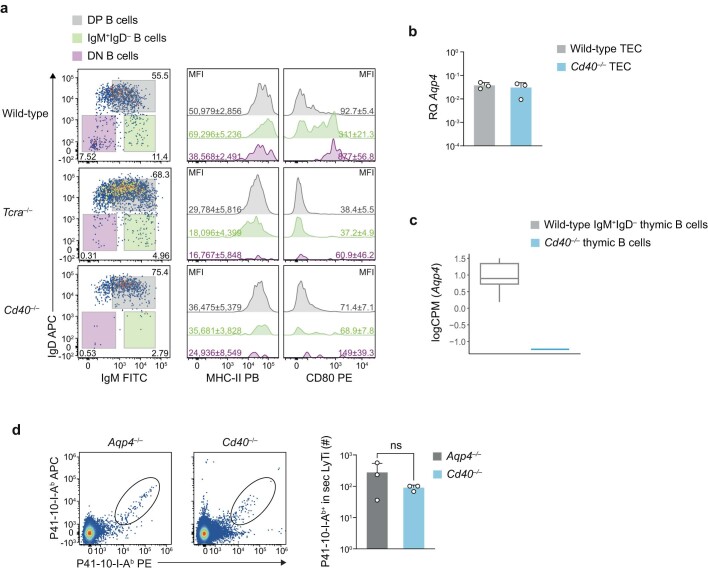
Extended Data Fig. 5. CD40 is essential in licensing APC properties in thymic B cells.
(a) Thymic B cells from wild-type, Tcra–/–, and Cd40–/– mice (all n = 5 biological replicates) were characterized for their expression of surface markers IgD, IgM, MHC class II, and CD80. Representative cytograms and histograms of thymic B cell subsets (DP = double positive IgM+IgD+, IgM+IgD–, and DN = double negative IgM–IgD–) are shown along with mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) ± SD of MHC class II and CD80 next to the corresponding histograms. (b) Aqp4 expression in EpCAM+ thymic epithelial cells (TECs) isolated from wild-type and Cd40–/– mice (n = 3 biological replicates). Mean RQ ± SD normalized to astrocytes. (c) Expression of Aqp4 in wild-type IgM+IgD– thymic B cells vs. Cd40–/– thymic B cells. Box plot derived from the RNAseq data in Fig. 3i, with the median as the centre, the first and third quartiles as the boundaries of the box, and 1.5 times the IQR as the whiskers. (d) Representative cytograms and quantification of P41/I-Ab-reactive T cells isolated from secondary lymphoid tissue (sec LyTi, spleen plus draining lymph nodes) of P41-immunized Aqp4–/– and Cd40–/– mice (both n = 3 biological replicates) on day 10 after immunization. Data are shown as mean ± SD tested with a two-tailed unpaired t-test, ns = not significant.