Dear Editor,
Over the past few decades, Cephalotaxus alkaloids (CAs) have been considered as significant natural agents with their intriguing chemical structures and diverse bioactivities, in particular, as anti-cancer mediator. However, the investigation of its medicinal values has put in dilemma due to the limited reservoir from nature. Furthermore, the chemical synthesis of the CAs required great demanding and trial-and-error. Thus, the aim of this study was to indicate the uppermost Cephalotaxus alkaloid (CA) in chemical repository, via integrated data analysis.
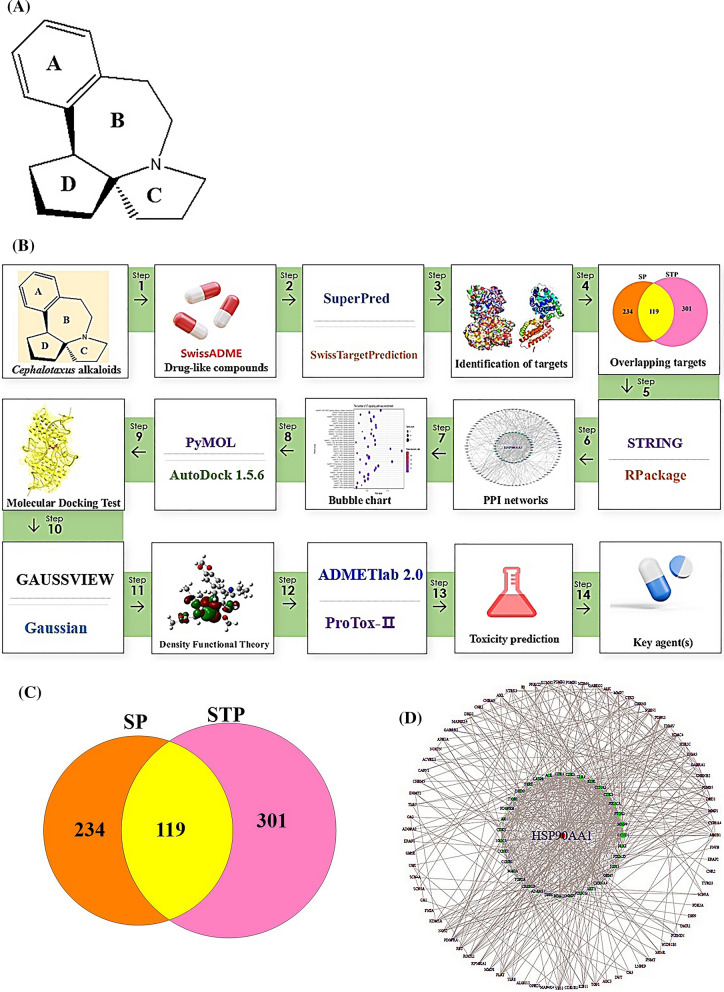
We hypothesized the uppermost CA(s), target(s), and signaling pathway(s) can be established via cheminformatics, bioinformatics, computer screening tools, and quantum chemistry software with the holistic prospect. The CAs have potent therapeutic activities such as antileukemic, and anticancer efficacy [1]. The mainframe of structures is an azaspiranic tetracyclic scaffold (Fig. 1A). The workflow was represented in Fig. 1B.
Fig. 1.
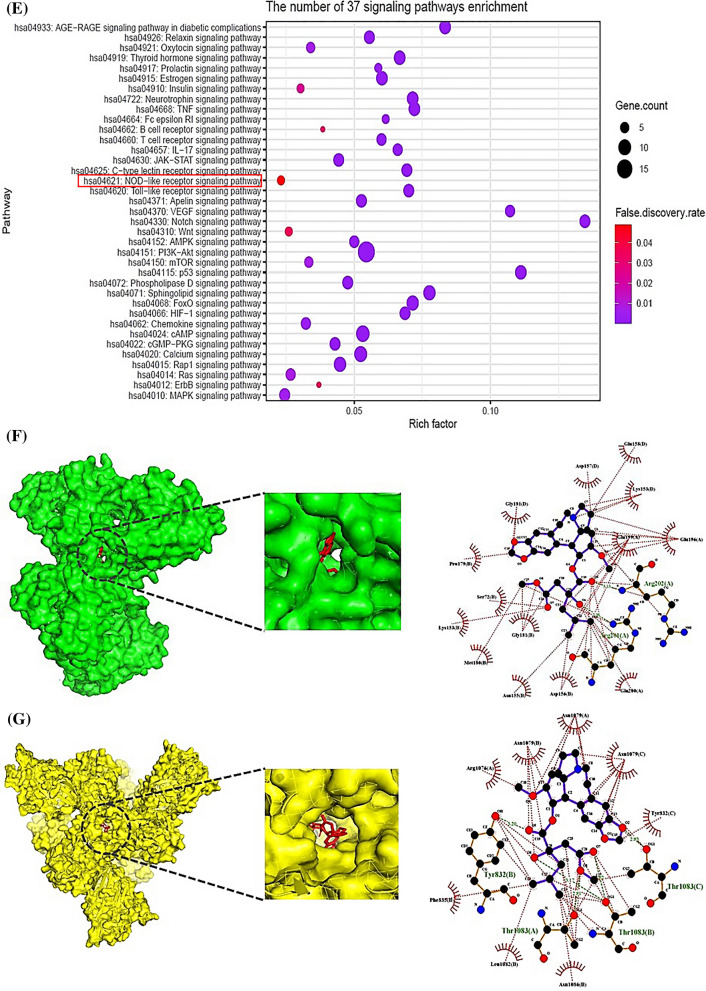
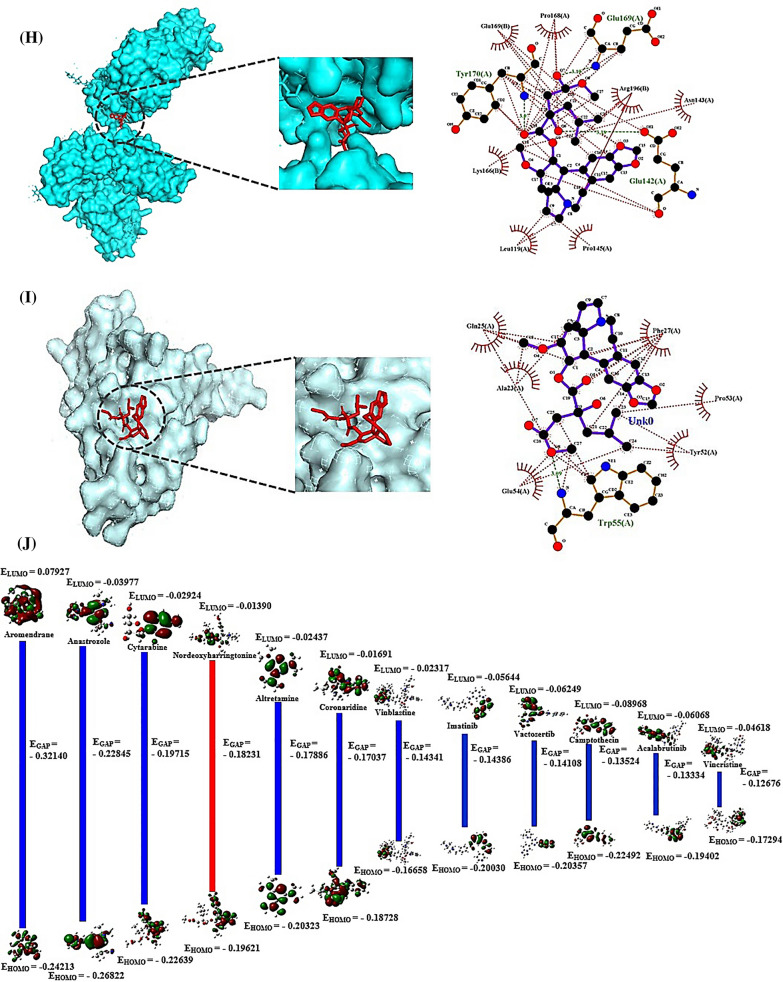
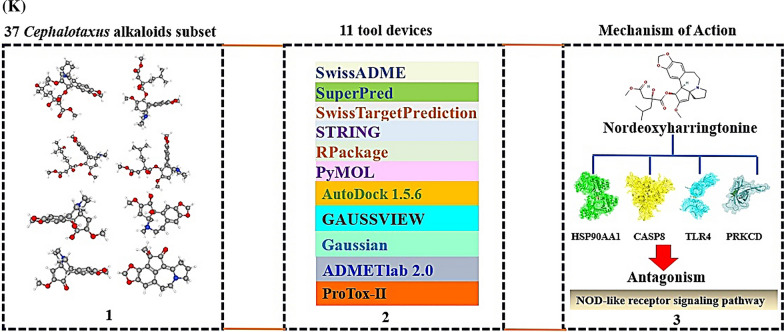
A The azaspiranic tetracyclic scaffold. B The workflow of this study. C The 119 overlapping targets between SP (353 targets) and STP (420 targets). D PPI networks (115 nodes, 603 edges). E A bubble chart of 37 signaling pathways against pan-cancer. F HSP90AA1—Nordeoxyharringtonine complex. G CASP8—Nordeoxyharringtonine complex. H TLR4—Nordeoxyharringtonine complex. I PRKCD—Nordeoxyharringtonine complex. J Density functional theory (DFT) plot and its energy gap (Egap) for Nordeoxyharringtonine and conventional anticancer drugs. Red bar was indicated Nordeoxyharringtonine. K The key summary of this study
First, the number of 37 CAs was piled by PubChem, and some literatures. The CAs were refined by Lipinski’s rule utilizing SwissADME platform, suggesting that the accepted 27 species are the key compounds for anti-cancer agents (Additional file 1: Table S1). Second, with accurate and rigor expanse, the intersecting targets (119) were selected between 353 and 420 targets obtained by SP and STP (Fig. 1C). The STRING database, and R Package were adopted to perform protein–protein interaction (PPI) networks (115 nodes, 603 edges), identifying certain target(s) with the highest connectivity. Consequently, heat shock protein 90 alpha family class A member 1 (HSP90AA1) with the greatest degree of value (DV; 48 degrees) was the uppermost protein coding gene to hamper cancer progression (Additional file 2: Table S2), (Fig. 1D). Notably, a report demonstrated that HSP90AA1 stabilizes the cancer cell, and overexpressed in leukemia and bladder cancer [2]. It implies that inhibition of HSP90AA1 might be a potential candidate against cancer. A bubble chart shows that the number of 37 signaling pathways associated with the 119 targets was related to the occurrence and progression of cancer (Additional file 3: Table S3). Of these, NOD-like receptor (NLR) signaling pathway indicated the smallest rich factor was defined as antagonism (Fig. 1E), indicating that the inhibitors of the signaling pathway might be promising agent(s) to treat cancer [3]. Third, an overlapping CA associated with the four targets was “Nordeoxyharringtonine”, which was also confirmed as a hub compound by molecular docking assessment (MDA), and density functional theory (DFT). The Nordeoxyharringtonine formed stable complex (< − 6.0 kcal/mol) [4] in all four targets via AutoDock 1.5.6. (Fig. 1F, G, H, I; Additional file 4: Table S4). To obtain the extensive confirmation, we performed the DFT analysis with eleven conventional anticancer drugs, indicating that the softness (S) value of the eleven anticancer drugs was between 15.77785 (eV) and 6.2278 (eV) (Fig. 1J). The softness (S) depends on EGAP (Energy gap; Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital (HOMO)—Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital (LUMO) energy gap), the molecule along the lower energy gap is defined as better reactivity level. The below mathematical set was used to establish the reactivation of leading compounds.
Thus, Nordeoxyharringtonine with 10.92061(eV) was within the range (15.77785–6.2278 eV), which means that Nordeoxyharringtonine might be a promising agent to use as anticancer mediator (Table 1). Finally, we investigated the toxicity via ADMETlab2.0 and ProTox-II, identifying that Nordeoxyharringtonine had no noticeable obstacles to develop a new medication (Additional file 5: Table S5).
Table 1.
The profiling of density functional theory (DFT) with eleven conventional anti-cancer drugs and Nordeoxyharringtonine
| No | Anti-cancer drugs and Nordeoxyharringtonine | LUMO | HOMO | EGAP (eV) | ɳ (eV) | S (eV) | χ (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Aromendrane (*) | 0.07927 | − 0.24213 | − 0.32140 | 0.16070 | 6.22278 | − 0.16070 |
| 2 | Anastrozole (*) | − 0.03977 | − 0.26822 | − 0.22845 | 0.11423 | 8.75465 | − 0.11423 |
| 3 | Cytarabine (*) | − 0.02924 | − 0.22639 | − 0.19715 | 0.09858 | 10.14456 | − 0.09858 |
| 4 | Nordeoxyharringtonine | − 0.01390 | − 0.19621 | − 0.18231 | 0.09116 | 10.97033 | − 0.09116 |
| 5 | Altretamine (*) | − 0.02441 | − 0.20323 | − 0.17882 | 0.08941 | 11.18443 | − 0.08941 |
| 6 | Coronaridine (*) | − 0.01691 | − 0.18728 | − 0.17037 | 0.08519 | 11.73916 | − 0.08519 |
| 7 | Vinblastine (*) | − 0.02317 | − 0.16658 | − 0.14341 | 0.07171 | 13.94603 | − 0.07171 |
| 8 | Imatinib (*) | − 0.05644 | − 0.20030 | − 0.14386 | 0.07193 | 13.90241 | − 0.07193 |
| 9 | Vactosertib (*) | − 0.06249 | − 0.20357 | − 0.14108 | 0.07054 | 14.17635 | − 0.07054 |
| 10 | Camptothecin (*) | − 0.08968 | − 0.22492 | − 0.13524 | 0.06762 | 14.78852 | − 0.06762 |
| 11 | Acalabrutinib (*) | − 0.06068 | − 0.19402 | − 0.13334 | 0.06667 | 14.99925 | − 0.06667 |
| 12 | Vincristine (*) | − 0.04618 | − 0.17294 | − 0.12676 | 0.06338 | 15.77785 | − 0.06338 |
(*): The conventional anti-cancer drug; LUMO: Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital; HOMO: Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital; ɳ: hardness; S: softness; χ: electronegativity
In this study, we have suggested that Nordeoxyharringtonine is the most significant CA against pan-cancer. The Nordeoxyharringtonine can be paved the way to validate anti-pan-cancer in CAs as inhibitors on multiple-targets (HSP90AA1, CASP8, TLR4, and PRKCD) to NLR signaling pathway. The key summary of this study was represented in Fig. 1K.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1. The physicochemical properties of chemical constituents.
Additional file 2: Table S2. The degree of value in key targets.
Additional file 3: Table S3. The 37 signaling pathways related to occurrence and development of cancer.
Additional file 4: Table S4. The binding energy of four key targets on NLR signaling pathway.
Additional file 5: Table S5. The toxic parameters of Nordeoxyharringtonine.
Acknowledgements
Open access publishing facilitated by Hallym University, the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology, and Bio Industrial Technology Development Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE, Korea).
Abbreviations
- DFT
Density functional theory
- DV
Degree of value
- χ
Electronegativity
- EGAP
Energy gap
- ɳ
Hardness
- HSP90AA1
Heat Shock Protein 90 Alpha family class A member 1
- HOMO
Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital
- LUMO
Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital
- MDA
Molecular docking assessment
- NLR
NOD-like receptor
- PPI
Protein–Protein Interaction
- S
Softness
- SP
SuperPred
- STP
Swiss Target Prediction
Author contributions
Methodology, Conceptualization, Data curation, Software, Writing-original draft: KKO, Methodology, Data curation, Software: SJY, Formal analysis, Validation: JAE, Methodology, Data curation: KJL, Methodology, Formal analysis: GHK, Supervision, Investigation, Project administration: DJK, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing-original draft, Writing—review editing: KTS.
Funding
This research was supported by Hallym University Research Fund, the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF2019R1I1A3A01060447 and NRF-2020R1A6A1A03043026), Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (P0020622), and Bio Industrial Technology Development Program (20018494) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE, Korea). All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its Additional files).
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Dixit P, Singh N, Singh L, Srivastava RP, Pandey S, Singh S, et al. Screening for the biochemical profile and biological activity in Cephalotaxus and Taxus collected from north-eastern Himalayas. ACS Agric Sci Technol Am Chem Soc. 2023;3:694–700. doi: 10.1021/acsagscitech.3c00126. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Xiao X, Wang W, Li Y, Yang D, Li X, Shen C, et al. HSP90AA1-mediated autophagy promotes drug resistance in osteosarcoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37:1–13. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0880-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Oh K, Yoon S, Lee S, Lee SY, Gupta H, Ganesan R, et al. The juxtaposition of Ilex cornuta fruit and gut microbiota against alcoholic liver disease based on the integrated pharmacology via metabolomics. Clin Transl Med. 2023 doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Shityakov S, Förster C. In silico predictive model to determine vector-mediated transport properties for the blood-brain barrier choline transporter. Advances and applications in bioinformatics and chemistry: AABC. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2014;7:23–36. doi: 10.2147/AABC.S63749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. The physicochemical properties of chemical constituents.
Additional file 2: Table S2. The degree of value in key targets.
Additional file 3: Table S3. The 37 signaling pathways related to occurrence and development of cancer.
Additional file 4: Table S4. The binding energy of four key targets on NLR signaling pathway.
Additional file 5: Table S5. The toxic parameters of Nordeoxyharringtonine.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its Additional files).