Abstract
Background.
Polygenic risk scores (PRSs) capture genetic vulnerability to psychiatric conditions. However, PRSs are often associated with multiple mental health problems in children, complicating their use in research and clinical practice. The current study is the first to systematically test which PRSs associate broadly with all forms of childhood psychopathology, and which PRSs are more specific to one or a handful of forms of psychopathology.
Methods.
The sample consisted of 4717 unrelated children (mean age = 9.92, s.d. = 0.62; 47.1% female; all European ancestry). Psychopathology was conceptualized hierarchically as empirically derived general factor (p-factor) and five specific factors: externalizing, internalizing, neurodevelopmental, somatoform, and detachment. Partial correlations explored associations between psychopathology factors and 22 psychopathology-related PRSs. Regressions tested which level of the psychopathology hierarchy was most strongly associated with each PRS.
Results.
Thirteen PRSs were significantly associated with the general factor, most prominently Chronic Multisite Pain-PRS (r = 0.098), ADHD-PRS (r = 0.079), and Depression-PRS (r = 0.078). After adjusting for the general factor, Depression-PRS, Neuroticism-PRS, PTSD-PRS, Insomnia-PRS, Chronic Back Pain-PRS, and Autism-PRS were not associated with lower order factors. Conversely, several externalizing PRSs, including Adventurousness-PRS and Disinhibition-PRS, remained associated with the externalizing factor (|r| = 0.040–0.058). The ADHD-PRS remained uniquely associated with the neurodevelopmental factor (r = 062).
Conclusions.
PRSs developed to predict vulnerability to emotional difficulties and chronic pain generally captured genetic risk for all forms of childhood psychopathology. PRSs developed to predict vulnerability to externalizing difficulties, e.g. disinhibition, tended to be more specific in predicting behavioral problems. The results may inform translation of existing PRSs to pediatric research and future clinical practice.
Keywords: Child Behavior Checklist, childhood, psychopathology, general factor, genetic, polygenic
Recent advances in molecular genetics promise to elucidate mental health etiology in young people (Dick et al., 2018; Thapar & Riglin, 2020). Specifically, hundreds of individual risk alleles discovered in genome-wide association studies (GWASs) can be aggregated into polygenic risk scores (PRSs), which capture an individual’ genetic vulnerability for a given disorder or trait. To date, PRSs have demonstrated an appreciable prediction of onset, severity, and developmental course of psychiatric conditions (Bogdan, Baranger, & Agrawal, 2018; Dick et al., 2018; Thapar & Riglin, 2020). Moreover, PRSs often show transdiagnostic associations with multiple mental health problems (Docherty et al., 2018; Krapohl et al., 2016), suggesting that they might better capture vulnerability to broad, higher-order dimensions of psychopathology. However, the specificity of associations between a wide range of major psychopathology-related PRSs, and higher-order dimensions of childhood psychopathology, remain unexplored, complicating PRS applications in research and clinical practice.
Transdiagnostic and age-specific associations between PRSs and psychopathology
A large genetic overlap among psychiatric disorders is well documented in adults and children, and the overarching pattern of findings from GWASs indicates widespread pleiotropy, meaning that many variants influence more than one psychiatric disorder (Martin, Taylor, & Lichtenstein, 2017; Wray et al., 2014). Consequently, PRSs developed for one disorder or a trait have been found to significantly predict many other conditions (Docherty et al., 2018; Krapohl et al., 2016). For example, a PRS for a personality trait neuroticism predicts depression, phobias, and multiple physical health outcomes in emerging adulthood (Docherty et al., 2018). Finally, due to changing manifestations of genetic risk across development, the associations between PRSs and youth psychopathology can show a different pattern than in adult samples (Belsky & Harden, 2019; Dick et al., 2018; Thapar & Riglin, 2020). For example, a recent study found that childhood-onset depression was associated with Depression-PRS, Schizophrenia-PRS, and ADHD-PRS, while adolescent-onset depression was only associated with Depression-PRS (Rice et al., 2018). Given the emerging evidence for age-specific associations between PRSs and psychopathology, studies focused on specific developmental periods are needed.
Hierarchical models of psychopathology can explicate PRSs
A major contributor to the precision of PRS summary statistics is the quality of psychiatric assessment in both the discovery GWAS and replication samples (Cai et al., 2020). Thus, the patterns of associations between PRSs and psychopathology outcomes can be affected by the known shortcomings of psychiatric measures, such as diagnostic unreliability, comorbidity among disorders, and heterogeneity within them (Waszczuk et al., 2020). Limitations in psychiatric assessment can impact not only traditional case–control designs (Kotov et al., 2017), but also quantitative phenotypes based on diagnostic phenotypes (Newson, Hunter, & Thiagarajan, 2020).
The empirically derived models of psychopathology, such as the Hierarchical Taxonomy of Psychopathology, offer solutions to these problems by organizing mental health concerns into general and specific spectra (Caspi et al., 2014; Forbes, Tackett, Markon, & Krueger, 2016; Kotov et al., 2017; Lahey et al., 2012; Lahey, Krueger, Rathouz, Waldman, & Zald, 2016). In particular, the overall level of childhood psychopathology is encompassed by a general factor (‘p-factor’), which can be separated into more specific lower order factors, including the internalizing and externalizing dimensions. When applied within genetically informed framework, this hierarchical approach can clarify the specificity of existing PRSs in predicting childhood psychopathology.
Four previous studies have tested associations between PRSs and higher-order phenotypic psychopathology factors. First, Schizophrenia-PRS and Neuroticism-PRS were associated with the general factor of psychopathology in 16-year-old adolescents, with little evidence for associations with specific factors (Jones et al., 2018). Second, Schizophrenia-PRS and ADHD-PRS were associated with the general factor in 7- and 13-year olds, with the ADHD-PRS and Depression-PRS also showing independent associations with specific factors (Riglin et al., 2019). A third study in 9–12-year-old children found that ADHD-PRS was associated both with the general factor and the hyperactivity/impulsivity symptoms (Brikell et al., 2018). Finally, a recent study derived a polygenic general psychopathology factor based on eight psychiatric PRSs, and found that it predicted the p-factor across development (Allegrini et al., 2020). Overall, these analyses demonstrated that in developmental samples, selected psychiatric PRSs appear to capture largely – but not exclusively – broad genetic influences at the level of the general factor of psychopathology. However, these studies had a limited scope, as tested only a small set of PRSs, thus not considering the genetic risk scores available for many psychiatric conditions and relevant traits.
Current study
Our group has recently delineated and validated a comprehensive higher-order structure of childhood psychopathology in a large sample of 9–10-year-old children from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study (Michelini et al., 2019). A simplified summary of the derived structure is presented in Fig. 1a, with the highest level in the hierarchy consisting of the general factor, and at the lowest level consisting of five moderately correlated factors: externalizing, internalizing, neurodevelopmental, somatoform, and detachment. The aim of the current study was to build directly on this phenotypic work in the ABCD sample, to explore the associations between a wide-range of psychiatric PRSs and the higher-order dimensions of childhood psychopathology. Specifically, we tested which level of the psychopathology hierarchy best captures contributions of each PRS.
Fig. 1.
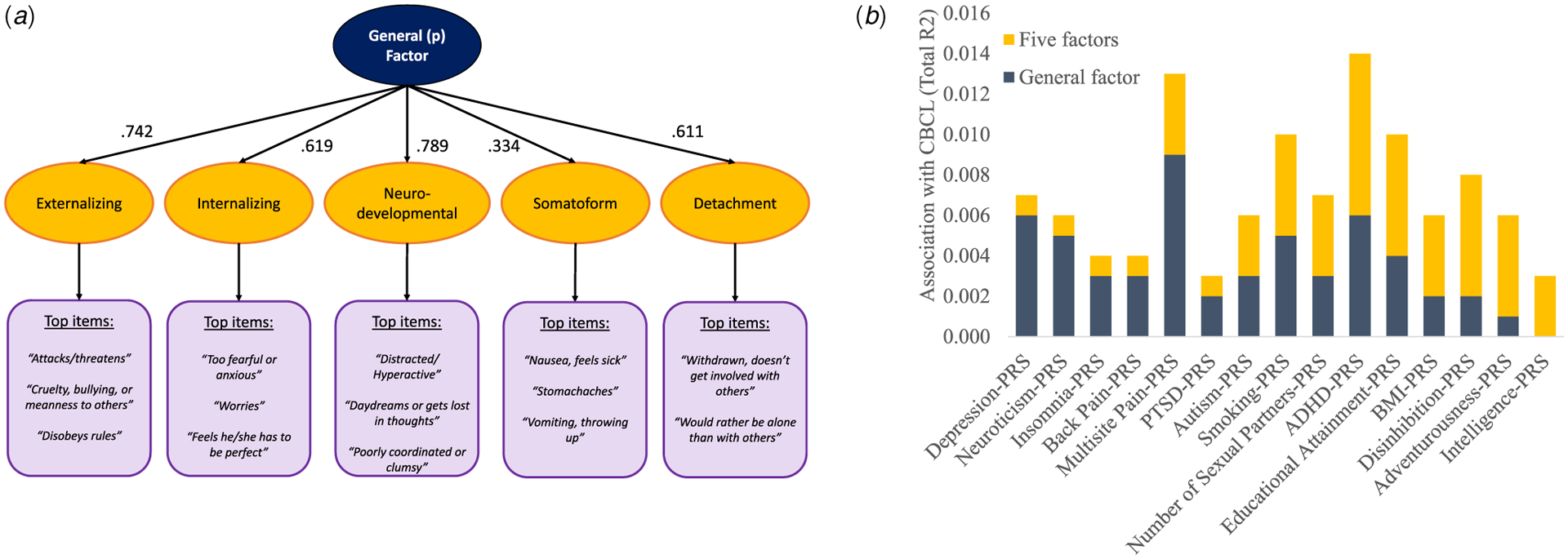
(a) Graphical representation of the 1- and 5-factor structure of the CBCL scales in the ABCD Sample; (b) Proportion of total associations between PRSs and CBCL psychopathology due to the factors.
Notes: (a) is a graphical representation of the CBCL structure from Michelini et al. (2019). The intermediate 2-, 3-, and 4-factor solutions reported in the original paper are not the focus of the current study and are omitted from the figure. The factor loadings come from a confirmatory factor analysis in the analytic subsample used in the current study. The model fit was appropriate in the current subsample: root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) = 0.031 (95% CI 0.030–0.031), standardized root mean square residual (SRMR) = 0.09, Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.90, Tucker–Lewis Index (TLI) = 0.90. In (b), only the 15 PRSs that showed significant associations with CBCL psychopathology factors in regression models are depicted. The total R2 reflects associations between PRSs and CBCL 1- and 5- factors, exclusive of 10 PCs.
Methods
Participants
Participants came from the ABCD study (Garavan et al., 2018). The total sample consists of over 11 000 children aged 9–10 years old recruited from 21 locations across the US. Inclusion criteria were the child’ age and attendance of selected schools within the catchment areas, with the exception for twin recruitment, which relied on birth registers. Exclusion criteria were the lack English proficiency; major sensory, medical, neuro-logical or psychiatric conditions; inability to complete an MRI scan; and gestational age <28 weeks or birthweight <1200 g. The total sample was 51.0% White, 21.4% Hispanic, 15.2% African American, 2.3% Asian, and 10.0% multiracial or from other backgrounds. The household annual income was 30.5% under $50 000, 28.1% between $ 50 000 and $ 100 000; and 41.3% over $ 100 000. The sample consisted of 73.3% families with parents either married or living together, and 58.9% with at least one parent holding a university-level degree. Overall, the sample approached socio-demographic characteristics of the US population, despite not being nationally representative (Compton, Dowling, & Garavan, 2019). All procedures were approved by a central Institutional Review Board at the University of California, San Diego. Parents provided written informed consent, and children provided assent prior to study participation.
The current study uses data from the Baseline ABCD 2.0 data release (NDAR-https://doi.org/10.15154/1503209). The analytic sample consisted of unrelated children, thus in case of genetic or self-reported familial relatedness, only one child was randomly selected into the analyses (N = 1422 excluded). Moreover, only participants of European Ancestry were included in analyses, with ancestry evaluated using genetic data (N = 4458 excluded). This is because PRSs are sensitive to ancestry (Martin et al., 2019), thus analyses were limited to individuals with ancestry matching the discovery GWASs. Overall, after the genotyping quality control (N = 62 excluded), the final analytic sample for which phenotype and genotype data was available totaled N = 4717. The mean age of the analytic sample was 9.92 years old (S.D. = 0.62, range = 9.00–10.92 years old) and 47.1% of participants were female.
The Child Behavior Checklist
The Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) (Achenbach & Rescorla, 2001) was used to assess childhood psychopathology. Parents rated child’ emotional and behavioral problems occurring in the past 6 months on a 119-item, 3-point scale questionnaire during an in-person visit. Items have been aggregated into higher-order dimensions that have been previously empirically delineated and validated in the ABCD sample, using an exploratory principal component analysis with an oblique (geomin) rotation (Michelini et al., 2019), see Fig. 1a. Specifically, the current analyses focused only on the 1 and 5-factor solutions, and examined whether these factors demonstrate a good fit in the analytic subsample using a confirmatory factor analysis.
Genotyping
Genotyping of saliva samples stored at the Rutgers University Cell and DNA Repository was performed using the Smokescreen Array (Baurley, Edlund, Pardamean, Conti, & Bergen, 2016), according to protocols of the manufacturer. Genotypes were imputed on the Michigan Imputation Server pipeline v1.2.4, using the Haplotype Reference Consortium reference panel (McCarthy et al., 2016). Before imputation, the genotypes were filtered for ambiguous strand orientation, missingness rate>5% (by marker exclusion, then by individual), Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium violation ( p < 10−6), sex mismatch (‘sex check’ function for X chromosome homozygosity estimate), and non-European ancestry (principal component analysis against the reference panel from the 1000 Genomes data). After imputation, the SNPs were excluded for imputation R2 < 0.5, average call rate below 90% and minor allele frequency below 0.1%. PLINK was used to handle genetic data and perform quality control (Purcell et al., 2007). The pi_hat > 37.5% was used for the identity by descent exclusion (one sample per pair was removed at random), and samples of less than 80% genetic European ancestry were excluded. Genotype imputation was performed on 487 562 SNPs, resulting in 19 519 349 SNPs after quality control which were used for the final polygenic risk scoring.
Polygenic risk scores
Polygenic risk scores were created for 22 phenotypes relevant to psychopathology, using summary statistics from GWAS discovery samples listed in Table 1. To minimize PRS standard error, only phenotypes from GWASs that included over 100 000 participants were selected. As an exception, we included PRSs for ADHD (total N = 55 374) and autism spectrum disorder (total N = 46 350), due to their unique relevance to developmental populations and neurodevelopmental psychopathology. PRSs were computed, using the PRSice 2.0 software (Euesden, Lewis, & O’Reilly, 2015), with r2 = 0.1 threshold of clumping, by aggregating genetic variants up to varying thresholds of significance, weighted by the associations in the GWAS sample. Our primary analysis used a full list of SNPs and weights a priori, to minimize multiple testing ( p-value threshold = 1). See online Supplementary Table S1 for bivariate associations between PRSs, and online Supplementary Table S2 for sensitivity analyses at other thresholds: 0.01, 0.05, 0.10, and 0.50. The first 10 genetic ancestry principle components (PCs) were obtained as measures of population stratification.
Table 1.
Discovery GWASs for the PRSs tested in the current study
| Phenotype for PRS | Author (year) | N cases | N controls | N total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Externalizing | ||||
| Adventurousness | Linner et al. (2019) | – | – | 557 923 |
| Disinhibition | Linner et al. (2019) | – | – | 315 894 |
| Number of sexual partners | Linner et al. (2019) | – | – | 370 711 |
| Risk tolerance | Linner et al. (2019) | – | – | 939 908 |
| Drinks per week (Linner) | Linner et al. (2019) | – | – | 414 343 |
| Drinks per week (Liu) | Liu et al. (2019) | – | – | 941 280 |
| Smoking - ever smoked regularly | Liu et al. (2019) | – | – | 1 232 091 |
| Internalizing | ||||
| Depression | Howard et al. (2019) | 170 756 | 329 443 | 500 199 |
| Neuroticism | Nagel et al. (2018) | – | – | 390 278 |
| PTSD | Nievergelt et al. (2019) | 29 262 | 165 764 | 195 026 |
| Insomnia | Jansen et al. (2019) | – | – | 1 331 010 |
| Thought disorder | ||||
| Bipolar disorder | Stahl et al. (2019) | 29 764 | 169 118 | 198 882 |
| Schizophrenia | Ripke et al. (2020) | 67 390 | 94 015 | 161 405 |
| Neurodevelopmental | ||||
| ADHD | Demontis et al. (2019) | 20 183 | 35 191 | 55 374 |
| Autism spectrum disorder | Grove et al. (2019) | 18 381 | 27 969 | 46 350 |
| Somatoform | ||||
| Knee pain | Meng et al. (2019) | 22 204 | 149 312 | 171 516 |
| Chronic multisite pain | Johnston et al. (2019) | – | – | 387 649 |
| Chronic back pain | Suri et al. (2018) | 29 531 | 128 494 | 158 025 |
| Other Psychopathology-related | ||||
| Educational attainment | Lee et al. (2018) | – | – | 766 344 |
| Intelligence | Savage et al. (2018) | – | – | 269 867 |
| Alzheimer’s disease | Jansen et al. (2019) | 71 880 | 383 378 | 455 258 |
| Body mass index (BMI) | Locke et al. (2015) | – | – | 234 069 |
Statistical approach
All variables were standardized prior to analyses. A false detection rate (FDR) of 5% was used to adjust for multiple comparisons. First, bivariate associations of PRSs with CBCL factors were tested using partial correlations, controlling for the first 10 PCs of the population structure. Second, bivariate partial correlations of PRSs with dimensions from the 5-factor solution were repeated, this time additionally controlling for the general factor variance, to capture specific associations. Post hoc power analyses were computed using the AVENGEME script (Dudbridge, 2013).
Third, in order to test which level of the phenotypic hierarchy (1 v. 5-factors) is most strongly associated with each PRS, the R2 change test in hierarchical linear regression models was used, adjusted for the number of degrees of freedom. Specifically, in each test, a PRS constituted a dependent variable. In the first block, 10 ancestry PCs were included to estimate baseline R2. In the second block, the general factor from the 1-factor solution was added, to estimate the incremental change in R2, and thus determine whether the general factor is significantly associated with each PRS. In the third block, all factors from the 5-factor solution were added simultaneously, with the change in R2 informing whether this level of the phenotypic hierarchy provides incremental association with PRS, over and above the PCs and the general factor. Finally, for each PRS, the proportion of total R2 due to associations with 1 v. 5-factors was calculated.
Results
Bivariate partial correlations with the general factor
The bivariate partial correlations indicated that 13 out of 22 tested PRSs were significantly associated with the general factor of psychopathology (Table 2). The largest associations were observed for Chronic Multisite Pain-PRS (r = 0.098, s.d. = 0.014, p < 0.001), ADHD-PRS (r = 0.079, s.d. = 0.015, p < 0.001), Depression-PRS (r = 0.078, s.d. = 0.015, p < 0.001), Smoking-PRS (r = −0.077, s.d. = 0.015, p < 0.001), Neuroticism-PRS (r = 0.075, s.d. = 0.014, p < 0.001), and Educational Attainment-PRS (r = −0.064, s.d. = 0.014, p < 0.001). The other PRSs significantly associated with the general factor were, in the order of effect size, Chronic back pain-PRS, Insomnia-PRS, Number of Sexual Partners-PRS, Autism-PRS, BMI-PRS, PTSD-PRS, and Disinhibition-PRS (r = 0.039–0.056). The pattern of associations was generally consistent across other p-value thresholds, although the most restrictive threshold ( p = 0.01) yielded the weakest associations (online Supplementary Table S2).
Table 2.
Bivariate partial correlations between PRSs and CBCL factors
| 5-Factor solution | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polygenic risk score | General (p) | Externalizing | Internalizing | Neurodevelopmental | Somatoform | Detachment |
| Externalizing | ||||||
| Adventurousness | 0.027 | 0.050 | −0.020 | 0.031 | 0.001 | −0.017 |
| Disinhibition | 0.039 | 0.060 | −0.022 | 0.043 | 0.023 | −0.011 |
| Number of sexual partners | 0.054 | 0.066 | 0.001 | 0.043 | 0.044 | 0.015 |
| Risk tolerance | 0.003 | 0.010 | −0.011 | 0.005 | 0.000 | −0.009 |
| Drinks per week (Linnér) | 0.002 | 0.009 | −0.010 | 0.004 | −0.005 | −0.036 |
| Drinks per week (Liu) | −0.004 | −0.015 | 0.008 | −0.008 | 0.013 | 0.035 |
| Smoking − ever smoked regularly | −0.077 | −0.095 | −0.015 | −0.070 | −0.043 | −0.028 |
| Internalizing | ||||||
| Depression | 0.078 | 0.065 | 0.050 | 0.067 | 0.065 | 0.039 |
| Neuroticism | 0.075 | 0.056 | 0.072 | 0.058 | 0.067 | 0.052 |
| PTSD | 0.051 | 0.044 | 0.043 | 0.037 | 0.051 | 0.014 |
| Insomnia | 0.054 | 0.036 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.051 | 0.021 |
| Thought disorder | ||||||
| Bipolar disorder | −0.024 | −0.026 | −0.011 | −0.020 | −0.014 | −0.021 |
| Schizophrenia | 0.021 | 0.019 | 0.025 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.020 |
| Neurodevelopmental | ||||||
| ADHD | 0.079 | 0.087 | −0.002 | 0.101 | 0.032 | 0.031 |
| Autism spectrum disorder | 0.052 | 0.035 | 0.028 | 0.057 | 0.022 | 0.057 |
| Somatoform | ||||||
| Knee pain | 0.008 | 0.014 | −0.027 | 0.026 | −0.003 | 0.011 |
| Chronic multisite pain | 0.098 | 0.090 | 0.038 | 0.101 | 0.082 | 0.030 |
| Chronic back pain | 0.056 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.051 | 0.033 | 0.013 |
| Other psychopathology-related | ||||||
| Educational attainment | −0.064 | −0.081 | 0.004 | −0.059 | −0.054 | −0.011 |
| Intelligence | −0.015 | −0.025 | 0.030 | −0.029 | 0.000 | −0.020 |
| Alzheimer’s disease | 0.010 | −0.001 | 0.023 | −0.001 | 0.024 | 0.013 |
| Body mass index | 0.052 | 0.059 | −0.006 | 0.062 | 0.033 | 0.041 |
Notes: All significant results at 5% FDR multiple testing correction are in bold. All correlations adjust for the first 10 ancestry PCs.
Bivariate partial correlations with the five specific factors
The associations between PRSs and the five specific factors emerged most frequently for the externalizing, neurodevelopmental, and somatoform factors, in part due to the largest number of PRSs representing the externalizing domain (Table 2). However, after adjusting for the general factor, none of the associations with the somatoform factor remained significant, and only ADHD-PRS was significantly associated with the neurodevelopmental factor (r = 0.062, s.d. = 0.026, p < 0.001) (Table 3). Conversely, the externalizing factor remained independently associated with Smoking-PRS, Adventurousness-PRS, Disinhibition-PRS, Educational Attainment-PRS, and Number of Sexual Partners-PRS (|r| = 0.040–0.058).
Table 3.
Bivariate partial correlations between PRSs and five lower-order CBCL factors, adjusted for the general factor
| Polygenic risk score | 5-Factor solution | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Externalizing | Internalizing | Neurodevelopmental | Somatoform | Detachment | |
| Externalizing | |||||
| Adventurousness | 0.055 | −0.055 | 0.015 | −0.023 | −0.040 |
| Disinhibition | 0.054 | −0.069 | 0.019 | −0.004 | −0.041 |
| Number of sexual partners | 0.040 | −0.051 | −0.003 | 0.011 | −0.019 |
| Risk tolerance | 0.017 | −0.018 | 0.004 | −0.003 | −0.012 |
| Drinks per week (Linnér) | 0.015 | −0.016 | 0.005 | −0.009 | −0.045 |
| Drinks per week (Liu) | −0.024 | 0.014 | −0.009 | 0.020 | 0.045 |
| Smoking - ever smoked regularly | −0.058 | 0.054 | −0.012 | 0.010 | 0.019 |
| Internalizing | |||||
| Depression | −0.008 | −0.006 | 0.005 | 0.018 | −0.007 |
| Neuroticism | −0.021 | 0.027 | −0.008 | 0.023 | 0.011 |
| PTSD | −0.003 | 0.010 | −0.009 | 0.023 | −0.019 |
| Insomnia | −0.025 | 0.018 | 0.010 | 0.020 | −0.012 |
| Thought disorder | |||||
| Bipolar disorder | −0.010 | 0.009 | 0.000 | 0.003 | −0.009 |
| Schizophrenia | 0.000 | 0.015 | −0.015 | −0.003 | 0.010 |
| Neurodevelopmental | |||||
| ADHD | 0.036 | −0.079 | 0.062 | −0.028 | −0.017 |
| Autism spectrum disorder | −0.023 | −0.011 | 0.025 | −0.017 | 0.033 |
| Somatoform | |||||
| Knee pain | 0.015 | −0.046 | 0.034 | −0.012 | 0.008 |
| Chronic multisite pain | 0.007 | −0.042 | 0.036 | 0.022 | −0.031 |
| Chronic back pain | −0.011 | 0.008 | 0.008 | −0.005 | −0.023 |
| Other Psychopathology-related | |||||
| Educational attainment | −0.052 | 0.068 | −0.011 | −0.015 | 0.031 |
| Intelligence | −0.025 | 0.056 | −0.029 | 0.013 | −0.014 |
| Alzheimer’s disease | −0.021 | 0.022 | −0.016 | 0.023 | 0.009 |
| Body mass index | 0.027 | −0.059 | 0.033 | −0.002 | 0.013 |
Notes: All significant results at 5% FDR multiple testing correction are in bold. All correlations adjust for the first 10 ancestry PCs and the general factor.
The internalizing and detachment factors demonstrated notably fewer associations with PRSs (Table 2). However, after adjusting for the general factor, many PRSs showed protective effects on the internalizing dimension (Table 3). For example, the internalizing factor was negatively associated with Number of Sexual Partners-PRS (r = −0.051, s.d. = 0.020, p = 0.001), and positively associated with Educational Attainment-PRS and Intelligence-PRS (r = 0.056–0.068). Similarly, after adjusting for the general factor, the detachment dimension was associated with lower genetic vulnerability to Alcohol, Disinhibition, and Adventurousness (|r| = 0.045 to 0.040, Table 3).
Finally, six PRSs showed no associations with any specific factor, beyond their significant associations with the general factor: Autism-PRS, Chronic Back Pain-PRS, Insomnia-PRS, Depression-PRS, Neuroticism-PRS, and PTSD-PRS (Table 3). Conversely, while not significantly associated with the general factor, five PRSs showed only associations with specific factors: Adventurousness-PRS with externalizing, internalizing, and detachment factors; Intelligence-PRS with internalizing factor; Knee Pain-PRS with internalizing factor; and two Alcohol-PRSs with detachment factor.
Mapping the hierarchical structure to PRSs
The regression analyses found that five PRSs – Chronic Back Pain-PRS, Insomnia-PRS, Depression-PRS, Neuroticism-PRS, and PTSD-PRS – were associated only with the general factor, so that the addition of the dimensions from the 5-factor solution did not significantly increase the association between PRS and psychopathology (Table 4). Between 66.7 and 85.7% of total associations between these five PRSs, as well as Chronic Multisite Pain-PRS, and childhood psychopathology was captured by the general factor (Fig. 1b). Autism-PRS, ADHD-PRS, Number of Sexual Partners-PRS, and Smoking-PRS contributed significantly and approximately equally to the general and specific forms of psychopathology.
Table 4.
Summary of incremental associations between PRS and CBCL general factor and five lower-order factors
| ΔR2 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Add 1-Factor solution | Add 5-Factor solution | |
| Externalizing | ||
| Adventurousness | 0.001 | 0.005* |
| Disinhibition | 0.002* | 0.006* |
| Number of sexual partners | 0.003* | 0.004* |
| Risk tolerance | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Drinks per week (Linnér) | 0.000 | 0.002 |
| Drinks per week (Liu) | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| Smoking – ever smoked regularly | 0.005* | 0.005* |
| Internalizing | ||
| Depression | 0.006* | 0.001 |
| Neuroticism | 0.005* | 0.001 |
| PTSD | 0.002* | 0.001 |
| Insomnia | 0.003* | 0.001 |
| Thought disorder | ||
| Bipolar disorder | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Schizophrenia | 0.001 | 0.000 |
| Neurodevelopmental | ||
| ADHD | 0.006* | 0.008* |
| Autism spectrum disorder | 0.003* | 0.003* |
| Somatoform | ||
| Knee pain | 0.000 | 0.003 |
| Chronic multisite pain | 0.009* | 0.004* |
| Chronic back pain | 0.003* | 0.001 |
| Other Psychopathology-related | ||
| Educational attainment | 0.004* | 0.006* |
| Intelligence | 0.000 | 0.003* |
| Alzheimer’s disease | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Body mass index | 0.002* | 0.004* |
Notes: Significant ΔR2 between regression blocks are demarked with an asterisk, after 5% FDR multiple testing correction.
For full hierarchical regression results, see online Supplementary Table S2.
Conversely, BMI-PRS, Disinhibition-PRS, Educational Attainment-PRS, Adventurousness-PRS, and Intelligence-PRS contributed more to the five dimensions than to the general factor, with 0–40.0% of total genetic associations captured by the general factor (Table 4 and Fig. 1b). In fact, the Adventurousness-PRS and Intelligence-PRS were not associated with the general factor, but there was a significant increase in the association with psychopathology once the five dimensions were added.
Discussion
The current study delineated a pattern of associations between a wide range of PRSs, and empirically derived, hierarchical factors of childhood psychopathology in the ABCD study. Specifically, the PRSs for internalizing and somatoform problems predominantly captured non-specific genetic vulnerability to psychopathology in childhood. Conversely, PRSs for a range of externalizing problems, ADHD, BMI, educational attainment, and intelligence contributed more to specific than to general psychopathology, most notably to the externalizing factor. Overall, the findings indicate that some genetic effects captured by major PRSs are non-specific, but the balance of general v. specific effects varied substantially across PRSs.
We found that a wide range of PRSs were associated with the general factor of psychopathology. This is in line with twin and molecular genetic studies showing widespread pleiotropy under-pinning psychiatric conditions in youth and adults (Martin et al., 2017; Wray et al., 2014). In particular, PRSs derived for internalizing and somatoform phenotypes were among the most strongly associated with the general factor. There are three possible explanations for this. First, the CBCL-based general factor in childhood might be predominantly characterized by internalizing and somatoform variance (e.g. distress, fears, pain). However, in the current higher-order model, the general factor did not have a disproportionate contribution from the internalizing or somatoform spectrum, as evidenced by Fig. 1a loadings and the original model in Michelini et al. (2019). Second possible explanation is that GWASs for internalizing and somatoform conditions were particularly saturated with general psychopathology variance, resulting in PRSs that captured little specificity. This is consistent with prior findings that genetic vulnerability to depression was the strongest marker of the general genetic factor (Selzam, Coleman, Caspi, Moffitt, & Plomin, 2018; Waldman, Poore, Luningham, & Yang, 2020). Third, genetic vulnerability for internalizing and somatoform difficulties in adulthood manifests primarily as a general risk for psychopathology in childhood.
The results demonstrated incremental validity of investigating associations between PRSs and specific factors of psychopathology. We found that Adventurousness-PRS, Disinhibition-PRS, Number of Sexual Partners-PRS, Smoking-PRS, and Education Attainment-PRS captured genetic vulnerability specific to the externalizing dimension in youth, over and above the genetic vulnerability to general psychopathology. Moreover, the ADHD-PRS predicted the neurodevelopmental factor, independently of its significant association with the general factor, in line with the pattern of results reported by Riglin et al. (2019) and Brikell et al. (2018). In fact, more than half of the total associations between these PRSs, and childhood psychopathology, were due to the specific factors. This suggests that GWASs for externalizing problems and ADHD might be better able to capture the narrow phenotypes of interest, resulting in more precise PRSs, perhaps because target phenotypes are characterized by observable behavioral symptoms. This interpretation is also consistent with prior finding that molecular genetic markers of antisocial behavior and substance use were only moderately associated with the general genetic factor (Waldman et al., 2020). Notably, the ADHD-PRS emerged as the most predictive PRS in the current study, accounting for a total of 1.4% of variance in CBCL factors. This suggests that ADHD-PRS might be one of the strongest currently available PRSs for capturing genetic vulnerability to psychopathology in youth.
Accounting for the genetic vulnerability to general psychopathology allowed to uncover potential protective genetic effects. For example, Adventurousness-PRS and Disinhibition-PRS were negatively associated with the detachment dimension, which is consistent with withdrawn behaviors captured by this factor. However, negative associations observed for the internalizing spectrum after accounting for the general factor, for example with the Educational Attainment-PRS, are more difficult to interpret. The reverse pattern of associations between the residual internalizing factor and a wide range of vulnerability factors has been reported previously, and might constitute a statistical artifact, such as too little variance remaining in the specific factor (Bornovalova, Choate, Fatimah, Petersen, & Wiernik, 2020; Watts, Poore, & Waldman, 2019). Overall, the potential protective effects of internalizing PRSs should be interpreted with caution. Finally, none of the PRSs tested in this study captured the variance unique to the somatoform factor, independently of the general factor. This may indicate that genetic risk for somatoform phenotypes is mediated by the general factor in childhood.
Overall, the pattern of results is in line with the evidence that, while some polygenetic vulnerability is broad and transdiagnostic, a significant proportion of polygenetic risk is specific to narrower psychiatric constructs, underscoring the added benefit of fine-grained modeling of psychopathology (Waszczuk et al., 2020). The hierarchical genetic architecture has previously been demonstrated in family and twin studies (Lahey et al., 2016; Pettersson, Larsson, & Lichtenstein, 2016; Waldman, Poore, van Hulle, Rathouz, & Lahey, 2016), and more recently using molecular genomic structural equation modeling (Grotzinger et al., 2019; Waldman et al., 2020). The results have several implications for the translation of PRS for research use.
First, the comprehensive pattern of associations between PRSs and hierarchical psychopathology was obtained in order to spotlight the varied degrees of predictive specificity of the currently available PRSs. The degree to which genetic risk is general or specific is relevant to the conduct and interpretation of applied genetic research, as it can confound mechanistic interpretations. For example, current internalizing and somatoform PRSs (i.e. Depression-PRS, Neuroticism-PRS, Insomnia-PRS, PTSD-PRS, Chronic Multisite Pain-PRS, Chronic Back Pain-PRS) need to be applied with an understanding that they largely capture risk factors for broad psychopathology rather than genetic mechanisms specific to a given disorder.
Second, the results also have implications for the design of future GWAS. As differential genetic discovery is expected to emerge at each level of the phenotypic structure, future GWASs on phenotypes at different levels of the hierarchy could help create more precise PRSs. Recently, Cai et al. (2020) empirically demonstrated that imprecise, minimal phenotyping yields Depression-PRS that broadly predicts psychopathology, while narrow phenotypic definitions markedly increase the prediction specificity of Depression-PRS. Thus, future discovery GWASs should explicitly calibrate target phenotypes to develop transdiagnostic and p-value PRSs alongside disorder-specific PRSs.
Limitations
The current study has several strengths, including a comprehensive assessment of child psychopathology in a large, well-characterized, and genotyped cohort. Nonetheless, some limitations are notable. First, analyses were restricted to participants of European Ancestry, who constitute only about half of the ABCD cohort, considerably curbing the representativeness of the current findings. The PRSs have been developed in discovery GWAS samples of European ancestry and are known to perform poorly in individuals from other ancestries (Martin et al., 2019). One improvement would be additional discovery GWASs including ancestry admixture. Second, the PRS–phenotype association is influenced by similarities between the discovery GWAS and the test sample, including demographic characteristics and instruments used to collect data in both samples. Thus, the pattern of phenotypic manifestation of PRSs reported in the current study might not replicate in other adolescent samples, and when GWASs based on larger and/or developmental discovery samples become available. The sample characteristics, specifically the lack of severe psychopathology in the ABCD cohort, might partially explain the unexpected null findings for Bipolar Disorder-PRS and Schizophrenia-PRS. Furthermore, we selected PRSs to ensure adequate power and nearly all of them predicted psychopathology dimensions (Dudbridge, 2013). However, strength of discovery samples differed substantially among these PRS, thus the precision in evaluating specificity of some PRSs was stronger than others. In particular, ADHD-PRS, Autism-PRS, Disinhibition-PRS, Number of Sexual Partners-PRS, and PTSD-PRS were estimated to have power somewhat lower than 80%, but nonetheless demonstrated their utility for present analyses by predicting psychopathology in ABCD data.
Third, the phenotypic structure was obtained using cross-sectional data and its stability or measurement invariance over time has not yet been established. Fourth, as typical for this age group, youth psychopathology was assessed only via parent-report. There are different strengths and limitations associated with self- and parent-reports (Bird, Gould, & Staghezza, 1992; Jensen et al., 1999), with informants showing only moderate agreement due to their different perspectives (Goodman, 2001; Stanger & Lewis, 1993). Nonetheless, twin studies suggest that different informants appear to measure a largely common genetic liability (Allegrini et al., 2020; Bartels, Boomsma, Hudziak, van Beijsterveldt, & van den Oord, 2007; Merwood et al., 2013). Finally, PRSs capture only a small proportion of genetic influences on psychiatric disorders, and account for too little variance to be clinically informative. We were not able to account for the associations with the remaining genetic liability that is not captured by the PRSs.
Conclusions
The current study investigated phenotypic manifestations of polygenic risk in a developmental sample. Genetic vulnerability captured by the internalizing and somatoform PRSs was largely associated with the general factor of psychopathology in childhood, indicating that these PRSs predominantly capture transdiagnostic genetic effects. Moreover, some externalizing PRSs showed independent and incremental associations with the specific psychopathology dimensions, most notably with the externalizing factor. Likewise, ADHD-PRS was uniquely associated with the neurodevelopmental factor, over and above the general factor. Overall, specific genetic effects were often at least as large as general effects, but varied substantially across PRSs. The results demonstrate that higher-order models of psychopathology can help to explain patterns of PRS prediction in childhood samples.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements.
This work was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (A.D., grant number K01MH093731) and the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (A.D. & A.S.). Data used in the preparation of this article were obtained from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study (https://abcdstudy.org), held in the NIMH Data Archive (NDA). This is a multisite, longitudinal study designed to recruit more than 10 000 children age 9–10 and follow them over 10 years into early adulthood. The ABCD Study is supported by the National Institutes of Health and additional federal partners under award numbers U01DA041022, U01DA041028, U01DA041048, U01DA041089, U01DA041106, U01DA041117, U01DA041120, U01DA041134, U01DA041148, U01DA041156, U01DA041174, U24DA041123, U24DA041147, U01DA041093, and U01DA041025. A full list of supporters is available at https://abcdstudy.org/federal-partners.html. A listing of participating sites and a complete listing of the study investigators can be found at https://abcdstudy.org/scientists/workgroups/. ABCD consortium investigators designed and implemented the study and/or provided data but did not necessarily participate in analysis or writing of this report. This manuscript reflects the views of the authors and may not reflect the opinions or views of the NIH or ABCD consortium investigators. The ABCD data repository grows and changes over time. The ABCD data used in this report came from NDAR-https://doi.org/10.15154/1503209.
Footnotes
Conflict of interest. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary material. The supplementary material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291721003639
References
- Achenbach T, & Rescorla L (2001). Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms and profiles. Child behavior checklist for age 6–18, teacher’s report from, youth self-report and integrated system of multi-informant assessment. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont.[Links]. [Google Scholar]
- Allegrini AG, Cheesman R, Rimfeld K, Selzam S, Pingault JB, Eley TC, & Plomin R (2020). The p factor: Genetic analyses support a general dimension of psychopathology in childhood and adolescence. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 61(1), 30–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels M, Boomsma DI, Hudziak JJ, van Beijsterveldt TC, & van den Oord EJ (2007). Twins and the study of rater (dis) agreement. Psychological Methods, 12(4), 451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baurley JW, Edlund CK, Pardamean CI, Conti DV, & Bergen AW (2016). Smokescreen: A targeted genotyping array for addiction research. BMC Genomics, 17(1), 145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsky DW, & Harden KP (2019). Phenotypic annotation: Using polygenic scores to translate discoveries from genome-wide association studies from the top down. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 28(1), 82–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird HR, Gould MS, & Staghezza B (1992). Aggregating data from multiple informants in child psychiatry epidemiological research. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 31(1), 78–85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogdan R, Baranger DA, & Agrawal A (2018). Polygenic risk scores in clinical psychology: Bridging genomic risk to individual differences. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 14, 119–157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornovalova MA, Choate AM, Fatimah H, Petersen KJ, & Wiernik BM (2020). Appropriate use of bifactor analysis in psychopathology research: Appreciating benefits and limitations. Biological Psychiatry, 88(1), 18–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brikell I, Larsson H, Lu Y, Pettersson E, Chen Q, Kuja-Halkola R, … Martin J (2018). The contribution of common genetic risk variants for ADHD to a general factor of childhood psychopathology. Molecular Psychiatry, 25(8), 1809–1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai N, Revez JA, Adams MJ, Andlauer TF, Breen G, Byrne EM, … Hamilton SP (2020). Minimal phenotyping yields genome-wide association signals of low specificity for major depression. Nature Genetics, 52 (4), 437–447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspi A, Houts RM, Belsky DW, Goldman-Mellor SJ, Harrington H, Israel S, … Poulton R (2014). The p factor one general psychopathology factor in the structure of psychiatric disorders? Clinical Psychological Science, 2(2), 119–137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton WM, Dowling GJ, & Garavan H (2019). Ensuring the best use of data: The adolescent brain cognitive development study. JAMA Pediatrics, 173(9), 809–810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demontis D, Walters RK, Martin J, Mattheisen M, Als TD, Agerbo E, … Bækvad-Hansen M (2019). Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nature Genetics, 51 (1), 63–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dick DM, Barr PB, Cho SB, Cooke ME, Kuo SIC, Lewis TJ, … Su J (2018). Post-GWAS in psychiatric genetics: A developmental perspective on the “other” next steps. Genes, Brain and Behavior, 17(3), e12447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty AR, Moscati A, Dick D, Savage JE, Salvatore JE, Cooke M, … Riley BP (2018). Polygenic prediction of the phenome, across ancestry, in emerging adulthood. Psychological Medicine, 48(11), 1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudbridge F (2013). Power and predictive accuracy of polygenic risk scores. PLoS Genetics, 9(3), e1003348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Euesden J, Lewis CM, & O’Reilly PF (2015). PRSice: Polygenic risk score software. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 31(9), 1466–1468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes MK, Tackett JL, Markon KE, & Krueger RF (2016). Beyond comorbidity: Toward a dimensional and hierarchical approach to understanding psychopathology across the life span. Development and Psychopathology, 28(4pt1), 971–986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garavan H, Bartsch H, Conway K, Decastro A, Goldstein R, Heeringa S, … Zahs D (2018). Recruiting the ABCD sample: Design considerations and procedures. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 32, 16–22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R (2001). Psychometric properties of the strengths and difficulties questionnaire. Journal of American Academic Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40(11), 1337–1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotzinger AD, Rhemtulla M, de Vlaming R, Ritchie SJ, Mallard TT, Hill WD, … Deary IJ (2019). Genomic structural equation modelling provides insights into the multivariate genetic architecture of complex traits. Nature Human Behaviour, 3(5), 513–525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J, Ripke S, Als TD, Mattheisen M, Walters RK, Won H, … Anney R (2019). Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nature Genetics, 51(3), 431–444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard DM, Adams MJ, Clarke TK, Hafferty JD, Gibson J, Shirali M, … McIntosh AM (2019). Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nature Neuroscience, 22(3), 343–352. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0326-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen IE, Savage JE, Watanabe K, Bryois J, Williams DM, Steinberg S, … Posthuma D (2019). Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies new loci and functional pathways influencing Alzheimer’s disease risk. Nature Genetics, 51(3), 404–413. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0311-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen PS, Rubio-Stipec M, Canino G, Bird HR, Dulcan MK, Schwab-Stone ME, & Lahey BB (1999). Parent and child contributions to diagnosis of mental disorder: Are both informants always necessary? Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 38 (12), 1569–1579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston KJ, Adams MJ, Nicholl BI, Ward J, Strawbridge RJ, Ferguson A, … Smith DJ (2019). Genome-wide association study of multisite chronic pain in UK biobank. PLoS Genetics, 15(6), e1008164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones HJ, Heron J, Hammerton G, Stochl J, Jones PB, Cannon M, … Linden DE (2018). Investigating the genetic architecture of general and specific psychopathology in adolescence. Translational Psychiatry, 8(1), 145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotov R, Krueger RF, Watson D, Achenbach TM, Althoff RR, Bagby M, … Zimmerman M (2017). The hierarchical taxonomy of psychopathology (HiTOP): A dimensional alternative to traditional nosologies. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 126(4), 454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapohl E, Euesden J, Zabaneh D, Pingault J, Rimfeld K, Von Stumm S, … Plomin R (2016). Phenome-wide analysis of genome-wide polygenic scores. Molecular Psychiatry, 21(9), 1188–1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahey BB, Applegate B, Hakes JK, Zald DH, Hariri AR, & Rathouz PJ (2012). Is there a general factor of prevalent psychopathology during adulthood? Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121(4), 971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahey BB, Krueger RF, Rathouz PJ, Waldman ID, & Zald DH (2016). A hierarchical causal taxonomy of psychopathology across the life span. Psychological Bulletin, 143(2), 142–186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee JJ, Wedow R, Okbay A, Kong E, Maghzian O, Zacher M, … Cesarini D (2018). Gene discovery and polygenic prediction from a genome-wide association study of educational attainment in 1.1 million individuals. Nature Genetics, 50(8), 1112–1121. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0147-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linner KR, Biroli P, Kong E, Meddens SFW, Wedow R, Fontana MA, … Beauchamp JP (2019). Genome-wide association analyses of risk tolerance and risky behaviors in over 1 million individuals identify hundreds of loci and shared genetic influences. Nature Genetics, 51(2), 245–257. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0309-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M, Jiang Y, Wedow R, Li Y, Brazel DM, Chen F, … Vrieze S (2019). Association studies of up to 1.2 million individuals yield new insights into the genetic etiology of tobacco and alcohol use. Nature Genetics, 51(2), 237–244. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0307-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI, Justice AE, Pers TH, Day FR, … Speliotes EK (2015). Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature, 518(7538), 197–206. doi: 10.1038/nature14177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin AR, Kanai M, Kamatani Y, Okada Y, Neale BM, & Daly MJ (2019). Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nature Genetics, 51(4), 584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J, Taylor MJ, & Lichtenstein P (2017). Assessing the evidence for shared genetic risks across psychiatric disorders and traits. Psychological Medicine, 48(11), 1759–1774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy S, Das S, Kretzschmar W, Delaneau O, Wood AR, Teumer A, … Sharp K (2016). A reference panel of 64976 haplotypes for genotype imputation. Nature Genetics, 48(10), 1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng W, Adams MJ, Palmer CN, Shi J, Auton A, Ryan KA, … Yau MS (2019). Genome-wide association study of knee pain identifies associations with GDF5 and COL27A1 in UK biobank. Communications Biology, 2(1), 1–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merwood A, Greven C, Price T, Rijsdijk F, Kuntsi J, McLoughlin G, … Asherson P (2013). Different heritabilities but shared etiological influences for parent, teacher and self-ratings of ADHD symptoms: An adolescent twin study. Psychological Medicine, 43(09), 1973–1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelini G, Barch DM, Tian Y, Watson D, Klein DN, & Kotov R (2019). Delineating and validating higher-order dimensions of psychopathology in the adolescent brain cognitive development (ABCD) study. Translational Psychiatry, 9(1), 1–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel M, Jansen PR, Stringer S, Watanabe K, de Leeuw CA, Bryois J, … Posthuma D (2018). Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for neuroticism in 449484 individuals identifies novel genetic loci and pathways. Nature Genetics, 50(7), 920–927. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newson JJ, Hunter D, & Thiagarajan TC (2020). The heterogeneity of mental health assessment. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 11, 76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nievergelt CM, Maihofer AX, Klengel T, Atkinson EG, Chen CY, Choi KW, … Koenen KC (2019). International meta-analysis of PTSD genome-wide association studies identifies sex- and ancestry-specific genetic risk loci. Nature Communications, 10(1), 4558. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12576-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson E, Larsson H, & Lichtenstein P (2016). Common psychiatric disorders share the same genetic origin: A multivariate sibling study of the Swedish population. Molecular Psychiatry, 21(5), 717–721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, … Daly MJ (2007). PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 81(3), 559–575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice F, Riglin L, Thapar AK, Heron J, Anney R, O’donovan MC, … Thapar A (2018). Characterizing developmental trajectories and the role of neuropsychiatric genetic risk variants in early-onset depression. JAMA Psychiatry, 76(3), 306–313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riglin L, Thapar AK, Leppert B, Martin J, Richards A, Anney R, … Lahey BB (2019). Using genetics to examine a general liability to childhood psychopathology. Behavior Genetics, 50(4), 213–220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripke S, Walters JT, O’Donovan MC, & The Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (2020). Mapping genomic loci prioritises genes and implicates synaptic biology in schizophrenia. MedRxiv. [Google Scholar]
- Savage JE, Jansen PR, Stringer S, Watanabe K, Bryois J, de Leeuw CA, … Posthuma D (2018). Genome-wide association meta-analysis in 269867 individuals identifies new genetic and functional links to intelligence. Nature Genetics, 50(7), 912–919. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0152-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selzam S, Coleman JR, Caspi A, Moffitt TE, & Plomin R (2018). A polygenic p factor for major psychiatric disorders. Translational Psychiatry, 8(1), 1–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl EA, Breen G, Forstner AJ, McQuillin A, Ripke S, Trubetskoy V, … Sklar P (2019). Genome-wide association study identifies 30 loci associated with bipolar disorder. Nature Genetics, 51(5), 793–803. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0397-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanger C, & Lewis M (1993). Agreement among parents, teachers, and children on internalizing and externalizing behavior problems. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 22(1), 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Suri P, Palmer MR, Tsepilov YA, Freidin MB, Boer CG, Yau MS, … Nethander M (2018). Genome-wide meta-analysis of 158000 individuals of European ancestry identifies three loci associated with chronic back pain. PLoS Genetics, 14(9), e1007601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thapar A, & Riglin L (2020). The importance of a developmental perspective in psychiatry: What do recent genetic-epidemiological findings show? Molecular Psychiatry, 25(8), 1631–1639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman ID, Poore HE, Luningham JM, & Yang J (2020). Testing structural models of psychopathology at the genomic level. World Psychiatry, 19(3), 350–359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman ID, Poore HE, van Hulle C, Rathouz PJ, & Lahey BB (2016). External validity of a hierarchical dimensional model of child and adolescent psychopathology: Tests using confirmatory factor analyses and multivariate behavior genetic analyses. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 125(8), 1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waszczuk MA, Eaton NR, Krueger RF, Shackman AJ, Waldman ID, Zald DH, … Kotov R (2020). Redefining phenotypes to advance psychiatric genetics: Implications from hierarchical taxonomy of psychopathology. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 129(2), 143–161. doi: 10.31234/osf.io/sf46g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts AL, Poore HE, & Waldman ID (2019). Riskier tests of the validity of the bifactor model of psychopathology. Clinical Psychological Science, 7(6), 1285–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Wray NR, Lee SH, Mehta D, Vinkhuyzen AA, Dudbridge F, & Middeldorp CM (2014). Research review: Polygenic methods and their application to psychiatric traits. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 55(10), 1068–1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


