Abstract
This Patent Highlight explores ground-breaking advancements in neurostimulation, psychedelic therapy, and brain function optimization from recent innovations. It examines methods for altering brain states through AI-driven non-invasive neurostimulation, potentially contributing to personalized brain therapy. The publication also delves into the therapeutic potential of N-isopropyl tryptamines and tryptamine derivatives. Furthermore, it discusses the therapeutic applications of psilocybin and psilocin crystalline forms in mental health and central nervous system disorders. By comparing and contrasting these diverse approaches, this work highlights their mechanistic insights, therapeutic implications, and contributions to the evolving fields of neuroscience and mental health.
Important Compound Classes
Titles
Systems and Methods to Measure, Predict and Optimize Brain Function; N-Isopropyl Tryptamines and Method of Making Monoalkylated and Dialkylated Tryptamine Analogs; Tryptamine Derivatives; and Compositions and Uses of Psilocybin and Psilocin
Patent Publication Numbers
WO 2023/239647 A2 (URL: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2023239647A2/en?oq=WO+2023%2f239647+A2);
WO 2023/225679 A2 (URL: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2023225679A2/en?oq=WO+2023%2f225679+A2);
WO 2023/225678 A2 (URL: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2023225678A2/en?oq=WO+2023%2f225678+A2); and
WO 2024/003610 A1 (URL: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2024003610A1/en?oq=WO+2024%2f003610+A1).
Publication Dates
December 14, 2023; November 23, 2023; November 23, 2023; and January 4, 2024
Priority Applications
US 63/354,469; US 63/385,289; US 63/344,140; and US 18/204.870
Priority Dates
June 22, 2022; November 29, 2022; May 20, 2022; June 1, 2023
Inventors
Santarnecchi, E. (WO 2023/239647 A2); Chadeayne, A. R. (WO 2023/225679 A2 and WO 2023/225678 A2); and Silverstone, P.; Laprairie, R.; Kurrasch, D. (WO 2024/003610 A1)
Assignee Companies
Horizon Neurosciences LLC [US/US], 82 Wendell Ave, Suite 100, Pittsfield, Massachusetts 01201, USA (WO 2023/239647 A2); Caamtech, Inc. [US/US], 58 East Sunset Way, Suite 208, Issaquah, WA 98027, USA (WO 2023/225679 A2 and WO 2023/225678 A2); and Zylorion Health Inc. [CA/CA], 202 6th Avenue, Suite 660, Calgary, Alberta T2P 2R9, Canada (WO 2024/003610 A1)
Disease Area
Neuropsychiatric disorders
Biological Target
5-HT2A
Summary
The brain’s complexity has always posed a challenge to the effective treatment of neurological and psychiatric conditions. Recent advancements in neurotechnology and pharmacology have led to innovative brain function optimization and mental health treatment approaches. Four patents, each addressing different aspects of brain science and therapy, exemplify these advancements.
Method for Changing Brain States (WO 2023/239647 A2)
This patent introduces a ground-breaking method for altering brain states, harnessing the synergy of non-invasive brain stimulation and artificial intelligence (AI). This approach begins with a detailed analysis of an individual’s initial brain state, encompassing structural composition and functional architecture. This method can use sophisticated AI algorithms to predict how the brain might respond to various stimuli and design a tailored stimulation protocol to transition the brain to a desired target state.
This technique marks an advancement in personalized medicine, allowing for customizing brain stimulation protocols based on individual brain profiles. By analyzing a person’s unique neural patterns, AI can optimize the stimulation parameters—such as frequency, intensity, and duration—to achieve the most effective results. The potential applications of this technology are vast, ranging from enhancing cognitive abilities and treating neurological disorders to improving mental well-being. Additionally, this method can aid in rehabilitation processes, for instance, from stroke or traumatic brain injury, by facilitating targeted brain plasticity and aiding in the re-establishment of neural connections.
Therapeutic Tryptamine Analogs (WO 2023/225679 A2 and WO 2023/225678 A2)
These patents focus on developing N-isopropyl tryptamines and their derivatives, introducing novel methods for their synthesis, and emphasizing their crystalline forms for improved pharmaceutical applications. These compounds, which interact with the serotonin system, have shown promising potential in treating various psychological disorders and promoting neurogenesis, the process of generating new neurons in the brain.
The importance of these patents lies in their ability to provide more stable and effective forms of tryptamine-based treatments. By optimizing the crystalline structure of these compounds, they can offer enhanced bioavailability, stability, and efficacy compared to their non-crystalline counterparts. This advancement is crucial in the development of medications for conditions such as depression, anxiety, PTSD, and other mental health disorders where serotonin plays a key role.
Furthermore, these patents shed light on the significance of the serotonin system in brain health and its potential as a target for therapeutic intervention. The refined synthetic methods outlined in these patents allow for precise control over the degree of alkylation, which is critical in defining the pharmacological profile of these compounds. These breakthroughs open new avenues for creating a range of tryptamine-based medications tailored to specific needs and conditions, potentially leading to more personalized and effective treatments.
Psilocybin and Psilocin for Mental Health (WO 2024/003610 A1)
This patent details the innovative use of crystalline forms of psilocybin and psilocin for treating mental health disorders. Unlike their traditional forms, these crystalline structures provide enhanced stability and a distinct pharmacological profile, which could lead to more effective treatments for a range of disorders, including depression, PTSD, and cognitive impairments.
The significance of this patent lies in its potential to transform how we approach mental health treatment. The crystalline forms of psilocin offer a stable and consistent dosage, addressing one of the significant challenges in the therapeutic use of these compounds. This stability ensures patients receive a precise dose, leading to more predictable and effective treatment outcomes.
Moreover, the patent explores the unique ways these compounds interact with serotonin receptors in the brain, which play a critical role in mood regulation and cognitive function. By modulating these receptors, psilocin can induce changes in brain connectivity and neuroplasticity, potentially improving mental health. This mechanism of action is vital for conditions that are resistant to traditional treatments, offering new hope to those with chronic mental health issues.
The therapeutic potential of these crystalline forms extends beyond the treatment of traditional mental health disorders. They can be used in neuroenhancement, improving cognitive abilities in individuals without diagnosed conditions. This opens up possibilities for their use in various cognitive and psychological applications, from enhancing creativity and problem-solving skills to alleviating the cognitive decline associated with aging.
A common theme from these patents is the pursuit of precision in treatment. While the neurostimulation patent focuses on external modulation of brain activity, the tryptamine and psilocybin patents emphasize internal biochemical pathways. Each method offers distinct advantages: neurostimulation allows for real-time adjustments and immediate effects, whereas pharmaceutical approaches provide systemic and potentially long-lasting changes in brain chemistry.
The applications of these patents extend beyond traditional healthcare. Neurostimulation methods can enhance cognitive performance and be utilized in gaming and the metaverse for personalized digital experiences. Tryptamine analogs and psilocybin compositions could transform the treatment of a wide range of psychiatric and neurological disorders, offering new hope for conditions that are currently difficult to treat.
Challenges and Future Directions
While these patents represent significant advancements, challenges remain. The safety and efficacy of long-term neurostimulation need thorough investigation. The pharmaceutical approaches, particularly those involving psychedelics, must navigate complex regulatory landscapes and societal perceptions. Future research should focus on large-scale clinical trials, long-term effects, and integrating these therapies into mainstream medical practice.
As such, the patents analyzed herein highlight the cutting-edge of brain science and mental health treatment. They offer novel approaches to understanding and manipulating brain function, each with unique mechanisms and potential applications. As neuroscience evolves, these patents will likely significantly shape future therapies and enhance our understanding of the brain.
Key Structures
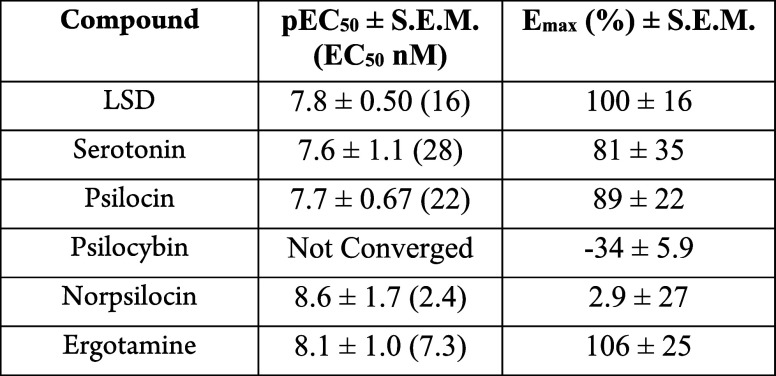
Biological Assay
Ca2+ release assay, β-arresterin2 recruitment assay, head-twitch response (HTR), pharmacokinetics, neurogenesis, and plasticity in healthy human brain organoids.
Biological Data
In this study, CHO-K1 cells were engineered
to express 5-HT2A-smBiT and β-arrestin2-lgBiT fusion proteins,
which interact to form a functional NanoBit luciferase enzyme. This
enzyme catalyzes the breakdown of coelenterazine, emitting light proportional
to the interaction between h5-HT2A and β-arrestin2, a measure
of their binding activity. The cells were treated with various concentrations
of compounds to measure chemiluminescence, with the intensity data
subjected to non-linear regression analysis to determine the potency
(EC50) and efficacy (Emax)
of the compounds, with results detailed in the table below. Furthermore,
the study investigated the impact of various concentrations of psilocybin,
psilocin, or a combination of both on the neurogenesis and plasticity
in human brain organoids.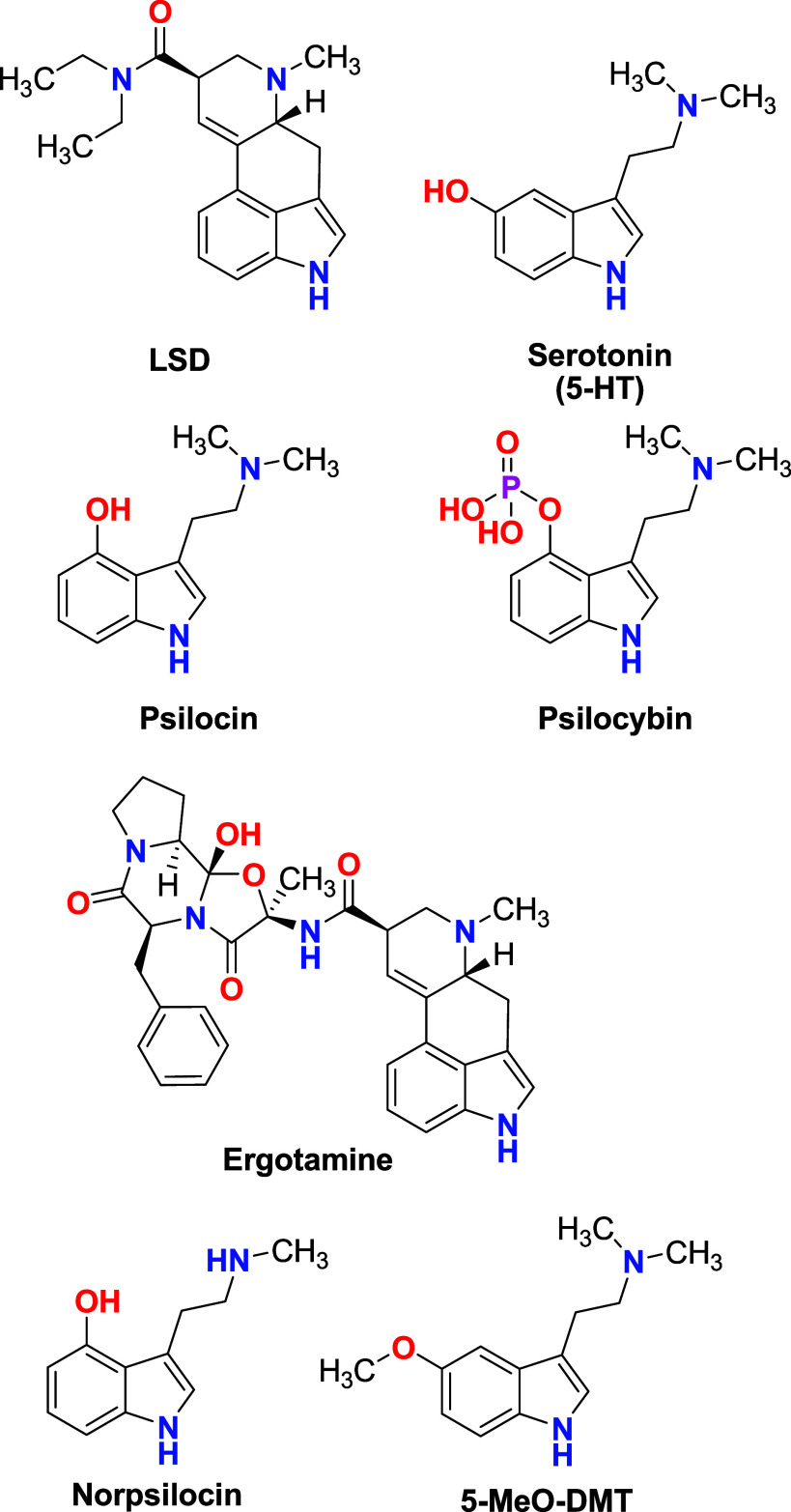
Recent Review Articles
The author declares no competing financial interest.
Special Issue
Published as part of ACS Medicinal Chemistry Lettersvirtual special issue “Exploring the Use of AI/ML Technologies in Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery”.
References
- Bouchet L.; Sager Z.; Yrondi A.; Nigam K. B.; Anderson B. T.; Ross S.; Petridis P. D.; Beaussant Y. Older Adults in Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy Trials: A Systematic Review. J. Psychopharmacol. 2024, 10.1177/02698811231215420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borissova A.; Rucker J. J. The Development of Psilocybin Therapy for Treatment-Resistant Depression: An Update. BJ Psych. Bull. 2024, 48, 38–44. 10.1192/bjb.2023.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barksdale B. R.; Doss M. K.; Fonzo G. A.; Nemeroff C. B. The Mechanistic Divide in Psychedelic Neuroscience: An Unbridgeable Gap?. Neurotherapeutics 2024, 10.1016/j.neurot.2024.e00322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veneziani I.; Marra A.; Formica C.; Grimaldi A.; Marino S.; Quartarone A.; Maresca G. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in the Neuropsychological Assessment of Dementia: A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 113. 10.3390/jpm14010113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings R.; Joseph A.; Callender T.; Janes S. M.; van der Schaar M.; Sheringham J.; Navani N. Factors Influencing Clinician and Patient Interaction with Machine Learning-Based Risk Prediction Models: A Systematic Review. Lancet Digit. Health 2024, 6, e131–e144. 10.1016/S2589-7500(23)00241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova C.; Cestonaro C.; Fava L.; Cinquetti A. AI and Professional Liability Assessment in Healthcare. A Revolution in Legal Medicine?. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2024, 10, 1337335. 10.3389/fmed.2023.1337335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




