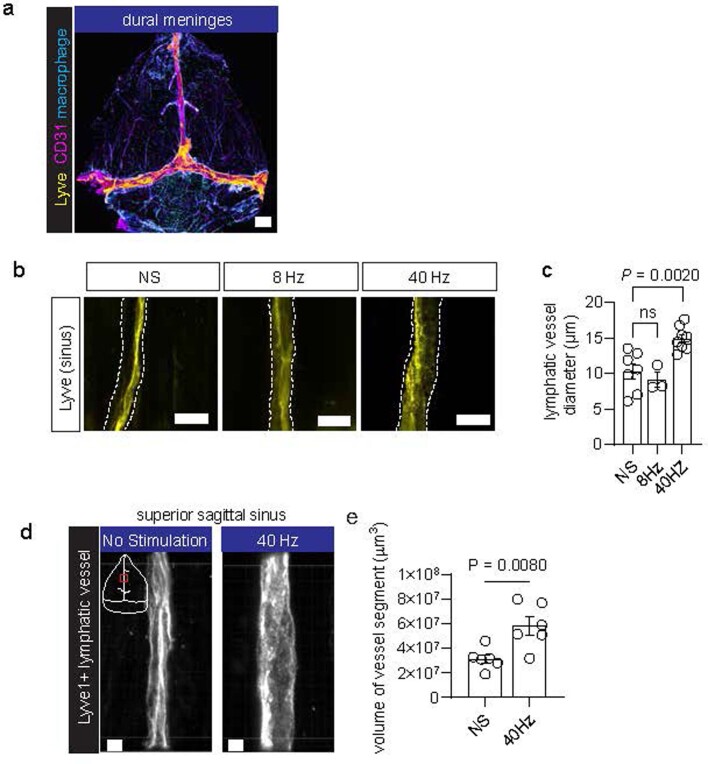
Extended Data Fig. 7. Meningeal lymphatic response to multisensory 40 Hz.
a. Example confocal tile z-stack image of a whole mount preparation of the dural meninges showing endothelial cells (CD31, magenta), lymphatic endothelial cells (LYVE1, yellow), and meningeal macrophages (Lyve1 non-vascular cells, cyan). Dural meninges were obtained from the skull caps of 6-month-old 5XFAD mice. Similar dural whole mounts were obtained for all images of the sinus regions. Scale bar, 1000 μm. b. Example confocal images of lymphatic vessels in the dural meninges in 6-month-old 5XFAD mice. c. Quantification of diameter of meningeal lymphatic vessel using confocal microscopy in 6-month-old 5XFAD mice (n = 7 mice for no stimulation, 3 mice for 8 Hz stimulation, and 8 mice for 40 Hz stimulation; each data point represents the mean lymphatic vessel diameter from 3 images of the superior sagittal sinus; data is presented as the mean ± s.e.m.; P value calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test). Scale bar, 20 μm. d. Example Airyscan confocal images of LYVE1+ lymphatic vessels in the meningeal superior sagittal sinus region (red box in the white schematic of the dural meninges) from 6-month-old 5XFAD mice receiving either 40 Hz stimulation or no stimulation. 3D images of z-stacks from lymphatic vessel segments were generated using Imaris. Scale bar, 5 μm. e. Quantification of lymphatic vessel volume in 6-month-old 5XFAD mice receiving 40 Hz or no stimulation (NS) (n = 6 mice per condition; each data point represents the mean volume from 3 segments of meningeal lymphatic vessel from the superior sagittal sinus for each mouse; data is presented as the mean ± s.e.m.; P value calculated by unpaired student’s two-tailed t-test).