2,667), Weisgraber KH (TLS = 1,717), and Utermann G (TLS = 1,088). The co-citation cited authors analysis is presented in Figure 3A.
Figure 3.
Visualization of co-citation cited authors mapping (A) and bibliographic coupling sources mapping (B) based on total link strength (TLS). (A) There are two clusters formed; cluster 1 (red, 11 authors), and cluster 2 (green color, 11 authors). (B) There are three clusters formed; cluster 1 (red color, six items), cluster 2 (green color, six items), and cluster 3 (blue color, five items).
Bibliographic coupling sources
Of the total sources, only 17 met the thresholds. The minimum number of documents from a publication source was fixed at two. The top three sources with highest TLS value were Proceeding of the National Academy of the United States of America (TLS = 613, documents = 12, citations = 11,640), Neuron (TLS = 381, documents = 4, citations = 3,086), and Journal of Clinical Investigation (TLS = 369, documents = 7, citations = 4,080). The source with the minimum TLS of 73 was Nature Medicine. The bibliographic coupling sources are presented in Figure 3B.
Discussion
In the current study, we systematically analyzed the most cited studies in ApoE research. The first study on the subject was published in 1975. The study “Gene dose of Apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families” was the most cited study in ApoE research. The published literature highlights a high growth rate of research in the past two decades indicating that ApoE has become a trending research topic in recent times. A total of 18 countries contributed to the 100 most cited studies. The results illustrate that the USA was the leading country producing 78 of the most influential studies. This finding is in line with previously published studies in different fields [14-19]. No resource limited country was found to be involved in the top 100 studies, which showed the significant disparity of scientific research and publication trends in ApoE between low-income and developed countries.
In addition, 151 institutions were involved in the 100 most influential studies in ApoE research, of which the majority institutions are in the USA. The top 100 most cited studies were published in 41 journals in the English language that were published from 1977 to 2017 and cited globally 86,181 times. Of the most influential studies on ApoE, most studies were published in 1994 and cited 7,383 times. However, studies published (n = 8) in 1993 received more than 17,000 citations. In ApoE research, 20 studies were cited at least 1,000 times (ranging from 1,00 to 6,327), 50 studies received more than 500 citations (ranging from 501 to 983), and 30 studies received above 400 citations (ranging from 426 to 497). The results show that the year of publication can affect number of citations. The studies that received maximum, totaling 59,132 citations (ranging from 3,042 to 17,790 per year) were published from 1988 to 2002. The most recent study, 2017, received only 556 citations. However, it is important to note that after publication, the most citations for an article often occurred after three to ten years [16].
A similar result has been reported in other studies - the most prolific period in intervertebral disk research was from 1990 to 2000 [16]. The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America was the most attractive journal for the top 100 most influential studies on ApoE. Of the 41 journals analyzed, only eight journals published at least five studies in ApoE research. However, journals with high IF and quartile rankings can attract good papers. The top ten IF scores for journals ranged from 4.238 to 60.392 and nine of these journals were ranked in Q1 with the other journal ranked in the Q2 category. Nevertheless, several factors should be considered while assessing journals.
As one of the limitations of this study, the dataset used in the analysis were obtained from one database. Other databases such as Scopus and Google Scholar can provide citation results, which may differ from those presented in the Web of Science database, used here.
Conclusion
In this study, we identified and presented a detailed systematic evaluation of the top 100 most influential studies in ApoE research. In ApoE research, 20 studies were cited at least 1,000 times. In recent years, research interest in ApoE has increased, particularly in developed countries such as the USA. The presented dataset can serve as a reference by academia, funding agencies, and researchers worldwide to contribute to the expanding scientific work and future research directions in ApoE.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Southeast University for providing free online access to the Web of Science
Core Collection database.
Declarations
Ethics approval
In this study no human and animal subjects were enrolled, therefore the ethical approval was not needed.
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Funding
None.
How to cite
Ahmad T, Dhama K, Tiwari R, et al. Bibliometric analysis of the top 100 most cited studies in apolipoprotein E (ApoE) research. Narra J 2021; 1(1): e2. http://doi.org/10.52225/narraj.v1i1.2.
References
- 1.Marais AD. Apolipoprotein E in lipoprotein metabolism, health and cardiovascular disease. Pathology 2019;51(2):165-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhao N, Liu CC, Qiao W, Bu G. Apolipoprotein E, receptors, and modulation of Alzheimer's disease. Biol Psychiatry 2018;83(4):347-357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Utermann G. Isolation and partial characterization of an Arginine-rich apolipoprotein from human plasma very-low-density lipoproteins: Apolipoprotein E. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem 1975;356(7):1113-1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJet al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science 1993;261(5123):921-923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D, et al. Apolipoprotein E: high-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993;90(5):1977-1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mahley RW. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science 1998;240(4852):622-630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel D, et al. Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 1993;43(8):1467-1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Farrer LA, Cupples LA, Haines JLet al. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. ApoEand Alzheimer Disease Meta-Analysis Consortium. JAMA 1997;278(16):1349-1356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hixson JE, Vernier DT. Restriction isotyping of human apolipoprotein E by gene amplification and cleavage with HhaI. J Lipid Res 1990;31(3):545-548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Plump AS, Smith JD, Hayek T, et al. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell 1992;71(2):343-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Davignon J, Gregg RE, Sing CF. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 1988, 8(1):1-21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang SH, Reddick RL, Piedrahita JA, Maeda N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science 1992;258(5081):468-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Corder EH, Saunders AM, Risch NJ, et al. Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet 1994;7(2):180-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ahmad T, Nasir S, Musa TH, et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis, vaccines, and bibliometric analysis of the 100 top-cited studies on Hepatitis E virus. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2021;17(3):857-871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang Y, Quan L, Du L. The 100 top-cited studies in cancer immunotherapy. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 2019;47(1):2282-2292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Yang G, Li Z, Ye Wet al. Bibliometric analysis of the 100 most cited articles on intervertebral disk research: From 1900 to 2017 year. Clin Spine Surg 2020;33(3):104-110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mohammed MF, Marais O, Qureshi AI, et al. The top 100 most-cited articles in stroke imaging: A bibliometric analysis. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol 2018;47(3):161-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Powell AG, Hughes DL, Brown J, et al. Esophageal cancer's 100 most influential manuscripts: A bibliometric analysis. Dis Esophagus 2017;30(4):1-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Foley KG, Powell A, Lewis WG, Roberts SA. The 100 most cited articles investigating the radiological staging of oesophageal and junctional cancer: A bibliometric analysis. Insights Imaging 2016;7(4):619-628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]