Abstract
Background
FLI1 is an oncogenic transcription factor that promotes diverse malignancies through mechanisms that are not fully understood. Herein, FLI1 is shown to regulate the expression of Ubiquitin Associated and SH3 Domain Containing A/B (UBASH3A/B) genes. UBASH3B and UBASH3A are found to act as an oncogene and tumor suppressor, respectively, and their combined effect determines erythroleukemia progression downstream of FLI1.
Methods
Promoter analysis combined with luciferase assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) analysis were applied on the UBASH3A/B promoters. RNAseq analysis combined with bioinformatic was used to determine the effect of knocking-down UBASH3A and UBASH3B in leukemic cells. Downstream targets of UBASH3A/B were inhibited in leukemic cells either via lentivirus-shRNAs or small molecule inhibitors. Western blotting and RT-qPCR were used to determine transcription levels, MTT assays to assess proliferation rate, and flow cytometry to examine apoptotic index.
Results
Knockdown of FLI1 in erythroleukemic cells identified the UBASH3A/B genes as potential downstream targets. Herein, we show that FLI1 directly binds to the UBASH3B promoter, leading to its activation and leukemic cell proliferation. In contrast, FLI1 indirectly inhibits UBASH3A transcription via GATA2, thereby antagonizing leukemic growth. These results suggest oncogenic and tumor suppressor roles for UBASH3B and UBASH3A in erythroleukemia, respectively. Mechanistically, we show that UBASH3B indirectly inhibits AP1 (FOS and JUN) expression, and that its loss leads to inhibition of apoptosis and acceleration of proliferation. UBASH3B also positively regulates the SYK gene expression and its inhibition suppresses leukemia progression. High expression of UBASH3B in diverse tumors was associated with worse prognosis. In contrast, UBASH3A knockdown in erythroleukemic cells increased proliferation; and this was associated with a dramatic induction of the HSP70 gene, HSPA1B. Accordingly, knockdown of HSPA1B in erythroleukemia cells significantly accelerated leukemic cell proliferation. Accordingly, overexpression of UBASH3A in different cancers was predominantly associated with good prognosis. These results suggest for the first time that UBASH3A plays a tumor suppressor role in part through activation of HSPA1B.
Conclusions
FLI1 promotes erythroleukemia progression in part by modulating expression of the oncogenic UBASH3B and tumor suppressor UBASH3A.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12885-024-12075-2.
Keywords: FLI1, Transcriptional regulation, UBASH3A, UBASH3B, HSPA1B, AP1, SYK, Leukemia proliferation, Oncogene, Tumor suppressor
Introduction
UBASH3A (STS-2/TULA/ CLIP4) and UBASH3B (STS-1/TULA-2) belong to the ubiquitin-associated and Src-homology 3 domain-containing (UBASH3) family [1]. While UBASH3B is ubiquitously expressed [2], UBASH3A expression is restricted to lymphoid tissues [3]. UBASH3A is a negative regulator of T-cell activation and function through regulation of ZAP70 and TCR activation [2, 4]. Genetic variants in this gene are associated with several distinct autoimmune diseases [5–8], including type 1 diabetes, and rheumatoid anthesis, although the underlying mechanism is still unknown. UBASH3A has three structural domains: 1) N-terminal UBA (ubiquitin-associated), 2) SH3 (Src homology 3), and 3) PGM (phosphoglycerate mutase-like/C-terminal histidine phosphatase) domain [8]. The UBA domain can bind to mono-ubiquitin and lysine-63 and methionine-1-linked polyubiquitin chains. UBASH3A has four known ubiquitination sites at lysine residues 15, 202, 309, and 358. Monoubiquitination at Lys 202 causes UBASH3A to adopt a closed conformation, which prevents the binding of the UBA domain to substrates [9]. The SH3 domain interacts with dynamin [10] (which is required for endocytosis) and with CBL [11] (an E3 ubiquitin ligase). The PGM domain mediates self-dimerization [12], which exhibits very weak, possibly acid-dependent, phosphatase activity (despite its structural similarity to the more active PGM domain in UBASH3B) [3, 13].
UBASH3B has similar structural domains to UBASH3A and some overlapping functions. However, UBASH3B suppresses T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling by dephosphorylating ZAP-70 and Syk, two key molecules involved in the amplification of TCR-triggered signals [3, 14, 15]. UBASH3A and UBASH3B knockout mice exhibit no obvious phenotype until the T cell receptor (TCR) is stimulated. Upon stimulation, T cells from UBASH3A / UBASH3B double deficient mice are hyper-proliferative and produce more IL-2 and IFNγ than wild-type T cells [3], underscoring the vital role UBASH3A/B in T cell regulation and autoimmunity. UBASH3B expression is implicated in various cancers through its ability to bind CBL and block its ubiquitination activity [16, 17].
We have previously shown that Protein Kinase C Delta (PKCẟ) downregulation in TPA (4b-12-O-tetradecanoylphobol-13-acetate)-resistant cell lines, can inhibit erythroleukemia when paired with UBASH3B knockdown [18]. Interestingly, TPA and several PKCẟ agonists have previously been reported to activate the transcription factor FLI1 through increased protein phosphorylation [19–21]. We hypothesized that this could be due to FLI1 regulation of UBASH3B. The ETS transcription factor Fli-1 was first identified as a target of retroviral insertional activation in erythroleukemia induced by the Friend virus [22, 23]. Human FLI1 oncogene was later implicated in various types of cancers through translocations or overexpression [24–37]. Indeed, Fli-1 transcriptional activation affects several hallmarks of cancer, including proliferation, survival, differentiation, angiogenesis, genomic instability, and immune surveillance [37]. In this study, we show that leukemias expressing high FLI1 produce either higher UBASH3B or lower UBASH3A. We also show that FLI1 controls the expression of these ubiquitin associated ligase genes in erythroleukemic cells. These results suggest that FLI1 promotes erythroleukemia and possibly progression of other cancers in part by balancing oncogenic effect of UBASH3B and tumor suppressor activity of UBASH3A.
Materials and methods
Cells, culture conditions and drug therapy
The human leukemia (HEL 92.1.7, K562) and epithelial-like HEK293T (CRL-3216) cell lines were obtained from ATCC (US) and tested negative for mycoplasma. These cell lines were cultured and maintained in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium supplemented with HyClone 5% fetal bovine serum (GE Healthcare, US).
For drug treatment, cells were treated with Camptothecin (MedChemExpress, CN), T5224 (APExBIO, CN) and R406 (Beyotime Biotechnology, CN) for indicated times and used for cell proliferation analysis. Generation of K562-fli1 cells was previously described [21]. For FLI1 induction, cells were treated with 5μM of doxycycline (Solarbio, CN).
RNA preparation and RT-qPCR
Total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, US), cDNA was synthesis using the PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (Takara Bio, CN) and RT-qPCR analysis using the FastStart Universal SYBR Green Master Mix (Roche, CH) on a Step One Plus Real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems/Thermo Fisher Scientific, US). The expression of the test genes was given as relative to β Actin. Three biological replicates in triplicate (n = 3) were performed for each gene. The primers sequences were listed in the Table 1.
Table 1.
Primers sequences used for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Sequence(5’-3’) | |
|---|---|---|
| UBASH3A | sense | GGTGCAAATCGTCAACACCT |
| antisense | GCAAAATCCCCACATTCCCG | |
| UBASH3B | sense | ACCATCAAGCATGGATCGGC |
| antisense | CCGACATGGGAGAATAACCAGT | |
| FLI1 | sense | CAGCCCCACAAGATCAACCC |
| antisense | CACCGGAGACTCCCTGGAT | |
| HSPA1B | sense | TTTGAGGGCATCGACTTCTACA |
| antisense | CCAGGACCAGGTCGTGAATC | |
| FOS | sense | CCGGGGATAGCCTCTCTTACT |
| antisense | CCAGGTCCGTGCAGAAGTC | |
| JUN | sense | TCCAAGTGCCGAAAAAGGAAG |
| antisense | CGAGTTCTGAGCTTTCAAGGT | |
| SYK | sense | TGCACTATCGCATCGACAAAG |
| antisense | CATTTCCCTGTGTGCCGATTT | |
| GAPDH | sense | GCCAGTAGAGGCAGGGATGATGTTC |
| antisense | CCATGTTCGTCATGGGTGTGAACCA |
Promoter analysis and luciferase assays
The UBASH3A and UBASH3B promoter regions (see Figs. 2A and 3A) were amplified by PCR, cloned into the luciferase reporter vector pGL3-basic (Promega, US), and used in a luciferase activity assay, as previously described [38]. Briefly, 2.5 μg of the indicated promoter was co-transfected with either MigR1 (2.5 μg) or MigR1-FLI1 (2.5 μg) using a Lipofectamine 2000 kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) into epithelial HEK-293T cells which seeded onto 6-well plates one day before, according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Renilla luciferase (Promega, US) was used as an internal control for transfection efficiency.
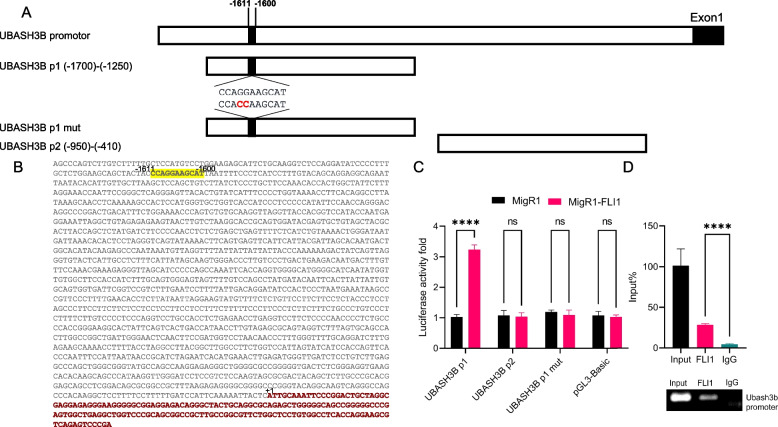
Fig. 2.
FLI1 binds to the UBASH3B promoter and activates its expression. A The genomic structure of the UBASH3B promoter its indicated derivatives UBASH3B P1, UBASH3B P2, and UBASH3B P1-mut, which were subcloned upstream from the PGL3 luciferase reporter plasmid. B The UBASH3B promoter sequence and its potential FLI1 binding site. C Luciferase activity in HEK293T cells transfected with the UBASH3B P1/P2 and UBASH3B P1-mut luciferase vectors transfected with either FLI1 expression vector MigR1-Fli1 or control plasmid MigR1. D Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIp) analysis of the human UBASH3B promoter in HEL erythroleukemic cells for binding to FLI1 by RT-qPCR (top panel). The lower panel shows the gel image for the immunoprecipitated PCR-amplified band relative to the input. P < 0.0001 (****). The full-length gel for Fig. 2D are presented in Supplementary Fig. 10
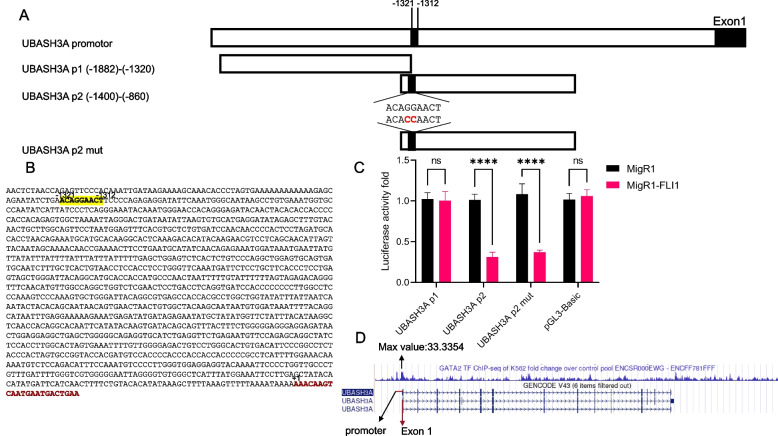
Fig. 3.
FLI1 interacts with the UBASH3A promoter and reduces its expression. A The genomic structure of the human UBASH3A promoter and its sub-derivatives UBASH3A P1 and UBASH3A P2 as well as their derivative mutant DNA subcloned downstream of the pGL3-basic luciferase reporter plasmid. B The sequence of the UBASH3A promoter and its potential FLI1 binding site. C HEK293T cells were co-transfected with the UBASH3A P1/P2 and mutant (UBASH3A P2-mut) luciferase vectors and either MigR1-Fli1 or control plasmid MigR1. Luciferase activity was determined, as described in materials and methods. D ENCODE data showing the binding of GATA2 to the UBASH3A promoter region—Maximum fold change: 33.3354
ShRNA and siRNA expression
The construction of shFLI1 cells has been previously described [38]. shUBASH3A, shUBASH3B, and shHSPA1B and scrambled control vectors were generated by inserting the corresponding shRNA sequence containing oligonucleotides and scrambled DNAs into the restriction enzyme sites BcuI within the PLent-GFP expression vector (obtained from Vigene Bioscience, US). The lentivirus particles were generated by co-transfecting shRNA PLent-GFPs (10 µg) with packaging plasmids psPAX2 (5 µg) and pMD2G (10 µg) (Addgene plasmid #12,259 & #12,260) into HEK293T cells, using lipofectamine 2000. The supernatants were collected two days after transfection to transduce HEL cells. The positive cells were then selected via incubation with a medium containing puromycin (5 µg/ml; Solarbio, CN). ShRNA sequences are listed in Table 2.
Table 2.
ShRNA sequences
| shRNA | Sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|
| shUBASH3A1 | GCTGCATGATCATTGCAATTTCAAGAGAATTGCAATGATCATGCAGCTTTTTT |
| shUBASH3A2 | GGGATCAAAGACTTTGAAATTCAAGAGATTTCAAAGTCTTTGATCCCTTTTTT |
| shUBASSH3A3 | CGAGTGGAACCTGGAATCTTTCAAGAAAAGATTCCAGGTTCCACTCGTTTTTT |
| shHSPA1B1 | GCTGACCAAGATGAAGGAGATTTCAAGAGAATCTCCTTCATCTTGGTCAGCTTTTTT |
| shHSPA1B2 | GCGCAACGTGCTCATCTTTGTTCAAGAGACAAAGATGAGCACGTTGCGCTTTTTT |
| shHSPA1B3 | GGGCCATGACGAAAGACAATTCAAGAGATTGTCTTTCGTCATGGCCCTTTTTT |
| shUBASH3B1 | GCGGCAGTATGAAGATCAAGGTTCAAGAGACCTTGATCTTCATACTGCCGCTTTTTT |
| shUBASH3B2 | GGTGAAGCCTTGTTAGAAAGTTTCAAGAGAACTTTCTAACAAGGCTTCACCTTTTTT |
| shUBASH3B3 | GCGTTCAGACTGCACATAATATTCAAGAGATATTATGTGCAGTCTGAACGCTTTTTT |
| shUBASH3B4 | GGATACCTCCATCAGAGTTAGTTCAAGAGACTAACTCTGATGGAGGTATCCTTTTTT |
| Scrambled | TTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGTTTCAAGAGAACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAATTTTTT |
UBASH3A siRNAs and negative control were purchased from GenePharma (CN). The UBASH3A siRNA was transfected into shUBASH3B cells using Lipofectamine 2000. Two days after transfection, cells were collected, RNA was extracted, and RT-qPCR was used to detect UBASH3A. For proliferation analysis, cells were transfected with siRNA for 48 h and assessed using an MTT assay every day for three days. SiRNA sequences listed in Table 3.
Table 3.
SiRNA sequences
| siRNA | Sequence(5’-3’) | |
|---|---|---|
| Negative control | sense | UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT’ |
| antisense | ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT’ | |
| GAPDH Positive control | sense | UGACCUCAACUACAUGGUUTT |
| antisense | AACCAUGUAGUUGAGGUCATT | |
| siUBASH3A1 | sense | GCUGCAUGAUCAUUGCAAUTT |
| antisense | AUUGCAAUGAUCAUGCAGCTT | |
| siUBASH3A2 | sense | GAGCCCUAUUCCAGUACAATT |
| antisense | UUGUACUGGAAUAGGGCUCTT | |
| siUBASH3A3 | sense | CCACUCCUGAUGGGAAAUATT |
| antisense | UAUUUCCCAUCAGGAGUGGTT | |
| siUBASH3A4 | sense | CGGGUGUCAUCCUAAUUGUTT |
| antisense | ACAAUUAGGAUGACACCCGTT |
RNAseq analysis and bioinformatics
Total RNA samples isolated from designated cells and appropriate controls were sent for RNAseq at BGI genomics (CN). BGI also performed the data preprocessing, which we used to analyze the gene expression profiles between shRNA-mediate knocked downed genes and the scrambled control group. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were determined by the condition (log2FoldChange ≤ -1 or ≥ 1, padj < 0.05) and then analyzed by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) for UBASH3B and UBASH3A were shown in Supplementary Tables 1 and 2, respectively. The TCGA data analysis was obtained using GEPIA2 resources (http://gepia2.cancer-pku.cn/).
Western blotting
Total protein from cell lines was extracted using RIPA buffer (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, CN) containing 1:100 PMSF (Solarbio, CN). The protein concentration was determined using a BCA kit (Solarbio, CN) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Load equal amounts of protein into the wells of the SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to PVDF membrane. The membrane was blocked using non-fat milk for 1 h at room temperature. Incubate the membrane with primary antibody in blocking buffer overnight at 4°C. After washed by TBST (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, CN) at room temperature for three times, the membrane was incubated with Anti-rabbit IgG (H + L) DyLight™ 800 4X PEG Conjugated secondary antibody (5151s, Cell Signaling Technology, US) in blocking buffer at room temperature for 1 h. The following primary antibodies were used: anti-FLI1 (ab133485, Abcam, UK), anti-UBASH3A (15,823–1-AP, Proteintech, DE), anti-UBASH3B (19,563–1-AP, Proteintech, DE), polyclonal rabbit test primary antibodies; anti-GAPDH (G9545, Sigma Aldrich, US). Antibody dilution was conducted according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The Odyssey system (LICOR Biosciences) was used for western blot membrane imaging and analysis.
Apoptosis
Cells were incubated with compounds or vehicle for 24 h, as previously described [29]. Treated cells were washed by PBS, stained by Annexin V and PI apoptosis detection kit (BD Biosciences, US), following the kit guidelines and analyzed by flow cytometer.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIp) analysis
The ChIp analysis was performed, as previously published [29]. In brief, formaldehyde was used to crosslink erythroleukemia HEL cells before they were centrifuged and the pellet was then resuspended in Magna ChIp A/G kit lysis solution (Sigma-Aldrich, US). The fixed pellet was sonicated using a Sonics Vibra VCX150 (Ningbo Scientz Biotechnology, CN). A small aliquot of the chromatin was taken out to serve as an input control. Protein G Sepharose beads (Cell Signaling Technology, US) were added to the chromatin and incubated for one hour at room temperature. The immunoprecipitations were performed overnight at 4°C with 1 μg of ChIp grade anti-FLI1 antibody (ab15289, Abcam, UK) and the negative control rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, US). After centrifugations, the chromatin precipitates were washed and reverse crosslinked. The precipitated chromatins were then incubated with proteinase K at 56°C for two hours, DNA purified with one phenol chloroform extraction and resuspended in TE buffer. RT-qPCR was performed using this DNA to determine the amount of FLI1 binding within the promoter region. The percentage of input was calculated as previously described [29]. Amplified DNAs were also resolved on a 2% agarose gel. The ChIp was performed at least in three independent experiments. The primer sequences for the ChIp PCRs are as follows. Forward: GTCCTGGAAGAGCATTCTGCA; Reverse: AGCAGGGAGATAAGACAGCT.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed Student t-test or a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test, using Prism 9 software (GraphPad Software Inc, US). The P values were indicated within the figures using a standard scheme, P < 0.05 (*), P < 0.01 (**), P < 0.001 (***), and P < 0.0001 (****). Where appropriate, the data were displayed using the mean (± SEM) from at least three independent experiments.
Results
FLI1 regulates UBASH3B positively and UBASH3A negatively in leukemic cells
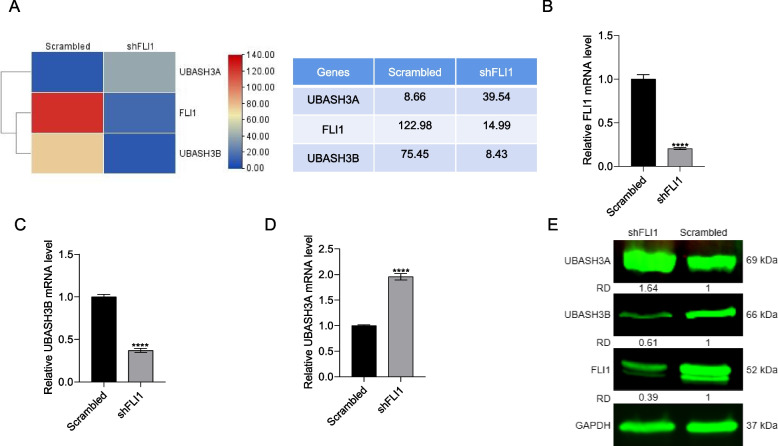
While FLI1 is known to promote the initiation and progression of leukemias and other cancers [37], the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. To uncover its downstream targets, RNAseq analysis was used to identify genes whose expression is modulated in response to shRNA knockdown of FLI1 (shFLI1) in leukemic HEL cells [38]. Knockdown of FLI1 in HEL cells was previously shown to slow down proliferation, alter the cell cycle and induce apoptosis [29, 37]. Among the affected genes, UBASH3B expression was strongly downregulated in shFLI1 versus scrambled controlled HEL cells, whereas UBASH3A was elevated (Fig. 1A). These results raised the possibility that the UBASH3AB/A variants may affect erythroleukemia progression through opposing functions. First, we confirmed these results by RT-qPCR, where reduced FLI1 expression (Fig. 1B) in shFLI1 cells was indeed associated with a decreased UBASH3B (Fig. 1C) and increased UBASH3A (Fig. 1D). Western blotting further confirmed this expression pattern (Fig. 1E). In K562-fli1 cells, expression of FLI1 resulted in upregulation of UBASH3B and downregulation of UBASH3A (Supplemental Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
FLI1 regulates UBASH3A and UBASH3B transcription in leukemic cells. A Heatmap of UBASH3A and UBASH3B expression following FLI1 knockdown (shFLI1) versus control leukemia cells. B-D RT-qPCR analysis for expression of FLI1 (B), UBASH3B (C), and UBASH3A (D) in shFLI1 cells versus scrambled control leukemic cells. E Western blot analysis for FLI1, UBASH3A, and UBASH3B compared to the loading control GAPDH in shFLI1 versus scrambled control HEL cells. P < 0.001 (***). Relative density (Rd) determined by densitometer is shown. The full-length blots/gels for Fig. 1E are presented in Supplementary Fig. 9
To determine whether the differential effect of FLI1 on UBASH3A and UBASH3B is mediated by direct transcriptional regulation, we performed an in vitro FLI1 promoter binding assays. Figure 2A depicts a schematic of the UBASH3B promoter (P1 and P2), which contains a putative FLI1 binding site at position -1611 to -1600 in P1 (Fig. 2B). The FLI1 binding site is absent in the UBASH3B-P2 promoter, which was used as a negative control (Fig. 2A). Transfection of these luciferase reporter plasmids into HEK293T cells alongside either the FLI1 expression vector (MigR1-FLI1) or vector control (MigR1) resulted in significantly higher luciferase activity for the P1 promoter when co-transfected with MigR1-FLI1. In contrast, the P2 promoter was refractory to FLI1 expression. Mutation within the FLI1 binding site on the P1 promoter (UBASH3B P1 mut, Fig. 2A) did not affect basal gene expression but conferred resistance to FLI1 over-expression (Fig. 2C). FLI1 binding to the UBASH3B promoter was further confirmed by Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIp) (Fig. 2D), in which significantly higher binding was observed using FLI1 antibody versus control IgG. Moreover, in ChIPseq in GEO database, FLI1 strongly binds to promoter of the UBASH3B gene (Supplemental Fig. 2). These results demonstrate direct regulation of the UBASH3B expression by FLI1.
A similar strategy was used to generate the plasmids containing UBASH3A-P1 and P2 promoters (Fig. 3A); the latter contained FLI1 binding site at positions -1321 to -1312 (Fig. 3B). Both the P1 and P2 promoters were associated with similar activation when co-transfected with the MigR1 expression vector (Fig. 3C), but MigR1-FLI1 inhibited luciferase activity supporting the negative regulation of UBASH3A by FLI1. Interestingly, MigR1-FLI1 also inhibited luciferase activity when the FLI1 binding site within the P2 promoter was mutated (UBASH3A P2 mut, Fig. 3A and C). In the ChIp assay, FLI1 failed to bind the putative binding site identified within the UBASH3A promoter (data not shown). These results suggest that FLI1 indirectly regulates UBASH3A expression through another site or transcription factor. Indeed, strong binding between the GATA2 transcription factor within the UBASH3A promoter has been identified in the ENCODE database [39] (Fig. 3D). GATA2 is regulated by FLI1[38] and thus may mediate the negative effect of FLI1 on UBASH3A expression in leukemic cells.
UBASH3A and UBASH3B downregulation affects leukemia cell proliferation
As FLI1 knockdown blocks leukemia cell proliferation [38], we next examined impact of UBASH3A and UBASH3B on cell growth. To this end, UBASH3B was knocked down in HEL cells using lentivirus vectors containing four shRNAs, which resulted in reduced mRNA expression (Fig. 4A) and protein levels (Fig. 4B). Reduced expression of shUBASH3B resulted in significant growth suppression compared to the control scrambled cells (Fig. 4C). The expression of FLI1 was also lightly reduced (possibly due to a positive feedback) in shUBASH3B cells (Supplemental Fig. 3A and B). These results suggest an oncogenic role for UBASH3B in leukemia progression.
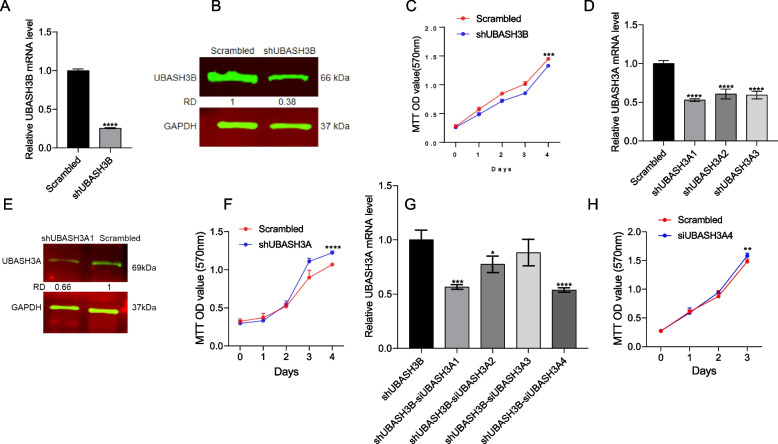
Fig. 4.
Control of cell proliferation by UBASH3A and UBASH3B. A, B The expression of UBASH3B by RT-qPCR (A) and western blot (B) in shUBASH3B and scrambled control cells. C The cell proliferation rate of shUBASH3B versus scrambled control cells. D Expression of UBASH3A in lentivirus transduced shUBASH3A1-A3 cells by RT-qPCR. E UBASH3A levels in shUBASH3A1 cells by western blot. F The cell proliferation rate for shUBASH3A1 versus the scrambled control. G Knockdown of UBASH3A in shUBASH3B cells via siRNA (siUBASH3A1-siUBASH3A4), as detected via RT-qPCR. H The proliferation of shUBASH3B cells after treatment with siUBASH3A4. P < 0.05 (*), P < 0.01 (**), P < 0.001 (***), and P < 0.0001 (****). The full-length blots/gels for Fig. 4B and 4E are presented in Supplementary Fig. 11
Three lentiviruses (shUBASH3A1-3) were also used to knock down UBASH3A in HEL cells (Fig. 4D), resulting in reduced mRNA expression (Fig. 4D) and protein levels (Fig. 4E). Unlike the effect of UBASH3B knockdown, UBASH3A depletion increased cell proliferation compared to scrambled control cells (Fig. 4F), suggesting an inhibitory role for this protein in erythroleukemic cells. As UBASH3B knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, we examined whether UBASH3A knockdown moderated this suppressive effect. Indeed, inhibition of UBASH3A in shUBASH3B cells using siRNA (Fig. 4G) significantly reduced growth inhibition compared to the control (Fig. 4H). The expression of the FLI1 oncogene was increased in shUBASH3A1 cells (Supplemental Fig. 3C and D). These results indicate that UBASH3A/B have opposing effects on leukemic cell proliferation.
UBASH3A and UBASH3B regulate the expression of common and unique genes
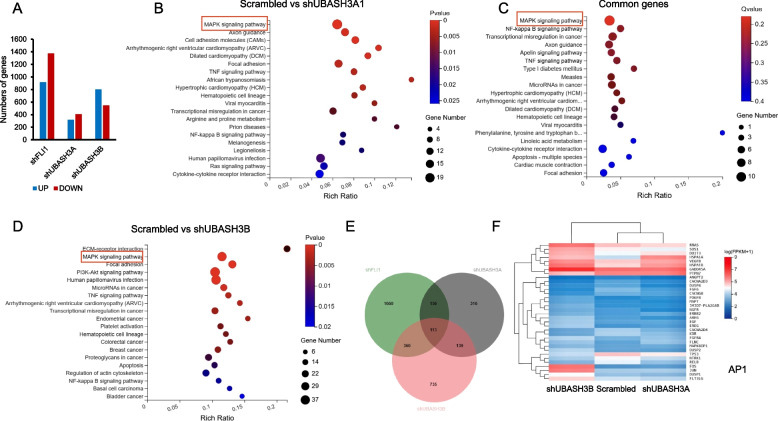
To uncover the mechanisms underlying the effect of UBASH3A and UBASH3B on leukemia progression, both shUBASH3B and shUBASH3A cells were assessed using RNAseq. Results from the Differentially Expressed Gene (DEG) analysis after UBASH3B knockdown revealed 800 genes with increased expression and 547 genes with decreased expression (Fig. 5A; Supplemental Table 2). Similarly, the DEGs in shUBASH3A1 versus scrambled control cells uncovered 317 DEGs were increased and 407 decreased (Fig. 5A; Supplemental Table 1). In comparison, in shFLI1 RNAseq data [38], we identified 1373 downregulated and 916 upregulated genes (Fig. 5A). A KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathway enrichment analysis for both the shUBASH3A (Fig. 5B) and shUBASH3B (Fig. 5D) regulated genes revealed significant changes associated with the MAP Kinase pathway (Fig. 5F), indicative of overlapping gene regulation. The MAP Kinase pathway genes were also altered in the shFLI1 RNAseq data (Supplemental Fig. 4A). In this analysis, 113 DEGs were common between shFLI1, shUBASH3A and shUBASH3B cells (Fig. 5E). In addition to DEGs observed in both UBASH3A and UBASH3B cells, we identified DEGs unique to one of the two ubiquitin associated ligases (Fig. 5E). A comparison between upregulated or downregulated DEGS from UBASH3B and UBASH3A cells is shown in Supplemental Fig. 5A-D. This analysis reveals upregulation of MAP Kinase pathway genes in UBASH3B and downregulation in UBASH3A cells. The common DEGs in the MAP Kinase pathway and expression variation between the shUBASH3A, shUBASH3B and shFLI1 effected genes are shown as a heatmap (Fig. 5F and Supplemental Fig. 4B). These changes may partially account for the suppressive and oncogenic differences between these UBASH3 isoforms in leukemia cells.
Fig. 5.
Regulation of the MAP Kinase pathway via UBASH3A and UBASH3B. A Compared to scrambled controls, many genes were upregulated or downregulated in shFLI1, shUBASH3A1 and shUBASH3B cells. B, C KEGG pathway enrichment analysis for shUBASH3A (B) and shUBASH3B cells (C). D KEGG pathway enrichment analysis for DEGs commonly affected by both UBASH3A and UBASH3B genes belonging to the MAP Kinase pathway. E Number of common or unique DEGs in shFLI1, shUBASH3A and UBASH3B cells. F Heatmap showing the differentially expressed MAP Kinase genes in shUBASH3A1 and shUBASH3B cells
UBASH3B ablation activates the AP1(FOS-JUN) pathway and blocks expression of SYK to inhibit leukemia proliferation
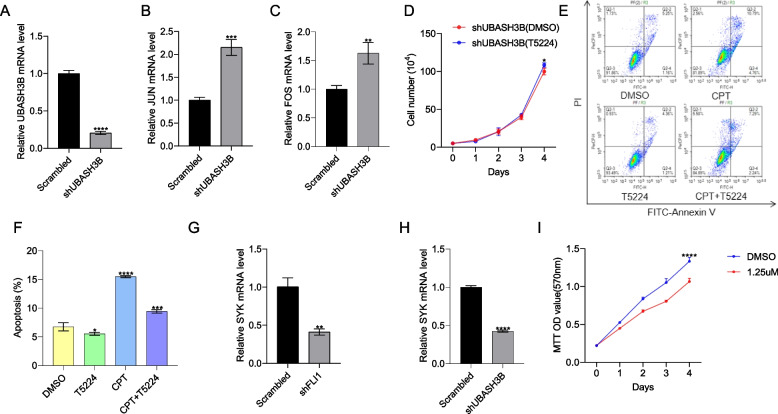
The MAP Kinase pathway (Fig. 5F) heatmap revealed that FOS and JUN expression was elevated in shUBASH3B knock-down cells (compared to shUBASH3A and scrambled control cells), and this was further confirmed by RT-qPCR (Fig. 6A-C). The AP1 genes were also induced in shFLI1 cells (Supplemental Fig. 4B). Moreover, overexpression of FLI1 in K562 (K562-fli1) cells resulted in downregulation of both FOS and JUN (Supplemental Fig. 6A-C). Since elevated FOS and JUN expression was associated with growth suppression in shUBASH3B cells, we treated shUBASH3B cells with the selective AP1 inhibitor T5224 [40], which significantly accelerated their proliferation (Fig. 6D). Moreover, T5224 significantly inhibited camptothecin (CPT, an anti-FLI1 compound [20, 41, 42])-induced HEL apoptosis in culture (Fig. 6E, F).
Fig. 6.
AP1 /SYK are regulated by UBASH3B. A-C Expression of UBASH3B (A), JUN (B), and FOS (C) was assessed by RT-qPCR in shUBASH3B cells. D The proliferation of shUBASH3B cells treated with the selective AP1 inhibitor T5224 (10μM) compared to vehicle-treated (DMSO) cells. E HEL cells were treated with 10nM camptothecin (CPT) (a FLI1 inhibitor) in combination with either DMSO or T5224 for 24 h; apoptosis was measured using flow cytometry. F The data is presented using the average from three experiments. G, H The expression of SYK in shFLI1 (G) and shUBASH3B (H) versus control cells, via RT-qPCR. I The proliferation of HEL cells treated with the SYK inhibitor R406 compared to vehicle-treated (DMSO). P < 0.05 (*), P < 0.01 (**), P < 0.001 (***), and P < 0.0001 (****)
RNAseq analyses in shFLI1 identified drastic downregulation in expression of the spleen tyrosine kinase SYK that was also detected in shUBASH3B cells, suggesting regulation of these genes by FLI1 [36]. The SYK gene has been previously linked to leukemia progression [43]. Indeed, RT-qPCR analysis confirmed downregulation of SYK in shFLI1 and shUBASH3B cells (Fig. 6G, H). Treatment of HEL cells with SYK inhibitor R406 [44] significantly suppressed growth in culture (Fig. 6I). These results suggest that UBASH3B may partially exert its oncogenic activity by suppressing AP1 and activating other oncogenic factors.
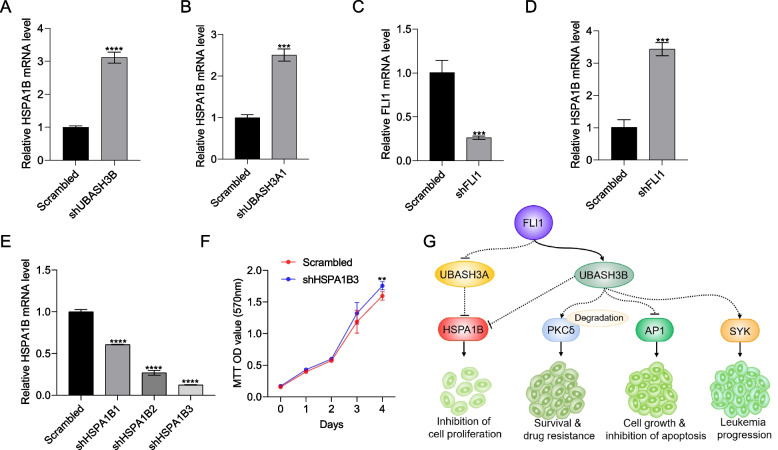
HSPA1B suppression by UBASH3A accelerates leukemia cell proliferation
Interestingly, expression of both Heat Shock Protein Family A (Hsp70) Member 1A (HSPA1A) and 1B (HSPA1B) increased in shUBASH3A and shUBASH3B cells relative to controls (Fig. 5F). The induction of HSPA1B in shUBASH3A1 and shUBASH3B was confirmed by RT-qPCR (Fig. 7A and B). Likewise, HSPA1B expression was significantly induced in shFLI1 cells (Fig. 7C, D and Supplemental Fig. 4B). Moreover, overexpression of FLI1 in K562 (K562-fli1) cells resulted in downregulation of HSPA1B (Supplemental Fig. 6A and D) suggesting a tumor suppressor role for this gene. To determine whether HSPA1B is involved in UBASH3A/B mediated tumor suppression, HSPA1B was then knocked-down in HEL cells using three shRNA (shHSPA1B-3; Fig. 7E). The proliferation of shHSPA1B-3 cells was significantly higher than in scrambled control cells (Fig. 7F). Thus, HSPA1B may mediate suppressive activity of FLI1. Since UBASH3A is induced in shFLI1, the level of HSPA1B expected to be lower causing cell growth acceleration. In contrast, lower UBASH3B expression in shFLI1 cells caused higher expression of HSPA1B, leading to growth deceleration. In the schematic in Fig. 7G, we propose that the oncogenic activity of FLI1 through UBASH3B activation may be partly mediated through AP1 suppression in erythroleukemic cells. Previously, we showed that UBASH3B upregulation increases PKCẟ degradation, which increased drug resistance and leukemia cell survival [18]. UBASH3B also activates the oncogene SYK to promote leukemia growth. Since HSPA1B is negatively regulated by both UBASH3A and UBASH3B, its tumor suppressor activity is dependent upon balance between the level of these UBASH3 proteins, negatively and positively regulated by FLI1, respectively. The balance between oncogenic and tumor suppressor activity of UBASH3B and UBASH3A, respectively, likely contributes to FLI1-induced leukemia cell proliferation.
Fig. 7.
Negative regulation of the HSPA1B by UBASH3A controls cell proliferation. A, B Expression of HSPA1B in shUBASH3B (A) and shUBASH3A1 (B) cells, via RT-qPCR. C, D Expression of FLI1 (C) and HSPA1B (D) in shFLI1 cells via RT-qPCR. E lentivirus-mediated downregulation of HSPA1B in HEL cells using the shHSPA1B1-3 expression vector, as determined via RT-qPCR. F The proliferation of shHSPA1B3 and scrambled control cells for the indicated days was assessed using an MTT assay. P < 0.01 (**), P < 0.001 (***). G Model showing the effect of FLI1 on UBASH3A and UBASH3B expression as well as erythroleukemia progression. UBASH3B induction via FLI1 overexpression suppresses PKCẟ and increased cell survival as well as drug resistance. Higher UBASH3B transcription following FLI1 overexpression also causes inhibition of AP1, which would otherwise suppress leukemia progression. In addition, UBASH3B controls the expression of SYK and partially contributes to erythroleukemia progression. Suppression of UBASH3A transcription via FLI1 overexpression increases the expression of leukemia growth suppressor HSPA1B, which blocks proliferation. On the other hand, activation of UBASH3B by FLI1 further decreases HSPA1B expression, causing acceleration of cell proliferation. Dotted lines represent indirect regulation
Correlation between FLI1 and the UBASH3A/B gene expression in other malignancies and prognostic impact
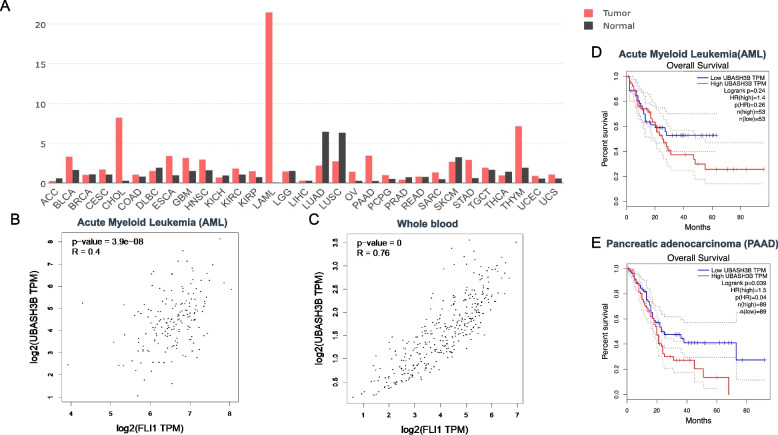
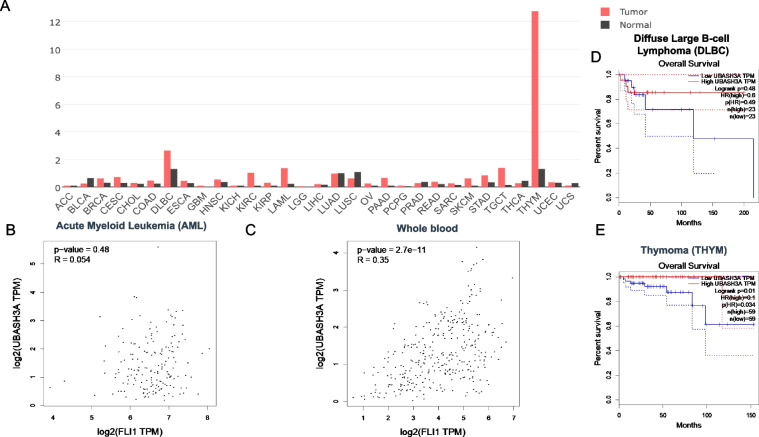
The aforementioned results demonstrated a positive and negative correlation between FLI1 and the UBASH3B and UBASH3A genes in erythroleukemia cell lines, respectively. To examine a broader role of these UBASH genes in cancer, we examined the correlation between FLI1 and UBASH3A or UBASH3B in the TCGA database by GEPIA2. In most tumors, expression analysis revealed a higher level of UBASH3B versus normal samples (Fig. 8A). In Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and whole blood cells, the expression of FLI1 was significantly correlated with the level of UBASH3B (Fig. 8B, C). Higher UBASH3B in AML, Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma, Brain lower grade glioma, Pancreatic adenocarcinoma and Lung squamous cell carcinoma were also correlated with worse prognosis (Fig. 8D, E and Supplementary Fig. 7A-C). These results further support the oncogenic function of UBASH3B in different tumors.
Fig. 8.
Correlation between FLI1 and UBASH3B expression in various tumors. A Relative expression of UBASH3B in various tumor in comparison to normal cells. Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma (ACC), Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma (BLCA), Breast Invasion Carcinoma (BRCA), Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Endocervical Adenocarcinoma (CESE), Cholangiocarcinoma (CHOL), Colonadenocarcinoma (COAD), Lymphoid Neoplasm Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBC), Esophageal Carcinoma (ESCA), Glioblastoma Multiform (GBM), Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSC), Kidney Chromophobe (KICH), Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma (KIRC), Kidney Renal Papillary Cell Carcinoma (KIRP), Acute Myeloid Leukemia (LAML), Brain Lower Grade Glioma (LGG), Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma (LIHC), Lung Adenocarcinoma (LUAD), Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma (LUSC), Ovarian Serous Cystadenocarcinoma (OV), Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma (PAAD), Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma (PCPG), Prostate Adenocarcinoma (PRAD), Rectum Adenocarcinoma (READ), Sarcoma (SARC), Skin Cutaneous Melanoma (SKCM), Stomach Adenocarcinoma (STAD), Testicular Germ Cell Tumors Thyroid Adenocarcinoma (TGCT), (THCA), Thymoma (THYM), Uterine Corpus Endometrial Carcinoma (UCEC), Uterine Carcinosarcoma (UCS). B, C Relative expression of human FLI1 and UBASH3B in AML (B) and whole blood cells (C). D, E Overall survival rate of high and low UBASH3B expression in AML (D) and PAAD (E) tumors. Abbreviations n(high) and n(low) shows the number of patients in UBASH3B high and low expressing tumors
A positive and negative correlations between FLI1 and UBASH3A were observed in various tumors (Fig. 9A). Interestingly, positive correlation between FLI1 and UBASH3A were seen in AML and whole blood cells (Fig. 9B and C). However, higher expression of UBASH3A had a better prognosis outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Breast invasive Carcinoma, Colon adenocarcinoma, Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, Liver hepatocellular carcinoma and Skin cutaneous melanoma (Fig. 9D and Supplementary Fig. 8A-E). Thymoma was the only tumor in which higher UBASH3A was significantly associated with worse patient outcome (Fig. 9E). These results suggest a tumor specific dependent suppressor function for UBASH3A.
Fig. 9.
Correlation between FLI1 and UBASH3A expression in various tumors. A Relative expression of UBASH3A in the indicated tumors in comparison to normal cells. B, C Relative expression of human FLI1 and UBASH3A in AML (B) and whole blood cells (C). D, E Overall survival rate of high and low expression of UBASH3A in DLBC (D) and PAAD (E) tumors
Discussion
The ETS oncogene FLI1 is a major driver of tumor initiation and progression of diverse types of malignancies [38]. FLI1 regulated genes have been identified to control various cancer hallmarks including cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, genomic stability, and immunity [37]. The combined effect of these downstream effectors contributes to robust oncogenic activity associated with FLI1 overexpression. Herein, we show that both UBASH3A and UBASH3B are strong downstream targets of FLI1. UBASH3B was found to be a direct target of FLI1, and its activation promotes erythroleukemia growth. In contrast, UBASH3A is indirectly downregulated by FLI1 through GATA2 or possibly other transcription factors and likely acts as an inhibitor of erythroleukemic cell proliferation. RNAseq analysis identified distinct and overlapping downstream pathways for UBASH3A and UBASH3B that likely contribute to their suppressive and oncogenic activity, respectively. This study provides novel insights into the role of these factors in leukemia progression.
In Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) induced by the oncogene AML-ETO, UBASH3B inactivates CBL, which is predicted to inhibit the ubiquitination of its downstream effectors responsible for leukemogenesis [16]. Similarly, in triple negative breast cancer, higher expression of UBASH3B promotes dephosphorylation and inactivation of CBL, which in turn loses ability to ubiquitinate and induce degradation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), leading to accelerated cancer progression [17]. We also previously identified PKCẟ as one of its downstream targets of UBASH3B [18]. Interaction between UBASH3B and PKCẟ accelerated ubiquitination of this kinase, resulting in leukemia cell survival and drug resistance. Moreover, a positive correlation between FLI1/UBASH3B was observed in several cancer types associated with worse prognosis. These results confirm oncogenic activity of UBASH3B in erythroleukemia and likely other cancers.
In a previous study [45], we reported regulation of FOS and JUN by FLI1 in leukemic cells. Herein, we showed that loss of FLI1 and consequently its downstream target UBASH3B in leukemia cells increased AP1 expression, leading to proliferation suppression and increased apoptosis. While AP1 is shown here to function as a tumor suppressor gene downstream of UBASHB, this transcription factor is also known to function as an oncogene in various cancers [46]. Like TGF signaling, the AP1 function in cancer could go both ways [47]. In our study, AP1(FOS and JUN) expression is negatively regulated during leukemia progression. Indeed, JUNB and JUNA are found critical downstream effectors of the tumor suppressor activity of another ETS gene family SPI1/PU.1, and that reduced expression of JUNB shown to be a common feature of acute myeloid leukemogenesis [48]. Since FLI1 knockdown or overexpressing cells exhibit increased or decreased expression of the AP1 genes, respectively [45], we propose a tumor suppressor role for AP1 in erythroleukemia. In addition to AP1, we identified the activation of the SYK gene by FLI1 through UBASH3B. Dephosphorylation of SYK and SAP70 by UBASH3B, two main factors involved in TCR signaling, was previously reported [3, 14, 15]. However, SYK kinase activation is also implicated in leukemia progression [43]. Thus, SYK activation likely contributed to the oncogenic activity of FLI1 through UBASH3B. The mechanisms by which UBASH3B suppresses AP1 transcription and activates SYK has yet to be determined. However, the interaction between UBASH3B and CBL or downregulation of PKCẟ may modify FOS/JUN and SYK regulation. This notion remains to be investigated in future studies.
Despite critical involvement in autoimmunity, the connection between UBASH3A and cancer has not yet been established. In contrast to UBASH3B, knockdown of FLI1 in erythroleukemia cells upregulates UBASH3A expression, raising the possibility of a tumor suppressor function for this variant. In support of this observation, ablation of UBASH3A in high FLI1 expressing erythroleukemic cells significantly accelerated cell proliferation in culture. Interestingly, UBASH3A expression was both induced and reduced relative to normal cells in various cancers. However, higher expression of UBASH3A was found to be a good prognosis marker for patient survival in most tumors, further supporting its anti-cancer activity. FLI1 indirectly controls the transcription of UBASH3A, likely through GATA2, which may warrant further investigation in future studies.
RNAseq analysis of UBASH3A and UBASH3B knocked-down cells revealed the highest effects on the MAP Kinase pathway. Specifically, expression of HSPA1A and HSPA1B increased in both shUBASH3B and shUBASH3A cells. Knockdown of HSPA1B in leukemia cells accelerated leukemogenesis indicating a role for these genes as negative regulators of leukemic cell growth. Interestingly, higher HSPA1A and HSPA1B expression was previously linked to poor survival in colon cancer. In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), expression of HSPA1B increased through Hepatitis B virus-mediated activation of ATF7, which accelerated cell proliferation by inhibiting apoptosis [49]. In contrast to solid tumors, the data presented herein suggest an inhibitory role for HSPA1B in leukemia progression, whose expression depend upon the level of UBASH3A and UBASH3B.
Finally, UBASH3A and UBASH3B knockdown affected similar as well as unique genes, as shown here for AP1, SYK and HSPA1B. Thus, the combined oncogenic and tumor suppressor activities of UBASH3A and UBASH3B and their downstream effectors influence leukemogenesis. Examining other genes regulated by UBASH3A and UBASH3B could further determine their role in leukemogenesis, and uncover additional therapeutic targets.
Conclusions
FLI1 is shown in this study to promote erythroleukemia progression by inhibiting UBASH3A and expression and inducing UBASH3B expression. UBASH3B acts as an oncogene to block the AP1 pathway and activate other genes, whereas UBASH3A transcriptional inactivation by FLI1 suppressed expression of HSPA1B. These results uncover critical roles of UBASH3A and UBASH3B in FLI1-driven leukemias.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- FLI1
Friend leukemia integration 1
- UBASH3A
Ubiquitin Associated and SH3 Domain Containing A
- UBASH3B
Ubiquitin Associated and SH3 Domain Containing B
- SYK
Spleen tyrosine kinase
- HSPA1B
Heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 1B
- ChIP
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- KEGG
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- DMSO
Dimethyl sulfate
- PKC
Protein Kinase C
- AP1
Activator protein 1
- MAPK
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase
- PGM
Phosphoglycerate mutase-like/C-terminal histidine phosphatase
Authors’ contributions
J.W., C.W., X.X., A.H., K.Y., Y.K., B.G., K.S. and, W.L. contributed to the conception, design of the study, as well as methodology, data acquisition and interpretation. W.L., X.X. and B.G. were involved in the statistical analysis and bioinformatics. J.W. and W.L. drafted the manuscript. Y.B.D., W.L. and E.Z. reviewed the manuscript critically. Y.B.D. supervised, conceived, funding acquisition and designed the study. All authors contributed to the interpretation of the findings, reviewed, edited and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by research grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1812403, 21867009, and 82260040), the Science and Technology Department of Guizhou Province grants (QKHJC-ZK [2022] YB297, QKHJC-ZK [2023] YB240) and the Key Laboratory of Chemistry for Natural Products of Guizhou Province and Chinese Academic of Sciences Research Grant (GZCNP202203Z) to XX and CW, the Guizhou Medical University Research Grant (RN21025) to BG.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) repository, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/1014802.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Jie Wang and Chunlin Wang contributed equally to this work.
Contributor Information
Wuling Liu, Email: emmalao@163.com.
Yaacov Ben-David, Email: yaacovbendavid@hotmail.com.
References
- 1.Tsygankov AY. TULA proteins in men, mice, hens, and lice: welcome to the family. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(11):9126. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Carpino N, Turner S, Mekala D, Takahashi Y, Zang H, Geiger TL, Doherty P, Ihle JN. Regulation of ZAP-70 activation and TCR signaling by two related proteins, Sts-1 and Sts-2. Immunity. 2004;20(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(03)00351-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Carpino N, Kobayashi R, Zang H, Takahashi Y, Jou ST, Feng J, Nakajima H, Ihle JN. Identification, cDNA cloning, and targeted deletion of p70, a novel, ubiquitously expressed SH3 domain-containing protein. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(21):7491–7500. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.21.7491-7500.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.San Luis B, Sondgeroth B, Nassar N, Carpino N. Sts-2 is a phosphatase that negatively regulates zeta-associated protein (ZAP)-70 and T cell receptor signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(18):15943–15954. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.177634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Concannon P, Onengut-Gumuscu S, Todd JA, Smyth DJ, Pociot F, Bergholdt R, Akolkar B, Erlich HA, Hilner JE, Julier C, et al. A human type 1 diabetes susceptibility locus maps to chromosome 21q22.3. Diabetes. 2008;57(10):2858–2861. doi: 10.2337/db08-0753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Smyth DJ, Plagnol V, Walker NM, Cooper JD, Downes K, Yang JH, Howson JM, Stevens H, McManus R, Wijmenga C, et al. Shared and distinct genetic variants in type 1 diabetes and celiac disease. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(26):2767–2777. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0807917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhernakova A, Stahl EA, Trynka G, Raychaudhuri S, Festen EA, Franke L, Westra HJ, Fehrmann RS, Kurreeman FA, Thomson B, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies in celiac disease and rheumatoid arthritis identifies fourteen non-HLA shared loci. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(2):e1002004. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chen YG, Ciecko AE, Khaja S, Grzybowski M, Geurts AM, Lieberman SM. UBASH3A deficiency accelerates type 1 diabetes development and enhances salivary gland inflammation in NOD mice. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):12019. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68956-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hoeller D, Crosetto N, Blagoev B, Raiborg C, Tikkanen R, Wagner S, Kowanetz K, Breitling R, Mann M, Stenmark H, et al. Regulation of ubiquitin-binding proteins by monoubiquitination. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(2):163–169. doi: 10.1038/ncb1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bertelsen V, Breen K, Sandvig K, Stang E, Madshus IH. The Cbl-interacting protein TULA inhibits dynamin-dependent endocytosis. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(8):1696–1709. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Feshchenko EA, Smirnova EV, Swaminathan G, Teckchandani AM, Agrawal R, Band H, Zhang X, Annan RS, Carr SA, Tsygankov AY. TULA: an SH3- and UBA-containing protein that binds to c-Cbl and ubiquitin. Oncogene. 2004;23(27):4690–4706. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wattenhofer M, Shibuya K, Kudoh J, Lyle R, Michaud J, Rossier C, Kawasaki K, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Berry A, et al. Isolation and characterization of the UBASH3A gene on 21q22.3 encoding a potential nuclear protein with a novel combination of domains. Hum Genet. 2001;108(2):140–147. doi: 10.1007/s004390000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chen Y, Jakoncic J, Carpino N, Nassar N. Structural and functional characterization of the 2H-phosphatase domain of Sts-2 reveals an acid-dependent phosphatase activity. Biochemistry. 2009;48(8):1681–1690. doi: 10.1021/bi802219n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mikhailik A, Ford B, Keller J, Chen Y, Nassar N, Carpino N. A phosphatase activity of Sts-1 contributes to the suppression of TCR signaling. Mol Cell. 2007;27(3):486–497. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen X, Ren L, Kim S, Carpino N, Daniel JL, Kunapuli SP, Tsygankov AY, Pei D. Determination of the substrate specificity of protein-tyrosine phosphatase TULA-2 and identification of Syk as a TULA-2 substrate. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(41):31268–31276. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.114181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Goyama S, Schibler J, Gasilina A, Shrestha M, Lin S, Link KA, Chen J, Whitman SP, Bloomfield CD, Nicolet D, et al. UBASH3B/Sts-1-CBL axis regulates myeloid proliferation in human preleukemia induced by AML1-ETO. Leukemia. 2016;30(3):728–739. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lee ST, Feng M, Wei Y, Li Z, Qiao Y, Guan P, Jiang X, Wong CH, Huynh K, Wang J, et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase UBASH3B is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancer and promotes invasion and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(27):11121–11126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1300873110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Yao Y, Liu W, Gajendran B, Wang C, Zacksenhaus E, Sample KM, Varier KM, Hao X, Ben-David Y. Ubash3b promotes TPA-mediated suppression of leukemogenesis through accelerated downregulation of PKCdelta protein. Biochimie. 2021;184:8–17. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2021.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Asano Y, Trojanowska M. Phosphorylation of Fli1 at threonine 312 by protein kinase C delta promotes its interaction with p300/CREB-binding protein-associated factor and subsequent acetylation in response to transforming growth factor beta. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29(7):1882–1894. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01320-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li YJ, Zhao X, Vecchiarelli-Federico LM, Li Y, Datti A, Cheng Y, Ben-David Y. Drug-mediated inhibition of Fli-1 for the treatment of leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2012;2(1):e54. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2011.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Liu T, Yao Y, Zhang G, Wang Y, Deng B, Song J, Li X, Han F, Xiao X, Yang J, et al. A screen for Fli-1 transcriptional modulators identifies PKC agonists that induce erythroid to megakaryocytic differentiation and suppress leukemogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8(10):16728–16743. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Bernstein A. Identification and mapping of a common proviral integration site Fli-1 in erythroleukemia cells induced by Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990;87(4):1332–1336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Letwin K, Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1. Genes Dev. 1991;5(6):908–918. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Azimi A, Tuominen R, Costa Svedman F, Caramuta S, Pernemalm M, Frostvik Stolt M, Kanter L, Kharaziha P, Lehtio J, Hertzman Johansson C, et al. Silencing FLI or targeting CD13/ANPEP lead to dephosphorylation of EPHA2, a mediator of BRAF inhibitor resistance, and induce growth arrest or apoptosis in melanoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(8):e3029. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bonetti P, Testoni M, Scandurra M, Ponzoni M, Piva R, Mensah AA, Rinaldi A, Kwee I, Tibiletti MG, Iqbal J, et al. Deregulation of ETS1 and FLI1 contributes to the pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2013;122(13):2233–2241. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-01-475772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chen N, Zhao G, Yan X, Lv Z, Yin H, Zhang S, Song W, Li X, Li L, Du Z, et al. A novel FLI1 exonic circular RNA promotes metastasis in breast cancer by coordinately regulating TET1 and DNMT1. Genome Biol. 2018;19(1):218. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1594-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Delattre O, Zucman J, Plougastel B, Desmaze C, Melot T, Peter M, Kovar H, Joubert I, de Jong P, Rouleau G, et al. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature. 1992;359(6391):162–165. doi: 10.1038/359162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kornblau SM, Qiu YH, Zhang N, Singh N, Faderl S, Ferrajoli A, York H, Qutub AA, Coombes KR, Watson DK. Abnormal expression of FLI1 protein is an adverse prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2011;118(20):5604–5612. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-348052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Liu T, Xia L, Yao Y, Yan C, Fan Y, Gajendran B, Yang J, Li YJ, Chen J, Filmus J, et al. Identification of diterpenoid compounds that interfere with Fli-1 DNA binding to suppress leukemogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(2):117. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1363-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Herrmann FR, Bshara W, Odunsi K, Terracciano L, Sauter G, Cheney RT, Groth J, Penetrante R, Mhawech-Fauceglia P. Friend leukaemia integration-1 expression in malignant and benign tumours: a multiple tumour tissue microarray analysis using polyclonal antibody. J Clin Pathol. 2007;60(6):694–700. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2006.039230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sakurai T, Kondoh N, Arai M, Hamada J, Yamada T, Kihara-Negishi F, Izawa T, Ohno H, Yamamoto M, Oikawa T. Functional roles of Fli-1, a member of the Ets family of transcription factors, in human breast malignancy. Cancer Sci. 2007;98(11):1775–1784. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2007.00598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Scheiber MN, Watson PM, Rumboldt T, Stanley C, Wilson RC, Findlay VJ, Anderson PE, Watson DK. FLI1 expression is correlated with breast cancer cellular growth, migration, and invasion and altered gene expression. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 2014;16(10):801–813. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Smeets MF, Chan AC, Dagger S, Bradley CK, Wei A, Izon DJ. Fli-1 overexpression in hematopoietic progenitors deregulates T cell development and induces pre-T cell lymphoblastic leukaemia/lymphoma. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(5):e62346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Song W, Li W, Li L, Zhang S, Yan X, Wen X, Zhang X, Tian H, Li A, Hu JF, et al. Friend leukemia virus integration 1 activates the Rho GTPase pathway and is associated with metastasis in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(27):23764–23775. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Torlakovic EE, Slipicevic A, Florenes VA, Chibbar R, DeCoteau JF, Bilalovic N. Fli-1 expression in malignant melanoma. Histol Histopathol. 2008;23(11):1309–1314. doi: 10.14670/HH-23.1309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yan X, Yu Y, Li L, Chen N, Song W, He H, Dong J, Liu X, Cui J. Friend leukemia virus integration 1 is a predictor of poor prognosis of breast cancer and promotes metastasis and cancer stem cell properties of breast cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2018;7(8):3548–3560. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ben-David Y, Gajendran B, Sample KM, Zacksenhaus E. Current insights into the role of Fli-1 in hematopoiesis and malignant transformation. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(3):163. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04160-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wang C, Sample KM, Gajendran B, Kapranov P, Liu W, Hu A, Zacksenhaus E, Li Y, Hao X, Ben-David Y. FLI1 induces megakaryopoiesis gene expression through WAS/WIP-dependent and independent mechanisms; implications for Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome. Front Immunol. 2021;12:607836. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.607836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sloan CA, Chan ET, Davidson JM, Malladi VS, Strattan JS, Hitz BC, Gabdank I, Narayanan AK, Ho M, Lee BT, et al. ENCODE data at the ENCODE portal. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(D1):D726–732. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Motomura H, Seki S, Shiozawa S, Aikawa Y, Nogami M, Kimura T. A selective c-Fos/AP-1 inhibitor prevents cartilage destruction and subsequent osteophyte formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;497(2):756–761. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wang X, Oates JC, Helke KL, Gilkeson GS, Zhang XK. Camptothecin and topotecan, inhibitors of transcription factor fli-1 and topoisomerase, markedly ameliorate lupus nephritis in (NZB x NZW)F1 mice and reduce the production of inflammatory mediators in human renal cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(8):1478–1488. doi: 10.1002/art.41685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schutt SD, Wu Y, Kharel A, Bastian D, Choi HJ, Hanief Sofi M, Mealer C, McDaniel Mims B, Nguyen H, Liu C, et al. The druggable transcription factor Fli-1 regulates T cell immunity and tolerance in graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(21):e143950. doi: 10.1172/JCI143950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Leveille E, Chan LN, Mirza AS, Kume K, Müschen M. SYK and ZAP70 kinases in autoimmunity and lymphoid malignancies. Cell Signal. 2022;94:110331. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sun S, Xue D, Chen Z, Ou-Yang Y, Zhang J, Mai J, Gu J, Lu W, Liu X, Liu W, et al. R406 elicits anti-warburg effect via syk-dependent and -independent mechanisms to trigger apoptosis in glioma stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(5):358. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1587-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chen B, Sheng D, Wang C, Liu W, Hu A, Xiao X, Gajendran B, Gao J, Hu J, Sample KM, et al. FLI1 regulates inflammation-associated genes to accelerate leukemogenesis. Cell Signal. 2022;92:110269. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2022.110269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Song D, Lian Y, Zhang L. The potential of activator protein 1 (AP-1) in cancer targeted therapy. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1224892. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1224892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shaulian E. AP-1–The Jun proteins: Oncogenes or tumor suppressors in disguise? Cell Signal. 2010;22(6):894–899. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.12.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Somervaille TC, Cleary ML. PU.1 and Junb: suppressing the formation of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cancer Cell. 2006;10(6):456–457. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2006.11.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Guan Y, Zhu X, Liang J, Wei M, Huang S, Pan X. Upregulation of HSPA1A/HSPA1B/HSPA7 and downregulation of HSPA9 were related to poor survival in colon cancer. Front Oncol. 2021;11:749673. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.749673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) repository, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/1014802.