Abstract
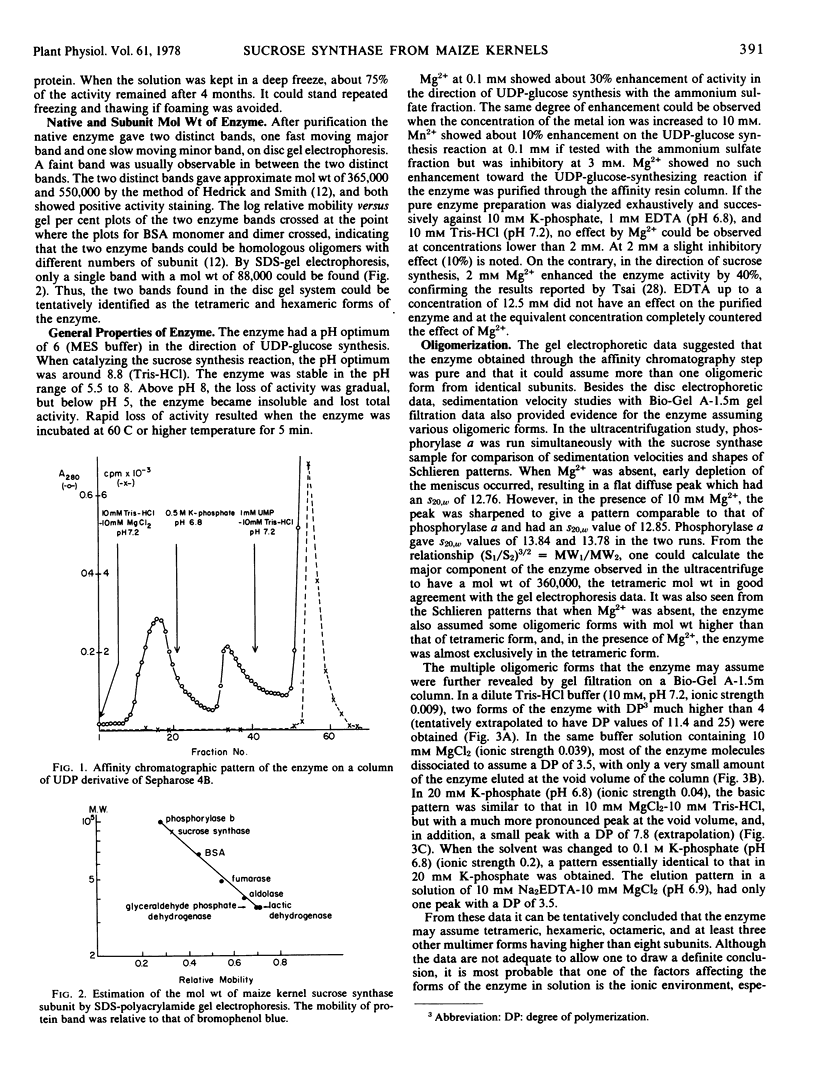
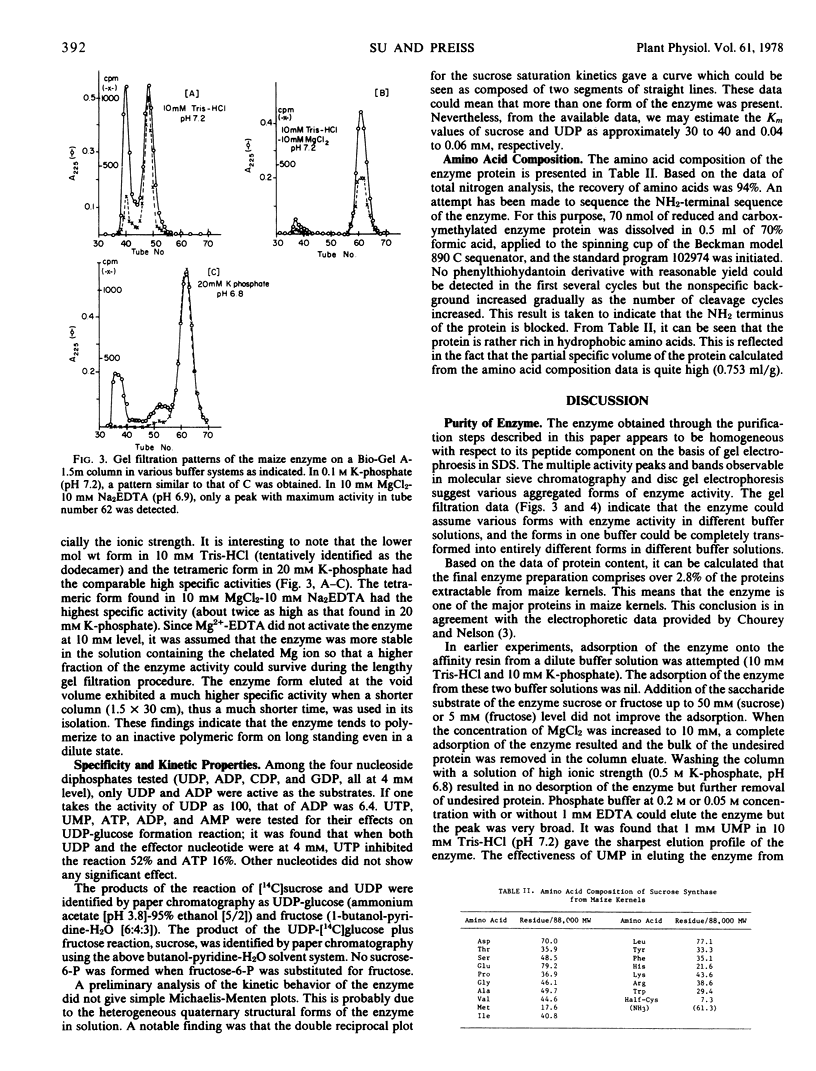
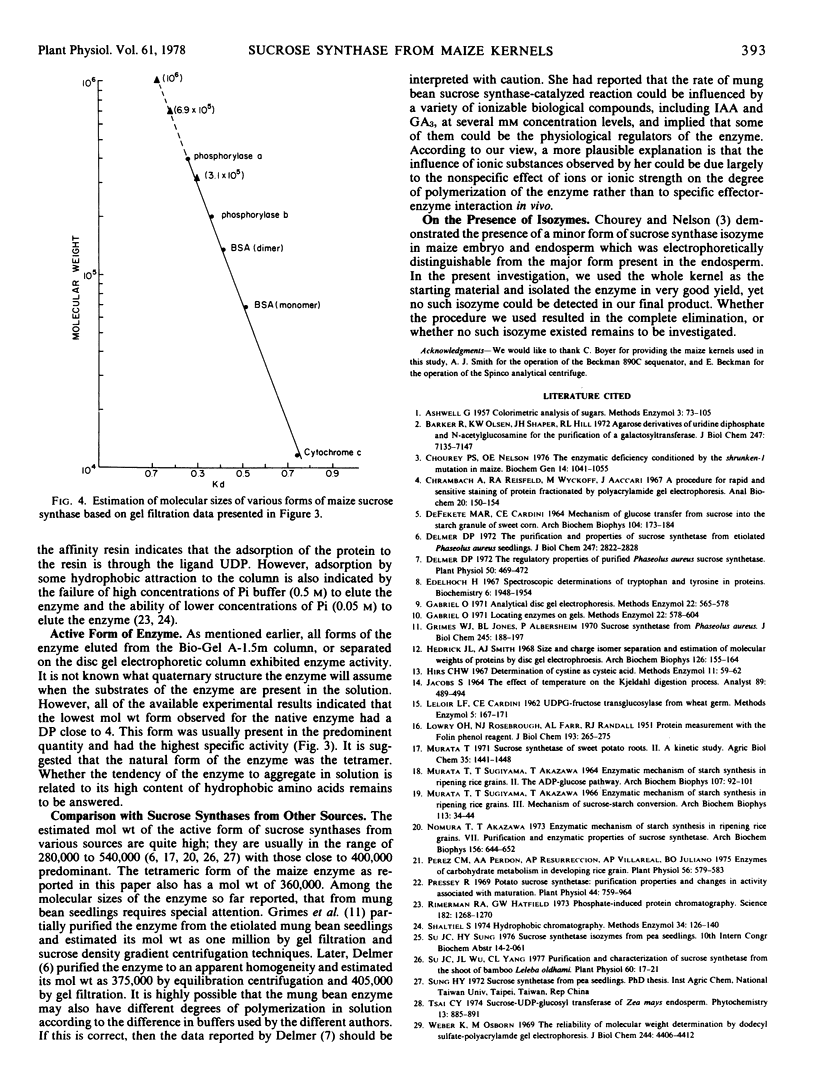
Sucrose synthase was purified from 22-day-old maize (Zea mays L.) kernels to homogeneity by the successive steps of ammonium sulfate fractionation, gel filtration through a Sephadex G-200 column, and affinity chromatography on a UDP-hexanol-amino-agarose column. The degree of purification is 42-fold and the yield is over 80%. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic techniques, sedimentation velocity, and gel filtration studies revealed that the enzyme has identical subunits and could assume tetrameric, octameric, and other higher aggregated forms which are dependent on the ionic species and ionic strength of the solution. All of the enzyme forms exhibit catalytic activity but show differences in their specific activities. In most cases, the tetramer is the predominant form and has the highest specific activity. It is thus concluded that the tetramer could be the native form of the enzyme. The subunit protein has a molecular weight of 88,000 and a blocked NH2 terminus which is not available to Edman degradation. Some general properties and the amino acid composition of the enzyme are also reported.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker R., Olsen K. W., Shaper J. H., Hill R. L. Agarose derivatives of uridine diphosphate and N-acetylglucosamine for the purification of a galactosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 25;247(22):7135–7147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chourey P. S., Nelson O. E. The enzymatic deficiency conditioned by the shrunken-1 mutations in maize. Biochem Genet. 1976 Dec;14(11-12):1041–1055. doi: 10.1007/BF00485135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrambach A., Reisfeld R. A., Wyckoff M., Zaccari J. A procedure for rapid and sensitive staining of protein fractionated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90272-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmer D. P. The Regulatory Properties of Purified Phaseolus aureus Sucrose Synthetase. Plant Physiol. 1972 Oct;50(4):469–472. doi: 10.1104/pp.50.4.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes W. J., Jones B. L., Albersheim P. Sucrose synthetase from Phaseolus aureus seedlings. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):188–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURATA T., SUGIYAMA T., AKAZAWA T. ENZYMIC MECHANISM OF STARCH SYNTHESIS IN RIPENING RICE GRAINS. II. ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE GLUCOSE PATHWAY. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jul;107:92–101. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(64)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Sugiyama T., Minamikawa T., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanism of starch synthesis in ripening rice grains. 3. Mechanism of the sucrose-starch conversion. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Jan;113(1):34–44. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura T., Akazawa T. Enzymic mechanism of starch stynthesis in ripening rice grains. VII. Purification and enzymic properties of sucrose synthetase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Jun;156(2):644–652. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez C. M., Perdon A. A., Resurreccion A. P., Villareal R. M., Juliano B. O. Enzymes of carbohydrate metabolism in the developing rice grain. Plant Physiol. 1975 Nov;56(5):579–583. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.5.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressey R. Potato sucrose synthetase: purification, properties, and changes in activity associated with maturation. Plant Physiol. 1969 May;44(5):759–764. doi: 10.1104/pp.44.5.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RONGINEDEFEKETE M. A., CARDINI C. E. MECHANISM OF GLUCOSE TRANSFER FROM SUCROSE INTO THE STARCH GRANULE OF SWEET CORN. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:173–184. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimerman R. A., Hatfield G. W. Phosphate-induced protein chromatography. Science. 1973 Dec 21;182(4118):1268–1270. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4118.1268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaltiel S. Hydrophobic chromatography. Methods Enzymol. 1974;34:126–140. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(74)34012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su J. C. Purification and Characterization of Sucrose Synthetase from the Shoot of Bamboo Leleba oldhami. Plant Physiol. 1977 Jul;60(1):17–21. doi: 10.1104/pp.60.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



