Abstract
槟榔药材及制剂广泛应用于临床,槟榔多酚为其主要化学成分之一,具有抗氧化、抗炎、抗菌等作用。随着高原活动的不断增加,高原低氧引起的组织氧化损伤严重影响了高原作业能力,因此,抗缺氧药物的研究尤为重要。最新研究表明槟榔多酚通过改善缺氧机体血气指标,提高组织超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化氢酶活性,清除机体过多的自由基,对缺氧引起的氧化应激损伤具有保护作用。槟榔多酚的抗缺氧及保护组织氧化损伤的作用提示其可作为潜在的抗缺氧药物,具有一定的开发前景。
Keywords: 槟榔多酚, 抗氧化, 抗缺氧, 化学成分
Abstract
Areca catechu L. medicinal materials and their preparations are widely used in clinical practice. Betelnut polyphenol is one of the main chemical components with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial effects. With continuous increase of high altitude activities, tissue oxidative damage caused by high altitude hypoxia seriously affects the ability to work, and the studies on anti-hypoxia drugs are particularly important. Recent studies have shown that betelnut polyphenols have protective effects on oxidative stress injury caused by hypoxia via improving blood gas index of hypoxic organism, increasing superoxide dismutase glutathione catalase activity, and scavenging excessive free radicals. The effects of betelnut polyphenols against hypoxia and oxidative damage protection suggest that betelnut polyphenols can be used as potential anti-hypoxia drugs and posses clinical prospects.
Keywords: betelnutpolyphenols, antioxidant, anti-hypoxia, chemical composition
槟榔(Areca catechu L.)为多年生棕榈科植物槟榔树的种子,又名仁频、白槟榔、橄榄子、洗瘴丹、青仔、大腹子、榔玉、槟榔子、洗樟脑、仙瘴丹、螺果、宾门及宾门药饯等[1],居我国著名的“四大南药”(槟榔、益智仁、砂仁、巴戟天)之首,其果皮、花、种子均可入药。槟榔作为一种传统的本草中药,临床应用广泛,文献记载最早可追溯至汉代,在中国引种已有2 100余年,药用历史已有1 800多年,入药最早记录在《李当之药录》中[2]。槟榔有抗寄生虫、抗菌、调节血脂及血糖等作用。目前,国内外研究多集中在槟榔生物碱的药理活性和安全性等方面,对槟榔多酚和其他化合物的研究多为成分分析,药理作用研究较少。最新研究[3-6]表明槟榔多酚具有良好的抗高原缺氧作用。槟榔多酚的抗氧化和抗缺氧作用有望为预防和治疗高原病的药物研究提供新思路。
1. 槟榔多酚的主要成分
槟榔含有多种化学成分,从槟榔中已分离得到60多种化合物,包括多酚类(31.1%)、多糖类(18.7%),脂肪酸类(14.0%),鞣质类、氨基酸、三萜类、矿物质、槟榔红色素及维生素等其他类(12.0%),粗纤维类(10.8%),水分类(9.9%),灰分类(3.0%)及生物碱类(0.5%)等多种物质[7-11]。按照多酚的化学结构可将其分为类黄酮和非类黄酮2大类[12-13]。其中类黄酮主要化学成分为儿茶素、表儿茶素、没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、异鼠李素及木犀草素等;非类黄酮主要化学成分为香草酸、阿魏酸等。王明月等[14]研究表明:槟榔成熟果中所含的多酚种类和数量比槟榔幼果多,且槟榔多酚中含量最多的是儿茶素(高达0.161%),其次是单宁(0.0622%)、表没食子儿茶素(0.0241%)、表儿茶素(0.0164%)、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(0.0077%)及没食子酸(0.00136%)。张春梅等[15]采用反相高效液相色谱-二极管阵列检测法(reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection,RP-HPLC-DAD)检测,发现槟榔花提取物中含有没食子酸、表儿茶素、阿魏酸、香豆酸、芦丁和柚皮素6种多酚类物质。祁静[16]采用毛细管电泳法确定槟榔多酚提取物中含有表儿茶素、儿茶素、阿魏酸、绿原酸、柚皮素及山奈素。Yuan等[17]从槟榔果仁中发现了2种新的黄酮类化合物,即calquiquelignan M和calquiquelignan N,该2种化合物对HepG2细胞有中等细胞毒活性,IC50值分别为49.8和53.6 μmol/L。槟榔多酚类化学成分见表1。槟榔多酚在槟榔中占比较高,其中儿茶素及表儿茶素在槟榔果实及种子中含量较高[10],在抗氧化及抗缺氧方面具有进一步研究的价值。
表1.
槟榔各部位多酚类化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of polyphenols in different parts of Areca catechu L.
| 编号 | 化合物名称 | 分子结构式 | 槟榔提取部位 | 提取溶剂 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 香草酸 |
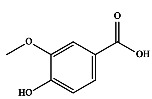
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [18] |
| 4 | 异鼠李素 |
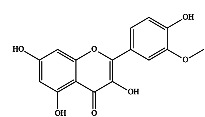
|
新鲜果实 | 乙醇 | [19] |
| 5 | 金圣草黄素 |
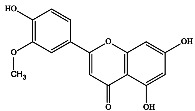
|
新鲜果实 | 乙醇 | [19] |
| 6 | 木犀草素 |
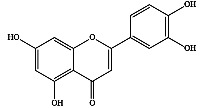
|
新鲜果实 | 乙醇 | [19] |
| 7 | 4',5-二羟基-3',5',7- 三甲氧基黄烷酮 |
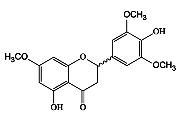
|
新鲜果实 | 乙醇 | [19] |
| 8 | 巴西红厚壳素 |
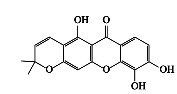
|
新鲜果实 | 乙醇 | [19] |
| 9 | 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲酸 |
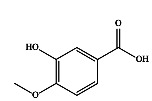
|
新鲜果实 | 乙醇 | [19] |
| 10 | 槲皮素 |
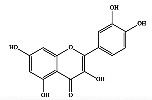
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [20] |
| 11 | 甘草素 |
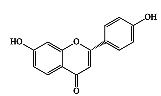
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [20] |
| 12 | 5,7,4′-三羟基-3′,5′- 二甲氧基二氢黄酮 |
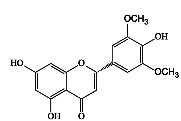
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [20] |
| 编号 | 化合物名称 | 分子结构式 | 槟榔提取部位 | 提取溶剂 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 儿茶素 |
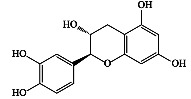
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [20] |
| 14 | 表儿茶素 |
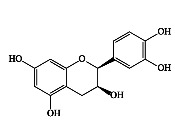
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [20] |
| 15 | Calquiquelignan M |
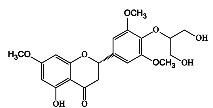
|
槟榔 | 乙醇(提取)、三氯甲烷(萃取) | [17] |
| 16 | Calquiquelignan N |
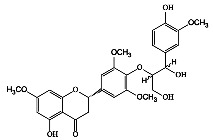
|
槟榔 | 乙醇(提取)、三氯甲烷 (萃取) | [17] |
| 17 | 原花青素B1 |
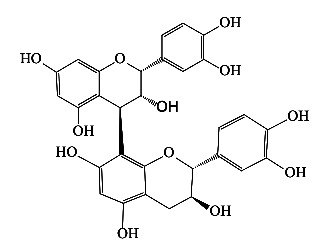
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [21] |
| 18 | 原花青素B2 |
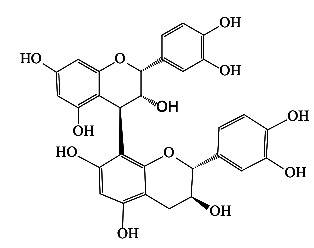
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [21] |
| 19 | 原花青素B7 |
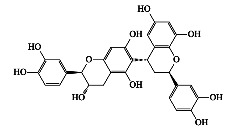
|
成熟种子 | 乙醇 | [21] |
2. 槟榔多酚的抗氧化作用
2.1. 体外抗氧化作用
槟榔多酚类化合物能够清除49.78%的羟自由基,且抗氧化能力随多酚含量的增加而增强[22]。Lin等[23]发现槟榔花的水提取物抗氧化活性能力强于50%的甲醇提取物;铁离子还原/抗氧化能力法(ferric ion reducing antioxidant power,FRAP)和超氧阴离子自由基清除实验表明:槟榔花提取物的抗氧化活性与总酚含量呈正相关。Sari等[24]研究发现:槟榔树的果、叶、花序及壳中多酚的含量及其抗氧化活性差异较大,且抗氧化活性与多酚含量有关,槟榔多酚的含量从高到低依次为果、叶、花序、壳;槟榔的抗氧化活性强度从大到小依次为果、叶、花序、壳。蒋晨凤[25]发现烟熏槟榔壳中的多酚成分为绿原酸、香草酸、原儿茶酸、对羟基苯甲酸和槲皮素;体外抗氧化活性研究表明该5种酚类化合物中原儿茶酸的抗氧化活性最强。Dsouza等[26]研究表明槟榔叶的三氯甲烷和甲醇提取物有显著的抗氧化活性。此外,Chavan等[27]使用80%的丙酮可得到多酚的最大提取量和槟榔碱的最小提取量,提取物中总酚的含量为407.47 mg/g、槟榔碱为1.73 mg/g,且自由基清除法和FRAP清除实验表明槟榔提取物的抗氧化作用与多酚含量有关,并通过高效液相色谱法(high performance liquid chromatography,HPLC)和液质联用(liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry,LC-MS)色谱图确认了槟榔提取物中有儿茶素和表儿茶素。
2.2. 体内抗氧化作用
Lee等[28]的研究结果表明:槟榔多酚提取物对H2O2诱导的中国仓鼠肺成纤维细胞V79-4氧化应激损伤有保护作用,其保护作用与消除自由基,增强过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)、超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)和谷胱甘肽过氧化氢酶(glutathione peroxidase,GPX)等抗氧化酶的活性有关。袁列江等[29]研究发现槟榔粗提取物、水溶出物和乙酸乙酯萃取物均能显著提高小鼠血清中的SOD水平。同时,3种提取物能降低小鼠血清中丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)的浓度,证明槟榔提取物在体内有很好的抗氧化作用。宋菲等[30]的实验发现H2O2可导致人正常成人纤维细胞(human skin fibroblast,HSF)线粒体膜肿胀,使线粒体功能受损;而表儿茶素和没食子酸均能降低H2O2引起的这种损伤,其对HSF的保护作用可能是通过清除活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS),抑制线粒体膜损伤而实现的。
3. 槟榔多酚的抗缺氧作用
研究[6,31]发现:槟榔多酚粗提取物能显著增强H9C2细胞的耐缺氧能力,其作用机制与提高细胞内抗氧化酶的活性和下调缺氧细胞中Nrf2 mRNA表达有关。进一步通过大孔吸附树脂纯化槟榔多酚粗提物,并进行高原实地缺氧实验,结果表明槟榔多酚能够显著改善缺氧大鼠的血气指标,与缺氧模型组相比,当多酚剂量为800 mg/kg时,大鼠的pH、标准碳酸氢盐(standard bicarbonate,SBC)、动脉血氧饱和度(oxygen saturaton,SatO2)分别增加了0.82%、7.70%、4.51%,动脉血二氧化碳分压(partial pressure of pcarbon dioxide,PaCO2)降低了11.01%;当多酚剂量为1 600 mg/kg时,大鼠的pH、SBC、SatO2分别增加了0.96%、7.95%、5.69%,PaCO2降低了12.39%;同时能提高肝、肺、心组织中GSH和SOD的酶活性,降低肝、肺、心组织中MDA的含量[3-4]。由此可知,槟榔多酚的抗缺氧作用与其改善大鼠的低氧血症、增强组织的抗氧化酶活性、减轻脂质过氧化和氧化应激损伤的作用有关。
4. 槟榔多酚预防高原肺水肿的作用
高原肺水肿(high altitude pulmonary edema,HAPE)是一种可危及生命的非心源性肺水肿[32],若不及时预防与治疗,将严重影响高原作业人群的健康。预防及治疗HAPE的药物主要有碳酸酐酶抑制剂乙酰唑胺、糖皮质激素类地塞米松、β受体激动剂沙美特罗[33]、支气管扩张剂氨茶碱[34]等,但这些药物均有一定程度的不良反应,因此,有必要寻找安全有效的治疗HAPE的药物。有学者[5,35]在前期槟榔多酚抗缺氧研究的基础上,更深入地研究槟榔多酚对急性高原病是否有预防保护作用,他们通过在海拔4 010 m的高原实地实验室进行辅助跑台力竭运动,建立大鼠HAPE模型,研究槟榔多酚的强抗氧化能力对于HAPE的预防保护作用。实验结果表明:与对照组相比,给予槟榔多酚低、中、高剂量后大鼠的血氧饱和度分别升高1.79%、6.10%和4.63%(均P<0.01);大鼠肺含水量分别降至(79.07±0.26)%、(78.49±0.30)%和(78.10±0.38)%;同时肺泡灌洗液蛋白质含量相比于模型组显著减低,基本降低至正常水平。病理组织观察发现:与模型组相比,预防性给予槟榔多酚后,大鼠的肺泡结构趋于完整,肺泡壁变薄,腔内渗出减少,炎症细胞减少。由此可知,槟榔多酚预防HAPE的发生与减轻肺水肿、维持肺泡毛细血管通透性、改善氧化应激损伤有关。综上所述,槟榔多酚对高原低氧引起的氧化应激损伤有一定的保护作用,同时对HAPE有预防作用。
槟榔多酚抗氧化、抗缺氧及其他药理作用见表2。
表2.
槟榔多酚的作用及其活性成分
Table 2 Roles and active components of betelnut polyphenols
| 药理作用 | 活性物质 | 作用机制 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 抗氧化 | 酚酸、花青素和黄酮类 | 清除自由基,增强CAT、SOD和GPX等抗氧化酶的活性 | [3, 27] |
| 抗缺氧 | 多酚类 | 提高细胞内抗氧化酶的活性,下调缺氧细胞中Nrf2的mRNA表达 | [6, 31] |
| 预防高原肺水肿 | 多酚类 | 减轻肺水肿,维持肺泡毛细血管通透性,改善氧化应激损伤及病理损伤 | [5, 35] |
| 消炎、镇痛 | 黄酮类、花青素类 | 抑制NO、TNF-α、IL-6、IL-1β、PGE2和ROS的形成 | [36-40] |
| 抗菌 | 巴西红厚壳素、儿茶素、表儿茶素和表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 | 抑制MRSA、结核分枝杆菌H37Rv等 | [19, 41, 42] |
| 改善骨质疏松 | 多酚类 | 与调节肠道微生物、减轻炎症有关 | [43] |
CAT:过氧化氢酶;SOD:超氧化物歧化酶;GPX:谷胱甘肽过氧化氢酶;Nrf2:核因子相关因子2;NO:一氧化氮;TNF-α:肿瘤坏死因子-α;IL-6:白细胞介素-6;IL-1β:白细胞介素-1β;PGE2:前列腺素E2;ROS:活性氧;MRSA:耐甲氧西林金黄色葡萄球菌。
5. 结 语
槟榔多酚具有抗氧化和抗缺氧作用。目前对于槟榔多酚的抗氧化作用以体外研究为主,而槟榔多酚在体内的抗氧化、抗缺氧作用及其机制和有效成分的研究鲜有报道。槟榔多酚的主要成分为儿茶素和表儿茶素[14, 16, 20],其在抗缺氧方面的作用仍有进一步研究的价值。同时,在槟榔多酚的提取工艺优化、质量标准建立、抗缺氧的有效组分和安全性评价等方面仍需进行深入研究。研究[3, 35]表明槟榔多酚抗缺氧效果优于红景天胶囊。此外,红景天胶囊的原料药为中药红景天,红景天属于高海拔植物,生长环境特殊,不易获取,且种植不易,过度开采也不利于高原生态环境;而槟榔资源丰富,原料药易得。因此,槟榔多酚在抗缺氧和保护组织氧化损伤方面可作为潜在药物,具有一定的开发应用前景。
基金资助
国家重大科技专项(2018ZX09J1809);中央高校创新团队项目(31920200009)。
This work was supported by the National Science and Technology Major Project (2018ZX09J1809) and the Innovation Team Project of the Central Universities (31920200009), China.
利益冲突声明
作者声称无任何利益冲突。
作者贡献
马江红 文献查阅,撰写和修改论文;杜兴,赵安鹏 论文写作指导和修改;王子晗、郭茜文、秦宁宁 文献查阅和整理;王荣 论文构思、校正和修订。所有作者阅读并同意最终的文本。
原文网址
http://xbyxb.csu.edu.cn/xbwk/fileup/PDF/202204512.pdf
参考文献
- 1. 孔丹丹, 李歆悦, 赵祥升, 等. 药食两用槟榔的国内外研究进展[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2021, 46(5): 1053-1059. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200709.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; KONG Dandan, LI Xinyue, ZHAO Xiangsheng, et al. Domestic and international research progress of edible and medicinal Arecae Semen[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2021, 46(5): 1053-1059. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200709.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. 贾哲, 韩婷, 刘欢, 等. 基于多元统计分析的食用槟榔及药用槟榔主要化学成分的含量对比研究[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2017, 32(11): 5158-5161. [Google Scholar]; JIA Zhe, HAN Ting, LIU Huan, et al. Comparative analysis of the determination of principal chemical components in edible betel nut and semen arecae based on multivariate statistical analysis[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2017, 32(11): 5158-5161. [Google Scholar]
- 3. 霍妍, 赵安鹏, 宋晶燕, 等. 槟榔多酚对急进高原大鼠具有抗缺氧作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 671-678. 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.05.06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; HUO Yan, ZHAO Anpeng, SONG Jingyan, et al. Betelnut polyphenols provide protection against high-altitude hypoxia in rats[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(5): 671-678. 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.05.06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. 宋晶燕. 槟榔多酚的提取分离及其抗高原缺氧药效学的研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏医科大学, 2020. [Google Scholar]; SONG Jingyan. Study on the extraction and separation of Areca polyphenols and its anti-plateau hypoxia pharmacodynamics[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia Medical University, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 5. 霍妍. 槟榔多酚对高原肺水肿的预防作用研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. [Google Scholar]; HUO Yan. Study on the preventive effects of betelnut polyphenols on high altitude pulmonary edema[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 6. 靳婷. 槟榔提取物抗高原缺氧药效学及其机制研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2018. [Google Scholar]; JIN Ting. Studies on pharmacodynamics and mechanism of Areca catechu L extracts against high-altitude hypoxia[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 7. 杨雅蛟, 孔维军, 孙兰, 等. 槟榔化学成分和药理作用及临床应用研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2019, 21(12): 2583-2591. 10.11842/wst.20180819003. 30920232 [DOI] [Google Scholar]; YANG Yajiao, KONG Weijun, SUN Lan, et al. Research progress on chemical composition and pharmacological effect and clinical application of Areca catechu [J]. Modernization of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Materia Medica-World Science and Technology, 2019, 21(12): 2583-2591. 10.11842/wst.20180819003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 8. 孙露, 宋海波, 张力, 等. 中药槟榔及其制剂的安全性系统评价[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(21): 4067-4073. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170919.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; SUN Lu, SONG Haibo, ZHANG Li, et al. Systematic evaluation for safety of traditional Chinese medicine Areca catechu and its preparations[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2017, 42(21): 4067-4073. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170919.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. 栾剑, 郭迪, 周晓馥. 槟榔致癌性和毒性的药理学研究进展[J]. 食品与机械, 2019, 35(2): 185-189, 236. 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2019.02.035. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; LUAN Jian, GUO Di, ZHOU Xiaofu. Advances of pharmacological research on carcinogenicity and toxicity of Areca nut[J]. Food & Machinery, 2019, 35(2): 185-189, 236. 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2019.02.035. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Peng W, Liu YJ, Wu N, et al. Areca catechu L. (Arecaceae): a review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 164: 340-356. 10.1016/j.jep.2015.02.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. 韩林. 槟榔中抗氧化成分的提取及分离研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2010. [Google Scholar]; HAN Lin. Studies on extraction and separation of antioxidant constituents from Areca nut[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 12. 李浩, 彭喜洋, 吴湃萱, 等. 植物多酚对肠道微生态影响的研究进展[J]. 食品与机械, 2019, 35(6): 222-226, 236. 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2019.06.040. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; LI Hao, PENG Xiyang, WU Paixuan, et al. Progress on effects of plant polyphenols on intestinal microecology[J]. Food & Machinery, 2019, 35(6): 222-226, 236. 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2019.06.040. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13. 郑晓宁, 李俊, 牟建楼, 等. 植物多酚改善胃肠功能研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(23): 309-315. 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.024580. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; ZHENG Xiaoning, LI Jun, MU Jianlou, et al. Advances on the improvement of gastrointestinal function by plant polyphenols[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(23): 309-315. 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.024580. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14. 王明月, 罗金辉, 李建国. HPLC法测定槟榔中的多酚类物质[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2011, 23(1): 101-104. 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2011.01.032. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; WANG Mingyue, LUO Jinhui, LI Jianguo. Determination of polyphenols in Areca catechu by HPLC[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2011, 23(1): 101-104. 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2011.01.032. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15. 张春梅, 黄玉林, 程芳芳, 等. 槟榔花提取物中没食子酸等9种多酚类化合物的测定[J]. 热带作物学报, 2011, 32(5): 965-969. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2011.05.036. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; ZHANG Chunmei, HUANG Yulin, CHENG Fangfang, et al. Analysis of nine phenolic compounds of Areca inflorescence extracts[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2011, 32(5): 965-969. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2011.05.036. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16. 祁静. 槟榔酚类化合物的提取、抗氧化及抗疲劳作用研究[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2011. [Google Scholar]; QI Jing. Extraction, antioxidant and anti-fatigue effects of phenolic compounds of betel nut[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 17. Yuan MF, Ao YL, Yao N, et al. Two new flavonoids from the nuts of Areca catechu [J/OL]. Molecules, 2019, 24(16): E2862 (2019-08-07)[2021-09-16]. 10.3390/molecules24162862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. 何细新, 李亚军, 胡小鹏, 等. 槟榔壳中三萜及蒽醌类成分的分离与结构鉴定[J]. 中药新药与临床药理, 2010, 21(6): 634-636. 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2010.06.022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; HE Xixin, LI Yajun, HU Xiaopeng, et al. Isolation and structural identification of triterpenoids and anthraquinones from pericarpium arecae[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2010, 21(6): 634-636. 10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2010.06.022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19. 张兴, 梅文莉, 曾艳波, 等. 槟榔果实的酚类化学成分与抗菌活性的初步研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2009, 17(1): 74-76. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3395.2009.01.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; ZHANG Xing, MEI Wenli, ZENG Yanbo, et al. Phenolic constituents from the fruits of Areca catechu and their anti-bacterial activities[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2009, 17(1): 74-76. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3395.2009.01.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20. 杨文强, 王红程, 王文婧, 等. 槟榔化学成分研究[J]. 中药材, 2012, 35(3): 400-403. 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2012.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; YANG Wenqiang, WANG Hongcheng, WANG Wenjing, et al. Chemical constituents from the fruits of Areca catechu [J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2012, 35(3): 400-403. 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2012.03.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. 牟肖男, 杨文强, 王文婧, 等. 槟榔的化学成分[J]. 暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版), 2014, 35(1): 56-60. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9965.2014.01.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; MU Xiaonan, YANG Wenqiang, WANG Wenjing, et al. Chemical constituents from the fruits of Areca catechu [J]. Journal of Jinan University. Natural Science & Medicine Edition, 2014, 35(1): 56-60. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9965.2014.01.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Wang N, Song JY, Zhou G, et al. Mechanism of salidroside relieving the acute hypoxia-induced myocardial injury through the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2020, 27(6): 1533-1537. 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.04.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Lin E, Li CC. Evaluation of superoxide radical scavenging capacity and reducing power of Areca flower extracts[J]. J Med Plants Res, 2010, 4: 975-981. 10.5897/JMPR10.194. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Sari EF, Prayogo GP, Loo YT, et al. Distinct phenolic, alkaloid and antioxidant profile in betel quids from four regions of Indonesia[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 16254. 10.1038/s41598-020-73337-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. 蒋晨凤. 水解对槟榔多酚抗氧化活性的影响及多酚协同抗氧化特性研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2016. [Google Scholar]; JIANG Chenfeng. Study on effect of hydrolysis on the antioxidant activity of Areca polyphenols and synergistic antioxidant activity of polyphenols[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 26. Dsouza NG, Fernandes J, D'Souza S, et al. In vitro antioxidant activity of leaves extracts of Areca catechu [J]. Rese Jour Pharm And Technol, 2019, 12(4): 1536. 10.5958/0974-360x.2019.00254.3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Chavan YV, Singhal RS. Separation of polyphenols and arecoline from Areca nut (Areca catechu L.) by solvent extraction, its antioxidant activity, and identification of polyphenols[J]. J Sci Food Agric, 2013, 93(10): 2580-2589. 10.1002/jsfa.6081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Lee KK, Cho JJ, Park EJ, et al. Anti-elastase and anti-hyaluronidase of phenolic substance from Areca catechu as a new anti-ageing agent[J]. Int J Cosmet Sci, 2001, 23(6): 341-346. 10.1046/j.0412-5463.2001.00102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. 袁列江, 李忠海, 郑锦星. 槟榔提取物对小白鼠体内抗氧化作用的研究[J]. 食品科学, 2009, 30(7): 225-228. 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.07.051. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; YUAN Liejiang, LI Zhonghai, ZHENG Jinxing. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities of varous Areca nut extracts[J]. Food Science, 2009, 30(7): 225-228. 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.07.051. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30. 宋菲, 王齐齐, 王挥, 等. 槟榔花中酚类物质对HSF细胞氧化损伤的保护作用[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2015, 36(23): 10-13, 46. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2015.23.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; SONG Fei, WANG Qiqi, WANG Hui, et al. Protective effects of phenolic compounds in Areca inflorescence on oxidative damage in HSF cells[J]. Food Research and Development, 2015, 36(23): 10-13, 46. 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2015.23.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31. 赵安鹏, 靳婷, 王荣. 槟榔醇提物对H9C2心肌细胞的抗缺氧保护作用[J]. 药学实践杂志, 2019, 37(4): 294-298. 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0111.2019.04.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; ZHAO Anpeng, JIN Ting, WANG Rong. Protective effect of Areca catechu linn ethanol extract against hypoxia in H9C2 cells[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical Practice, 2019, 37(4): 294-298. 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0111.2019.04.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Luks AM, Swenson ER, Bärtsch P. Acute high-altitude sickness[J]. Eur Respir Rev, 2017, 26(143): 160096. 10.1183/16000617.0096-2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. 马四清, 宋青. 高原肺水肿防治研究进展[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2021, 46(6): 603-608. 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.06.12. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; MA Siqing, SONG Qing. Prevention and treatment of acute high pulmonary edema: research progress[J]. Medical Journal of Chinese People's Liberation Army, 2021, 46(6): 603-608. 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.06.12. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34. 王昌, 王荣, 谢华, 等. 氨茶碱对急进高原大鼠部分生理病理变化的影响[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2015, 40(1): 39-45. 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2015.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; WANG Chang, WANG Rong, XIE Hua, et al. Effect of aminophylline on physiological and pathological changes in acute exposure to high altitude in rats[J]. Journal of Central South University. Medical Science, 2015, 40(1): 39-45. 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2015.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. 霍妍, 赵安鹏, 宋晶燕, 等. 槟榔多酚对大鼠高原肺水肿的预防作用[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2021, 46(10): 961-967. 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.10.02. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; HUO Yan, ZHAO Anpeng, SONG Jingyan, et al. The preventive effect of Betelnut polyphenols on high altitude pulmonary edema[J]. Medical Journal of Chinese People’s Liberation Army, 2021, 46(10): 961-967. 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2021.10.02. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36. 易攀, 汤嫣然, 周芳, 等. 槟榔的化学成分和药理活性研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2019, 50(10): 2498-2504. 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.10.034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; YI Pan, TANG Yanran, ZHOU Fang, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Areca catechu [J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2019, 50(10): 2498-2504. 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.10.034. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37. 唐敏敏, 宋菲, 陈华, 等. 槟榔籽提取物抗炎作用及化学成分研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2021, 42(7): 2035-2042. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.07.030. 33729465 [DOI] [Google Scholar]; TANG Minmin, SONG Fei, CHEN Hua, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects and chemical constituent analysis of the ethanol extract of Areca catechu seeds[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(7): 2035-2042. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2021.07.030. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38. 唐敏敏, 陈华, 李瑞. 响应面法优化超声波提取槟榔多糖工艺及其抗炎活性[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2019, 25(9): 21-24, 74. 10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2019.09.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; TANG Minmin, CHEN Hua, LI Rui. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of Areca nut polysaccharides based on response surface methodology and anti-inflammatory activity[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 25(9): 21-24, 74. 10.16377/j.cnki.issn1007-7731.2019.09.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39. 唐敏敏, 宋菲, 王辉, 等. 槟榔多糖的抗氧化活性及其对细胞内氧化损伤抑制作用的研究[J]. 热带作物学报, 2015, 36(6): 1136-1141. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2015.06.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; TANG Minmin, SONG Fei, WANG Hui, et al. In vitro antioxidant activities and protective effects of polysaccharides from Areca catechu L.Seed[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2015, 36(6): 1136-1141. 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2015.06.020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Huang PL, Chi CW, Liu TY. Effects of Areca catechu L. containing procyanidins on cyclooxygenase-2 expression in vitro and in vivo[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2010, 48(1): 306-313. 10.1016/j.fct.2009.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Hong H, Lee JH, Kim SK. Phytochemicals and antioxidant capacity of some tropical edible plants[J]. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci, 2018, 31(10): 1677-1684. 10.5713/ajas.17.0903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Raju A, De SS, Ray MK, et al. Antituberculosis activity of polyphenols of Areca catechu [J]. Int J Mycobacteriol, 2021, 10(1): 13-18. 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_199_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Mei FF, Meng KK, Gu ZP, et al. Arecanut (Areca catechu L.) seed polyphenol-ameliorated osteoporosis by altering gut microbiome via LYZ and the immune system in estrogen-deficient rats[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2021, 69(1): 246-258. 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]