Abstract
Background
The predominant feature of cancer cells during the process of carcinogenesis is the inclination towards glycolytic metabolism rather than mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Nevertheless, there is a scarcity of research investigating the correlation between bladder cancer and mitochondrial energy metabolism.
Methods
A qPCR array comprising 90 genes associated with mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation was employed to discern metabolic disparities between three sets of bladder cancer tissue and adjacent normal tissue. Wound healing and transwell assays were utilized to assess cell migration and invasion capabilities, respectively. Colony formation assays were conducted to ascertain the tumorigenic potential of the cells. The proliferative capacity of the cells was examined through in vitro CCK-8 assays. Additionally, nude mouse models were established to evaluate the impact of bladder tumor cells on in vivo proliferation. The Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer was utilized to quantify mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, while the levels of glucose-6-phosphate and pyruvate were assessed to evaluate glycolysis.
Results
Examination of qPCR array data demonstrated a noteworthy inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in bladder cancer tissue, as evidenced by the down-regulation of a majority of genes associated with mitochondrial energy metabolism. Notably, GADD45B may potentially exert a significant influence on bladder cancer development, warranting further investigation. The down-regulation of GADD45B in bladder cancer cells resulted in impaired mitochondrial respiration and elevated levels of glycolysis, thereby enhancing cell migration and invasion. Conversely, up-regulation of GADD45B had the opposite effect. Furthermore, over-expression of GADD45B inhibited tumor proliferation and tumorigenesis in both in vitro and in vivo settings.
Conclusion
These findings from our study indicate that the down-regulation of GADD45B promotes the shift of cell mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation towards glycolysis, thereby facilitating the progression of bladder cancer.
Keywords: GADD45B, Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, Glycolysis, Bladder cancer
1. Introduction
Annually, a global count of 430,000 fresh instances of bladder cancer are identified, resulting in a mortality toll exceeding 165,000 individuals [1]. Following localized surgical resection and subsequent adjuvant therapy, the 5-year survival rate for the majority of patients afflicted with non-metastatic bladder cancer can attain 90% [2]. However, upon progression to metastatic bladder cancer, the 5-year survival rate plummets to a mere 18.6% for patients [3,4]. Platinum-based drugs serve as the primary modality of chemotherapy for managing metastatic bladder cancer. However, a substantial proportion of patients with metastatic bladder cancer are precluded from receiving chemotherapy due to the pronounced toxicities and adverse effects associated with this treatment approach [5]. Consequently, it becomes imperative to delve deeper into the molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of bladder cancer to facilitate the advancement of targeted therapeutic interventions.
The development of bladder cancer is a multifaceted phenomenon that arises from genetic alterations and/or epigenetic irregularities. While the progression of primary tumors is primarily driven by transcriptional modifications (such as the loss of genes that repress oncogenes) and environmental factors (such as local hypoxia and oxidative stress), these environmental stressors also play a role in selecting cells that can adapt to these changes by modifying their metabolic processes to match nutrient availability. Mitochondria, which serve as the central hub for cellular energy metabolism, are now acknowledged to function as cellular pressure sensors, allowing tumors to adapt to fluctuations in energy levels during their transformation [6]. The chemiosmotic process known as oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), occurring in the presence of oxygen, serves as the final step in cellular respiration, thereby enabling mitochondria to primarily provide energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) [7]. Nevertheless, the prevailing feature observed in cells during carcinogenesis is the preference of cancer cells for aerobic glycolysis over OXPHOS within tumors. Despite the comparatively reduced ATP production resulting from glycolysis as opposed to OXPHOS, the accumulation of metabolites during glycolysis promotes the progression of cancer cells [8]. For instance, the presence of OXPHOS machinery deficiencies in colorectal cancer cells triggers the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) thereby promoting the advancement of cancer [9]. Mitochondrial genetic and functional impairments serve as molecular indicators correlated with aggressive triple negative breast cancers [10]. The impairments in OXPHOS, particularly the decline in ATP synthase activity leading to decreased OXPHOS efficacy and heightened glycolysis, are associated with unfavorable prognosis and resistance to medication in acute myeloid leukemia [11]. However, there is a dearth of research examining the correlation between bladder cancer and mitochondrial energy metabolism.
In this study, we focus on the relationship between mitochondrial energy metabolism and the advancement of bladder cancer. Our findings demonstrated that the decrease in GADD45B expression triggers a shift from cellular oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis, thereby facilitating the progression of bladder cancer.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Tissue samples
Bladder cancer tumors and adjacent normal tissue samples were procured from patients diagnosed with bladder cancer who had undergone surgery at the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University. The study protocol received approval from the Ethical Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University (Approval NO.2022-065A), and written informed consent was obtained from participants.
2.2. Cell culture
The bladder cancer cell lines, namely J82, T24, 5637, and UMUC-3, were procured from the Shanghai Institute of Cell Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. These cell lines were cultivated in an appropriate medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and were maintained under controlled conditions of 37 °C,5% CO2, and a humid atmosphere.
2.3. GADD45B over-expression and knockdown for stable cell lines
The lentivirus construct for GADD45B knockdown or over-expression was acquired from Genechem (Shanghai, China). The plasmids, designated as GV492 were employed for the packaging of the aforementioned lentivirus. Detailed information regarding GV492 can be accessed via the following URL: http://www.genechem.com.cn/index/supports/zaiti_info.html?id = 82.
Bladder cancer cells J82 were cultured in 6-well dishes at 50% confluence and subsequently infected with a lentivirus over-expressing GADD45B (referred to as J82-GADD45B-OE), as well as a negative control (referred to as J82-NC). Similarly, T24 cells were infected with a lentivirus targeting GADD45B knockdown (referred to as T24-GADD45B-KD), or a scramble control (referred to as T24-NC). Following lentivirus transfection cells were selected using a complete medium containing 2 mg/ml puromycin after 72 h. The expression of GADD45B protein was confirmed through western blot analysis.
2.4. Quantitative real-time PCR
Total RNA was extracted from bladder cancer tumors and adjacent normal tissue samples using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, United States), followed by cDNA synthesis using a reverse transcription kit (Thermo, United States). The gene expression patterns were examined using the Human Targets of Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism Related Gene qPCR Array (Wcgene Biotech, Shanghai, China) as per the manufacturer's instructions (specific genes are provided in Table S1 in the Supplementary material). The data were analyzed utilizing the Wcgene Biotech software (http://www.wcgene.com). The quantification of GADD45B mRNA levels in bladder tissues was performed through qRT-PCR using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Roche) on a LightCycler480 system, with normalization to the expression of the endogenous control, ACTN. The specific PCR primers employed are provided in the list below:
GADD45B Forward primer 5′-GTCGGCCAAGTTGATGAAT-3′
Reverse primer 5′-CACGATGTTGATGTCGTTGT-3′
ACTN Forward primer 5′-TGAGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTG-3′,
Reverse primer 5′-TGCTTGCTGATCCACATCTGC-3′.
2.5. Western blot analysis
The proteins were separated using sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis based on their molecular weight. Subsequently, they were transferred onto a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane (Bio-Rad) and blocked using TBS-T solution containing 5% non-fat dry milk. The following antibodies were diluted in TBS-T and incubated overnight at 4 °C: Anti-GADD45B (1:500, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), Anti-HK2 (1:1000, Cell Signaling Technology), Anti-PKM2 (1:1000, Cell Signaling Technology) and anti-ACTIN (1:1000, Abcam). Following the TBS-Tr washing step, the membranes were subjected to incubation with a horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:5000; Abcam) for a duration of 1 h. Subsequently, another round of TBS-T washing was performed, and the membranes were then subjected to development using ECL-Plus (GE Healthcare, Life Sciences).
2.6. Colony formation assays
A total of 2000 cells were evenly distributed into each well of 24-well plates in triplicate. At specified time intervals, the culture medium was removed and the cells were immobilized using a 4% paraformaldehyde solution for 30 min at ambient temperature. Subsequently, the cells were subjected to staining with a 0.2% crystal violet staining solution for a duration of 15 min. Following the removal of the staining solution, the plates were rinsed twice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). The plates were then allowed to air-dry overnight, after which the number of colonies was enumerated.
2.7. Invasion assays
Cellular invasion was conducted using trans-well chambers with a pore diameter of 8 mm. The upper chambers were seeded with cells in a serum-free media at a density of 2 × 104 cells/well. The filters in the upper chambers were coated with BD Matrigel. The cells were added to the upper chamber and incubated at 37C for 48 h. The surface cells were subsequently removed using a Q-tip, while the cells that had invaded through the membrane were fixed with paraformaldehyde and stained with crystal violet. The crystal violet-stained infiltrated cells were then decolorized using glacial acetic acid, and the number of cells was indirectly quantified by measuring the absorbance at 570 nm.
2.8. Migration assays
Cell motility was assessed through wound healing assays. Once the seeded cells achieved 95% confluence in a 6-well plate, a linear wound was generated across the well's diameter using a micropipette tip. Subsequently, non-adherent cells were flushed out using PBS. To facilitate cell migration without promoting cell growth, a medium containing 0.5% FBS was introduced. At 0 h and 24 h, three equidistant points within the scratched area were measured and imaged using an inverted phase contrast microscope (Olympus, Japan).
2.9. In vitro proliferation assays
A total of 10,000 cells were seeded in each well of 96-well plates, with 100 μL of medium per well. Following a culture period of 4, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h, the cells were subjected to an additional 2-h incubation at 37 °C with a 10% CCK8 solution in 100 μL of medium to assess their proliferative capacity. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a SpectraMax M5 instrument manufactured by MolecularDevices, USA.
2.10. In vivo tumor growth assays
A total of five male BALB/c-nu mice were subcutaneously administered with J82 cells (2 × 106 cells/100 μl) containing the GADD45B expressing lentiviral vector, while an equal number of J82 cells with an empty vector were injected into another group of five mice. The tumor volume was determined using the formula V = L × W2 × π/6 (where V represents volume, L represents length and W represents width of the tumor). On the 28th day post implantation, the tumors were harvested and weighed. The experimental procedure was granted ethical approval by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Ningbo University (Approval NO.11830).
2.11. Oxygen consumption rate analysis
The Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer, manufactured by Seahorse Bioscience in Massachusetts, USA, was employed to assess the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) through Mitochondrial Stress Test. To conduct the experiment, a total of 2 × 104 cells were seeded in quadruplicate within a 96-well XF culture plate containing XF assay media. The concentrations of oligomycin (1.5 μM), FCCP (1 μM), and Rotenone/Antimycin A (0.5 μM) were optimized for this study. Following the completion of the assay, the OCR measurements were normalized based on the total cell content within each well.
2.12. Glucose-6-phosphate (G-6-P) and pyruvate (PA) examinations
The G-6-P and PA examinations were conducted in accordance with the manufacturer instructions provided by Beyotime Biotech company (Nanjing, China) and Solarbio company (Beijing, China) respectively. The specific experimental procedures employed were derived from previously documented protocols [12].
2.13. Statistical analysis
The differences between the two groups were analyzed using an unpaired t-test. The figures or legends provided information on the number of biological replicas used in the experiment. Statistical significance was determined at a threshold of p < 0.05 (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001).
3. Results
3.1. Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation is inhibited in bladder cancer tissue
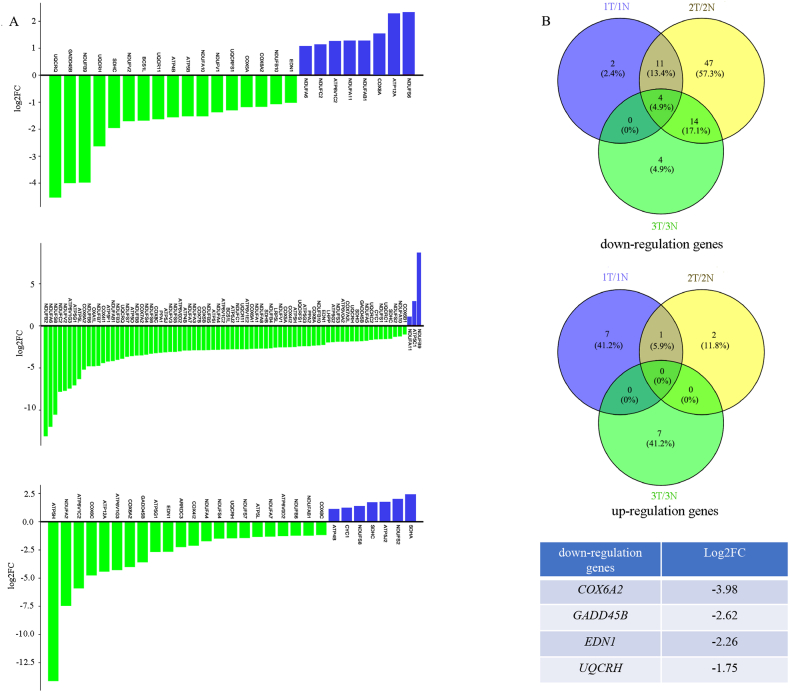
Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is a widely employed method for characterizing mitochondrial energy metabolism. In order to gain insights into the energy metabolism of mitochondria in bladder cancer, a qPCR array comprising 90 genes associated with OXPHOS was employed to identify metabolic disparities between three sets of bladder cancer tissue and their corresponding normal adjacent tissue [[13], [14], [15]]. The findings revealed that, in comparison to the adjacent tissues, a majority of the genes exhibited down-regulation in all three bladder cancer tissues (Fig. 1A). Furthermore, our investigation revealed a simultaneous down-regulation of mRNA expressions of COX6A2, GADD45B, EDN1 and UQCRH in all three cancer tissues, while no genes were found to be simultaneously up-regulated (Fig. 1B). Collectively, these findings suggest a down-regulation of mitochondrial energy metabolism in bladder cancer tissues, with potential significance attributed to the involvement of COX6A2, GADD45B, EDN1 and UQCRH in this process.
Fig. 1.
The inhibition of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation has been observed in bladder cancer tissue. (A) The gene expression of three pairs of bladder cancer and adjacent tissue was analyzed using the Human Targets of Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation Related Gene qPCR Array. In comparison to adjacent tissues, a majority of genes exhibited down-regulation in all three bladder cancer tissues. (B) A Venn plot was generated to illustrate the overlap between down-regulated and up-regulated genes. The mRNA expressions of COX6A2, GADD45B, EDN1 and UQCRH were found to be concurrently down-regulated in all three cancer tissues.
3.2. The expression of GADD45B is significantly reduced in bladder cancer compared to the normal control group
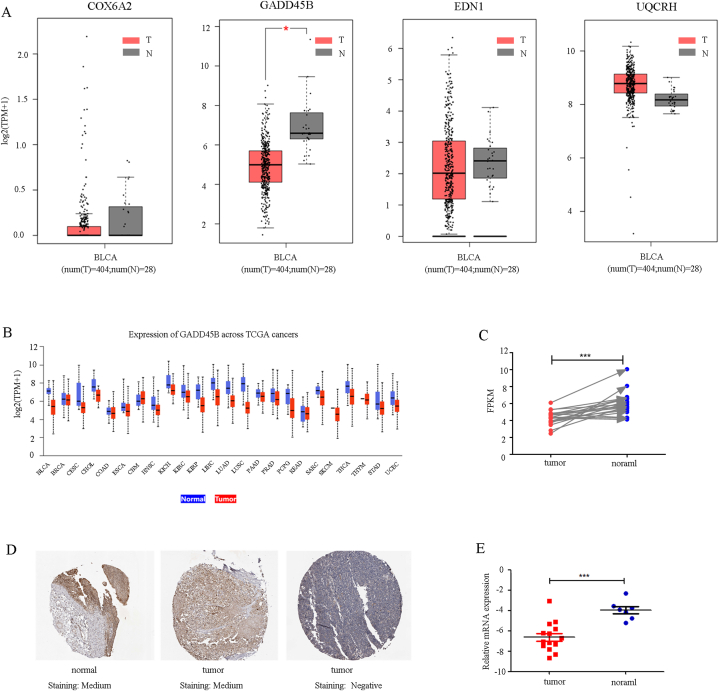
In order to further investigate the involvement of the four down-regulated genes in bladder cancer, we conducted an analysis of the TCGA and GTEx datasets using the GEPIA tool. Our analysis revealed that among the four genes, GADD45B exhibited a significantly lower mRNA level in tumors compared to normal tissues (Fig. 2A). Additionally, we utilized the UALCAN tool to examine the mRNA expression of GADD45B across various cancer types (Fig. 2B). Our findings indicated a consistent down-regulation of GADD45B in multiple tumor types, including cholangiocarcinoma, renal papillary cell carcinoma, and prostate cancer among others. Subsequently, we procured paired samples of bladder cancer tissues from the TCGA database and also observed a down-regulation of GADD45B at the mRNA level (Fig. 2C). Furthermore, we obtained our own clinical samples, comprising 7 normal tissues and 14 cancerous tissues from patients with bladder cancer, and detected higher mRNA levels of GADD45B in normal tissues than in cancer tissues consistent with the analysis of the TCGA dataset (Fig. 2E). At the protein level, an examination of the Human Protein Atlas database was conducted, revealing that the protein expression of GADD45B exhibited concordance with the mRNA level as evidenced by the obtained tissue microarray staining (Fig. 2D). These findings provide evidence suggesting the down-regulation of GADD45B in bladder cancer tissues.
Fig. 2.
The expression of GADD45B is significantly reduced in bladder cancer compared to the normal control group (A) The mRNA expression levels of COX6A2, GADD45B, EDN1 and UQCRH were compared between bladder tumor samples and normal samples. This comparison was conducted using the TCGA and GTEx datasets and analyzed through the utilization of GEPIA. (B) The mRNA expression level of GADD45B was examined across various cancer types using TCGA data. This analysis was performed using UALCAN. (C) The mRNA expression levels of bladder cancer tissues were investigated in paired samples obtained from the TCGA dataset. (D) The Human Protein Atlas database was utilized to obtain representative images depicting the immunohistochemistry staining intensities of GADD45B in both normal bladder tissue and bladder tumor. (E) The quantification of GADD45B mRNA expression was performed using qRT-PCR in both normal bladder tissues and cancer samples.
3.3. The up-regulation of GADD45B inhibits the invasion and migration of bladder cancer cells
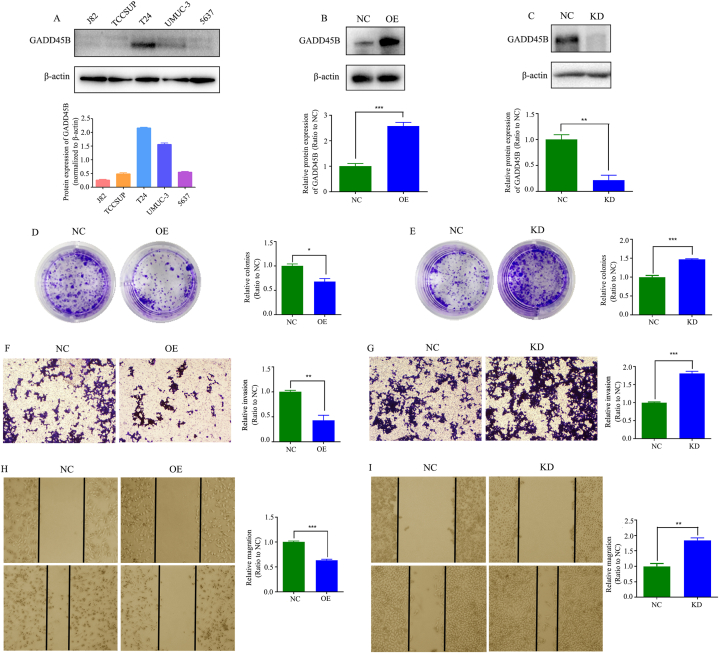
To investigate the function of GADD45B, J82 cells within low background expression of GADD45B were chosen to establish a stable cell line that over-expresses GADD45B (J82-GADD4B-OE), along with corresponding control cells (J82-NC). Similarly, T24 cell within high background expression of GADD45B were selected to establish a stable cell line with low expression of GADD45B (T24-GADD45B-KD), along with corresponding control cells (T24-NC) (Fig. 3A). The effectiveness of GADD45B over-expression and silencing was confirmed through western blot analysis (Fig. 3B and C). Subsequently, the investigation focused on the impact of GADD45B on tumorigenicity, invasion and migration in bladder cancer progression. The results of the colony formation assay demonstrated a decrease in tumorigenicity in GADD45B-overexpressed J82 cells, while an increase was observed in GADD45B-depleted T24 cells (Fig. 3D and E). Similarly, trans-well and wound healing assays revealed that GADD45B over-expression suppressed bladder cancer cell invasion and migration. Conversely, the down-regulation of GADD45B was found to accelerate cell invasion and migration (Fig. 3F–I). Taken together, the aforementioned findings elucidate that the up-regulation of GADD45B exerts inhibitory effects on the invasion and migration of bladder cancer cells.
Fig. 3.
GADD45B up-regulation inhibits bladder cancer cell invasion and migration. (A) The protein expression level of GADD45B in various bladder cancer cell lines (T24, UMUC3, 5637, TCCSUP and J82) was assessed using western blot analysis. (B) Introduction of a lentiviral vector containing GADD45B significantly augmented the expression level of GADD45B in J82 cells. (C) Transfection of T24 cells with a shGADD45B lentiviral vector resulted in down-regulation of GADD45B protein expression. (D.E) Following modulation of GADD45B expression in J82 and T24 cells, tumorigenesis was evaluated through colony formation assays, involving a 10-day incubation period followed by crystal violet staining. (F.G) The cell invasion ability was assessed using the matrigel transwell assay. (H.I) The cell migration ability was measured by wound-healing assays. The GADD45B over-expressed group exhibited a substantial reduction in tumorigenesis, invasion, and migration abilities, whereas the GADD45B depleted group displayed a significant increase in these abilities. All data presented represent the mean of three independent experiments, with the standard error of the mean (SEM) indicated.
3.4. The excessive expression of GADD45B demonstrates the ability to inhibit the proliferation of bladder cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo
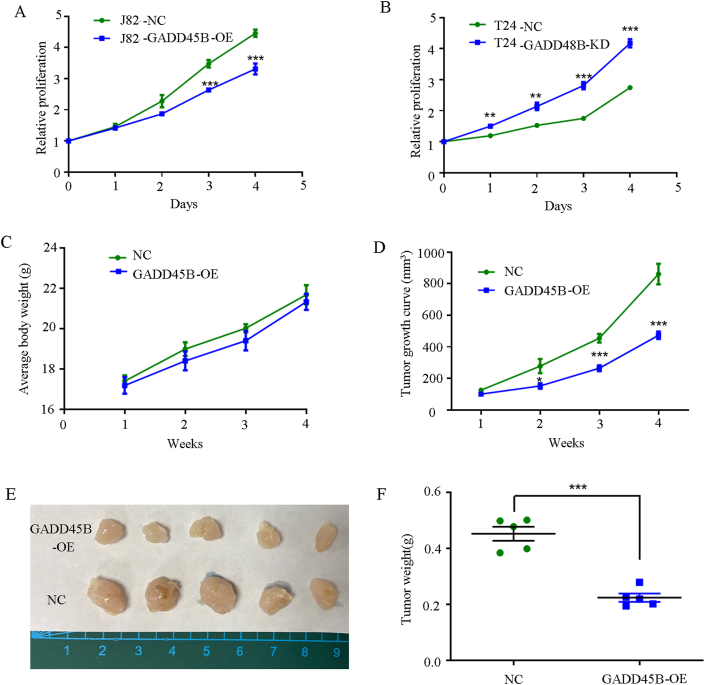
In order to provide additional evidence regarding the involvement of GADD45B in the regulation of bladder cancer progression, we conducted an in vitro assessment of the proliferation rate using the CCK-8 assay. The findings revealed that the ectopic over-expression of GADD45B in J82 cells resulted in a significant decrease in the proliferative abilities compared to the negative control (Fig. 4A). Conversely, the knockdown of GADD45B expression in T24 cells noticeably enhanced cell growth (Fig. 4B). Additionally, we investigated the impact of GADD45B on tumor xenograft growth in nude mice. The xenografted mice model revealed that the up-regulation of GADD45B led to a notable reduction in tumor growth compared to control xenografts (Fig. 4C–F). These findings collectively provide evidence that GADD45B possesses the ability to inhibit the growth of bladder cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo.
Fig. 4.
The excessive expression of GADD45B has been observed to impede the proliferation of bladder cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo.
CCK-8 assays were performed to test the proliferation capacity of the cells. (A) The overexpression of GADD45B resulted in a decrease in the proliferative capacity of J82 cells compared to the negative control. (B) Knocking down GADD45B significantly increased the proliferative capacity of T24 cells. The data represents the average of three independent experiments ± SEM. Nude mice were injected with lentiviral-delivered GADD45B and control plasmid (NC)-infected J82 cells, and the weight of the mice is presented in (C). (D) Tumor growth was periodically measured and depicted in the line chart. (E) After a four-weeks period following the injection of transfected J82 cells, the tumors were harvested for imaging. The final weight of the tumor is shown in (F). All the values represent the means ± SEM.
3.5. The down-regulation of GADD45B shifts bladder cancer cells from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis
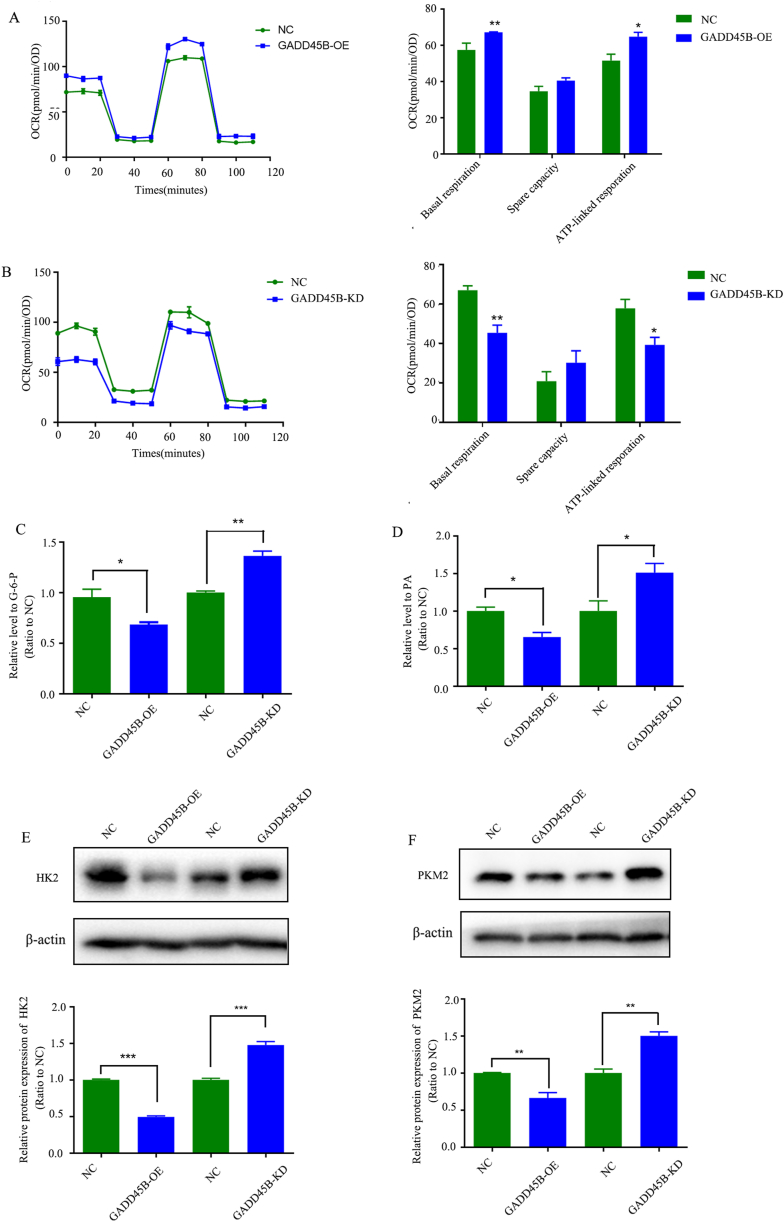
In order to investigate the impact of GADD45B levels on OXPHOS, a mitochondrial stress test was conducted using the Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analyzer to measure the oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in J82-NC, J82-GADD4B-OE, T24-NC, and T24-GADD45B-KD cells. Compared to J82-NC, J82-GADD4B-OE cells exhibited significantly higher levels of basal respiration and ATP-linked respiration (Fig. 5A). Conversely, knockdown of GADD45B in T24 cells resulted in a significant decrease in basal respiration and ATP-linked respiration (Fig. 5B). Aerobic glycolysis, commonly referred to as the “Warburg effect” is a well-known characteristic of cancer cells, that enables them to meet their metabolic demands for cell growth. In light of our observation of diminished mitochondrial energy metabolism subsequent to the down-regulation of GADD45B, we assessed the levels of glucose-6-phosphate(G-6-P) and pyruvate (PA), which are the products of the initial and final irreversible steps of glycolysis, respectively. Our findings indicate that the over-expression of GADD45B significantly decreased the levels of G-6-P and PA, whereas the down-regulation of GADD45B resulted in an up-regulation of G-6-P and PA (Fig. 5C and D). Furthermore, the down-regulation of GADD45B has been observed to result in a negative correlation with the expression of HK2 and PKM2, which are rate-limiting enzymes involved in the catalysis of G-6-P and PA formation (Fig. 5E and F). Taken together, these findings demonstrate that the shift from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis in bladder cancer cells is facilitated by the down-regulation of GADD45B.
Fig. 5.
Down-regulation of GADD45B shifts bladder cancer cells from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis. (A) (B) The Seahorse XF mitochondrial stress test was used to measure basal and ATP-linked oxygen consumption following modulation of GADD45B expression. Up-regulation of GADD45B in J82 cells resulted in increased basal and ATP-linked oxygen consumption, whereas down-regulation of GADD45Bin T24 cells had the opposite effects. (C) (D)Up-regulation of GADD45B in J82 cells led to a significant decrease in glucose-6-phosphate and pyruvate level, while down-regulation of GADD45B in T24 cells also had the opposite effect. (E)(F) Western blot analysis revealed the presence of HK2 and PKM2 proteins. Notably, a negative correlation was observed between the expression levels of these proteins and GADD45B. All of the data show an average of three independent experiments ± SEM.
4. Discussion
Recent research has provided compelling evidence linking the accumulation of mitochondrial dysfunction, specifically mitochondrial metabolic reprogramming, to the onset and progression of cancer [16]. However, there is a dearth of studies examining the potential association between mitochondrial energy metabolism and bladder cancer. In this present study, we examined 90 genes implicated in mitochondrial OXPHOS using three sets of bladder cancer tissue samples and corresponding normal adjacent tissue. The findings of this study indicate a significant down-regulation of the majority of genes in all three bladder cancer tissues when compared to adjacent tissues, suggesting a notable suppression of mitochondrial energy metabolism in bladder cancer. Furthermore, the analysis revealed a simultaneous down-regulation of COX6A2, GADD45B, EDN1 and UQCRH mRNA expressions in all three cancer tissues, while no genes were identified as being simultaneously up-regulated. Subsequently, an examination of the TCGA and GTEx datasets was conducted utilizing the GEPIA tool, revealing that GADD45B exhibited notably diminished mRNA levels in bladder tumors in comparion to normal tissues, distinguishing it as the sole down-regulated gene among the four investigated. Consequently, it is postulated that GADD45B potentially assumes a crucial function in both mitochondrial energy metabolism and the pathogenesis of bladder cancer.
GADD45B (growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible beta) belongs to a cluster of genes that exhibit elevated transcript levels in response to growth arrest induced by stress and exposure to agents that cause DNA damage [17]. Apart from its conventional roles, GADD45B has been implicated in mitochondrial metabolism [10] and has the ability to impede Fas-induced mitochondrial depolarization [18]. Several studies have examined the role of GADD45B in cancer, with some suggesting that it is up-regulated and involved in carcinogenesis through the DNA damage response [19,20]. However, other studies argue that GADD45B is down-regulated in human cancers that led to tumorigenesis and malignant progression [21]. Additionally, one study found that a high level of GADD45B significantly enhances chemosensitivity in prostate cancer and promotes cell apoptosis via the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway [22]. In non-small cell lung cancer cells, TFAP2C increases cell proliferation by down-regulating GADD45B and PMAIP1 [23]. These studies indicate that GADD45B exhibits a unique function in various tumor types. Nevertheless, the involvement of GADD45B in bladder cancer remains unexplored in existing literature.
To further explore the function of GADD45B in bladder cancer, tumorigenicity, invasion and migration capabilities were identified. The findings demonstrated that the over-expression of GADD45B effectively impeded the growth of bladder cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, heightened levels of GADD45B were found to inhibit colony formation, cell invasion, and migration capacities. Conversely, the down-regulation of GADD45B yielded contrasting results. Consequently, these results provide novel evidence that GADD45B functions as a tumor suppressor effectively impeding progression of bladder cancer.
In light of the known correlation between GADD45B and mitochondrial energy metabolism, we conducted a comprehensive investigation into the role of GADD45B down-regulation in the advancement of bladder tumors. Mitochondrial OXPHOS is commonly used to characterize mitochondrial energy metabolism [24]. Consequently, we employed the Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analyzer to measure mitochondrial OXPHOS subsequent to the manipulation of GADD45B expression. Our findings unequivocally demonstrated that the inhibition of GADD45B expression significantly diminished both basal respiration and ATP-linked respiration, indicating a notable suppression of mitochondrial energy metabolism. The "Warburg effect" refers to the preference of cancer cells for aerobic glycolysis over OXPHOS, which a prominent metabolic characteristic of transformed cancer cells. Despite the lower ATP production associated with oxidative glycolysis compared to OXPHOS, the accumulation of metabolites during glycolysis promotes cancer cell proliferation [8]. Furthermore, the metabolic shift from OXPHOS to aerobic glycolysis can create a hypoxic environment, thereby facilitating the activation and metastasis of tumor cells [25]. Hence, the concentrations of G-6-P and PA, which are the products of the initial and final irreversible steps of glycolysis, were measured. Our findings demonstrate that the suppression of GADD45B expression significantly augmented the levels of G-6-P and PA, indicating an upregulation of glycolysis. Additionally, the expression of HK2 and PKM2, enzymes that control the rate of G-6-P and PA formation, exhibited a negative correlation with GADD45B. Taken together, our results provide evidence that the down-regulation of GADD45B can induce a metabolic shift in bladder cancer cells from mitochondrial energy metabolism to glycolytic metabolism.
5. Conclusion
Our study presents novel findings indicating that GADD45B may function as a potential tumor suppressor gene in bladder cancer. This conclusion is supported by the observed inhibitory effects of GADD45B up-regulation on cell proliferation, invasion and migration in vitro, as well as its impact on tumor growth in vivo. Additionally, our study reveals that knockdown of GADD45B can induce a metabolic shift in bladder cancer cells from mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis, which may play a significant role in driving bladder cancer progression. Therefore, we suggest that GADD45B be regarded as a putative tumor suppressor in bladder cancer, potentially useful as a prognostic target during bladder cancer therapy.
Funding
This work was supported by Ningbo Clinical Research Center for Ophthalmology (2022L003).
Data availability statement
Data included in article/supplementary material/referenced in article.
Ethical approval
This study was reviewed and approved by the Ethical Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University, with the approval number: NO.2022-065A.
All participants/patients (or their proxies/legal guardians) provided informed consent to participate in the study.
For animal experiments, the study protocol was approved by the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Ningbo University, with the approval number: NO.11830.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Kai-yun Wang: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. Ke-jie Wang: Writing – review & editing. Li-liang Shen: Funding acquisition, Data curation. Xu-hui Wang: Data curation.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Footnotes
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27427.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following is/are the supplementary data to this article:
References
- 1.Patel V.G., Oh W.K., Galsky M.D. Treatment of muscle-invasive and advanced bladder cancer in 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:404–423. doi: 10.3322/caac.21631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Magers M.J., Lopez-Beltran A., Montironi R., Williamson S.R., Kaimakliotis H.Z., Cheng L. Staging of bladder cancer. Histopathology. 2019;74:112–134. doi: 10.1111/his.13734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wu X.-R. Urothelial tumorigenesis: a tale of divergent pathways. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5:713–725. doi: 10.1038/nrc1697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hautmann R.E., de Petriconi R.C., Pfeiffer C., Volkmer B.G. Radical cystectomy for urothelial carcinoma of the bladder without neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy: long-term results in 1100 patients. Eur. Urol. 2012;61:1039–1047. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.02.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Loriot Y., Necchi A., Park S.H., Garcia-Donas J., Huddart R., Burgess E., Fleming M., Rezazadeh A., Mellado B., Varlamov S., Joshi M., Duran I., Tagawa S.T., Zakharia Y., Zhong B., Stuyckens K., Santiago-Walker A., De Porre P., O'Hagan A., Avadhani A., Siefker-Radtke A.O. BLC2001 study group, Erdafitinib in locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;381:338–348. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1817323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Vyas S., Zaganjor E., Haigis M.C. Mitochondria and cancer. Cell. 2016;166:555–566. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.07.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tan Y.Q., Zhang X., Zhang S., Zhu T., Garg M., Lobie P.E., Pandey V. Mitochondria: the metabolic switch of cellular oncogenic transformation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Canc. 2021;1876 doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Locasale J.W., Grassian A.R., Melman T., Lyssiotis C.A., Mattaini K.R., Bass A.J., Heffron G., Metallo C.M., Muranen T., Sharfi H., Sasaki A.T., Anastasiou D., Mullarky E., Vokes N.I., Sasaki M., Beroukhim R., Stephanopoulos G., Ligon A.H., Meyerson M., Richardson A.L., Chin L., Wagner G., Asara J.M., Brugge J.S., Cantley L.C., Vander Heiden M.G. Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase diverts glycolytic flux and contributes to oncogenesis. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:869–874. doi: 10.1038/ng.890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wu Z., Zuo M., Zeng L., Cui K., Liu B., Yan C., Chen L., Dong J., Shangguan F., Hu W., He H., Lu B., Song Z. OMA1 reprograms metabolism under hypoxia to promote colorectal cancer development. EMBO Rep. 2021;22 doi: 10.15252/embr.202050827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Guha M., Srinivasan S., Raman P., Jiang Y., Kaufman B.A., Taylor D., Dong D., Chakrabarti R., Picard M., Carstens R.P., Kijima Y., Feldman M., Avadhani N.G. Aggressive triple negative breast cancers have unique molecular signature on the basis of mitochondrial genetic and functional defects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Basis Dis. 2018;1864:1060–1071. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Song K., Li M., Xu X., Xuan L.I., Huang G., Liu Q. Resistance to chemotherapy is associated with altered glucose metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol. Lett. 2016;12:334–342. doi: 10.3892/ol.2016.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang K.-J., Meng X.-Y., Chen J.-F., Wang K.-Y., Zhou C., Yu R., Ma Q. Emodin induced Necroptosis and inhibited glycolysis in the renal cancer cells by enhancing ROS. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021;2021 doi: 10.1155/2021/8840590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhu J.-J., Liu Y.-F., Zhang Y.-P., Zhao C.-R., Yao W.-J., Li Y.-S., Wang K.-C., Huang T.-S., Pang W., Wang X.-F., Wang X., Chien S., Zhou J. VAMP3 and SNAP23 mediate the disturbed flow-induced endothelial microRNA secretion and smooth muscle hyperplasia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2017;114:8271–8276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1700561114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yue S., Yu J., Kong Y., Chen H., Mao M., Ji C., Shao S., Zhu J., Gu J., Zhao M. Metabolomic modulations of HepG2 cells exposed to bisphenol analogues. Environ. Int. 2019;129:59–67. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yr Z., Jl W., C X., Ym L., S B., Ly Y. Clinical Science; London, England: 2019. HEG1 Indicates Poor Prognosis and Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Invasion, Metastasis, and EMT by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling; p. 133. 1979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Seyfried T.N. Cancer as a mitochondrial metabolic disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015;3:43. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2015.00043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Salvador J.M., Brown-Clay J.D., Fornace A.J. Gadd45 in stress signaling, cell cycle control, and apoptosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013;793:1–19. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-8289-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zazzeroni F., Papa S., Algeciras-Schimnich A., Alvarez K., Melis T., Bubici C., Majewski N., Hay N., De Smaele E., Peter M.E., Franzoso G. Gadd45 beta mediates the protective effects of CD40 costimulation against Fas-induced apoptosis. Blood. 2003;102:3270–3279. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-03-0689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jin X., Liu X., Zhang Z., Guan Y., Xv R., Li J. Identification of key pathways and genes in lung carcinogenesis. Oncol. Lett. 2018;16:4185–4192. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang L., Xiao X., Li D., Chi Y., Wei P., Wang Y., Ni S., Tan C., Zhou X., Du X. Abnormal expression of GADD45B in human colorectal carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2012;10:215. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sha X., Hoffman B., Liebermann D.A. Loss of Gadd45b accelerates BCR-ABL-driven CML. Oncotarget. 2018;9:33360–33367. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.W Q., W W., G Z., L K., P S., F H., X Z., G Z., H H. GADD45B is a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target gene in chemotherapy-resistant prostate cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021;9 doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.716501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Do H., Kim D., Kang J., Son B., Seo D., Youn H., Youn B., Kim W. TFAP2C increases cell proliferation by downregulating GADD45B and PMAIP1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Biol. Res. 2019;52:35. doi: 10.1186/s40659-019-0244-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bergman O., Ben-Shachar D. Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system (OXPHOS) deficits in Schizophrenia: possible interactions with cellular processes. Can. J. Psychiatr. 2016;61:457–469. doi: 10.1177/0706743716648290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nagao A., Kobayashi M., Koyasu S., Chow C.C.T., Harada H. HIF-1-Dependent reprogramming of glucose metabolic pathway of cancer cells and its therapeutic significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:238. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Data included in article/supplementary material/referenced in article.