Abstract
BACKGROUND
This study presents a case of rapidly developing respiratory failure due to antisynthetase syndrome (AS) following coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a 33-year-old man diagnosed with Klinefelter syndrome (KS).
CASE SUMMARY
A 33-year-old man with a diagnosis of KS was admitted to the Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine of a tertiary hospital in China for fever and shortness of breath 2 wk after the onset of COVID-19. Computed tomography of both lungs revealed diffuse multiple patchy heightened shadows in both lungs, accompanied by signs of partial bronchial inflation. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing of the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid suggested absence of pathogen. A biopsy specimen revealed organizing pneumonia with alveolar septal thickening. Additionally, extensive auto-antibody tests showed strong positivity for anti-SSA, anti-SSB, anti-Jo-1, and anti-Ro-52. Following multidisciplinary discussions, the patient received a final diagnosis of AS, leading to rapidly progressing respiratory failure.
CONCLUSION
This study underscores the clinical progression of AS-associated interstitial lung disease subsequent to viral infections such as COVID-19 in patients diagnosed with KS.
Keywords: Antisynthetase syndrome, COVID-19, Klinefelter syndrome, Interstitial lung disease, Anti-Jo-1, Case report
Core Tip: Antisynthetase syndrome (AS) presents as an idiopathic inflammatory muscle disease typified by the presence of anti-Jo1 antibodies. Mainstream treatments encompass corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. Occasionally, certain rheumatic immune diseases can be precipitated by infectious diseases. Herein, we present a case detailing the rapid onset of respiratory failure due to AS subsequent to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in an individual diagnosed with Klinefelter syndrome (KS). Following a multidisciplinary discussion, the conclusive diagnosis for the patient’s rapid respiratory decline was AS. This investigation accentuates the clinical progression of AS-associated interstitial lung disease following viral infections such as COVID-19 in individuals with KS.
INTRODUCTION
Since January 2023, reported cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have notably surged in China. A large study revealed that more than 30% of patients with severe COVID-19 concurrently exhibit a second active clinical condition[1]. Although the impact of COVID-19 on individuals with rheumatic disorders has been partially evaluated, its influence on the progression of these diseases remains incompletely understood[2-4]. Antisynthetase syndrome (AS) is an idiopathic inflammatory muscle disease characterized by anti-Jo1 antibodies, showcasing diverse clinical presentations and a female-to-male sex bias[5]. Evidence from a review suggests a relatively robust association between Klinefelter syndrome (KS) and various rheumatic and autoimmune diseases, including AS and systemic lupus erythematosus[6]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported clinical case of AS subsequent to COVID-19 in a male patient with KS.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 33-year-old man was admitted to the Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at a tertiary hospital located in China with a complaint of fever and shortness of breath for 2 d on June 30, 2023.
History of present illness
His symptoms commenced 2 d before admission, marked by fever and difficulty breathing. Upon arrival, the patient’s condition required high-flow nasal cannula oxygen (HFNC) to maintain normal transcutaneous oxygen saturation.
History of past illness
His past medical history included KS and novel coronavirus pneumonia diagnosis. At the age of approximately 10-years-old, the patient had a confirmed diagnosis of KS in a tertiary children’s hospital because of small external genitalia. Two weeks before the current hospitalization, the patient had fever and tested positive for COVID-19 by nucleic acid assay at a local county hospital. A chest computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a few patchy ground glass shadows outside the upper lungs. Following a 5-d oral paxlovid treatment and subsequent chest CT confirming lesion absorption, he was discharged, as detailed in the discharge record.
Personal and family history
The patient denied any family history related to malignant tumors, rheumatoid diseases, or immune conditions.
Physical examination
Upon admission, his initial vital signs were as follows: blood pressure, 100/80 mmHg; pulse rate, 130 beats per minute; respiratory rate, 40 breaths per minute; and body temperature, 38°C. He exhibited flushed cheeks, agitated nostrils, and shallow, rapid breathing, along with significant wet rales heard in both lungs. No other abnormalities were observed during physical examination.
Laboratory examinations
His laboratory findings indicated a red blood cell count of 3.94 × 1012/L, white blood cell count of 2.95 × 109/L, lymphocyte count of 0.59 × 109/L, platelet count of 272 × 109/L, C-reactive protein level of 20.75 mg/L, albumin level of 29 g/L, creatine kinase level of 1150 U/L, and creatine kinase isoenzyme level of 36.8 U/L. These results revealed reduced white blood cell and lymphocyte counts, mildly elevated C-reactive protein, hypoproteinemia, and significantly increased muscle enzymes. Arterial blood gas analysis indicated type I respiratory failure with an oxygenation index of approximately 138. Procalcitonin, coagulation function, 1,3-β-D-glucan detection, and galactomannan antigen detection assays yielded normal results.
Imaging examinations
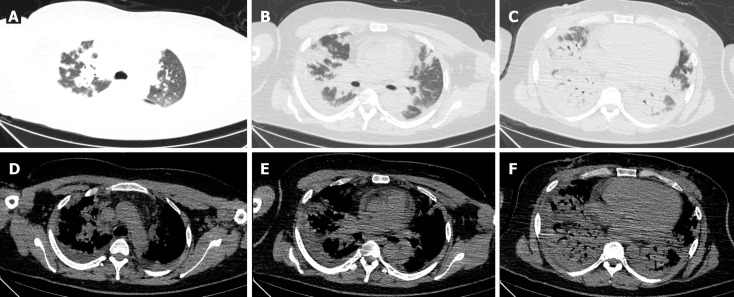
Lung CT examination revealed diffuse multiple patchy areas of increased shadows in both lungs, displaying a partial bronchial inflation sign (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Lung computed tomography examination in admission. There were diffuse multiple patchy heightening shadows in both lungs, with a partial bronchial inflation sign. A: Both upper lungs in the lung window; B: Middle lobe and tongue lobe in the lung window; C: Both lower lungs in the lung window; D: Both upper lungs in the mediastinal window; E: Middle lobe and tongue lobe in the mediastinal window; F: Both lower lungs in the mediastinal window.
Further diagnostic work-up
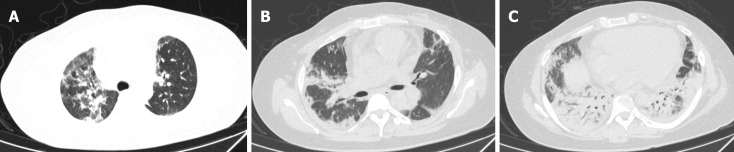
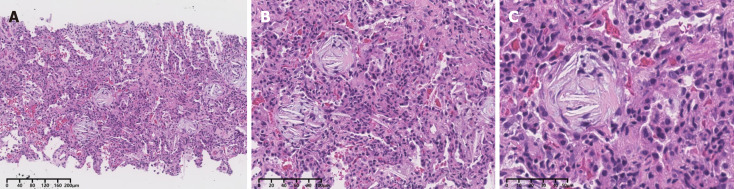
On the 2nd day, a bronchoscopy was conducted on suspicion of infectious pneumonia. The cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were counted, showing a notably elevated ratio of neutrophils at 53%, lymphocytes at 15%, and eosinophils at 9%. Subsequently, microbial next-generation sequencing of BALF showed no detectable pathogens. On the 5th day, additional testing for autoimmune disease-related antibodies indicated strong positive results for anti-SSA, anti-SSB, anti-Jo-1, and anti-Ro-52. To prevent infection, the patient received cefoperazone and sulbactam. Moreover, a dosage of methylprednisolone (40 mg once daily) was initiated 6 d after hospitalization. Remarkably, the diffuse multiple patches of increased density in both upper lungs significantly diminished (Figure 2). To ascertain the nature of the diffuse multiple lesions in both lungs, a color ultrasound-guided percutaneous lung biopsy was performed on day 10 while the patient received HFNC oxygen from a mobile oxygen cylinder. The biopsy specimen obtained on day 14 revealed organizing pneumonia with alveolar septal thickening (Figure 3).
Figure 2.
Lung computed tomography examination after methylprednisolone 40 mg paxlovid 6 d. Diffuse multiple patches of increased density in both upper lungs were significantly absorbed. A: Both upper lungs in the lung window; B: Middle lobe and tongue lobe in the lung window; C: Both lower lungs in the lung window.
Figure 3.
Color ultrasound-guided percutaneous lung puncture. Organizing pneumonia with alveolar septal thickening was found under the microscope (hematoxylin-eosin). A: Original magnification × 10; B: Original magnification × 20; C: Original magnification × 40.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Following a comprehensive multidisciplinary team meeting (MDT) discussion, the patient had a final diagnosis of AS-associated interstitial lung disease (ILD).
TREATMENT
Subsequently, the patient underwent treatment with methylprednisolone at 500 mg paxlovid for 3 d, followed by a regimen of methylprednisolone at 80 mg paxlovid in conjunction with tacrolimus at 1 mg bid.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
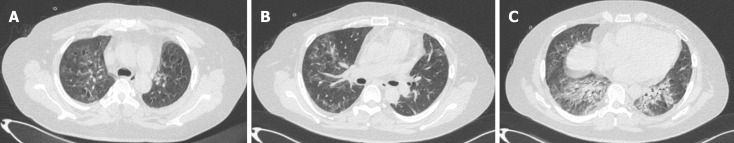
By day 30, the patient regained the ability to walk without requiring oxygen inhalation. A follow-up chest CT examination indicated substantial absorption of diffuse multiple consolidations in both lower lungs (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Lung computed tomography examination at 1 mo follow-up. Diffuse multiple consolidations in both lower lungs were significantly absorbed. A: Both upper lungs in the lung window; B: Middle lobe and tongue lobe in the lung window; C: Both lower lungs in the lung window.
DISCUSSION
In this case study, we report a case of rapidly developing respiratory failure 2 wk after COVID-19 onset in a man with KS. A previous study revealed that all KS patients with COVID-19 experienced mild symptoms, suggesting that the presence of an extra X chromosome might contribute to a more favorable clinical outcome[7]. However, the patient with KS in this study encountered respiratory failure shortly after contracting COVID-19. To address this, we performed a color ultrasound-guided percutaneous lung puncture on the patient and conducted relevant autoimmune tests. Following multidisciplinary team (MDT) discussion, we made a diagnosis of AS alongside KS. Treatment with glucocorticoids and tacrolimus rapidly alleviated the respiratory failure. A 6-mo follow-up analysis indicated that following recovery, COVID-19 could trigger AS flares, leading to previously absent clinical manifestations[8].
AS is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetase antibodies, often accompanied by clinical manifestations such as ILD, myopathy, and nonerosive arthritis. AS occurs distinct from other inflammatory myopathies owing to its significant lung involvement and rapidly progressive ILD (AS-ILD). Hence, managing AS-ILD necessitates thorough clinical, serologic, and radiologic assessments[9]. While several scientific models aid in diagnosing AS, an MDT discussion is frequently valuable in confirming AS-ILD. Lung biopsies should be sparingly performed, as diagnosis primarily relies on high-resolution CT findings, patient symptoms, physical examination, serologic data, and pulmonary function testing[10]. Radiological examination results commonly include an interstitial pattern or ground glass lesions, with patients exhibiting organizing pneumonia generally experiencing a better prognosis[11].
Currently, there is no standardized treatment for AS-ILD because of the absence of randomized controlled trials. The selection of immunosuppression is usually consistent with treatment strategies adopted for ILD secondary to inflammatory myopathies. Treatment options encompass corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, with rituximab often reserved as salvage therapy for refractory cases[12]. Similarly, due to a lack of randomized controlled trials, there are no evidence-based medicine guidelines outlining a recommended corticosteroid treatment strategy. Based on our past clinical practice, we suggest initiating corticosteroid therapy by starting oral prednisone at 1 mg/kg/d. In patients with acute respiratory failure, higher doses of methylprednisolone (approximately 7.5 mg/kg for 3 d) may be required[10]. Although there is no specific method to reduce steroid dosages, we choose to gradually reduce the dosage within 6-8 wk to achieve a maintenance dose in our clinical practice.
While the prevalence of autoimmune diseases in KS remains unknown, it is believed that the estimated frequency is higher in men, nearly reaching the levels observed in women. This could be elucidated by several genes on the X chromosome that regulate immune system function and are associated with the escape of X inactivation during embryogenesis in the early development of KS[13]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported clinical case of AS-associated ILD after COVID-19 in a male patient with KS.
CONCLUSION
In summary, we have described a rare clinical case of AS-associated ILD following COVID-19 in a male patient with KS in China. Clinicians should be cognizant of this rare clinical entity, and timely MDT discussions can significantly contribute to the diagnosis of AS in patients with KS, especially those facing potentially severe respiratory failure.
Footnotes
Informed consent statement: All study participants or their legal guardian provided informed written consent prior to study enrollment.
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors report no relevant conflicts of interest for this article.
CARE Checklist (2016) statement: The authors have read the CARE Checklist (2016), and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the CARE Checklist (2016).
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Peer-review started: October 11, 2023
First decision: December 5, 2023
Article in press: January 12, 2024
Specialty type: Medicine, research and experimental
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Freund O, Israel S-Editor: Wang JJ L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Xu ZH
Contributor Information
Xiang-Xiang Wu, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; China-Japan Friendship Jiangxi Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China.
Jian Cui, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; China-Japan Friendship Jiangxi Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China.
Shi-Yao Wang, China-Japan Friendship Jiangxi Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Center of Respiratory Medicine, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China.
Tian-Tian Zhao, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China.
Ya-Fei Yuan, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; China-Japan Friendship Jiangxi Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China.
Long Yang, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; China-Japan Friendship Jiangxi Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China.
Wei Zuo, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; China-Japan Friendship Jiangxi Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China.
Wen-Jian Liao, Department of Respiratory and Critical Care, The First Affiliated Hospital, Jiangxi Medical College, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China; China-Japan Friendship Jiangxi Hospital, Nanchang 330006, Jiangxi Province, China. 897854867@qq.com.
References
- 1.Freund O, Azolai L, Sror N, Zeeman I, Kozlovsky T, Greenberg SA, Epstein Weiss T, Bornstein G, Tchebiner JZ, Frydman S. Diagnostic delays among COVID-19 patients with a second concurrent diagnosis. J Hosp Med. 2023;18:321–328. doi: 10.1002/jhm.13063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bozzalla Cassione E, Zanframundo G, Biglia A, Codullo V, Montecucco C, Cavagna L. COVID-19 infection in a northern-Italian cohort of systemic lupus erythematosus assessed by telemedicine. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:1382–1383. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Monti S, Balduzzi S, Delvino P, Bellis E, Quadrelli VS, Montecucco C. Clinical course of COVID-19 in a series of patients with chronic arthritis treated with immunosuppressive targeted therapies. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79:667–668. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ferri C, Giuggioli D, Raimondo V, Dagna L, Riccieri V, Zanatta E, Guiducci S, Tavoni A, Foti R, Cuomo G, De Angelis R, Cozzi F, Murdaca G, Cavazzana I, Romeo N, Codullo V, Ingegnoli F, Pellegrini R, Varcasia G, Rossa AD, De Santis M, Abignano G, Colaci M, Caminiti M, L'Andolina M, Lubrano E, Spinella A, Lumetti F, De Luca G, Bellando-Randone S, Visalli E, Bilia S, Giannini D, Masini F, Pellegrino G, Pigatto E, Generali E, Dall'Ara F, Mariano GP, Barsotti S, Pettiti G, Zanframundo G, Brittelli R, Aiello V, Scorpiniti D, Ferrari T, Caminiti R, Campochiaro C, D'Angelo S, Iannone F, Matucci-Cerinic M, Doria A, Miccoli M, Fallahi P, Antonelli A COVID-19 & Autoimmune Systemic Diseases Italian Study Group. COVID-19 and systemic sclerosis: clinicopathological implications from Italian nationwide survey study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021;3:e166–e168. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00007-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rovenský J, Kovalancík M, Payer J, Kohler K. Klinefelter syndrome with antisynthetase syndrome: why might they be associated? J Clin Rheumatol. 2003;9:62–63. doi: 10.1097/01.RHU.0000049718.58846.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rovenský J, Imrich R, Lazúrová I, Payer J. Rheumatic diseases and Klinefelter's syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1193:1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05292.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Aliberti L, Gagliardi I, Lupo S, Verrienti M, Bondanelli M, Zatelli MC, Ambrosio MR. Investigation of COVID-19 infection in subjects with Klinefelter syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest. 2022;45:1065–1069. doi: 10.1007/s40618-021-01727-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Vertui V, Zanframundo G, Castañeda S, Biglia A, Palermo BL, Cavazzana I, Meloni F, Cavagna L. Clinical evolution of antisynthetase syndrome after SARS-CoV2 infection: a 6-month follow-up analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2022;41:2601–2604. doi: 10.1007/s10067-022-06216-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fu H, Zheng Z, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Cui J, Wang Z, Xue J, Chi S, Cao M, Chen J. Prediction of progressive pulmonary fibrosis in patients with anti-synthetase syndrome-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2023;42:1917–1929. doi: 10.1007/s10067-023-06570-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sawal N, Mukhopadhyay S, Rayancha S, Moore A, Garcha P, Kumar A, Kaul V. A narrative review of interstitial lung disease in anti-synthetase syndrome: a clinical approach. J Thorac Dis. 2021;13:5556–5571. doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-3328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zanframundo G, Faghihi-Kashani S, Scirè CA, Bonella F, Corte TJ, Doyle TJ, Fiorentino D, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Hudson M, Kuwana M, Lundberg IE, Mammen A, McHugh N, Miller FW, Monteccucco C, Oddis CV, Rojas-Serrano J, Schmidt J, Selva-O'Callaghan A, Werth VP, Sakellariou G, Aggarwal R, Cavagna L. Defining anti-synthetase syndrome: a systematic literature review. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2022;40:309–319. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/8xj0b9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Witt LJ, Curran JJ, Strek ME. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Antisynthetase Syndrome. Clin Pulm Med. 2016;23:218–226. doi: 10.1097/CPM.0000000000000171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kalayci Yigin A, Alay MT, Uğurlu S, Seven M. The First Case Report of 47,XXY/46,XX/46,XY Mosaic Klinefelter Syndrome Patient With Mixed Connective Tissue Disorder. Am J Mens Health. 2023;17:15579883231165173. doi: 10.1177/15579883231165173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]