Corresponding Author

Key Words: anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity, cardio-oncology, CRISPR, human induced pluripotent stem cells, single nucleotide polymorphisms
Anthracyclines can result in cardiotoxic effects, which can occur acutely and chronically. Patients with breast cancer, lymphoma, sarcoma, and leukemia are still treated with anthracyclines, resulting in a higher likelihood of cardiovascular complications such as left ventricular dysfunction.1 Among these patients, 2% to 5% are at the risk of heart failure within 30 years after treatment.2,3 Additionally, several risk factors contribute toward cardiac dysfunction such as radiation therapy, hypertension, genetic predisposition, and cumulative dose higher than 250 mg/m2.4 Furthermore, interindividual variation in drug response and genetic risk factors may also contribute to cardiotoxicity at lower doses over a delayed timeline. Most studies focus on the identification of biomarkers shortly before or after the treatment and correlate these with changes in cardiac parameters in high-risk patients.5 However, despite improved clinical evaluation, risk stratification, and lifelong surveillance for high-risk patients to prevent anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity (AIC), there is a pertinent need to understand the genetic risk factors and toxicity risks using a pharmacogenomics approach. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have enabled the identification of several gene loci and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for AIC. As systematically reviewed by Magdy et al,6 approximately 80 genetic variants have been identified and are associated with AIC. Of these, major interest has shifted toward genes responsible for drug uptake and metabolism and that further alter the redox state of the cell and trigger oxidative stress, inhibit key enzymes that aid in DNA repair, or interfere with cardiac excitation-contraction machinery.
The identification of SNPs involved in AIC not only provides adverse associations related to heart failure or fibrosis as seen with rs18831127 but also protective associations such as rs1045642 identified to have an effect in preventing ejection fraction decline.8 One of the consistent SNPs, rs2229774 linked to specific genotypes, has been shown to be associated with AIC across low- to high-dosage regimens.9 However, a subsequent study classified the same SNP as being associated with a decreased risk for cardiotoxicity.10 Such contradictory associations not only raise questions about the reliability of the results but also underscore the complexity and nuances of genetic influences on AIC. In several cases, the validation of SNPs in subsequent study cohorts is hindered because of smaller patient sample sizes, differences in underlying comorbidities, and inadequate stratification with regard to the use of multiple treatment modalities. Hence, robust validation studies using human in vitro or animal models are needed to establish and validate the link between gene variants and their implication in cardiotoxicity.
By leveraging the advancements in induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology and implementing robust derivation of cardiomyocytes (induced pluripotent stem cell–derived cardiomyocytes [iPSC-CMs]), Burridge et al11 have demonstrated that the sensitivity to anthracyclines is imprinted in the cellular memory of cancer patients, thereby altering phenotype and gene expression in iPSC-CMs. Moreover, the Burridge lab has conducted a series of studies using iPSC-CMs as a model to unravel the mechanistic basis for AIC through the direct validation of genetic variants identified in GWAS. In 1 study, the authors validated the functional role of SLC28A3, a solute carrier transmembrane transporter, in increasing sensitivity to cell death upon doxorubicin treatment.12 Another study validated doxorubicin sensitivity in patients with a retinoic acid receptor gamma and the potential use of a retinoic acid receptor gamma agonist in attenuating AIC.13
In this issue of JACC: CardioOncology, Fonoudi et al14 selected 38 genes from GWAS studies that are consistently expressed in human-induced pluripotent stem cell–derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CMs), in the fetal and adult human heart, to study their role in inducing AIC through a series of loss-of-function experiments using CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockouts. The authors were able to successfully generate 35 knockout human-induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) lines, which were differentiated to hiPSC-CMs and exposed to 5-log doses of doxorubicin. The authors then assessed the sensitivity of hiPSC-CMs to doxorubicin by measuring cell survival, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), DNA damage, and their capacity for iron uptake. The authors were able to validate the impact of the functional knockout (KO) to its cellular function through the endpoint measures in a systematic manner. Dysregulation of enzymes involved in metabolism and scavenging ROS is one of the major hallmarks of AIC. Indeed, the authors noted a reduction in hydrogen peroxide production in CBR1-KO and CBR3-KO, which indicated hampered conversion for doxorubicin to toxic alcohol metabolite. On the other hand, HAS3-KO, SPG7-KO, GSTM1-KO, and RAC2-KO increased ROS production, highlighting their beneficial role in reducing cellular oxidative stress. Importantly, the authors were able to precisely distinguish the targets that prevented AIC in the absence of genes that prevented DNA damage (PRDM2 and MHL1) and increased drug influx by transmembrane solute transporters (SLC28A3, SCL22A17, and SLC28A1). In contrast, gene targets important for iron uptake (HFE), drug efflux (ABCC10, ABCC2, ABCB4, ABCC5, and ABCC9), calcium handling (CELF4 and MYH7), and contractility (ZFN, RIN3, and CYP2J2) when knocked out increased cellular toxicity and functional impairment, highlighting their role in cardioprotection.
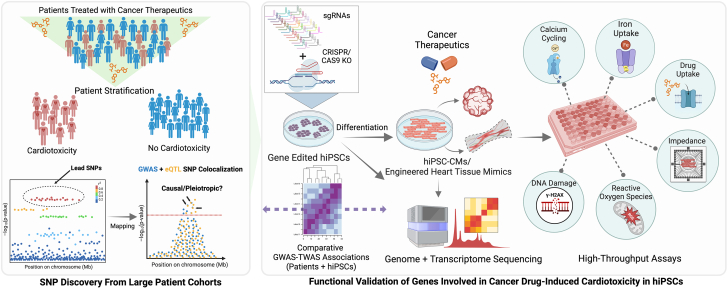
Overall, this study underscores the importance of incorporating GWAS hits identified at a population scale coupled with hiPSC modeling (Figure 1). This approach is significant and powerful in decoding interindividual variability and laying the foundation for personalized and targeted cardioprotective therapies. Reproducibility and diversity of patient-derived iPSC model systems not only allow for an understanding of such key roles of genetic variants but also an understanding of the genetic regulation of transcription. Investigations into identifying causal variants often involve a multifaceted strategy, incorporating both transcriptome-wide and genome-wide association studies, fine mapping of causal variants with weighted scores, prediction of allelic-specific expression, and comparative genomics with other cell types relevant to the disease. The iPSC platform also offers an unprecedented opportunity to integrate transcriptomic responses and GWAS gene variants with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL). eQTL variants modulate transcriptomic response indirectly or directly in response to the treatment, whereas GWAS-discovered variants alone may or may not demonstrate expressional dependence to the transcriptome. Integration with large-scale transcriptome-wide association studies helps in prioritizing putative causal targets in which several disease-causing cis-regulatory elements could be identified. Knowles et al15 were able to use hiPSCs from 45 patients to reveal hundreds of genetic variants that modulate transcriptomic response and reduced post-transcriptional splicing fidelity. Despite the insufficient power of the GWAS data used in this study, Fonoudi et al14 mapped SNPs that have a response eQTL (with P < 10−5) with a variable effect size to the GWAS variants. Interestingly, the authors also noted that an increased transcriptomic response to higher doses of doxorubicin is associated with reduced cardiac troponin levels, suggesting that the bulk of expression changes that precede AIC are protective against cardiac damage.
Figure 1.
Causal Variant Discovery in Cardio-Oncology
An overview of the identification of targets in large and diverse patient cohorts to systematic validation of causal targets in drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Biorender was used to generate this figure. eQTL = expression quantitative trait loci; GWAS = genome-wide association study; hiPSC = human-induced pluripotent stem cell; hiPSC-CM = human-induced pluripotent stem cell–derived cardiomyocyte; SNP = single-nucleotide polymorphism; TWAS = transcriptome-wide association study.
Despite these pioneering efforts, there are several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed in future studies. In this study by Fonoudi et al,14 the authors acknowledge loss-of-function targets do not fully recapitulate the contribution of SNPs associated with AIC. Furthermore, relying on the median lethal dose as an acute measure to assess function at a single time point (72 hours) may not be sufficient in revealing the functional deficit or augmentation of the genes over a prolonged period, indicative of the chronic pathophysiology of AIC. The correlation between loss of function and dysfunction may be confounded in cases in which variants are known to exhibit pleiotropic effects, compounded effects, or noncausal occurrences caused by linkage disequilibrium. For example, CYP2J2, a member of the cytochrome P450 family of enzymes involved in doxorubicin metabolism, also modulates diverse transcriptional networks in cardiomyocytes.16 Such limitations could be addressed using pooled genome-wide CRISPR screens with enhancer-specific guide RNAs to filter secondary target genes regulated by the same enhancer. This approach could be combined with crisprQTL to study gene-regulatory functions of multiple GWAS variants across diverse patient groups in a high-throughput manner.17 However, when using such approaches, one should also consider the contribution of other cell types. In the case of the heart, it is essential to include cells such as endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and smooth muscle cells in a physiologically relevant model such as engineered heart tissues or cardiac organoids. This comprehensive approach will help unravel the identification of cell-specific variants that play a role in coordinated functions, arising because of cellular cross talk.18 The work of Fonoudi et al14 provides a strong foundation and a blueprint for investigators in the field of cardio-oncology to functionally validate genotype with phenotype using the hiPSC-CRISPR tool kit, elucidating the biologic mechanisms of drug action. Pharmacogenomic studies such as this help decipher complex drug interactions in a reductionist fashion, transforming the landscape of precision medicine by unveiling cardioprotective therapeutic targets to alleviate the risk of cardiotoxicity to patients.
Funding Support and Author Disclosures
Dr Thomas is supported by National Institutes of Health grant K99 HL163443-01A1. Dr Sayed is supported by National Institutes of Health grants R01 HL158641 and R01 HL161002 and American Heart Association SFRN grant 869015. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Footnotes
The authors attest they are in compliance with human studies committees and animal welfare regulations of the authors’ institutions and Food and Drug Administration guidelines, including patient consent where appropriate. For more information, visit the Author Center.
References
- 1.DeRemer D.L., Nguyen N.K., Guha A., et al. Racial and ethnic differences in cardiac surveillance evaluation of patients treated with anthracycline-based chemotherapy. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023;12(10) doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.027981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.van der Pal H.J., van Dalen E.C., van Delden E., et al. High risk of symptomatic cardiac events in childhood cancer survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(13):1429–1437. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.4730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jeyaprakash P., Sangha S., Ellenberger K., et al. Cardiotoxic effect of modern anthracycline dosing on left ventricular ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo arms from randomized controlled trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10(6) doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.018802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Neuendorff N.R., Loh K.P., Mims A.S., et al. Anthracycline-related cardiotoxicity in older patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a Young SIOG review paper. Blood Adv. 2020;4(4):762–775. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cartas-Espinel I., Telechea-Fernández M., Manterola Delgado C., et al. Novel molecular biomarkers of cancer therapy-induced cardiotoxicity in adult population: a scoping review. ESC Heart Fail. 2022;9(3):1651–1665. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Magdy T., Burridge P.W. Use of hiPSC to explicate genomic predisposition to anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity. Pharmacogenomics. 2021;22(1):41–54. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2020-0104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Serie D.J., Crook J.E., Necela B.M., et al. Genome-wide association study of cardiotoxicity in the NCCTG N9831 (Alliance) adjuvant trastuzumab trial. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2017;27(10):378–385. doi: 10.1097/FPC.0000000000000302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hertz D.L., Caram M.V., Kidwell K.M., et al. Evidence for association of SNPs in ABCB1 and CBR3, but not RAC2, NCF4, SLC28A3 or TOP2B, with chronic cardiotoxicity in a cohort of breast cancer patients treated with anthracyclines. Pharmacogenomics. 2016;17(3):231–240. doi: 10.2217/pgs.15.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Aminkeng F., Bhavsar A.P., Visscher H., et al. A coding variant in RARG confers susceptibility to anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity in childhood cancer. Nat Genet. 2015;47(9):1079–1084. doi: 10.1038/ng.3374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schneider B.P., Shen F., Gardner L., et al. Genome-wide association study for anthracycline-induced congestive heart failure. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(1):43–51. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-0908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Burridge P.W., Li Y.F., Matsa E., et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes recapitulate the predilection of breast cancer patients to doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat Med. 2016;22(5):547–556. doi: 10.1038/nm.4087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Magdy T., Jouni M., Kuo H.-H., et al. Identification of drug transporter genomic variants and inhibitors that protect against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Circulation. 2022;145(4):279–294. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Magdy T., Jiang Z., Jouni M., et al. RARG variant predictive of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity identifies a cardioprotective therapy. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28(12):2076–2089.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fonoudi H., Jouni M., Cejas R.B., et al. Functional validation of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity-related genes. J Am Coll Cardiol CardioOnc. 2024;6(1):38–50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.11.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Knowles D.A., Burrows C.K., Blischak J.D., et al. Determining the genetic basis of anthracycline-cardiotoxicity by molecular response QTL mapping in induced cardiomyocytes. Elife. 2018;7:1079. doi: 10.7554/eLife.33480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Evangelista E.A., Aliwarga T., Sotoodehnia N., et al. CYP2J2 modulates diverse transcriptional programs in adult human cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):5329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62174-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Morris J.A., Caragine C., Daniloski Z., et al. Discovery of target genes and pathways at GWAS loci by pooled single-cell CRISPR screens. Science. 2023;380(6646) doi: 10.1126/science.adh7699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Thomas D., Shenoy S., Sayed N. Building multi-dimensional induced pluripotent stem cells-based model platforms to assess cardiotoxicity in cancer therapies. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:39. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.607364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]