Abstract
Pea (Pisum sativum) chloroplast thylakoid membranes were prepared by washing in hypotonic buffers. These membranes contained bound ribosomes which were active in protein synthesis when supplemented with soluble components from a strain of Escherichia coli low in ribonuclease. After dissolving the membranes by Triton and purification of the ribosomes, sucrose density gradient profiles indicated the presence of polysomal material as well as monomeric ribosomes. Most of the products of protein synthesis remained associated with the thylakoid membranes even after ribosomes were removed completely by high salt concentrations in the absence of Mg2+. Of the newly formed products, 50% could be digested by pronase, while the remainder were protected by their association with the thylakoid membranes. The products are likely to be a mixture of intrinsic and extrinsic membrane proteins, with only the former completely protected by the membranes from attack by proteases.
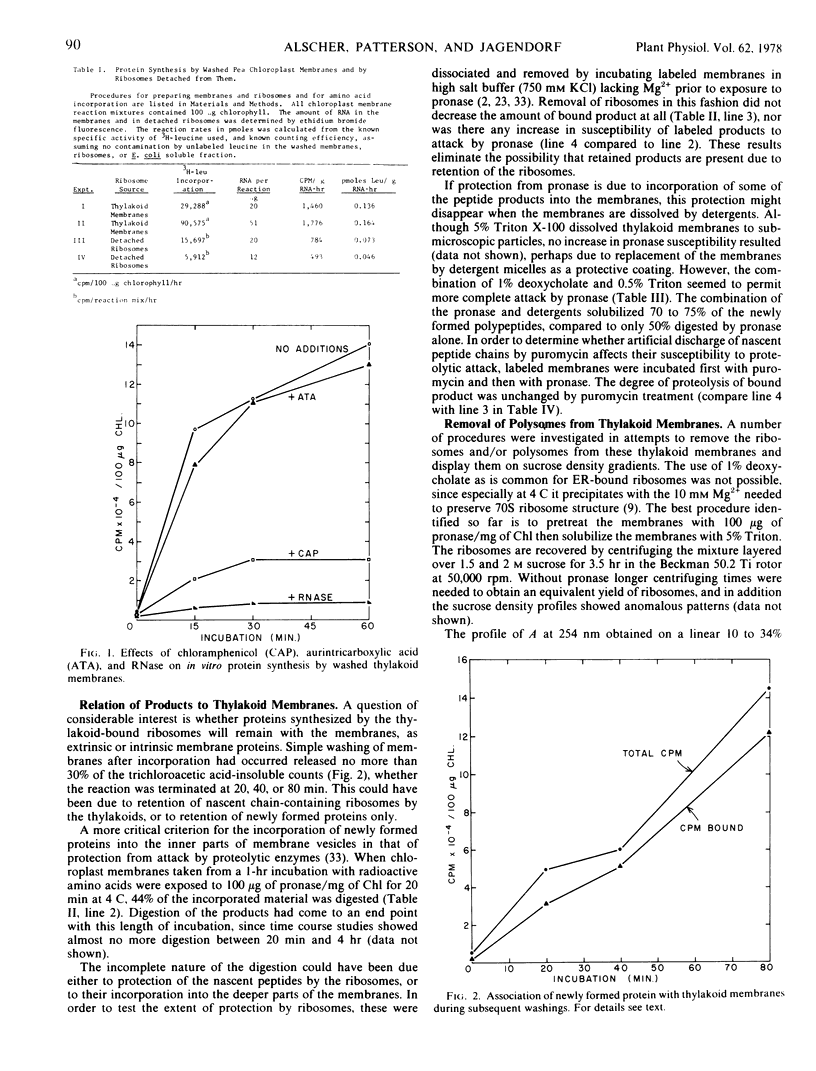
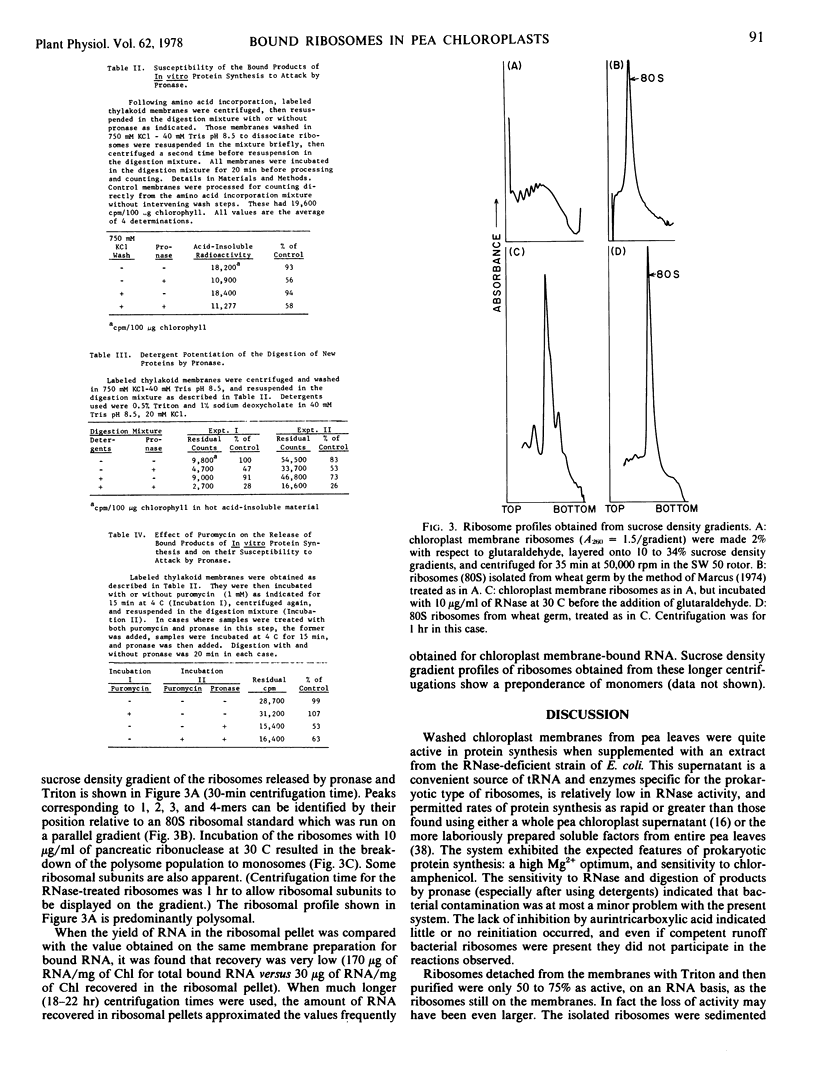
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman M. R., Sabatini D. D., Blobel G. Ribosome-membrane interaction. Nondestructive disassembly of rat liver rough microsomes into ribosomal and membranous components. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):206–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alscher R., Smith M. A., Petersen L. W., Huffaker R. C., Criddle R. S. In vitro synthesis of the large subunit of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase on 70 S ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 May;174(1):216–225. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair G. E., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. I. Light-driven synthesis of the large subunit of fraction I protein by isolated pea chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 24;319(2):223–234. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90013-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. II. Reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from heterologous components. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):852–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boardman N. K., Francki R. I., Wildman S. G. Protein synthesis by cell-free extracts of tobacco leaves. 3. Comparison of the physical properties and protein synthesizing activities of 70 s chloroplast and 80 s cytoplasmic ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jun;17(2):470–487. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley W., Spencer D., Whitfeld P. R. Protein synthesis in isolated spinach chloroplasts: comparison of light-driven and ATP-driven synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):106–117. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. L., Wildman S. G. "Free" and membrane-bound ribosomes, and nature of products formed by isolated tobacco chloroplasts incubated for protein synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 21;209(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90677-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Blobel G., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Attachment of chloroplast polysomes to thylakoid membranes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1554–1558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Blobel G., Siekevitz P., Palade G. E. Periodic variations in the ratio of free to thylakoid-bound chloroplast ribosomes during the cell cycle of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):497–514. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El Hamalawi A. R., Thompson J. S., Barker G. R. The fluorometric determination of nucleic acids in pea seeds by use of ethidium bromide complexes. Anal Biochem. 1975 Aug;67(2):384–391. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk H. Rough thylakoids: polysomes attached to chloroplast membranes. J Cell Biol. 1969 Aug;42(2):582–587. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joy K. W., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. IV. Polypeptides of the chloroplast envelope. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 6;378(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Sabatini D. D. Microsomal membranes and the translational apparatus of eukaryotic cells. Fed Proc. 1973 Nov;32(11):2133–2138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Davies E. Polyribosomes from Peas: V. An Attempt to Characterize the Total Free and Membrane-bound Polysomal Population. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):749–756. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M. M., Gantt E., Parenti F. In vitro Protein Synthesis by Plastids of Phaseolus vulgaris. II. The Probable Relation Between Ribonuclease Insensitive Amino Acid Incorporation and the Presence of Intact Chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 1968 Apr;43(4):495–503. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.4.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M. M., Michaels A. Free and membrane-bound chloroplast polyribosomes Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 1;402(3):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M. M., Michaels A. Ribosomes bound to chloroplast membranes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):65–77. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M. M., Tiffany H. L., Michaels A. Vectorial discharge of nascent polypeptides attached to chloroplast thylakoid membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 19;64(2):735–739. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90381-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh P. R., O'Toole K. The interaction of ribosomes and membranes in animal cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):171–212. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendiola-Morgenthaler L. R., Morgenthaler J. J., Price C. A. Synthesis of coupling factor CF1 protein by isolated spinach chloroplasts. FEBS Lett. 1976 Feb 1;62(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaels A., Margulies M. M. Amino acid incorporation into protein by ribosomes bound to chloroplast thylakoid membranes: formation of discrete products. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 16;390(3):352–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenthaler J. J., Mendiola-Morgenthaler L. Synthesis of soluble, thylakoid, and envelope membrane proteins by spinach chloroplasts purified from gradients. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenti F., Margulies M. M. In Vitro Protein Synthesis by Plastids of Phaseolus vulgaris. I. Localization of Activity in the Chloroplasts of a Chloroplast Containing Fraction from Developing Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1967 Sep;42(9):1179–1186. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.9.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Sabatini D. D. Vectorial discharge of peptides released by puromycin from attached ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):608–615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Blobel G. Controlled proteolysis of nascent polypeptides in rat liver cell fractions. II. Location of the polypeptides in rough microsomes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Apr;45(1):146–157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Blobel G. Controlled proteolysis of nascent polypeptides in rat liver cell fractions. II. Location of the polypeptides in rough microsomes. J Cell Biol. 1970 Apr;45(1):146–157. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.1.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone A. B. A simplified method for preparing sucrose gradients. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;137(1):117–118. doi: 10.1042/bj1370117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Davis B. D. Rapid exchange of subunits between free ribosomes in extracts of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2453–2457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao K. L., Jagendorf A. T. The ratio of free to membrane-bound chloroplast ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Nov 14;324(4):518–532. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90211-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



