Correction to: Scientific Reports 10.1038/s41598-017-06872-y, published online 26 July 2017
The original Article contains errors. Due to mistakes during Figure assembly, there are overlaps within two Figures and with previously published articles.
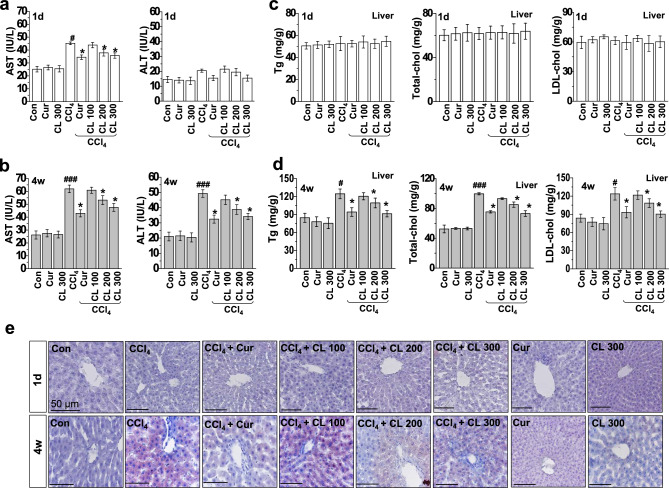
Within Figure 1e the panel “CL 300” is a duplication of panel “1d CCl4 + Cur”. In addition, the panel “4w Cur” overlaps with panel “Curcumin” of Figure 2 in Lee, HY et al.1.
Figure 1.
Curcumin and Curcuma longa L. extract regulate serum levels of AST and ALT and hepatic lipid accumulation in acute and chronic CCl4-models. Rats were intraperitoneally treated with CCl4 (0.1 mL/100 g, body weight) one time for (a) 1 day or (b) every other day for 4 weeks. Curcumin (200 mg/kg) or Curcuma longa L. extract (100, 200, or 300 mg/kg) was given each day for 3 days before CCl4 treatment and once daily after CCl4 treatment. Liver and blood samples were collected from all sacrificed animals. Six-h fasting serum levels of AST and ALT were determined. Six h fasting liver triglyceride, total cholesterol, and LDL-cholesterol levels were measured in the (c) 1 day and (d) 4 week CCl4-treated rats. (e) Representative images of liver sections from each group stained with hematoxylin–eosin and Oil-Red-O for lipid content. Scale bars = 50 µm. The experiments were repeated three times using tissues from at least three different rats. #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 vs. the control group; *P < 0.01 vs. the CCl4 group (n = 10 rats per group). Cur: curcumin, CL: Curcuma longa L., AST: aspartate aminotransferase, ALT: alanine aminotransferase.
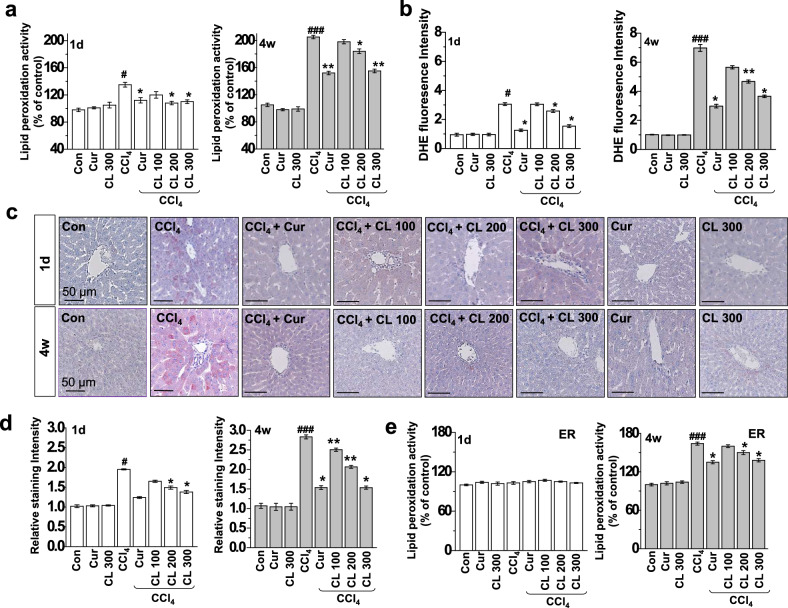
Figure 2.
Curcumin and Curcuma longa L. extract regulate ROS accumulation in acute and chronic CCl4-models. Rats were intraperitoneally treated with CCl4 (0.1 mL/100 g body weight) one time for 1 day or every other day for 4 weeks. Curcumin (200 mg/kg) or Curcuma longa L. extract (100, 200, and 300 mg/kg) was given once daily. (a) Lipid peroxidation activity was measured in 1 day and 4 week CCl4-treated rats. (b) DHE staining in the liver was measured in 1 day and 4 week CCl4-treated rats. (c) Liver tissues from 1 day and 4 week CCl4-treated rats were stained with 4-HNE, and (d) the staining intensity of 4-HNE-positive cells was calculated. (e) Lipid peroxidation activity was measured in the ER fractions from the liver tissues of CCl4-treated rats. The experiments were repeated three times using tissues from at least three different rats. #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 vs. the control group; *P < 0.01, **P < 0.05 vs. the CCl4 group (n = 10 rats per group). Cur: curcumin, CL: Curcuma longa L.
The corrected Figure 1 and accompanying legend appear below as Figure 1.
Within Figure 2c the panel “4w CL 300” duplicated panel “1d Con”, the panel “1d CCl4” is a duplication of “4w CCl4”, and the panel “4w CCL4 + CL 300” is duplicated from panel “1d CL 300”.
Additionally, in Figure 2c, the panel “4w Con” is similar to the panel “Control, Anti-4HNE” of Figure 4b in Lee, GH et al.2, the panel “4w CCl4 + CL 100” overlaps with “CCl4, Anti-4HNE” of Figure 4b in2, the panel “1d Cur” overlaps with “Curcumin + CCl4” of Figure 4b in2, and “4w Cur” shows similarities to “Curcumin, Anti-4HNE” of Figure 4b in2.
The corrected Figure 2 and accompanying legend appear below as Figure 2.
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally: Hwa-Young Lee and Seung-Wook Kim.
Contributor Information
Ho Jeong Kwon, Email: kwonhj@yonsei.ac.kr.
Han-Jung Chae, Email: hjchae@jbnu.ac.kr.
References
- 1.Lee HY, Kim SW, Lee GH, et al. Turmeric extract and its active compound, curcumin, protect against chronic CCl4-induced liver damage by enhancing antioxidation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016;16:316. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1307-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lee GH, Lee HY, Choi MK, et al. Protective effect of Curcuma longa L. extract on CCl4-induced acute hepatic stress. BMC Res. Notes. 2017;10:77. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2409-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]