Abstract
Transdiagnostic cognitive behavioural psychotherapy (TD-CBT) may facilitate the treatment of emotional disorders. Here we investigate short- and long-term efficacy of TD-CBT for emotional disorders in individual, group and internet-based settings in randomized controlled trials (PROSPERO CRD42019141512). Two independent reviewers screened results from PubMed, MEDLINE, PsycINFO, Google Scholar, medRxiv and OSF Preprints published between January 2000 and June 2023, selected studies for inclusion, extracted data and evaluated risk of bias (Cochrane risk-of-bias tool 2.0). Absolute efficacy from pre- to posttreatment and relative efficacy between TD-CBT and control treatments were investigated with random-effects models. Of 56 identified studies, 53 (6,705 participants) were included in the meta-analysis. TD-CBT had larger effects on depression (g = 0.74, 95% CI = 0.57–0.92, P < 0.001) and anxiety (g = 0.77, 95% CI = 0.56–0.97, P < 0.001) than did controls. Across treatment formats, TD-CBT was superior to waitlist and treatment-as-usual. TD-CBT showed comparable effects to disorder-specific CBT and was superior to other active treatments for depression but not for anxiety. Different treatment formats showed comparable effects. TD-CBT was superior to controls at 3, 6 and 12 months but not at 24 months follow-up. Studies were heterogeneous in design and methodological quality. This review and meta-analysis strengthens the evidence for TD-CBT as an efficacious treatment for emotional disorders in different settings.
Subject terms: Therapeutics, Psychology
This systematic review and meta-analysis examines the evidence for transdiagnostic cognitive behavioural psychotherapy for the treatment of emotional disorders.
Main
Mental disorders are highly prevalent and show high comorbidity between them. Disorders across different diagnostic categories share commonalities and underlying processes on cognitive, neuropsychological and genetic levels1–3. Transdiagnostic cognitive behavioural therapy (TD-CBT) as an umbrella term encompasses different treatment approaches to tackle comorbidity4. In unified transdiagnostic treatments, patients with different disorders receive the same ‘broadband’ treatment that targets shared commonalities between these disorders. Examples of this approach include the unified protocol (UP) for emotional disorders5, the anxiety treatment protocol6 or transdiagnostic behaviour therapy7. Typically, unified transdiagnostic interventions apply the same selection and sequence of modules to all patients, independent of their characteristics. In tailored interventions, patients receive a treatment that is personalized to them. Different approaches to tailoring exist, from tailoring unified transdiagnostic treatments by personalizing the sequence of modules based on baseline characteristics to using idiographic case formulation to aggregate methods across different treatment packages. The key difference between unified transdiagnostic treatments and tailored interventions lies in their scope and focus. Unified transdiagnostic treatments have been specifically developed to target comorbidity by addressing shared mechanisms across different disorders in a comprehensive manner that is applicable to a range of patients. Tailored interventions, on the other hand, focus on addressing the specific needs and characteristics of individuals. Thus, unified transdiagnostic treatments offer a broad, overarching approach that can be applied to many disorders, while tailored interventions provide a more individualized treatment approach that considers the unique aspects of each person’s condition.
TD-CBT is a highly relevant approach to addressing treatment gaps and disseminating evidence-based treatments. Unified transdiagnostic approaches are especially promising in health care systems with notable treatment gaps, for example, by offering one transdiagnostic approach for emotional disorders instead of several disorder-specific approaches. In addressing a broader range of psychopathology, unified TD-CBT specifically may provide a more comprehensive treatment for patients, facilitate clinical training8 and lower treatment costs by reducing time invested by patients and therapists9–11. It can also be flexibly adapted to various treatment settings, ranging from individual and group face-to-face formats, to scalable internet-based self-help formats12,13.
Several reviews and meta-analyses investigated TD treatments. However, these previous meta-analyses differed in the settings they investigated (group, individual or internet-based), the target population (anxiety, anxiety and depression or emotional disorders) and the breadth of the transdiagnostic definition they applied (unified TD approaches, tailored interventions or specific treatment protocols). Others14 focused on face-to-face treatments in anxiety disorders and another meta-analysis15 compared TD treatments to disorder-specific treatments. Two meta-analyses16,17 investigated unified TD and tailored interventions in the internet-based setting and another18 focused on TD interventions in group format. Others, such as ref. 19, focused on a specific TD treatment, the UP5. The most recent meta-analysis20 aggregated findings from their large database on treatments for depression (https://www.metapsy.org/) that had a transdiagnostic stance. However, the authors did not focus exclusively on CBT and did not include transdiagnostic treatments targeting anxiety or other emotional disorders, although most transdiagnostic treatments are aimed at anxiety disorders. Two studies21,22 are the most comprehensive meta-analyses on TD-CBT for emotional disorders to date, including all settings as well as a focus on anxiety and depression. However, the search conducted by ref. 21 ended in 2013 and—given the novelty of TD-CBT then—they could only include four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in their meta-analysis. On the other hand, ref. 22 only included clinician-guided internet-based interventions and did not restrict their study selection to RCTs. Thus, self-guided internet-based treatments without clinician support have not been included in their review, although it is a scalable format which has a particularly strong potential to reach larger populations.
Overall, unified TD treatments seem to produce large pre- to posttreatment effects in different settings. However, several questions need to be addressed: the comparability of unified TD-CBT to disorder-specific treatments, as there is conflicting meta-analytic evidence15,22, the comparability across different settings and the long-term effects. The surge in research activity on TD protocols in recent years warrants an updated comprehensive review and meta-analysis that aggregates findings across different unified TD protocols and settings. The current review and meta-analysis expands previous reviews and meta-analyses by investigating unified TD-CBT for emotional disorders in individual and group face-to-face settings, including internet-based interventions with and without clinician guidance.
We focused on treatments based on CBT principles and unified approaches (excluding tailored treatments), to (1) update results on short- and long-term efficacy of TD-CBT and (2) compare effects of transdiagnostic protocols to different types of control conditions, including waitlist control, treatment-as-usual (TAU), disorder-specific CBT (DS-CBT) and other active interventions. To summarize: in adult patients with emotional disorders (population), what is the effect of TD-CBT (intervention) on anxiety and depression (outcome) compared with waitlist, TAU, DS-CBT and other active interventions (comparison) at posttreatment and follow-ups?
Results
Included studies
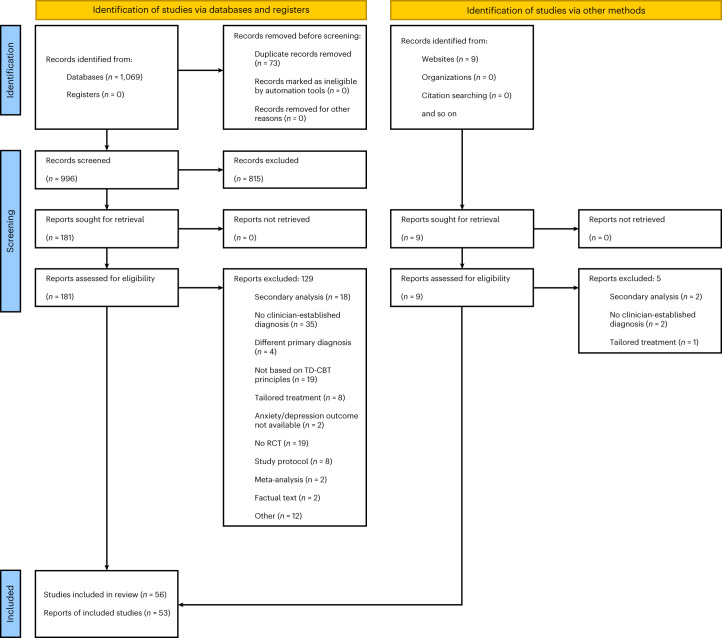
Figure 1 shows the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) flowchart of the literature search and screening procedure. By systematic search and screening, we identified 56 eligible RCTs, including 6,916 individuals, published between 2005 and 2023. No preprints could be included in the final selection. Half the included studies were published after 2019 and RCTs with internet-based treatment format date from 2010 and later. Table 1 summarizes characteristics of the individual studies.
Fig. 1. PRISMA flowchart of the literature search and screening procedure.
Three studies could not be included in the meta-analysis because either no self-report of anxiety or depression was available29 or no data were available27,28. For one study106, treatment effects at 12 months follow-up were reported in a separate publication118 which was not included in the final number of studies as this reflects the number of RCTs identified. However, we included the follow-up values in our meta-analysis.
Table 1.
RCTs investigating TD-CBT for emotional disorders in individual, group and internet-based format
| Authors | Country | Included diagnoses | Sample | TD-CBT protocol | Number of TD-CBT sessions | Control group(s) | Relevant measures (anxiety and depression) | Assessment times | Attrition (%)a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual treatment format | |||||||||
| Ref. 70 | Iran | PD, SAD, GAD, OCD, PTSD, MDD | N = 40; mean age 22 yr; female 85% | UP, n = 13 | 13–16 | Other: CS-CBT, n = 13; WLC, n = 14 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU, 6MFU | UP: 7% post, 7% 3MFU, 7% 6MFU; CS-CBT: 7% post, 7% 3MFU, 7% 6MFU; WLC: 0% post, 0% 3MFU, 0% 6MFU |
| Ref. 32 | United States | PA, GAD, OCD, SAD | N = 223; mean age 31 yr; female 56% | UP, n = 88 | 16 | DS-CBT, n = 91; WLC, n = 44 | OASIS, ODSIS | Pre, post, 6MFU | UP: 26% post, 31% 6MFU; DS-CBT: 31% post, 34% 6MFU; WLC: 27% post, NA 6MFU |
| Ref. 71 | Spain | Somatoform disorder, depression disorder, PD, GAD | N = 102; mean age 38 yr; female 88% | Brief individual psychotherapy, n = 34; brief group psychotherapy, n = 34 | 8 | TAU, n = 34 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post | Brief individual: 18% post; brief group: 6% post; TAU: 12% post |
| Ref. 72 | United States | Bipolar disorder, comorbid anxiety | N = 29; mean age 44 yr; female 59% | UP + TAU, n = 13 | 18 | TAU (pharmacotherapy), n = 16 | ASI, QIDS | Pre, post | UP + TAU: 39% post; TAU: 38% post |
| Ref. 73 | United States | GAD, SAD, OCD, PA | N = 37; mean age 30 yr; female 59% | UP, n = 26 | 18 | WLC, n = 11 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 6MFU | UP: 15% post 6MFU not reported; WLC: 9% post, 6MFU not reported |
| Ref. 74 | United States | GAD, PA, PTSD, OCD, SAD, MDD, persistent depressive disorder | N = 93; mean age 43 yr; female 24% | TBT, n = 46 | 12 | Other: BA, n = 47 | DASS-A, DASS-D | Pre, post, 6MFU | TBT: 37% post, 57% 6MFU; BA: 55% post, 72% 6MFU |
| Ref. 75 | United States | Adjustment disorder, GAD, MDD, persistent depressive disorder, PD, SAD, PTSD, SUD, other-specified trauma and stress-related disorder, other-specified depressive disorder | N = 37 mean age 47 yr; female 19% | UP, n = 13 | 12 | TAU, n = 11; other: present centred therapy, n = 13 | OASIS, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU | UP: 0% post, 0% 3MFU; TAU: 0% post, 0% 3MFU; present centred therapy: 15% post, 15% 3MFU |
| Ref. 29 | Japan | MDD, DD, PD with AG, AG without history of PD, SAD, GAD, OCD, PTSD | N = 104; mean age 37 yr; female 61% | UP + TAU, n = 52 | 12–16 | WLC + TAU, n = 52 | No self-report measure of anxiety or depression | Pre, mid, post, 5.5MFU | UP + TAU: 6% post, 8% 43WFU; WLC + TAU: 10% post, 17% 43WFU |
| Ref. 76 | Iran | OCD, GAD, SAD, PD, MDD | N = 24; mean age 23 yr; female 79% | UP, n = 12 | 20 | WLC, n = 12 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post | UP: 0% post; WLC: 0% post |
| Ref. 77 | Iran | GAD, SAD, PA, anxiety NOS, MDD | N = 23 mean age 34 yr; female 65% | UP, n = 11 | 8 | DS-CBT, n = 12 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post | UP: 15% post; DS-CBT: 20% post |
| Ref. 78 | Iran | GAD, SAD, PD, MDD | N = 64; mean age 27 yr; female 53% | UP, n = 22 | 12 | WLC, n = 19; other: CBT-P, n = 23 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 6MFU | UP: 0% post, 0% 6MFU; CBT-P: 0% post, 0% 6MFU; WLC: 0% post, 0% 6MFU |
| Ref. 28 | Canada | PD, SAD, GAD, SP, PTSD, anxiety NOS | N = 59; mean age 30 yr; female 79% | RT + CBT, n = 21 | 4 | WLC, n = 19; RT, n = 19 | GAD-7, DASS-D | Pre, 1WFU, 1MFU, 3MFU | RT + CBT: 10% 1WFU, 19% 1MFU, 43% 3MFU; RT: 0% 1WFU, 0% 1MFU, 5% 3MFU; WLC: 0% 1WFU, 16% 1MFU, 16% 3MFU |
| Ref. 79 | United States | GAD, MDD | N = 53; mean age 39 yr; female 75% | ERT, n = 28 | 20 | MAC, n = 25 | STAI-7, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU, 9MFU | ERT: 11% post, 25% 3MFU, 29% 9MFU; MAC: 20% post |
| Ref. 80 | Iran | GAD, MDD | N = 43; mean age 21 yr; female 74% | UP, n = 15; UP-tDCS, n = 13 | 12 | WLC, n = 15 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU | UP: 0% post, 0% 3MFU; UP-tDCS: 0% post, 0% 3MFU; WLC: 0% post, 0% 3MFU |
| Ref. 81 | United States | MDD, DD, PD, AG, SAD, OCD, PTSD, GAD, AUD, SUD | N = 254; mean age 27 yr; female 0% | ESTEEM, n = 100 | 10 | Other: LGBQ-affirmative counselling, n = 102; TAU (HIV testing and counselling), n = 52 | OASIS, ODSIS | Pre, 4MFU, 8MFU, 12MFU | ESTEEM: 17% 4MFU, 18% 8MFU, 19% 12MFU; LGBQ-affirmative counselling: 25% 4MFU, 25% 8MFU, 21% 12MFU; TAU: 17% 4MFU, 31% 8MFU, 19% 12MFU |
| Ref. 31 | United States | PD, GAD, SAD, PTSD | N = 1,004; mean age 44 yr; female 71% | CALM, n = 503 | 6-8 | TAU (pharmacotherapy and/or counselling by physician), n = 501 | BSI-12 subscale for anxiety, PHQ-9 | Pre, 6MFU, 12MFU, 18MFU | CALM: 11% 6MFU, 19% 12MFU, 19% 18MFU; TAU: 14% 6MFU, 20% 12MFU, 21% 18MFU |
| Ref. 27 | Iran | OCD, GAD, SAD, anxiety NOS, MDD | N = 24; mean age not reported; female 83% | UP, n = 12 | 20 | WLC, n = 12 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 1MFU | UP: 0% post, 0% 1MFU; WLC: 0% post, 0% 1MFU |
| Ref. 82 | Australia | MDD (depressive disorder with melancholic features), PD, AG, SAD, GAD, OCD, PTSD | N = 19; mean age 62 yr; female 53% | UP, n = 9 | 12 | other: EUC, n = 10 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 6MFU | UP: 0% post, 0% 6MFU; EUC: 0% post, 0% 6MFU |
| Group treatment format | |||||||||
| Ref. 83 | Germany | MDD | N = 218; mean age 39 yr; female 64% | ART, n = 76 | 7 | WLC, n = 72; CFC, n = 70 | BDI-II | Pre, post, 4WFU | ART: 32% post, 29% 4WFU; WLC: 29% post, 29% 4WFU; CFC: 40% post, 29% 4WFU |
| Ref. 84 | Spain | GAD, MDD, PD, somatization disorder | N = 105; mean age 40 yr; female 69% | Brief group TD therapy, n = 53 | 8 | TAU, n = 52 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post | Brief group TD: 11% post; TAU: 19% post |
| Ref. 85 | Brazil | PA, GAD, SAD, PTSD, SP, MDD | N = 67; mean age 34 yr; female 81% | UP, n = 33 | 14 | TAU (pharmacotherapy), n = 34 | BAI, BDI | Pre, post | UP: 27% post; TAU: 29% post |
| Ref. 86 | United Kingdom | Mood disorders, anxiety disorders, stress and somatoform disorders, eating disorders, alcohol dependence | N = 235; mean age 46 yr; female 84.26% | MMI, n = 80 | 12 | CBT and TAU (pharmacotherapy), n = 84; TAU only, n = 81 | CPRS-S-A, anxiety; CPRS-S-A, depression | Pre, post, 12MFU | MMI: 18% post, 5% 12MFU; CBT and TAU: 18% post, 4% 12MFU; TAU: 20% post, 4% 12MFU |
| Ref. 87 | Canada | SAD, PA, GAD, PTSD69, OCD, SP | N = 60; mean age 41 yr; female 64% | TD group CBT for patients with various anxiety disorders, n = 33 | 11 | WLC, n = 27 | BAI (anxiety only) | Pre, post, 6MFU | TD group CBT: 55% post, 55% 6MFU; WLC: 66% post, 66% 6MFU |
| Ref. 88 | Spain | Depressive disorder, anxiety disorder | N = 128; mean age 41 yr; female 77% | TD-CBT, n = 33 | 8 | WLC, n = 34; other: BA, n = 34; other: ACT, n = 27 | GAD-7, BDI-IA | Pre, post, 3MFU, 6MFU | TD-CBT: 15% post, 18% 3MFU, 21% 6MFU; WLC: 24% post, 24% 3MFU, 24% 6MFU; BA: 29% post, 38% 3MFU, 38% 6MFU; ACT: 22% post, 26% 3MFU, 30% 6MFU |
| Ref. 89 | Germany | PTSD, MDD | N = 24; mean age 22 yr; female 0% | CA-CBT+, n = 12 | 12 | WLC, n = 12 | PHQ-9 (depression only) | Pre, post, 12MFU | CA-CBT+: 0% post, 0% 12MFU; WLC: 0% post, 0% 12MFU |
| Ref. 90 | the Netherlands | SAD, GAD, PD, AG, SP, anxiety NOS | N = 129; mean age 34 yr; female 71% | CBT, n = 67 | 15 | Other: AET, n = 62 | SCL-90 subscale for anxiety, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU, 6MFU, 12MFU | CBT: 25% post, 39% 3MFU, 53% 6MFU, 63% 12MFU; AET: 18% post, 27% 3MFU, 50% 6MFU, 71% 12MFU |
| Ref. 91 | Iran | MDD, DD, GAD, SAD | N = 70; mean age 35 yr; female 63% | UP, n = 35 | 12 | TAU, n = 35 | HADS-A, HADS-D | Pre, post | UP: 20% post; TAU: 34% post |
| Ref. 92 | Iran | Depressive disorder, anxiety disorder | N = 64; mean age 35 yr; female 100% | UP, n = 32 | 14 | TAU, n = 32 | HADS-A, HADS-D | Pre, post, 3MFU | UP: 6% post, 13% 3MFU; TAU: 13% post, 28% 3MFU |
| Ref. 93 | United States | PA, GAD, SAD, SP, OCD, PTSD, anxiety NOS, MDD, DD, depression NOS, SUD | N = 44; mean age 36 yr; female 66% | DBT-ST, n = 22 | 16 | Other: client-centred ST, n = 22 | OASIS, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 2MFU | DBT-ST: 32% post, 32% 2MFU; ST: 59% post, 59% 2MFU |
| Ref. 94 | United States | SAD, PA, GAD, anxiety NOS, OCD, SP | N = 85; mean age 33 yr; female 62% | TD group CBT, n = 64 | 12 | Other: comprehensive relaxation training programme, n = 21 | BAI (anxiety only) | Pre, post | TD group CBT: 36% post relaxation, 62% post |
| Ref. 95 | United States | SAD, GAD, PA | N = 46; mean age 31 yr; female 50% | TD group CBT, n = 23 | 12 | DS-CBT, n = 23 | STAI-S, BDI-II | Pre, post | TD group CBT: 30% post; DS-CBT: 48% post |
| Ref. 6 | United States | SAD, OCD, GAD, PA, PTSD | N = 19; mean age 40 yr; female 61% | TD group CBT, n = 9 | 12 | WLC, n = 10 | DASS-A DASS-Db | Pre, post | TD group CBT: 30% post; WLC: 10% post |
| Ref. 96 | Spain | GAD, PA, AG, OCD, PTSD, SAD, hypochondria, anxiety NOS, MDD, DD, unspecified mood disorder | N = 243; mean age 43 yr; female 79% | UP, n = 131 | 12 | TAU, n = 112 | PDSS, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU, 6MFU | UP: 34% post, 40% 3MFU, 51% 6MFU; TAU: 28% post, 39% 3MFU, 59% 6MFU |
| Ref. 97 | Spain | GAD, PA, AG, OCD, PTSD, SAD, hypochondria, anxiety NOS, MDD, DD, unspecified mood disorder | N = 488; mean age 43 yr; female 79% | UP, n = 279 | 12 | TAU, n = 209 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU, 6MFU | UP: 35% post, 43% 3MFU, 54% 6MFU; TAU: 28% post, 40% 3MFU, 52% 6MFU |
| Ref. 33 | Denmark | MDD, SAD, PD, AG | N = 191; mean age 32 yr; female 65% | UP, n = 98 | 14 | DS-CBT, n = 93 | HAM-A, HAM-D | Pre, post, 6MFU | UP: 0% post, 0% 6MFU; DS-CBT: 0% post, 0% 6MFU |
| Ref. 98 | Canada | GAD, SAD, PD, AG | N = 231; mean age 37 yr; female 86% | TD-CBT + TAU, n = 117 | 12 | TAU, n = 114 | BAI, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 4MFU, 8MFU | TD-CBT: 19% post; TAU: 7% post |
| Ref. 99 | Belgium | GAD, MDD | N = 80; mean age 43 yr; female 66% | RNT-G, n = 45 | 8 | WLC, n = 35 | STAI-S, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU, 9MFU | RNT-G: 7% post, 7% 3MFU, 7% 9MFU; WLC: 14% post |
| Ref. 46 | United States | PA, GAD, SAD | N = 96; mean age 36 yr; female 72% | F-SET, n = 57 | 10 | WLC, n = 39 | SPRAS, BDI-II | Pre, post, 6MFU | F-SET: 7% post, 26% 6MFU; WLC: 0% post, NA 6MFU |
| Ref. 100 | Iran | GAD, SAD, PD | N = 43; mean age 23 yr; female 67% | UP, n = 20 | 14 | WLC, n = 23 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU | UP: not reported; WLC: not reported |
| Internet-based treatment format | |||||||||
| Ref. 101 | Switzerland, Germany and Austria | SAD, PA, GAD | N = 139; mean age 42 yr; female 71% | Velibra, unguided (TD-iCBT + TAU), n = 70 | 6 | TAU (everything; no restrictions), n = 69 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 6MFU | Velibra: 19% post, 37% 6MFU; TAU: 9% post, NA 6MFU |
| Ref. 102 | Australia | GAD | N = 338; mean age 44 yr; female 76% | Well-being course, guided and unguided (TD-iCBT), n = 170 | 5 | DS-iCBT for GAD, guided and unguided, n = 168 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU, 12MFU, 24MFU | Well-being course: 16% post, 21% 3MFU, 25% 12MFU, 26% 24MFU; DS-iCBT: 17% post, 15% 3MFU, 21% 12MFU, 20% 24MFU |
| Ref. 103 | Australia | SAD | N = 220; mean age 42 yr; female 58% | Well-being course, guided and unguided (TD-iCBT), n = 105 | 5 | DS-iCBT for SAD, guided and unguided, n = 115 | MINI-SPIN, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU, 12MFU, 24MFU | Well-being course: 21% post, 22% 3MFU, 27% 12MFU, 22% 24MFU; DS-iCBT: 23% post, 28% 3MFU, 23% 12MFU, 23% 24MFU |
| Ref. 104 | Spain | MDD, DD, GAD, PD/AG, PD, AG, SAD, OCD, anxiety NOS, depression NOS | N = 216; mean age 34 yr; female 72% | TIBP, unguided, n = 71; TIBP + positive affect, unguided, n = 73 | 18 | WLC, n = 72 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post | TIBP: 37% post; TIBP + positive affect: 37% post; WLC: 24% post |
| Ref. 105 | Australia | PA | N = 145; mean age 41 yr; female 79% | Well-being course, guided and unguided (TD-iCBT), n = 72 | 5 | DS-iCBT for PA, guided and unguided, n = 73 | PDSS, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU, 12MFU, 24MFU | Well-being course: 11% post, 12% 3MFU, 18% 12MFU, 24% 24MFU; DS-iCBT: 20% post, 20% 3MFU, 26% 12MFU, 23% 24MFU |
| Ref. 106 | Spain | GAD, AG, PD, SAD, OCD, MDD, DD, anxiety NOS, depression NOS | N = 200; mean age 38 yr; female 69% | Emotion regulation, guided (TIBP), n = 99 | 18 | TAU, n = 101 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post, 3MFU, 12MFUc | Emotion regulation: 36% post, 48% 3MFU, 57% 12MFU; TAU: 34% post, 45% 3MFU, 56% 12MFU |
| Ref. 107 | Australia | GAD, SAD, PA | N = 131; mean age 42 yr; female 59% | Anxiety programme, guided (TD-iCBT), n = 89 | 8 | WLC, n = 42 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU | Anxiety programme: 9% post, 17% 3MFU; WLC: 2% post, 19% 3MFU |
| Ref. 108 | Australia | MDD, GAD, SAD, PD, AG, OCD | N = 158; mean age 39 yr; female 86% | iCBT, guided, n = 39; ME-iCBT, guided, n = 40 | 6 | TAU, n = 39; iMT, guided, n = 40 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU | iCBT: 23% post, 33% 3MFU; ME-iCBT: 33% post, 28% 3MFU; TAU: 15% post, NA 3MFU; iMT: 38% post, 48% 3MFU |
| Ref. 109 | China | Anxiety disorders, depressive disorders, other emotion-related disorders | N = 75; mean age 32 yr; female 71% | iMIED + TAU, n = 37 | 8 | TAU, n = 38 | BAI, BDI-II | Pre, post | iMIED+TAU: 22% post; TAU: 5% post |
| Ref. 110 | Australia | GAD, PA, SAD, MDD | N = 53; mean age 28 yr; female 64% | UniWellbeing course, guided (TD-iCBT for students), n = 30 | 5 | WLC, n = 23 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU | UniWellbeing: 30% post, 40% 3MFU; WLC: 9% post, NA 3MFU |
| Ref. 111 | Australia | GAD, MDD | N = 100; mean age 44 yr; female 78% | Worry and sadness programme, guided (TD-iCBT), n = 46 | 6 | WLC, n = 54 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU | Worry and sadness: 7% post, 13% 3MFU; WLC: 2% post, NA 3MFU |
| Ref. 112 | Germany | AG, GAD, PD, SAD, MDD, persistent depressive disorder, somatic symptom disorder, illness anxiety disorder | N = 129; mean age 37 yr; female 68% | Internet-based UP, guided, n = 65 | 10 | WLC, n = 64 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post | UP: 35% post; WLC: 11% post |
| Ref. 113 | Australia | GAD, SAD, PA | N = 78; mean age 40 yr; female 68% | Anxiety programme, guided (TD-iCBT), n = 40 | 6 | WLC, n = 38 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU | TD: 10% post, 20% 3MFU; WLC: 5% post, NA 3MFU |
| Ref. 114 | Australia | GAD, PA, SAD, MDD | N = 74; mean age 44 yr; female 73% | Well-being programme, guided (TD-iCBT), n = 37 | 8 | WLC, n = 37 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU | TD: 8% post, 14% 3MFU; WLC: 5% post, NA 3MFU |
| Ref. 115 | Australia | MDD | N = 290; mean age 44 yr; female 72% | Well-being course, guided (TD-iCBT), n = 149 | 5 | DS-iCBT for MDD, n = 142 | GAD-7, PHQ-9 | Pre, post, 3MFU, 12MFU, 24MFU | TD: 5% post, 20% 3MFU, 30% 12MFU, 24% 24MFU; DS-iCBT: 16% post, 16% 3MFU, 20% 12MFU, 18% 24MFU |
| Ref. 116 | Romania | GAD, SAD, PA, PTSD, SP, OCD, NOS, MDD | N = 97; mean age 34 yr; female 81% | Internet-based UP, guided, n = 64 | 9 | WLC, n = 33 | OASIS, BDI-II | Pre, post, 6MFU | UP: 22% post, 45% 3MFU; WLC: 6% post, NA 6MFU |
| Ref. 117 | Afghanistan | Depressive disorder, anxiety disorder | N = 102; mean age 28 yr; female 47% | Internet-based UP, unclear whether guided or unguided, n = 51 | 12–14 | TAU, n = 51 | OASIS, ODSIS | Pre, post | UP: 22% post; TAU: 39% post |
ACT, acceptance and commitment therapy; AET, autonomy enhancing therapy; AG, agoraphobia; ART, affect regulation training; ASI, anxiety sensitivity index; AUD, alcohol use disorder; BA, behavioural activation; BDI, Beck depression inventory; BSI, brief symptom inventory; CALM, coordinated anxiety learning and management; CA-CBT+, culturally adapted cognitive behaviour therapy plus problem management; CBT-P, CBT for perfectionism; CFC, common factor control; CPRS-S-A, self-rating-scale for affective syndromes; CS, construct-specific; DASS, short form of depression, anxiety and stress scale; DBT-ST, dialectical behaviour therapy skills training; DD, dysthymic disorder; DS, disorder-specific; ERT, emotion regulation therapy; ESTEEM, effective skills to empower effective men; EUC, enhanced usual care; F-SET, false safety behaviour elimination therapy; HADS, hospital anxiety and depression scale; HAM-A, Hamilton anxiety rating scale; HAM-D, Hamilton depression rating scale; iCBT, internet-based CBT; iMIED, internet-based self-help mindfulness intervention for emotional distress; iMT, mindfulness training; MAC, modified attention control; ME-iCBT, mindfulness-enhanced iCBT; MFU, month follow-up; MINI-SPIN, mini-social phobia inventory; MMI, multimodal intervention; NOS, not otherwise specified; OASIS, overall anxiety severity and impairment scale; OCD, obsessive compulsive disorder; ODSIS, overall depression severity and impairment scale; PA, panic disorder with/without agoraphobia; PD, panic disorder; PDSS, panic disorder severity scale; PHQ, patient health questionnaire; PTSD, post-traumatic stress disorder; QIDS, quick inventory of depressive symptomatology; RNT-G, group treatment for repetitive negative thinking; RT, resistance training; SCL, symptom checklist; SP, specific phobias; SPRAS, Sheehan patient-rated anxiety scale; ST, supportive therapy; STAI-S, state-trait anxiety inventory—state; SUD, substance use disorder; TBT, transdiagnostic behaviour therapy; tDCS, transcranial direct current stimulation; TIBP, transdiagnostic internet-based protocol; UP, unified treatment protocol for emotional disorders; WFU, week follow-up; WLC, waitlist control.
aMissing data as a percentage of randomized individuals who did not provide further assessments.
bData on depression-related outcomes (DASS-D) were provided by the authors upon request.
cData for 12MFU were provided in ref. 118.
Most of the studies were conducted in Europe (n = 16), the United States (n = 13) and Australia (n = 11). We could also include several RCTs from Iran (n = 9) and other countries. Samples investigated ranged in size from 19 to 1,004 participants (median = 94.5) and were mainly comprised of females (M = 66%, s.d. = 19%), with a median age of 37 years. Most frequent among included diagnoses were generalized anxiety disorder (GAD; 79%), social anxiety disorder (SAD; 70%) and major depressive disorder (MDD; 55%). Most studies investigated the UP (n = 23) or similar treatments. Supplementary Table 1 gives an overview of the TD-CBT protocols we included in our review. The mean number of sessions was 11.19 (s.d. = 4.32), with a range of 4–20 sessions. TD-CBT was most frequently compared to a waitlist condition (n = 25), followed by TAU (n = 18), other active treatments (n = 15) and DS-CBT (n = 8). Some RCTs included many comparison groups. Treatments were mainly carried out in a group setting (n = 21), followed by individual formats (n = 18) and internet-based approaches (n = 17). Self-report questionnaires on symptoms of anxiety and depression were included in nearly all studies, except for five (one included no self-reports, two assessed only anxiety and another two only depression). Most RCTs used many questionnaires. The Beck anxiety inventory (BAI) (k = 17) (ref. 23) and generalized anxiety disorder screener (GAD-7) (k = 14) (ref. 24) were most commonly used to measure anxiety and the Beck depression inventory (BDI-II) (k = 21) (ref. 25) and patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9) (k = 19) (ref. 26) to assess depression. Around 75% of RCTs included at least one follow-up assessment (typically at 3 or 6 months), allowing for the investigation of longer-term effectiveness. Sixteen studies included a second follow-up (mostly at 6 or 12 months) and eight reassessed participants for a third time (mostly at 24 months). Attrition rates at posttreatment in TD-CBT samples were similar compared to control condition samples but differed by treatment format (individual setting: M = 12%, s.d. = 13%; group setting: M = 21%, s.d. = 14%; internet-based setting: M = 20%, s.d. = 10%).
For the meta-analytic calculations, we excluded refs. 27,28 because the data were not available and ref. 29 because no self-report of anxiety or depression was available, which resulted in a total N = 6,705 individuals for the meta-analytic calculations.
Risk of bias assessment
Agreement between the two independent raters in coding the risk of bias criteria was strong (M = 90.31%, s.d. = 7.82%, range 73.58–100%). Instances of disagreement mainly reflect differing levels of a rating; for example, ‘yes’ versus ‘probably yes’ but not the general direction. All ratings and the code for analysis of percentage agreement can be found on the Open Science Framework repository (see Data availability and Code availability). Figure 2 provides an overview of the risk of bias assessment for the five domains rated (see the section on ‘Study quality assessment’) for the individual studies. In Supplementary Fig. 1, we also provide a summary plot, depicting the percentage of studies showing low/high risk of bias or some concerns in each domain. We found that, overall, the risk of bias assessment of most of the included studies showed some concerns and no study was free from any risk of bias. Although there were hardly any concerns about bias in the randomization process, all studies showed some concerns for blinding of therapists, as they needed to be aware of the protocol they were providing, and assessors because we only included self-report outcomes. While intention-to-treat analyses were conducted in most studies, few reported comprehensive tests of potential bias in results due to missing outcome data, raising some concerns. Finally, although trial registrations were available for almost all included RCTs, hardly any studies provided an a priori specified analysis plan.
Fig. 2. Risk of bias assessment.
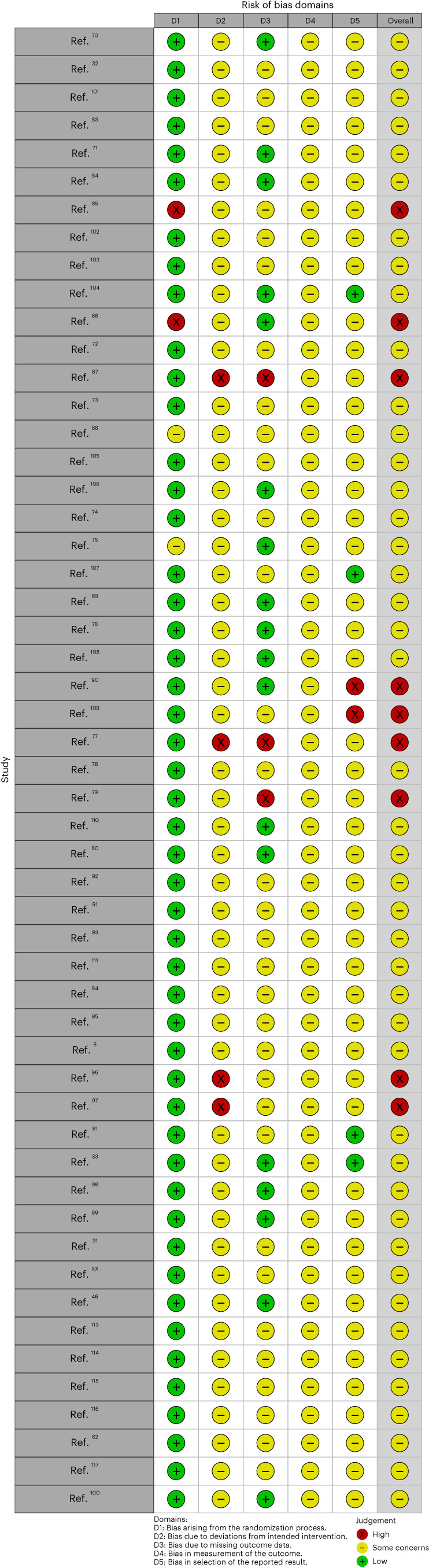
Traffic-light plot of the domain-level judgements. Risk of bias was assessed across five domains for each study included in the meta-analysis using the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (RoB 2.0). The combination of assessments in the five domains results in an overall risk of bias rating.
Meta-analysis
Controlled effect sizes
Tables 2 and 3 show controlled effect sizes as well as measures of heterogeneity (Q statistic and I2) for depression and anxiety outcomes for individual, group or internet-based settings, comparing TD-CBT to DS-CBT, TAU, waitlist and other treatments and for posttreatment as well as follow-ups. In addition, effect sizes and confidence intervals (CI) comparing TD-CBT to control for all three settings are displayed in the forest plots in Figs. 3 and 4 (posttreatment). Forest plots for the follow-up assessments are included in Supplementary Figs. 2–9.
Table 2.
Between-group effect sizes of depressive and anxiety symptoms for transdiagnostic treatments compared to control groups at posttreatment
| Depression | Anxiety | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | g | P | LL | UL | I2 | Q | P | k | g | P | LL | UL | I2 | Q | P | ||
| TD-CBT (all treatment formats) versus | Control | 63 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 0.57 | 0.92 | 88.29 | 344.96 | <0.001 | 61 | 0.77 | <0.001 | 0.56 | 0.97 | 91.72 | 398.55 | <0.001 |
| DS-CBT | 9 | 0.09 | 0.269 | -0.07 | 0.25 | 53.96 | 17.82 | 0.023 | 9 | 0.09 | 0.091 | −0.01 | 0.20 | 5.79 | 12.56 | 0.128 | |
| TAU | 18 | 0.90 | <0.001 | 0.66 | 1.14 | 77.28 | 61.55 | <0.001 | 17 | 0.98 | <0.001 | 0.63 | 1.33 | 89.75 | 101.68 | <0.001 | |
| Other | 13 | 0.27 | <0.001 | 0.13 | 0.42 | 0.010 | 13.76 | 0.316 | 13 | 0.14 | 0.128 | −0.04 | 0.31 | 17.67 | 15.33 | 0.224 | |
| WL | 23 | 1.23 | <0.001 | 0.80 | 1.66 | 92.85 | 124.8 | <0.001 | 22 | 1.24 | <0.001 | 0.82 | 1.67 | 92.26 | 122.48 | <0.001 | |
| Individual TD-CBT versus | Control | 18 | 0.90 | <0.001 | 0.57 | 1.23 | 75.88 | 68.17 | <0.001 | 17 | 1.09 | <0.001 | 0.62 | 1.56 | 87.16 | 98.86 | <0.001 |
| DS-CBT | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| TAU | 4 | 1.08 | <0.001 | 0.73 | 1.43 | 0 | 3.11 | 0.374 | 3 | 1.33 | 0.002 | 0.49 | 2.16 | 74.24 | 7.23 | 0.027 | |
| Other | 5 | 0.49 | 0.011 | 0.11 | 0.86 | 25.73 | 5.99 | 0.200 | 5 | 0.25 | 0.187 | −0.12 | 0.62 | 26.40 | 5.28 | 0.259 | |
| WL | 7 | 1.40 | <0.001 | 0.87 | 1.93 | 71.24 | 23.89 | <0.001 | 7 | 1.71 | <0.001 | 0.87 | 2.55 | 87.80 | 34.67 | <0.001 | |
| Group-based TD-CBT versus | Control | 24 | 0.87 | <0.001 | 0.41 | 1.32 | 96.09 | 167.38 | <0.001 | 23 | 0.76 | <0.001 | 0.32 | 1.20 | 95.56 | 188.36 | <0.001 |
| DS-CBT | 3 | 0.16 | 0.307 | −0.15 | 0.48 | 59.79 | 4.98 | 0.083 | 3 | 0.14 | 0.331 | −0.14 | 0.41 | 49.59 | 3.69 | 0.158 | |
| TAU | 8 | 0.94 | <0.001 | 0.49 | 1.40 | 88.94 | 39.16 | <0.001 | 8 | 1.04 | 0.003 | 0.36 | 1.73 | 95.08 | 68.66 | <0.001 | |
| Other | 6 | 0.23 | 0.017 | 0.04 | 0.41 | 0.010 | 5.50 | 0.358 | 6 | 0.07 | 0.669 | −0.24 | 0.37 | 49.27 | 9.49 | 0.091 | |
| WL | 7 | 1.88 | 0.027 | 0.21 | 3.55 | 98.14 | 84.02 | <0.001 | 6 | 1.52 | 0.033 | 0.12 | 2.92 | 96.85 | 66.10 | <0.001 | |
| Internet-based TD-CBT versus | Control | 21 | 0.61 | <0.001 | 0.42 | 0.80 | 78.45 | 101.63 | <0.001 | 21 | 0.58 | <0.001 | 0.39 | 0.78 | 79.16 | 97.35 | <0.001 |
| DS-CBT | 4 | 0.08 | 0.563 | −0.18 | 0.33 | 70.37 | 11.37 | 0.010 | 4 | 0.03 | 0.662 | −0.11 | 0.17 | 0 | 0.47 | 0.925 | |
| TAU | 6 | 0.79 | <0.001 | 0.46 | 1.12 | 69.03 | 15.73 | 0.008 | 6 | 0.76 | <0.001 | 0.43 | 1.09 | 69.15 | 16.09 | 0.007 | |
| Other | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| WL | 9 | 0.86 | <0.001 | 0.72 | 1.01 | 0 | 7.89 | 0.444 | 9 | 0.83 | <0.001 | 0.66 | 1.00 | 20.87 | 11.07 | 0.198 | |
k = number of comparisons; LL = lower limit of 95% CI; UL = upper limit of 95% CI. I2 values are reported as percentage (%). Comparisons with k < 3 studies are not reported.
Table 3.
Between-group effect sizes of depressive and anxiety symptoms for transdiagnostic treatments compared to control groups at follow-up
| Depression | Anxiety | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | g | P | LL | UL | I2 | Q | P | k | g | P | LL | UL | I2 | Q | P | |||
| 3 month FU | TD-CBT (all treatment formats) versus | Control | 29 | 0.55 | <0.001 | 0.30 | 0.80 | 89.98 | 143.19 | <0.001 | 24 | 0.48 | 0.002 | 0.18 | 0.79 | 92.31 | 131.28 | <0.001 |
| DS-CBT | 5 | 0.11 | 0.376 | −0.14 | 0.37 | 77.81 | 15.73 | 0.003 | 5 | −0.01 | 0.912 | −0.18 | 0.16 | 52.62 | 8.48 | 0.075 | ||
| TAU | 6 | 0.42 | <0.001 | 0.26 | 0.59 | 6.45 | 6.77 | 0.238 | 4 | 0.49 | <0.001 | 0.22 | 0.76 | 51.43 | 6.24 | 0.101 | ||
| Other | 10 | 0.33 | 0.014 | 0.07 | 0.59 | 57.15 | 20.99 | 0.013 | 8 | 0.24 | 0.009 | 0.06 | 0.42 | 0 | 9.69 | 0.207 | ||
| WL | 8 | 1.29 | 0.002 | 0.47 | 2.10 | 93.43 | 70.96 | <0.001 | 7 | 1.31 | 0.016 | 0.24 | 2.37 | 94.84 | 77.31 | <0.001 | ||
| Individual TD-CBT versus | Control | 8 | 1.38 | <0.001 | 0.64 | 2.13 | 90.69 | 51.37 | <0.001 | 5 | 1.88 | 0.002 | 0.72 | 3.03 | 91.25 | 50.83 | <0.001 | |
| Group-based TD-CBT versus | Control | 12 | 0.39 | 0.002 | 0.14 | 0.63 | 74.49 | 31.78 | <0.001 | 10 | 0.42 | <0.001 | 0.20 | 0.65 | 61.80 | 22.45 | 0.008 | |
| Internet-based TD-CBT versus | Control | 9 | 0.18 | 0.127 | −0.05 | 0.42 | 73.17 | 27.64 | <0.001 | 9 | −0.05 | 0.409 | −0.17 | 0.07 | 2.55 | 7.89 | 0.444 | |
| 6 month FU | TD-CBT (all treatment formats) versus | Control | 17 | 0.20 | <0.001 | 0.10 | 0.30 | 17.75 | 24.09 | 0.088 | 19 | 0.23 | <0.001 | 0.11 | 0.36 | 42.99 | 34.74 | 0.010 |
| DS-CBT | 3 | −0.01 | 0.937 | −0.23 | 0.21 | 39.89 | 3.28 | 0.194 | 3 | 0.04 | 0.650 | −0.15 | 0.24 | 22.99 | 2.33 | 0.312 | ||
| TAU | 4 | 0.26 | <0.001 | 0.15 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.74 | 0.864 | 4 | 0.32 | 0.001 | 0.13 | 0.52 | 47.22 | 5.67 | 0.129 | ||
| Other | 7 | 0.15 | 0.163 | −0.06 | 0.37 | 10.92 | 6.13 | 0.409 | 8 | 0.19 | 0.050 | 0 | 0.38 | 0 | 6.19 | 0.518 | ||
| WL | 3 | 0.63 | 0.019 | 0.10 | 1.15 | 47.71 | 3.82 | 0.148 | 4 | 0.62 | 0.065 | −0.04 | 1.27 | 77.44 | 11.90 | 0.008 | ||
| Individual TD-CBT versus | Control | 9 | 0.24 | 0.012 | 0.05 | 0.44 | 44.45 | 14.07 | 0.080 | 10 | 0.28 | <0.001 | 0.18 | 0.38 | 0 | 18.92 | 0.026 | |
| Group-based TD-CBT versus | Control | 8 | 0.16 | 0.033 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 16.49 | 9.45 | 0.222 | 9 | 0.17 | 0.065 | −0.01 | 0.36 | 46.53 | 14.41 | 0.072 | |
| Internet-based TD-CBT versus | Control | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| 12 month FU | TD-CBT (all treatment formats) versus | Control | 11 | 0.24 | <0.001 | 0.13 | 0.35 | 33.53 | 13.48 | 0.198 | 11 | 0.22 | <0.001 | 0.12 | 0.32 | 24.83 | 10.52 | 0.396 |
| DS-CBT | 4 | 0.13 | 0.247 | −0.09 | 0.36 | 58.91 | 7.48 | 0.058 | 4 | 0.08 | 0.253 | −0.06 | 0.23 | 0 | 0.87 | 0.832 | ||
| TAU | 4 | 0.35 | <0.001 | 0.24 | 0.47 | 0 | 0.30 | 0.960 | 4 | 0.36 | <0.001 | 0.24 | 0.48 | 0 | 0.70 | 0.872 | ||
| Other | 3 | 0.23 | 0.030 | 0.02 | 0.44 | 0 | 0.03 | 0.985 | 3 | 0.21 | 0.044 | 0.01 | 0.42 | 0 | 0.10 | 0.950 | ||
| WL | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Individual TD-CBT versus | Control | 3 | 0.33 | <0.001 | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0 | 0.58 | 0.748 | 3 | 0.34 | <0.001 | 0.20 | 0.47 | 9.71 | 1.67 | 0.434 | |
| Group-based TD-CBT versus | Control | 3 | 0.30 | 0.006 | 0.09 | 0.51 | 0 | 0.59 | 0.745 | 3 | 0.27 | 0.012 | 0.06 | 0.48 | 0 | 0.24 | 0.888 | |
| Internet-based TD-CBT versus | Control | 5 | 0.17 | 0.098 | −0.03 | 0.38 | 54.63 | 8.93 | 0.063 | 5 | 0.11 | 0.116 | −0.03 | 0.24 | 0 | 1.95 | 0.746 | |
| 24 month FU | TD-CBT (all treatment formats) versus | Control | 5 | 0.20 | 0.111 | −0.05 | 0.46 | 80.63 | 16.44 | 0.003 | 5 | 0.14 | 0.092 | −0.02 | 0.31 | 56.46 | 8.63 | 0.071 |
| DS-CBT | 4 | 0.20 | 0.259 | −0.14 | 0.54 | 81.90 | 16.15 | 0.001 | 4 | 0.11 | 0.344 | −0.12 | 0.35 | 62.33 | 8.25 | 0.041 | ||
| TAU | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Other | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| WL | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||
| Individual TD-CBT versus | Control | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Group-based TD-CBT versus | Control | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | |
| Internet-based TD-CBT versus | Control | 4 | 0.20 | 0.259 | −0.14 | 0.54 | 81.90 | 16.15 | 0.001 | 4 | 0.11 | 0.344 | −0.12 | 0.35 | 62.33 | 8.25 | 0.041 | |
FU, follow-up.
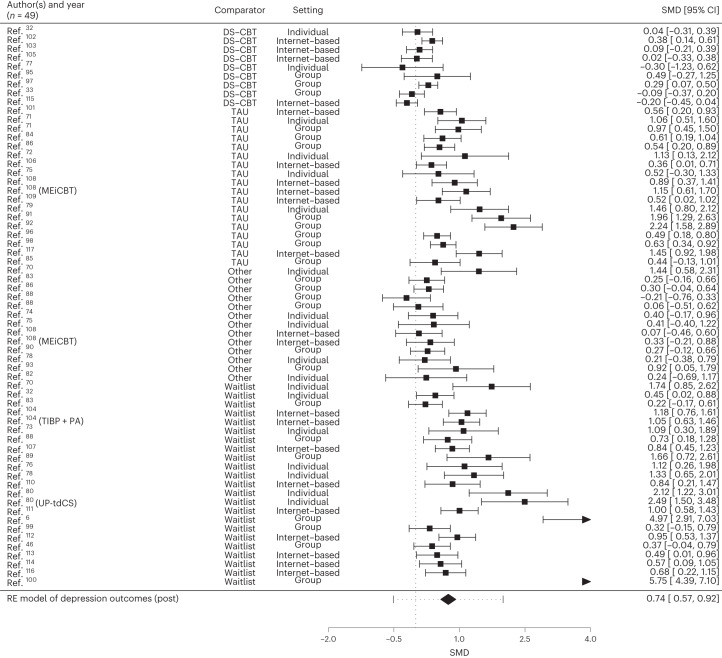
Fig. 3. Forest plots of controlled effect sizes (posttreatment) for depression.
Studies are clustered according to the setting in which they investigated TD-CBT. One study88 compared TD-CBT to ACT and BA. We used a random-effects (RE) model to estimate pooled effects. n denotes the number of studies included. For each study, the black square represents the effect size (standardized mean difference, SMD) and the horizontal bars represent the 95% CI. The overall estimated effect size (Hedges‘ g) is depicted by the diamond with the dotted bars representing its 95% CI.
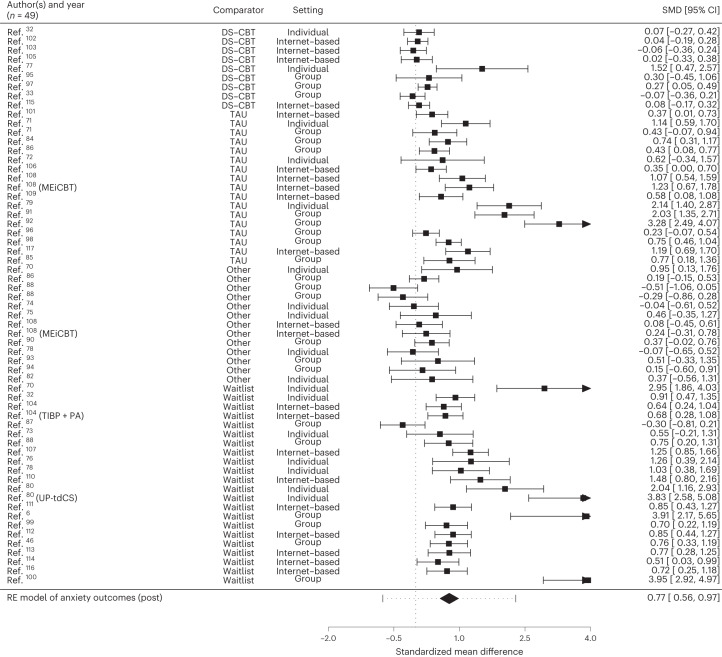
Fig. 4. Forest plots of controlled effect sizes (posttreatment) for anxiety.
Studies are clustered according to the setting in which they investigated TD-CBT. One study88 compared TD-CBT to ACT and BA. We used an RE model to estimate pooled effects. n denotes the number of studies included. For each study, the black square represents the effect size SMD and the horizontal bars represent the 95% CI. The overall estimated effect size (Hedges‘ g) is depicted by the diamond with the dotted bars representing its 95% CI.
Across settings, TD-CBT revealed significantly stronger symptom reduction in depression (g = 0.74, 95% CI = 0.57–0.92, P < 0.001) and anxiety (g = 0.77, 95% CI = 0.56–0.97, P < 0.001) than controls at posttreatment. TD-CBT showed superiority to waitlist for depression (g = 1.23, 95% CI = 0.80–1.66, P < 0.001) and anxiety (g = 1.24, 95% CI = 0.82–1.67, P < 0.001) and to TAU for depression (g = 0.90, 95% CI = 0.66–1.14, P < 0.001) and anxiety outcomes (g = 0.98, 95% CI = 0.63–1.33, P < 0.001) with large effects. We found no statistically significant difference between TD-CBT and DS-CBT in alleviating depressive (g = 0.09, 95% CI = −0.07–0.25, P = 0.269) and anxiety symptoms (g = 0.09, 95% CI = −0.01–0.20, P = 0.091). The comparison between TD-CBT and DS-CBT was corroborated by conducting more Bayesian analyses. A description of the statistical procedure for the Bayesian analyses as well as forest plots for the original model and sensitivity analyses can be found in Supplementary Figs. 22–27. Estimated effect sizes confirmed the frequentist findings for depression (g = 0.09, 95% CI = −0.12–0.27) and anxiety (g = 0.09, 95% CI = −0.04–0.24). In comparison to other active control groups (including bona fide treatments), TD-CBT was more effective for depression (g = 0.27, 95% CI = 0.13–0.42, P < 0.001) with small effects but not for anxiety (g = 0.14, 95% CI = −0.04–0.31, P = 0.128). TD-CBT was superior to controls at 3 months follow-up (depression g = 0.55, 95% CI = 0.30–0.80, P < 0.001; anxiety g = 0.48, 95% CI = 0.18–0.79, P = 0.002), at 6 months follow-up (depression g = 0.20, 95% CI = 0.10–0.30, P < 0.001; anxiety g = 0.23, 95% CI = 0.11–0.36, P < 0.001) and at 12 months follow-up (depression g = 0.24, 95% CI = 0.13–0.35, P < 0.001; anxiety g = 0.22, 95% CI = 0.12–0.32, P < 0.001) but not at 24 months follow-up (depression g = 0.20, 95% CI = −0.05–0.46, P = 0.111; anxiety g = 0.14, 95% CI = −0.02–0.31, P = 0.092). Overall, we found high and significant heterogeneity amongst studies (against all controls at posttreatment: I2 = 88.29% for depression and I2 = 91.72% for anxiety), which remained high after isolating treatment format. Results for sensitivity analyses are provided in Supplementary Tables 5–8. When removing outliers (Supplementary Tables 5 and 6) heterogeneity was reduced with comparable effects.
Uncontrolled effect sizes
Uncontrolled effect sizes and their CI as well as measures of heterogeneity (Q statistic and I2) for anxiety and depression outcomes for all three settings, from pre- to postassessment and at follow-ups, are reported in Supplementary Table 4 and Supplementary Figs. 10–19.
Publication bias
Statistical analyses indicated asymmetry of funnel plots for controlled effects (Kendall’s tau = 0.36–0.38, P < 0.001; Egger’s test Z = 6.89–7.45, P < 0.001). Funnel plots, with and without trim and fill method, for the controlled effects for anxiety and depression (posttreatment) are provided in Supplementary Figs. 20 and 21.
Discussion
TD-CBT for emotional disorders attracted increased attention and considerable research activity in recent years. This is reflected in the large number of 56 RCTs with 6,916 patients included in our comprehensive review on individual, group and internet-based formats.
Overall, TD-CBT was effective in both the short and long terms. Most studies compared TD-CBT to waitlist-control conditions and yielded large effect sizes in line with previous benchmarks30. Our review and meta-analysis also included active control groups. We found that TD-CBT produced large effects in comparison to TAU which comprised very heterogeneous setups, ranging from low-key treatments to clinician-tailored personalized interventions (for example, ref. 31). In comparison to other active treatments, such as behavioural activation or CBT for perfectionism, TD-CBT had a stronger impact on depression, with small effects but not on anxiety. Of special interest is how TD-CBT compares to gold-standard DS-CBT (for example, evidence-based manualized individual therapy in one trial32 or group treatments in another trial33). Overall, TD-CBT produced comparable effects to DS-CBT, with no significant differences emerging between both approaches. The comparability of TD-CBT to DS-CBT was investigated in previous meta-analyses with mixed findings: ref. 22 found TD-CBT to produce comparable effects to DS-CBT for anxiety outcomes but to surpass DS-CBT in its efficacy for depression outcomes. While ref. 15 found TD-CBT to produce significantly greater effects than DS-CBT, their results also suggested that these differences may not be clinically significant. With our meta-analysis including more studies that directly compare TD-CBT and DS-CBT in RCTs, our findings provide further evidence of the comparability of TD-CBT and DS-CBT.
We have also investigated effects beyond the immediate end of treatment. While uncontrolled effects should be interpreted cautiously as they cannot be causally interpreted, we did find that the effects of TD-CBT remained stable over time, based on follow-up assessments at 3, 6 and 12 months. Five studies—four of them stemming from the same research group and investigating internet-based interventions—also included a long-term follow-up up to 24 months. For this long-term follow-up, we found large effects over time for TD-CBT on anxiety and depression outcomes (standardized mean changes (dSMC)) = 1.47–1.75), with no significant differences between TD-CBT and DS-CBT. While more research by independent groups is warranted, this comparability underlines the potential of TD-CBT and strengthens the argument for a broadly applicable, transdiagnostic approach, with high scalability and reach.
Concerning the different settings we have investigated, we found comparable effects between all three settings, individual, group and internet-based. There was a strong uptake of TD protocols in group and internet-based settings. Applying TD-CBT as a group treatment may be beneficial in health care systems with limited resources. On top of groups saving therapeutic resources, TD-CBT groups specifically may be a more feasible approach to delivering evidence-based care than offering disorder-specific groups. The comparable effects of the individual and internet-based setting strengthen the evidence for the comparability of both settings12,34. Delivering TD protocols online or in conjunction with in-person sessions (‘blended care’) may even boost the potential of TD-CBT to reduce the treatment gap for those in need: TD internet-based interventions are not only highly effective, they also address barriers to treatment access and can reach underserved communities, such as those living in geographically remote areas (for example, refs. 35,36) or those with limited mobility, for example, due to chronic physical conditions37.
Our study is not without limitations. We included anxiety, obsessive compulsive, depressive as well as adjustment disorders as primary diagnoses in our review, with most studies investigating TD-CBT for GAD, SAD and MDD. We can neither draw conclusions about the efficacy of TD-CBT for individual diagnoses nor judge its efficacy for other diagnoses which, depending on the definition, are also counted among the emotional disorders (for example, somatic symptom disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder or borderline personality disorder). TD-CBT was investigated in different continents and countries, speaking to its dissemination potential. However, investigations from South America and Africa were under-represented.
The risk of bias assessment revealed possible sources of bias especially in terms of blinding of assessors, patients and therapists—which can be expected given our focus on self-report measures and psychotherapy trials. However, we also found concerns in terms of selective reporting which highlighted that more open science practices in psychotherapy research are warranted, from preregistered analyses plans to open data sharing. This would facilitate replications by independent research groups which are needed to explore the generalizability of our findings and preclude allegiance effects which some of our included studies may be at risk of38–40. The implementation of such practices may also help to counteract publication bias. We found exceptionally high heterogeneity of effects. Overall heterogeneity decreased when taking treatment format into account and removing outliers. Future research should investigate whether other clinical or methodological factors such as mechanisms targeted in the TD-CBT protocol, treatment dose, patient or study characteristics might have an impact. An individual participant data meta-analysis would be a key next step in this regard. It also remains unclear if there are any contraindications for TD-CBT, since symptom deterioration, comorbidity and dropout were not systematically examined. Moreover, the clinical relevance of symptom improvement is yet to be investigated and outcome measures beyond symptoms of depression and anxiety, such as quality of life or level of functioning, should be explored. We chose to exclusively study adult populations for our investigation of TD-CBT due to differences in developmental adaptations of treatments, classifications of emotional disorders, outcome measures and treatment efficacy between child/adolescent and adult populations. We focused our review on unified ‘broadband’ TD-CBT that aims at changing mechanisms shared between disorders. With the surge of research on personalized interventions41, it may be a fruitful next step to investigate the merit of personalizing unified TD-CBT interventions as well. TD-CBT promises to facilitate training and clinical decision-making, rendering training and treatment less costly. A first study investigated the cost-effectiveness of TD-CBT and found that it may be a cost-effective alternative to TAU42,43. However, more research on whether the proposed advantages, for example, in terms of training times and cost-effectiveness, generally hold true is needed.
Our analyses provide evidence that TD-CBT in face-to-face individual, group and internet-based formats is efficacious in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression. Evidence from trials on internet-based TD-CBT revealed large and stable long-term effects. Taken together, these findings further strengthen the transdiagnostic approach to the treatment of emotional disorders across settings.
Methods
This study is based exclusively on published literature, therefore no ethics approval was required. In conducting and reporting this review and meta-analysis, we followed the Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews44 and the updated PRISMA45. The protocol was registered with PROSPERO on 27 September 2019 (registration no. CRD42019141512).
Search strategy
A systematic literature search was conducted on PubMed and MEDLINE, PsycINFO, Google Scholar, medRxiv (including bioRxiv) and OSF Preprints up to 16 June 2023. Different to what we preregistered, our search covered preprint servers to consider also the most recent findings. We built a search string by combining the concepts ‘transdiagnostic’, ‘CBT’, ‘emotional disorder’ and ‘RCT’ using the AND Boolean operator. Each concept included terms connected with the OR Boolean operator. The concept ‘CBT’ also covered terms describing the treatment setting (for example, ‘internet-based intervention’). We searched for relevant medical subject headings (MeSH), used by the United States National Library of Medicine to index articles in PubMed and MEDLINE (for example, ‘cognitive behavioural therapy’, ‘anxiety’, ‘depression’). In addition, we included terms commonly used in the relevant literature (for example, ‘unified’). The resulting string was then slightly adapted according to the search options of the different databases (see Supplementary Table 2 for the complete search strings). We included additional studies if they were identified by reference lists and met our inclusion criteria. We used Zotero (v.6.0.23) and Google Sheets.
Inclusion criteria
We included studies published between January 2000 up until June 2023.
Population
Studies were included if the treatment was delivered to treatment-seeking adults. Deviating from our preregistration, we did not apply an upper age limit of 65 years, if the study was not solely targeted at older adults and the mean age of the study population was comparable to other studies with adult populations. We opted for this change to provide a more comprehensive review. Participants had at least one clinician-established diagnosis of an emotional disorder. We included SAD, panic disorder, agoraphobia, GAD, obsessive compulsive disorder, unipolar depressive disorders and adjustment disorders as treatment targets.
Interventions
We selected studies that investigated TD-CBT in an individual, group or internet-based setting (with or without clinician guidance). This included established unified comprehensive TD protocols that were specifically developed to target underlying processes or comorbidity such as the UP5, false behaviour elimination therapy46, emotion regulation therapy47, affect regulation training48 or transdiagnostic behaviour therapy7. We also included protocols that contained CBT components that modified dysfunctional cognitions and behavioural patterns across diagnostic groups, for example, cognitive restructuring. Following this definition, we included ‘common elements approaches’49 if they were presented in a UP, that is, a combination of effective components across disorders. As our focus was not on third wave or experiential approaches within CBT, we excluded standalone mindfulness-based treatment approaches50,51, metacognitive therapy/ training52 and acceptance and commitment therapy53,54. We also excluded protocols targeting transdiagnostic phenomena that cannot be considered shared mechanisms between disorders, such as protocols focusing on self-worth or loneliness.
Comparison groups
We included studies that compared TD-CBT to a control group, including (1) waitlist-control condition (that is, delayed treatment), (2) TAU, (3) DS-CBT and (4) other active psychological interventions. TAU included all treatments that the original study defined as ‘usual care’, ‘standard care’ or ‘care as usual’55. Other active psychological interventions included interventions that are based on a psychological rationale but are neither considered TAU nor diagnosis-specific treatments, for example, behavioural activation.
Outcomes
Included studies applied a continuous self-report measure of anxiety and/or depression severity at pre- and posttreatment and (if available) at follow-up.
Study design
RCTs were included.
Exclusion of studies
We excluded studies if (1) the treatment was not based on CBT principles, such as psychodynamic interventions and process-experiential principles and (2) they investigated a modularized or tailored treatment, as we did not consider this in line with the concept of unified TD-CBT. Supplementary Table 3 provides an overview of reasons for exclusions for all excluded studies that were full-text screened.
Study selection and data extraction
Two reviewers independently screened search results based on title and abstract, evaluated potentially eligible publications through full-text read, selected studies matching the inclusion criteria and extracted data for the meta-analysis. Selection results were compared and any disagreements about eligibility were resolved through discussion and in consultation with the project leaders. Interrater-agreement was reached for 95% of the reviewed studies. If not reported in the publication, data were requested directly from study authors. We contacted 35 authors and sent up to two follow-up emails in case of no response, 69% of the authors sent us requested data. We extracted means and standard deviations of self-reported anxiety and/or depression at all available time points corresponding to pre- and posttreatment as well as follow-up. We grouped follow-up time points on the basis of the most frequent reassessments in the included studies. Most of the studies reassessed participants at exactly 3 months (n = 22 studies), 6 months (n = 16 studies), 12 months (n = 10 studies) or 24 months (n = 4 studies). Only one study had a shorter follow-up than 3 months, two studies had a follow-up between 3 and 6 months, four studies between 6 and 12 months and one study between 12 and 24 months. For the few studies with follow-ups falling in between those four measurement points, we allocated the data to the time point to which they were closest.
As many studies reported more than one outcome measure for anxiety or depression, we used the primary outcome measure defined by the study authors or, if this was not available, the measure most commonly used across studies in our final sample. Other variables extracted were control group (waitlist/TAU/DS-CBT/other) and treatment setting (individual/group/internet-based). Studies were grouped for synthesis by type of control group and treatment setting.
Statistical analyses
All analyses were conducted in R (v.4.3.1), using the metafor56 (v.4.2-0), meta57 (v.6.5-0) and dmetar packages58 (v.0.1.0).
We calculated controlled effect sizes for the difference between the transdiagnostic treatment and the control conditions in main outcomes (depression and anxiety) at posttreatment (relative efficacy), using the bias-corrected Hedges’ g and the 95% CI59. These were calculated by subtracting the mean posttreatment score of the transdiagnostic condition from the mean score of the control condition, divided by the pooled standard deviation of both conditions. Values of 0.2, 0.5 and 0.8 of Hedges’ g represent a small, moderate and large effect size, respectively60.
Building on previous work14,22, we expected considerable variability and thus used a random-effects model61 to account for heterogeneity of included studies62. We tested heterogeneity of effect sizes with the Q statistic, the I2 statistic and by visual inspection of forest plots. A P value of the Q statistic below 0.05 indicates heterogeneity63. I2 ranges from 0 to 100%, with 25% representing low, 50% moderate and 75% high heterogeneity64. We addressed heterogeneous effect sizes by conducting subgroup analyses for the three different treatment formats (individual, group or internet-based), if at least three studies per subgroup were available. Additionally, we investigated whether excluding outliers impacted effect sizes and heterogeneity. In line with previous meta-analyses, outliers were defined as studies whose 95% CI did not overlap with the 95% CI of the overall effect size20.
We calculated uncontrolled effect sizes from pre- to posttreatment (absolute efficacy) for main outcomes (depression and anxiety) and from pretreatment to follow-up assessment. If reported, we used the intention-to-treat data from the studies for these analyses. As recommended by ref. 56, we estimated the uncontrolled effect sizes using dSMC and their respective 95% CI. Raw score standardization with heteroscedastic population variances at baseline (pretreatment) and posttreatment/follow-up were applied for more reliable estimates65,66. The effect sizes dSMC were determined using the means, standard deviations (s.d.) at each time point and the retest correlation between these time points. Values of 0.2, 0.5 and 0.8 for dSMC represent a small, moderate and large effect size, respectively60. If the correlation was not available from the studies included, retest correlations were calculated from the original study data. If not available, a default value of 0.5 was set61. In addition, we performed sensitivity analyses using 0.3 and 0.7 as retest correlations.
We assessed publication bias by inspecting the funnel plot on the depression and anxiety outcome measures as well as calculating rank correlations and Egger’s tests. Additionally, we applied the Trim and Fill procedure67.
Study quality assessment
As an updated version of the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool had become available since we registered this review on PROSPERO, deviating from our preregistration, we evaluated the risk of bias of the studies by using the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (RoB 2.0)68. We assessed the risk as ‘low’, ‘some concerns’ or ‘high’ in the following five domains: (1) bias of the randomization process; (2) bias of deviations from intended interventions; (3) bias of missing outcome data; (4) bias in measurement of the outcome; and (5) bias in selection of the reported results. Each domain is made up of several criteria. For example, the first question in domain (1) asks ‘Was the allocation sequence random?’ which, after consulting the respective manuscript, is answered as ‘yes’, ‘probably yes’, ‘probably no’, ‘no’ or ‘no information’. The RoB 2.0 provides examples and decision trees that clearly specify that certain combinations of ratings across questions within a domain result in the risk of bias of that domain being rated as ‘low’, ‘some concerns’ or ‘high’. In domain (1), a ‘high’ risk of bias would be noted if differences between intervention groups were evident at baseline, suggesting a problem with the randomization—regardless of whether no risk of bias was indicated in the evaluation of all other criteria. Two reviewers independently rated each study for bias. Final assessments were cross-checked and disagreements were resolved through discussions between the reviewers. We created the visualization of the risk of bias assessment with the shiny app robvis69.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Tables 1–8 and Figs. 1–27.
Completed PRISMA 2020 checklist detailing adherence to the PRISMA reporting guidelines.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a Swiss National Science Foundation grant no. 169827 (B.K.) and Freie Universitaet Berlin/University of Zurich joint seed funding, FSP-2019-501 (B.K. and B.R). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript. We thank L. Bakirtas and A. Olsson for their help with data extraction and all authors who provided additional data or information on their papers, supporting this review and meta-analysis.
Author contributions
A.S. and B.K. conceived this work. A.S., J.B., B.R., C.F. and B.K. developed the methodology. C.S., L.M., A.S. and M.W. produced the software. C.S., L.M., A.S. and M.W. undertook the formal analysis. C.S., L.M. and A.S. undertook the investigation. B.K. obtained resources. C.S., L.M. and A.S. undertook data curation. C.S. created the visualizations. J.B., B.R., C.F. and B.K. supervised the project. B.K. was responsible for project administration. B.K. and B.R. obtained funding. C.S., L.M. and A.S. wrote the original draft of the paper. C.S., L.M., A.S., M.W., A.M., C.P., D.R., J.B., B.R., C.F. and B.K. were involved in reviewing and editing.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Human Behaviour thanks Christina Boisseau, Warren Mansell and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study, along with data collection templates, are publicly available at the Open Science Framework and can be accessed at https://osf.io/ta4fg/.
Code availability
Custom analysis code that supports the findings of this study is publicly available at the Open Science Framework and can be accessed at https://osf.io/ta4fg/.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Carmen Schaeuffele, Laura E. Meine, Ava Schulz.
Contributor Information
Carmen Schaeuffele, Email: carmen.schaeuffele@fu-berlin.de.
Laura E. Meine, Email: laura.meine@bli.uzh.ch
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41562-023-01787-3.
References
- 1.Dalgleish T, Black M, Johnston D, Bevan A. Transdiagnostic approaches to mental health problems: current status and future directions. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2020;88:179–195. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fusar-Poli P, et al. Transdiagnostic psychiatry: a systematic review. World Psychiatry. 2019;18:192–207. doi: 10.1002/wps.20631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mansell W, McEvoy PM. A test of the core process account of psychopathology in a heterogenous clinical sample of anxiety and depression: a case of the blind men and the elephant? J. Anxiety Disord. 2017;46:4–10. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2016.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schaeuffele C, Schulz A, Knaevelsrud C, Renneberg B, Boettcher J. CBT at the crossroads: the rise of transdiagnostic treatments. J. Cogn. Ther. 2021;14:86–113. doi: 10.1007/s41811-020-00095-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Barlow, D. H. et al. Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders: Therapist Guide (Oxford Univ. Press, 2011).
- 6.Norton PJ, Hope DA. Preliminary evaluation of a broad-spectrum cognitive-behavioral group therapy for anxiety. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry. 2005;36:79–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jbtep.2004.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gros DF. Development and initial evaluation of Transdiagnostic Behavior Therapy (TBT) for veterans with affective disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2014;220:275–282. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2014.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barlow DH, Allen LB, Choate ML. Toward a unified treatment for emotional disorders—republished article. Behav. Ther. 2016;47:838–853. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2016.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Farmer C, Fenu E, O’Flynn N, Guthrie B. Clinical assessment and management of multimorbidity: summary of NICE guidance. Brit. Med. J. 2016;354:i4843. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i4843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Norton PJ, Philipp LM. Transdiagnostic approaches to the treatment of anxiety disorders: a quantitative review. Psychol. Psychother. Theory Res. Pr. 2008;45:214–226. doi: 10.1037/0033-3204.45.2.214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wilamowska ZA, et al. Conceptual background, development and preliminary data from the unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders. Depress. Anxiety. 2010;27:882–890. doi: 10.1002/da.20735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Carlbring P, Andersson G, Cuijpers P, Riper H, Hedman-Lagerlöf E. Internet-based vs. face-to-face cognitive behavior therapy for psychiatric and somatic disorders: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 2018;47:1–18. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2017.1401115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Spek V, et al. Internet-based cognitive behaviour therapy for symptoms of depression and anxiety: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2007;37:319–328. doi: 10.1017/S0033291706008944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reinholt N, Krogh J. Efficacy of transdiagnostic cognitive behaviour therapy for anxiety disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published outcome studies. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 2014;43:171–184. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2014.897367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pearl SB, Norton PJ. Transdiagnostic versus diagnosis specific cognitive behavioural therapies for anxiety: a meta-analysis. J. Anxiety Disord. 2017;46:11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2016.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Newby JM, Twomey C, Yuan Li SS, Andrews G. Transdiagnostic computerised cognitive behavioural therapy for depression and anxiety: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2016;199:30–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Păsărelu CR, Andersson G, Bergman Nordgren L, Dobrean A. Internet-delivered transdiagnostic and tailored cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cogn. Behav. Ther. 2017;46:1–28. doi: 10.1080/16506073.2016.1231219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Joaquim SB, Simões de Almeida R, Marques AJ. Transdiagnostic cognitive behavioral group interventions: a systematic review. Cogn. Ther. Res. 2023;47:303–326. doi: 10.1007/s10608-023-10372-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Carlucci L, Saggino A, Balsamo M. On the efficacy of the unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2021;87:101999. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2021.101999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cuijpers, P. et al. Transdiagnostic treatment of depression and anxiety: a meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 10.1017/S0033291722003841 (2023). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Andersen P, Toner P, Bland M, McMillan D. Effectiveness of transdiagnostic cognitive behaviour therapy for anxiety and depression in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav. Cogn. Psychother. 2016;44:673–690. doi: 10.1017/S1352465816000229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Newby JM, McKinnon A, Kuyken W, Gilbody S, Dalgleish T. Systematic review and meta-analysis of transdiagnostic psychological treatments for anxiety and depressive disorders in adulthood. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2015;40:91–110. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2015.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1988;56:893–897. doi: 10.1037/0022-006X.56.6.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW, Löwe B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: the GAD-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006;166:1092–1097. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.10.1092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Beck, A. T., Steer, R. A. & Brown, G. K. BDI-II: Manual (Pearson PsychCorp, 1996).
- 26.Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW. Validation and utility of a self-report version of PRIME-MD: the PHQ primary care study. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1999;282:1737–1744. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.18.1737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Saed, O., Arani, A. M., Taremian, F., Bakhtyari, M. & Morsali, Y. The efficacy of transdiagnostic cognitive behavior therapy on reducing symptoms severity of obsessive compulsive disorder with co-occurring anxiety and mood disorders. Int. J. Appl. Behav. Sci.2, 11 (2015).
- 28.Mason JE, Asmundson GJG. Cognitive behavioural techniques reduce exercise anxiety and improve adherence to a resistance training program for people with anxiety-related disorders: a randomized controlled trial. J. Anxiety Disord. 2023;95:102693. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2023.102693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ito, M. et al. Efficacy of the unified protocol for transdiagnostic cognitive-behavioral treatment for depressive and anxiety disorders: a randomized controlled trial. Psychol. Med.10.1017/S0033291721005067 (2022). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 30.Munder T, et al. Is psychotherapy effective? A re-analysis of treatments for depression. Epidemiol. Psychiatr. Sci. 2019;28:268–274. doi: 10.1017/S2045796018000355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Roy-Byrne P, et al. Delivery of evidence-based treatment for multiple anxiety disorders in primary care: a randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2010;303:1921. doi: 10.1001/jama.2010.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Barlow DH, et al. The unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders compared with diagnosis-specific protocols for anxiety disorders: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74:875. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.2164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Reinholt N, et al. Transdiagnostic versus diagnosis-specific group cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety disorders and depression: a randomized controlled trial. Psychother. Psychosom. 2022;91:36–49. doi: 10.1159/000516380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Andrews G, et al. Computer therapy for the anxiety and depression disorders is effective, acceptable and practical health care: an updated meta-analysis. J. Anxiety Disord. 2018;55:70–78. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2018.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jolstedt M, et al. Implementation of internet-delivered CBT for children with anxiety disorders in a rural area: a feasibility trial. Internet Interv. 2017;12:121–129. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2017.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kirkpatrick T, Manoukian L, Dear BF, Johnston L, Titov N. A feasibility open trial of internet-delivered cognitive-behavioural therapy (iCBT) among consumers of a non-governmental mental health organisation with anxiety. PeerJ. 2013;1:e210. doi: 10.7717/peerj.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Andersson G, Titov N. Advantages and limitations of internet-based interventions for common mental disorders. World Psychiatry. 2014;13:4–11. doi: 10.1002/wps.20083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jacobson NS. The role of the allegiance effect in psychotherapy research: controlling and accounting for it. Clin. Psychol. Sci. Pract. 1999;6:116–119. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Podina IR, Vîslă A, Fodor LA, Flückiger C. Is there a sleeper effect of exposure-based vs. cognitive-only intervention for anxiety disorders? A longitudinal multilevel meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2019;73:101774. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2019.101774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Spielmans GI, Flückiger C. Moderators in psychotherapy meta-analysis. Psychother. Res. 2018;28:333–346. doi: 10.1080/10503307.2017.1422214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nye, A., Delgadillo, J. & Barkham, M. Efficacy of personalized psychological interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol.91, 389–397 (2023). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Chapdelaine, A., Vasiliadis, H.-M., Provencher, M. D., Norton, P. J. & Roberge, P. Cost-effectiveness of transdiagnostic group cognitive behavioural therapy for anxiety disorders v. treatment as usual: economic evaluation of a pragmatic randomized controlled trial over an 8-month time horizon using self-reported data. Psychol. Med.10.1017/S0033291722003920 (2023). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Vasiliadis, H.-M. et al. Cost-effectiveness of group transdiagnostic cognitive behavioural therapy for anxiety disorders in primary care settings: economic evaluation from the healthcare system perspective over a 1-year time horizon. Can. J. Psychiatry10.1177/07067437231187459 (2023). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 44.Higgins JPT, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Brit. Med. J. 2011;343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Page MJ, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Brit. Med. J. 2021;372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schmidt NB, et al. Randomized controlled trial of false safety behavior elimination therapy: a unified cognitive behavioral treatment for anxiety psychopathology. Behav. Ther. 2012;43:518–532. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2012.02.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mennin, D. S. & Fresco, D. M. in Handbook of Emotion Regulation 2nd edn (ed. Gross, J. J.) 469–490 (The Guilford Press, 2014).
- 48.Berking, M. & Whitley, B. Affect Regulation Training: A Practitioners’ Manual (Springer, 2014).
- 49.McAleavey, A. A. & Castonguay, L. G. in Psychotherapy Research: Foundations, Process and Outcome (eds Gelo, O. et al.) 293–310 (Springer-Verlag, 2015).
- 50.Goldberg SB, et al. Mindfulness-based interventions for psychiatric disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2018;59:52–60. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2017.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hayes SC, Hofmann SG. The third wave of cognitive behavioral therapy and the rise of process‐based care. World Psychiatry. 2017;16:245–246. doi: 10.1002/wps.20442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Philipp R, et al. Effectiveness of metacognitive interventions for mental disorders in adults—a systematic review and meta-analysis (METACOG) Clin. Psychol. Psychother. 2019;26:227–240. doi: 10.1002/cpp.2345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bai Z, Luo S, Zhang L, Wu S, Chi I. Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) to reduce depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020;260:728–737. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.09.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Öst L-G. The efficacy of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav. Res Ther. 2014;61:105–121. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2014.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Flückiger C, Del Re AC, Munder T, Heer S, Wampold BE. Enduring effects of evidence-based psychotherapies in acute depression and anxiety disorders versus treatment as usual at follow-up—a longitudinal meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2014;34:367–375. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2014.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Soft. 36, 1–48 (2010).
- 57.Balduzzi S, Rücker G, Schwarzer G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: a practical tutorial. BMJ Ment. Health. 2019;22:153–160. doi: 10.1136/ebmental-2019-300117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Harrer, M., Cuijpers, P., Furukawa, T. A. & Ebert, D. D. dmetar: Companion R package for the guide ‘Doing Meta-Analysis in R’. R package version 0.1.0 (2019).
- 59.Hedges, L. V. & Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis (Academic, 1985).
- 60.Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (L. Erlbaum Associates, 1988).
- 61.Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. T. & Rothstein, H. R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis (Wiley, 2009).
- 62.DerSimonian R, Kacker R. Random-effects model for meta-analysis of clinical trials: an update. Contemp. Clin. Trials. 2007;28:105–114. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2006.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Cochran WG. The combination of estimates from different experiments. Biometrics. 1954;10:101–129. doi: 10.2307/3001666. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Higgins JPT, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002;21:1539–1558. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bonett DG. Meta-analytic interval estimation for standardized and unstandardized mean differences. Psychol. Methods. 2009;14:225–238. doi: 10.1037/a0016619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bonett DG. Confidence intervals for standardized linear contrasts of means. Psychol. Methods. 2008;13:99–109. doi: 10.1037/1082-989X.13.2.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 2000;56:455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00455.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sterne JAC, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Brit. Med. J. 2019;366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.McGuinness LA, Higgins JPT. Risk‐of‐bias VISualization (robvis): an R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk‐of‐bias assessments. Res. Syn. Meth. 2021;12:55–61. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ahmadi R, Ahmadizadeh R, Hasani M, Saed O. Transdiagnostic versus construct-specific cognitive behavioural therapy for emotional disorders in patients with high anxiety sensitivity: a double-blind randomised clinical trial. Behav. Change. 2021;38:177–192. doi: 10.1017/bec.2021.6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Corpas J, Moriana JA, Venceslá JF, Gálvez-Lara M. Brief psychological treatments for emotional disorders in primary and specialized care: a randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2021;21:100203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2020.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ellard KK, et al. Transdiagnostic treatment of bipolar disorder and comorbid anxiety using the unified protocol for emotional disorders: a pilot feasibility and acceptability trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2017;219:209–221. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.05.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Farchione TJ, et al. Unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders: a randomized controlled trial. Behav. Ther. 2012;43:666–678. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2012.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Gros DF, Allan NP. A randomized controlled trial comparing Transdiagnostic Behavior Therapy (TBT) and behavioral activation in veterans with affective disorders. Psychiatry Res. 2019;281:112541. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Gutner CA, et al. A pilot randomized effectiveness trial of the unified protocol in trauma-exposed veterans. Depress. Anxiety. 2022;39:813–823. doi: 10.1002/da.23288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Khakpoor S, Saed O, Armani Kian A. Emotion regulation as the mediator of reductions in anxiety and depression in the Unified Protocol (UP) for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders: double-blind randomized clinical trial. Trends Psychiatry Psychother. 2019;41:227–236. doi: 10.1590/2237-6089-2018-0074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lotfi M, Bakhtiyari M, Asgharnezhad-Farid AA, Amini M. Comparison of the effect of transdiagnostic therapy and cognitive-behavior therapy on patients with emotional disorders: a randomized clinical trial. Zahedan J. Res. Med. Sci. 2014;16:15–18. [Google Scholar]
- 78.Mahmoodi, M., Bakhtiyari, M., Masjedi A. A., Mohammadi, A. & Saberi I. M. The comparison between CBT focused on perfectionism and CBT focused on emotion regulation for individuals with depression and anxiety disorders and dysfunctional perfectionism: a randomized controlled trial. Behav. Cogn. Psychother.10.1017/S1352465820000909 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 79.Mennin DS, Fresco DM, O’Toole MS, Heimberg RG. A randomized controlled trial of emotion regulation therapy for generalized anxiety disorder with and without co-occurring depression. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2018;86:268–281. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Nasiri F, Mashhadi A, Bigdeli I, Chamanabad AG, Ellard KK. Augmenting the unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders with transcranial direct current stimulation in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder and comorbid depression: a randomized controlled trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2020;262:405–413. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.11.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Pachankis JE, et al. LGBQ-affirmative cognitive-behavioral therapy for young gay and bisexual men’s mental and sexual health: a three-arm randomized controlled trial. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 2022;90:459–477. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Tully PJ, et al. Transdiagnostic cognitive-behavioral therapy for depression and anxiety disorders in cardiovascular disease patients: results from the CHAMPS pilot-feasibility trial. Front. Psychiatry. 2022;13:741039. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.741039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Berking M, et al. Affect regulation training reduces symptom severity in depression—a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0220436. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Corpas J, Moriana JA, Venceslá JF, Gálvez-Lara M. Effectiveness of brief group transdiagnostic therapy for emotional disorders in primary care: a randomized controlled trial identifying predictors of outcome. Psychother. Res. 2022;32:456–469. doi: 10.1080/10503307.2021.1952331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.de Ornelas Maia ACC, Sanford J, Boettcher H, Nardi AE, Barlow D. Improvement in quality of life and sexual functioning in a comorbid sample after the unified protocol transdiagnostic group treatment. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017;93:30–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2017.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ejeby K, et al. Randomized controlled trial of transdiagnostic group treatments for primary care patients with common mental disorders. Fam. Pract. 2014;31:273–280. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmu006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Erickson DH, Janeck AS, Tallman K. A cognitive-behavioral group for patients with various anxiety disorders. Psychiatr. Serv. 2007;58:7. doi: 10.1176/ps.2007.58.9.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Fernández-Rodríguez, C., Coto-Lesmes, R., Martínez-Loredo, V., González-Fernández, S. & Cuesta, M. Is activation the active ingredient of transdiagnostic therapies? A randomized clinical trial of behavioral activation, acceptance and commitment therapy and transdiagnostic cognitive-behavioral therapy for emotional disorders. Behav. Modif. 10.1177/01454455221083309 (2022). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 89.Kananian S, Soltani Y, Hinton D, Stangier U. Culturally adapted cognitive behavioral therapy plus problem management (CA-CBT+) with Afghan refugees: a randomized controlled pilot study. J. Trauma Stress. 2020;33:928–938. doi: 10.1002/jts.22615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kunst LE, et al. Group autonomy enhancing treatment versus cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety disorders: a cluster-randomized clinical trial. Depress. Anxiety. 2022;39:134–146. doi: 10.1002/da.23231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Nazari N, Sadeghi M, Ghadampour E, Mirzaeefar D. Transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders in people with multiple sclerosis: randomized controlled trial. BMC Psychol. 2020;8:114. doi: 10.1186/s40359-020-00480-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Nazari N, Aligholipour A, Sadeghi M. Transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders for women with multiple sclerosis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Women’s Health. 2020;20:245. doi: 10.1186/s12905-020-01109-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Neacsiu AD, Eberle JW, Kramer R, Wiesmann T, Linehan MM. Dialectical behavior therapy skills for transdiagnostic emotion dysregulation: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Behav. Res. Ther. 2014;59:40–51. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2014.05.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Norton PJ. A randomized clinical trial of transdiagnostic cognitve-behavioral treatments for anxiety disorder by comparison to relaxation training. Behav. Ther. 2012;43:506–517. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2010.08.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Norton PJ, Barrera TL. Transdiagnostic versus diagnosis-specific CBT for anxiety disorders: a preliminary randomized controlled noninferiority trial. Depress. Anxiety. 2012;29:874–882. doi: 10.1002/da.21974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Osma J, Navarro Haro MV, Baquero ÓP, Ribera CS. Unified protocol in a group format for improving specific symptoms of emotional disorders in the Spanish public health system. Psicothema. 2022;34:25–34. doi: 10.7334/psicothema2021.246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Osma J, Peris-Baquero O, Suso-Ribera C, Farchione TJ, Barlow DH. Effectiveness of the unified protocol for transdiagnostic treatment of emotional disorders in group format in Spain: results from a randomized controlled trial with 6-months follow-up. Psychother. Res. 2022;32:329–342. doi: 10.1080/10503307.2021.1939190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Roberge P, et al. Group transdiagnostic cognitive-behavior therapy for anxiety disorders: a pragmatic randomized clinical trial. Psychol. Med. 2022;52:2460–2470. doi: 10.1017/S0033291720004316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Rogiers R, et al. Group intervention ‘Drop It!’ decreases repetitive negative thinking in major depressive disorder and/or generalized anxiety disorder: a randomised controlled study. Cogn. Ther. Res. 2022;46:182–196. doi: 10.1007/s10608-021-10240-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Zemestani M, Imani M, Ottaviani C. A preliminary investigation on the effectiveness of unified and transdiagnostic cognitive behavior therapy for patients with comorbid depression and anxiety. Int. J. Cogn. Ther. 2017;10:175–185. doi: 10.1521/ijct.2017.10.2.175. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Berger T, et al. Effects of a transdiagnostic unguided internet intervention (‘velibra’) for anxiety disorders in primary care: results of a randomized controlled trial. Psychol. Med. 2017;47:67–80. doi: 10.1017/S0033291716002270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Dear BF, et al. Transdiagnostic versus disorder-specific and clinician-guided versus self-guided internet-delivered treatment for generalized anxiety disorder and comorbid disorders: a randomized controlled trial. J. Anxiety Disord. 2015;36:63–77. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2015.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Dear BF, et al. Transdiagnostic versus disorder-specific and clinician-guided versus self-guided internet-delivered treatment for social anxiety disorder and comorbid disorders: a randomized controlled trial. J. Anxiety Disord. 2016;42:30–44. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2016.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Díaz-García A, et al. Negative and positive affect regulation in a transdiagnostic internet-based protocol for emotional disorders: randomized controlled trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2021;23:e21335. doi: 10.2196/21335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Fogliati VJ, et al. Disorder-specific versus transdiagnostic and clinician-guided versus self-guided internet-delivered treatment for panic disorder and comorbid disorders: a randomized controlled trial. J. Anxiety Disord. 2016;39:88–102. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2016.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.González-Robles A, et al. Effectiveness of a transdiagnostic guided internet-delivered protocol for emotional disorders versus treatment as usual in specialized care: randomized controlled trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020;22:e18220. doi: 10.2196/18220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Johnston L, Titov N, Andrews G, Spence J, Dear BF. A RCT of a transdiagnostic internet-delivered treatment for three anxiety disorders: examination of support roles and disorder-specific outcomes. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e28079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kladnitski N, et al. Transdiagnostic internet-delivered CBT and mindfulness-based treatment for depression and anxiety: a randomised controlled trial. Internet Interv. 2020;20:100310. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2020.100310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Li, Y. et al. A randomized controlled trial of an online self-help mindfulness intervention for emotional distress: serial mediating effects of mindfulness and experiential avoidance. Mindfulness 14, 510–523 (2023).
- 110.Mullin A, et al. The UniWellbeing course: a randomised controlled trial of a transdiagnostic internet-delivered cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) programme for university students with symptoms of anxiety and depression. Internet Interv. 2015;2:128–136. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2015.02.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Newby JM, et al. Internet cognitive behavioural therapy for mixed anxiety and depression: a randomized controlled trial and evidence of effectiveness in primary care. Psychol. Med. 2013;43:2635–2648. doi: 10.1017/S0033291713000111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Schaeuffele C, et al. The unified protocol as an internet-based intervention for emotional disorders: randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0270178. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Titov N, Andrews G, Johnston L, Robinson E, Spence J. Transdiagnostic internet treatment for anxiety disorders: a randomized controlled trial. Behav. Res. Ther. 2010;48:890–899. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2010.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Titov N, et al. Transdiagnostic internet treatment for anxiety and depression: a randomised controlled trial. Behav. Res. Ther. 2011;49:441–452. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2011.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Titov N, et al. Disorder-specific versus transdiagnostic and clinician-guided versus self-guided treatment for major depressive disorder and comorbid anxiety disorders: a randomized controlled trial. J. Anxiety Disord. 2015;35:88–102. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2015.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Tulbure BT, Rusu A, Sava FA, Sălăgean N, Farchione TJ. A web-based transdiagnostic intervention for affective and mood disorders: randomized controlled trial. JMIR Ment. Health. 2018;5:e36. doi: 10.2196/mental.8901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Yan K, Yusufi MH, Nazari N. Application of unified protocol as a transdiagnostic treatment for emotional disorders during COVID-19: an internet-delivered randomized controlled trial. World J. Clin. Cases. 2022;10:8599–8614. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i24.8599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.González-Robles A, Roca P, Díaz-García A, García-Palacios A, Botella C. Long-term effectiveness and predictors of transdiagnostic internet-delivered cognitive behavioral therapy for emotional disorders in specialized care: secondary analysis of a randomized controlled trial. JMIR Ment. Health. 2022;9:e40268. doi: 10.2196/40268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Tables 1–8 and Figs. 1–27.
Completed PRISMA 2020 checklist detailing adherence to the PRISMA reporting guidelines.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study, along with data collection templates, are publicly available at the Open Science Framework and can be accessed at https://osf.io/ta4fg/.
Custom analysis code that supports the findings of this study is publicly available at the Open Science Framework and can be accessed at https://osf.io/ta4fg/.