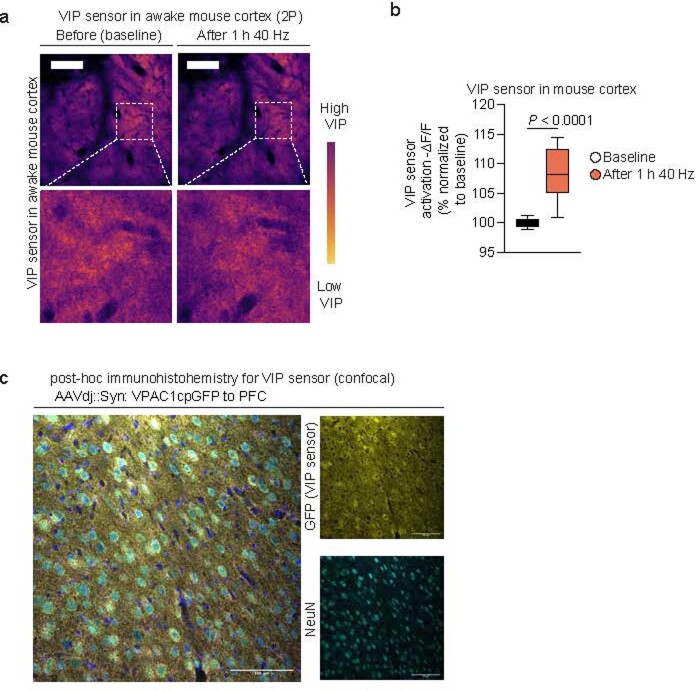
Extended Data Fig. 12. VIP sensor in awake mouse cortex.
a. Example 2 P images of VIP sensor (VPAC1cpGFP) expressed in awake mouse cortex visualized through a cranial window centered over prefrontal cortex before and after 1 h of multisensory gamma stimulation. The reduction in signal signifies an increase in VIP sensor activation following 40 Hz treatment; the experiment was repeated twice. Scale bar, 25 μm. b. Quantification of VPAC1cpGFP fluorescence change before and after 40 Hz treatment in 6-month-old 5XFAD mouse cortex via a closed cranial window. The increase in fluorescence change signifies an increase in VIP sensor activation following noninvasive multisensory gamma stimulation (presented as VIP sensor activation, i.e., -ΔF/F). A two-sided Student’s t-test was performed for data analysis (n = 15 ROIs from 3 mice imaged before and after gamma stimulation; box plots depict the median, interquartile range, and minimum and maximum; *P < 0.0001 by unpaired two-tailed student’s t-test). c. Immunohistochemistry of VIP sensor in mouse cortex; the experiment was repeated twice. Scale bar, 100 µm.