Abstract
Gene therapy is capable of efficiently regulating the expression of abnormal genes in diseased tissues and expected to be a therapeutic option for refractory diseases. However, unidirectional targeting gene therapy is always desired at the tissue interface. In this study, inspired by the principle that like charges repulse each other, a positively charged micro-nano electrospun fibrous membrane with dual-layer structure was developed by electrospinning technology to achieve unidirectional delivery of siRNA-loaded cationic nanocarriers, thus realizing unidirectional gene therapy at the tendon-paratenon interface. Under the charge repulsion of positively charged layer, more cationic COX-2 siRNA nanocarriers were enriched in peritendinous tissue, which not only improved the bioavailability of the gene drug to prevent the peritendinous adhesion formation, but also avoided adverse effects on the fragile endogenous healing of tendon itself. In summary, this study provides an innovative strategy for unidirectional targeting gene therapy of tissue interface diseases by utilizing charge repulsion to facilitate unidirectional delivery of gene drugs.
Keywords: Unidirectional delivery, Charge repulsion, Gene therapy, Tendon repair
Graphical abstract
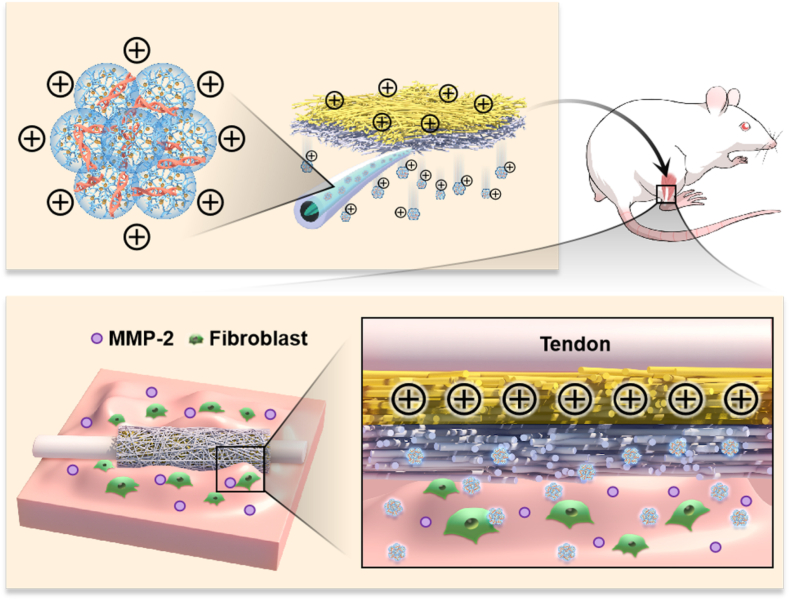
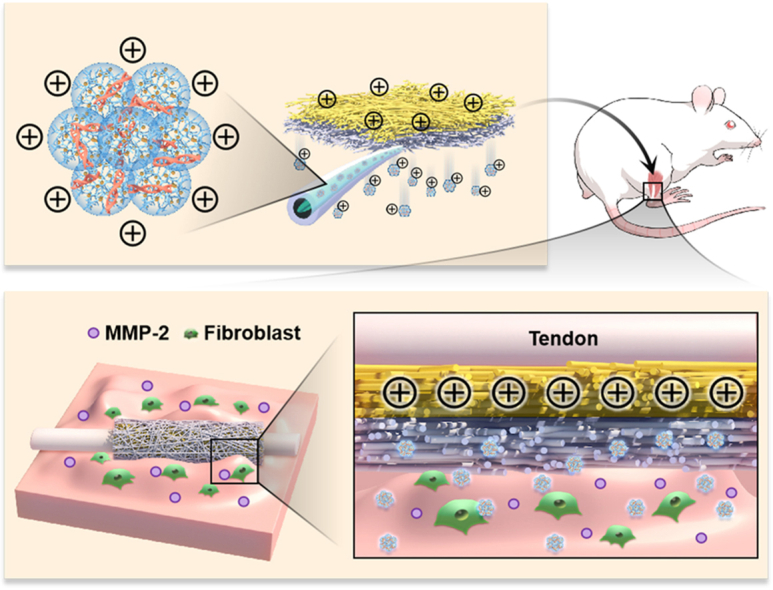
Graphic Abstract. The dual-layer positively charged micro-nano electrospun fibrous membrane with unidirectional gene delivery via charge repulsion and MMP-2 responsiveness was fabricated for tendon repair by unidirectional silencing of COX-2 to modulate the inflammation of peritendinous tissue and on-demand release by responding to up-regulated MMP-2.
Highlights
-
•
A dual-layer electrospun fibrous membrane that releases gene drug unidirectionally was developed.
-
•
Positively charged layer drives unidirectional delivery of cationic siRNA ployplexes through charge repulsion.
-
•
MMP-2-responsive gene pool was encapsulated in fibers with core-shell structure by microsol electrospinning technology.
-
•
Unidirectional delivery of siRNA improves the bioavailability of gene drugs and avoids side effects on adjacent tissues.
-
•
This dual-layer electrospun fibrous membrane is highly effective in promoting scarless tendon repair.
1. Introduction
Gene therapy has shown great potential in the treatment of various diseases, including sports injuries [1]. Among them, small interfering RNA (siRNA) have been used to treat diseases characterized by gene over-expression by targeting the silencing of specific messenger RNA (mRNA) and inhibiting the expression of related proteins [2,3]. Efficient and safe gene delivery vectors and appropriate administration routes are important factors affecting the effectiveness of gene therapy [3,4]. Compared with viral vectors, non-viral vectors such as peptides [5], lipids [6] and cationic polymers [7] are widely used because of their low immunogenicity and inexpensive cost [8]. Particularly, cationic polymers and their derivatives are commonly utilized for gene delivery attributed to their stable molecular structure and the ease of modification [9]. PAMAM dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles (Au DENPs) as one of them, can form positively charged polyplexes with negatively charged nucleic acid materials by electrostatic interaction [10]. The cationic polyplexes further bind electrostatically to the negatively charged components of the cell membrane and are taken up intracellularly by adsorption and endocytosis to exert therapeutic effects [11]. Local controlled release of siRNA is considered an attractive and rational route of drug delivery, which can improve bioavailability and also reduce toxicities compared with systemic administration [4]. Various local delivery systems have been successfully developed to achieve sustained delivery of siRNA, such as microspheres [12,13], hydrogels [14], microneedles [15] and electrospun fibrous membranes (EFMs) [16,17]. The loaded siRNA polyplexes act on the surrounding target tissues by directionless diffusion through body fluids after their implantation into the lesion tissue. However, the variability of physiological function of adjacent tissues at tissue interface determines their different requirement for siRNA drugs. Thanks to their bionic extracellular matrix (ECM) structure and excellent biocompatibility, EFMs are often chosen as physical barriers and drug delivery platforms to be placed at the tissue interface [18]. Hence, there is an urgent need to develop EFMs with unidirectional gene drug delivery to improve their therapeutic efficacy at tissue interface.
The hydrophobic properties of EFMs are often utilized to constitute a steric hindrance in body fluids to prevent drug diffusion across EFMs, thus achieving unidirectional drug release [19]. On this basis, a variety of EFM-based composite drug delivery systems with unidirectional drug release function have been successfully constructed [[19], [20], [21]]. We have successfully constructed a hydrogel-EFM composite patch in our previous work, in which siRNA nanoparticles loaded in the hydrogel layer were blocked by EFM layer to release unidirectionally [22]. However, when EFM layer is fully infiltrated by body fluids, the drugs also diffuse with the body fluids through the microporous structure of EFMs, which makes it difficult to maintain a long-lasting unidirectional drug delivery [19]. Hence, Santocildes-Romero et al. [19] facilitated durable unidirectional drug release by heat treating and melting the polycaprolactone (PCL) barrier layer, which has a lower melting point, to eliminate the microporous structure and form a dense barrier layer. However, this strategy sacrificed the bionic ECM structure of EFMs, which not only hinders the transport of nutrients on both sides of the membrane, but also impedes biological signaling. Electrostatic interactions are widespread in vivo, such as the charge barrier of the glomerular filtration membrane. The negative charge barrier impedes the filtration of negatively charged albumin through charge repulsion, which is essential for glomerular filtration function [23]. Recently, electrostatic interactions have also been introduced into the design of drug release material [24]. For example, the positively charged treatment of drug facilitates the deep drug penetration across the negative charge barrier of cartilage [25]. Therefore, it is theoretically feasible to construct EFMs for unidirectional gene delivery using charge repulsion.
Tissue injury is usually limited by the fragile proliferation capacity of its intrinsic cells, which makes it difficult to restore the original structure and is mostly replaced by fibrotic repair, thus affecting its biological function [26]. In addition, fibrotic repair of tissues can also disrupt the balance of tissue interface, such as adhesion formation. Tendon adhesion remains a common complication of tendon repair that needs to be addressed urgently [27]. Tendon and paratenon, as a typical tissue interface, represent different tendon healing pathways, namely endogenous healing and exogenous healing [28]. It is now generally accepted that an imbalance between endogenous and exogenous tendon healing is the main cause of tendon adhesion formation [29]. During tendon healing, the low cell count, weak energy metabolic activity, and limited blood and nerve supply of endogenous healing allow overactive exogenous healing to invade the tendon section, not only impeding tendon endogenous healing, but also resulting in adhesion of the tendon to peritendinous tissue [30]. In our previous study, siRNA-loaded EFMs proved to be an efficient and safe therapeutic physical barrier to prevent tendon adhesion [16]. Despite its effective inhibition the proliferation and differentiation of peritendinous fibroblasts, its effect on tendon stem cells should not be overlooked. Among the pathogenic factors, inflammation has a long-lasting effect on adhesion formation, which promotes proliferation and differentiation of fibroblasts and synthesis of ECM [31]. COX-2, which modulates synthesis of prostaglandin, has been recognized as a positive regulator in pathological process like inflammation and oxidative stress [32]. Moreover, COX-2 has also been identified as a promoter of fibroblast proliferation, differentiation and migration [33]. Hence, COX-2 and the downstream signaling pathway are important therapeutic targets to hinder adhesion formation. Nevertheless, it has been reported that anti-inflammatory treatment may inhibit the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to tendon cell, which is detrimental to tendon regeneration [34,35]. Therefore, it is necessary to construct EFMs with unidirectional delivery of COX-2 siRNA for better tendon repair.
In this study, a dual-layer positively charged micro-nano EFM with unidirectional gene delivery function was fabricated inspired by the physical principle of mutual repulsion of like charges. First, COX-2 siRNA self-assembled with Au DENPs via electrostatic interaction to form cationic siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes for efficient intracellular delivery. And then the polyplexes were subsequently wrapped into matrix metallopeptidase-2 (MMP-2)-responsive Methacrylate Gelatin (GelMA) solution, and the gene-loaded layer with MMP-2 responsiveness was prepared by microsol-electrospinning technique. Finally, the natural cationic polymer chitosan (CS) was introduced into the PCL solution to modulate the surface charge of the EFMs, and the mixed solution was continuously electrospun onto the surface of the gene-loaded layer. By examining the surface zeta potential of CS@PCL EFMs, it was found that the negative charge property of pure PCL EFMs converted to positive charge property at pH values below 7.2 when the mass ratio (w/w) of CS: PCL was greater than 10%. The cationic siRNA-loaded nanocarriers were delivered unidirectionally into the peritendinous tissue under the charge repulsion effect of CS@PCL EFMs. This not only improved the bioavailability of the gene, but also avoided interference with fragile endogenous tendon healing and reduced toxic side effects. COX-2 siRNA reduced inflammation in peritendinous tissue, inhibited excessive proliferation and migration of fibroblasts, and prevented tendon adhesion formation by specifically knocking down the expression of COX-2 (Fig. 1). The results of in vitro and in vivo experiments also demonstrated the better therapeutic effect of tendon injury with the unidirectional gene delivery EFMs. In conclusion, this EFM with unidirectional gene delivery has wide applicability and provides an innovative strategy for achieving efficient gene therapy for tissue interface diseases.
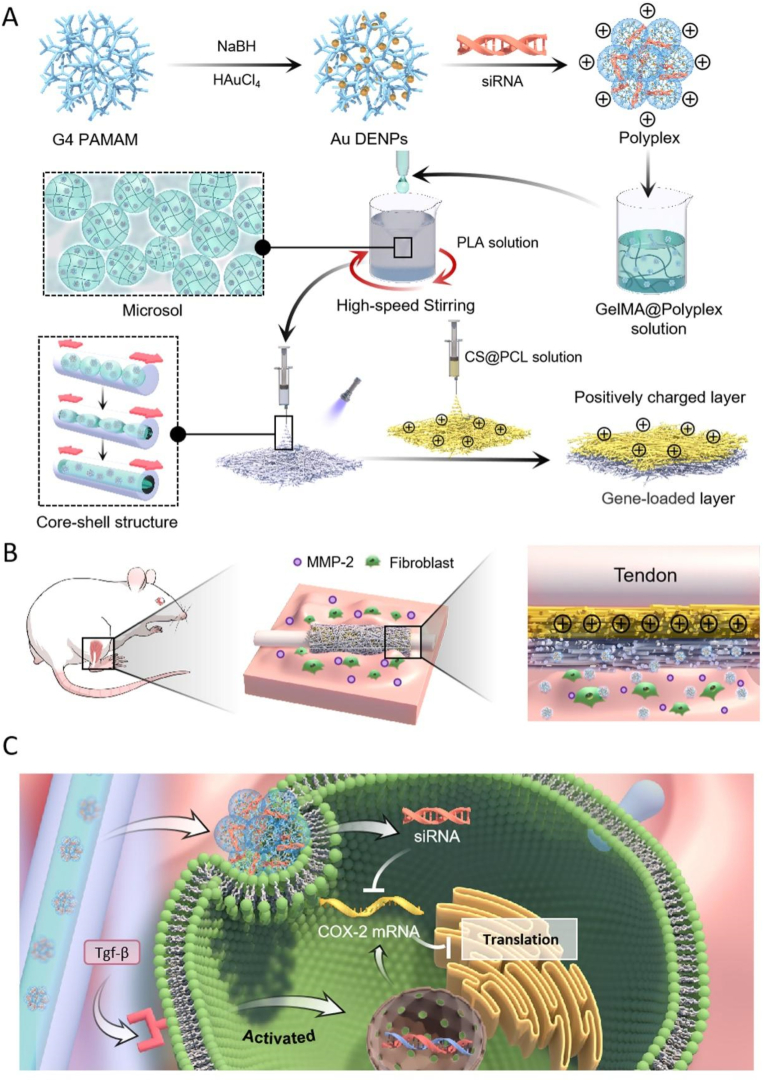
Fig. 1.
The schematic diagram of the proposed unidirectional gene delivery electrospun fibrous membrane. (A) Schematic representation of the synthesis of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes and the fabrication of the dual-layer siRNA@GP/CS@PCL electrospun fibrous membrane consisted of the gene-loaded layer and positively charged layer. (B) Double-layer smart electrospun fibrous membranes were able to respond to the upregulated MMP-2 in the microenvironment, releasing more gene drugs and enriching them in peritendinous tissues via charge repulsion. (C) Inhibits COX-2 synthesis by targeting silencing of COX-2 mRNA, thereby alleviating inflammation.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Materials
PLA [molecular weight (MW) = 100 kDa] and Polycaprolactone (PCL) [MW = 80 kDa] were purchased from Daigang Bioenginnering Co., Ltd. (Jinan, China). Chitosan (CS, degree of deacetylation ≥99%) was obtained from Macklin. Dichloromethane (DCM; ≥99%), Gelatin from porcine skin, Phenyl-2,4,6-trimethylbenzoylphosiphinate (LAP) and N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF; ≥99%) were all purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexaffuoro-2-propanol (HFIP), acetone and formic acid were products of Aladdin. COX-2 siRNA sequences were designed and synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai, China). Sequences of siRNAs (5′-3′) were 5′-CCAGACUAGAUGACAUUAATT-3’.
2.2. Synthesis and characterization of CS@PCL
We prepared the CS@PCL EFMs as previously reported with slight differences [36]. Briefly, CS was dissolved in a mixture of formic acid and acetone with 3:7 vol ratio and stirred overnight to obtain a 2.5 wt% CS solution. And PCL was dissolved in HFIP and stirred overnight to obtain a 15 wt% PCL solution. Subsequently, CS solution was mixed with PCL solution at different mass ratios to obtain CS@PCL mixed solutions with mass ratios of 0, 5%, 10% and 15%, respectively. The four solutions were then electrospun into membranes (voltage: 18 kV, collection distance: 20 cm, flow rate: 1 mL/h). The prepared CS@PCL EFMs were vacuum-dried for 24 h to volatilize residual organic reagents. The morphological features of the four EFMs were characterized with a scanning electron microscope (SEM, MIR3, Czech) and ImageJ software was subsequently used to analysis the diameters and porosities. Water contact angles (WCA) were measured by an OCA 20 contact angle analyzer (Dataphysics, Germany). A Fourier Transform infrared (FTIR) spectrometer (Nicolet Nexus 670) were used to test ingredients of membranes. The surface zeta potentials of the membranes were measured using a SurPass Electrokinetic Analyser (Anton Paar, GmbH, Austria). The mechanical properties were further analyzed using a mechanical measuring instrument at a strain rate of 5 mm/min. The tension and displacement were recorded until the membranes were completely broken.
2.3. Synthesis and characterization of Au DENPs
Au DENPs were created according to the reported protocols [10]. Briefly, G4 dendrimer with amine termini (50 mg) was dissolved in 5 mL of deionized water (DI water). Subsequently, an aqueous solution of HAuCl4·4H2O (88.29 × 10−3 M) was added to G4 dendrimer and stirred magnetically for 30 min with gold salt/dendrimer molar ratio of 25:1. Then NaBH4 (2.105 mg, 1 mL) was added rapidly and stirred for another 2 h. The reaction mixture was dialyzed and lyophilized to Au DENPs solids. The Au DENPs were characterized with UV–vis spectroscope and transmission electron microscope (TEM, Hitachi, Japan).
2.4. Preparation of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes
Polyplexes of siRNA@Au DENPs with different N/P ratios (the molar ratios of primary amines of Au DENPs to phosphates in the siRNA backbone) were prepared according to the previous literature [22]. Briefly, 1 μg COX-2 siRNA was dissolved and diluted in diethylpyrocarbonate-treated (DEPC-treated) water and mixed with Au DENPs to prepare polyplexes with different N/P ratios. The mixtures were incubated for 20 min following gentle vortex before characterization. The siRNA binding ability of Au DENPs was investigated by agarose gel electrophoresis (Beyotime Biotechnology, China). The EB-stained gel was observed with a UV illuminator and the bands were photographed with an UVI Pro Gel Documentation system (Tanon 2500, China). TEM was used to observe the morphology of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes with N/P of 20. The particle size and zeta potential of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes were further analyzed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) (Malvern, UK) at 25 °C.
2.5. Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes
The cellular uptake efficiency and cytotoxicity of the polyplexes were verified using 208F cells. Before being transfected, 208F cells at a density of 2 × 104 cells/well were seeded onto 24-well plates and activated with 10 nM Tgf-β for 24 h. Then, polyplexes with N/P ratios of 10, 20, 30 and 40 were prepared, respectively. The polyplexes solutions of Au DENPs and 20 pmol fluorescent dye carboxyfluorescein (FAM) labeled siRNA were diluted with 250 μL DMEM followed by incubation of 30 min at room temperature (RT). Then, the cells were co-cultured with the prepared polyplexes solutions for 6 h and observed with a fluorescence microscope and the cellular uptake efficiency was further quantified by flow cytometry. To observe the cytotoxicity of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes, 208F cells were cultured for 24 h in polyplexes solutions with different N/P ratios, and the rate of cell proliferation were detected using the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8). The optimal N/P ratio (N/P = 20) was selected for subsequent experiments based on the above experimental results.
2.6. Gene silencing efficiency of COX-2 siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes
208F cells were seeded onto 24-well plates and activated with 10 nM Tgf-β for 24 h. And then 20 pmol COX-2 siRNA was incubated with Au DENPs for 30 min at N/P ratio of 20 in 200 μL serum-free DMEM and was added to well to co-culture with 208F cells for 6 h. And additional 500 μL DMEM complete medium was added to each well to continue incubation for 42h. Gene silencing efficiency (relative mRNA levels of COX-2) was assessed by Quantitative Real-time PCR (qRT-PCR).
2.7. The charge repulsion effect of CS@PCL
To verify the charge repulsion effect of CS@PCL layer on the cationic nanoparticles, 1 μg siRNA were mixed with Au DENPs (N/P = 20). After incubation for 20 min, 100 μL 1 × PBS was added to the polyplexes solution and then placed in the upper chamber of a 24-well Transwell plate (Corning, USA). After 24 h, 48 h, 72 h, 120 h, 168 h and 216 h, 500 μL of the lower chamber solution was taken and 500 μL of an equal volume of 1 × PBS was added. The siRNA in the lower chamber was subsequently quantified using the Ribogreen quantification kit (Invitrogen, USA) to assess the charge repulsion effect.
2.8. Synthesis and characterization of siRNA@GP
GelMA was synthesized according to the previous method [37]. In brief, 20 g gelatin was absolutely dissolved in 200 mL Dulbecco's PBS (DPBS) (stirred for 1 h at 60 °C), followed by the addition of 16 mL Methacrylic anhydride (MA). After stirring for 4 h, 800 mL pre-warmed DPBS was added. The solution was dialyzed and then lyophilized for 2 days to obtain white porous foam. We incubated 2 OD of COX-2 siRNA with 444 μL of Au DENPs solution for 20 min at RT (N/P = 20). The polyplex solution was then slowly added to 1 wt% GelMA solution containing 0.25 wt % LAP photoinitiator and stirring for 10 min. The siRNA@GelMA solution was added to 6 mL of DCM solution containing 0.01 g Span-80 and 1 g PLA with vigorous stirring. After one night, 4 mL DMF was added and stirred thoroughly. The siRNA@GelMA@PLA (siRNA@GP) membrane was prepared using microsol electrospinning technique. The siRNA@GP was cross-linked under UV for 1 min and then vacuumed overnight. Morphological characterization of the fibers was performed with SEM and TEM. The average diameters and porosities were analyzed with ImageJ software. WCA was measured by an OCA 20 contact angle analyzer.
2.9. MMP-2 responsive release of siRNA@GP
The MMP-2 responsive release behavior of the siRNA polyplexes in siRNA@GP was investigated according to the previous method [38]. Immerse a 2 cm × 2 cm piece of siRNA@GP into 2 mL PBS containing MMP-2 (0, 0.1 μg/mL). At the indicated time points, 1 mL supernatant was collected and supplemented with an equal amount of MMP-2 solution (0, 0.1 μg/mL). The concentration of released siRNA was quantified using the Ribogreen quantification kit.
2.10. Synthesis and characterization of siRNA@GP/CS@PCL
The siRNA@GP/CS@PCL was prepared by sequential electrospinning technology, consisting of a positively charged layer (CS@PCL) and a gene-loaded layer (siRNA@GP). A 10 wt% CS@PCL mixture solution was electrospun, followed immediately by sequential electrospinning of the siRNA@GP solution. The siRNA@GP/CS@PCL was dried in vacuum and used for the following in vitro and in vivo experiments. The morphologies of dual-layer EFMs were characterized using SEM, and their mechanical properties were also examined. A total of four tendon scaffolds with different compositions were prepared, namly GP/PCL, GP/CS@PCL, siRNA@GP/PCL and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL.
To further study the unidirectional release behavior, three sets of dual-layer EFMs were constructed using the above-mentioned electrospinning technology, namly siRNA@GP/PCL, siRNA@GP/5%CS@PCL and siRNA@GP/10%CS@PCL. A 14 mm diameter circular membrane was cut out from each sample and clamped in the middle of a bioreactor filled with 1 mL PBS each side (pH = 6.8). After 1 day, 3 days, 7 days, 10 days and 15 days, 500 μL of solution from that side of the barrier layer was taken and 500 μL of an equal volume of 1 × PBS was added. The concentration of released siRNA was quantified using the Ribogreen quantification kit.
2.11. In vitro experiments
To assess the biocompatibility of the dual-layer EFMs, 208F at a density of 2 × 104 cells were seeded and activated with 10 nM Tgf-β for 24 h and co-cultured with different EFMs extracts at 37 °C in a humidified incubator under 5% CO2. After culture for 1 and 3 days, live/dead assay was used to study the biocompatibility of EFMs. Cell scratch test and cell migration test were used to detect the effect of the dual-layer EFMs on cell migration capacity. The 6-well plate was used for the scratch test. Wound scratches were created using a 200 μL pipette tip when the cells were spread out and were co-cultured with different EFM extracts, then observed and photographed under light microscope after co-incubation for 0 and 24 h. Cell migration test was performed on 8 μm 24-transwell plates. 208F cells were grown in the upper chamber at a density of 5 × 103 with incubation with different EFM extracts and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde after 24h. The results were obtained using a light microscope after crystalline violet staining.
To better demonstrate the unidirectional release effect of siRNA@GP/CS@PCL, 12-well Transwell plates were used for the in vitro experiments to evaluate the long gene silencing efficiency, anti-cell proliferation effect and anti-adhesion effect. The dual-layer EFMs were spread on the bottom of the upper chamber and 208F cells were seeded onto the dual-layer EFMs and activated with 10 nM Tgf-β for 24 h before the following cell experiments. Gene silencing efficiency of membranes was detected by qRT-PCR on Days 1, 3 and 5. CCK-8 study was performed on Days 1, 3 and 5, followed by the measurement of OD values at 450 nm. The cell adhesions were evaluated after stained with Phalloidin/DAPI on Day 3.
The antibacterial activity of each dual-layer EFM was determined by the agar disc diffusion test using E. coli (ATCC 25922) and S. aureus (ATCC 23235) according to the reported protocol [39]. Briefly, 100 μL bacterial suspension with a concentration of 108 CFU/mL was spread evenly on blood agar plates with different sample placed in the middle of each plate. After 24 h of co-incubation, the size of the inhibition zone was measured. The bacteria counting assessment was further performed to assess the antibacterial property. Briefly, the membranes with 300 μL bacterial suspension with a concentration of 106 CFU/mL were cultured for 6 h at 37 °C. Then, the obtained bacterial suspensions were diluted 1000-fold steps and coated on blood agar plates followed 24 h co-incubation. The antibacterial rate was calculated following the equation “Antibacterial rate (%) = (Nc - Nm)/Nc × 100%”, where Nc and Nm were the numbers of CFUs in the control and membranes groups, respectively.
2.12. Animal models
The in vivo experiment was approved by the institutional review committee of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SYXK (Hu) 2021-0028). Thirty male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats weighing 250–300 g were chosen for the in vivo experiment. The hind limbs of rats were sterilized and tendon injury models were made by repairing the ruptured Achilles tendon using modified Kessler technique. The sutured Achilles tendons were wrapped with different dual-layer EFMs (1 cm × 1.5 cm). All rats were divided into 3 groups (n = 10), named control group (no membrane), siRNA@GP/PCL group and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group.
2.13. Gross evaluation and histological evaluation
The rats were observed for inflammation or infected ulcers at the surgical site 3 weeks after surgery. The hind limbs were incised longitudinally to expose the repaired tendon. The degree of tendon adhesions was classified into 5 grades [40]. The hind limbs were amputated and fixed in the paraformaldehyde for 24 h and then decalcified in 10% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid disodium salt for 5 weeks. After that, the samples were stained with hematoxylin-eosin (HE), Masson's staining and immunohistochemical staining of type III collagen (Col III). Then a light microscope (Leica DM6000) was used to observe the stained sections. The repaired sites were classified into grades 1–5 according to the histological scoring system of adhesions [40]. Then, the tendon healing status was further classified using the reported scoring system: Score 1, good continuity and smooth epitenon surface defined as excellent; Score 2, structured intratendinous collagen bundles with interrupted epitenon defined as good; Score 3, ill-structured and partly broken intratendinous collagen bundles defined as fair; Score 4, massive granulation tissue formation defined as poor [41]. Furthermore, inflammation response evaluation was conducted by assessing the magnitude and aggregation of inflammatory cells and classified into following scores. Score 1, only sporadic inflammatory cells; Score 2, mild inflammatory cell infiltration; Score 3, moderate inflammatory cell infiltration; Score 4, severe inflammatory cell infiltration [42].
2.14. Immunofluorescence analysis
For Immunofluorescence staining, block the section first for 0.5 h with 5% BSA at RT. Next, COX-2 and α-SMA primary antibody (Servicebio Co., Ltd., China) was added dropwise and then incubated overnight at 4 °C. The area to be tested was incubated with corresponding COX-2 and α-SMA secondary antibody (Servicebio Co., Ltd., China) for 1 h, followed by observation under a fluorescence microscope.
2.15. Quantitative Real-time PCR
TRIzol total RNA reagent was used to isolated total RNA from peritendinous tissue following the operating instructions. Then RNA was reversed to complementary DNA (cDNA) by reverse transcription using the PrimeScript RT Master Mix. Real-time PCR was performed using an Applied BiosystemsTM 7500 (ThermoFisher Scientific, USA). The relative mRNA expressions were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method and normalized to GAPDH.
2.16. Western blotting
Western blotting was performed to quantify the expression of COX-2, PDK1, pAKT, AKT and Col III with β-actin as an internal control. Briefly, sample tissues were isolated and lysed to obtain proteins. The protein concentrations were measured using a BCA Protein Assay Kit. The sample proteins were then incubated with COX-2, PDK1, pAKT, AKT, Col III, and β-actin antibodies after sequential SDS-PAGE treatment, membrane transfer and closure of the transferred membranes. Subsequent incubation with secondary antibodies. The blots were detected by chemiluminescence system and their optical density was detected by ImageJ software.
2.17. Enzyme linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
The concentrations of PGE2 in the sample tissues was determined by ELISA. Briefly, diluted samples were added to microtiter plates coated with antibodies for incubation, and PGE2 antibody was added to the wells followed by the addition of substrate to generate an enzymatic reaction. After the enzyme reaction reaches a certain level, the reaction was stopped with stop solution. The absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a microplate reader.
2.18. Gait analysis
The healing outcomes of the injured Achilles tendon was evaluated after surgery for 3 weeks. Briefly, rat hind paws were evenly dipped with ink and allowing them to pass a restrictive roadway covered with a white paper. Then, footprint parameter including pawprint length (PL), toe spreading length (TS, defined as the distance between the first and fifth toes) and intermediate toe width (IT, defined as the distance between the second and fourth toes) were acquired based on pawprint images using ImageJ software. Then, according to the difference between the normal (N) and the experimental values (E), three footprint dimension factors (PLF, TSF, ITF) could be obtained according to the following equations: PLF = (NPL-EPL)/EPL, TSF = (ETS-NTS)/NTS, ITF = (EIT-NIT)/NIT. The AFI was finally calculated following to an established equation: AFI = 74 (PLF) + 161 (TSF) + 48 (ITF) [43].
2.19. Biomechanical testing
The mechanical properties of the repaired tendons including the maximal fracture strength, stiffness, tensile strength and Youngs’ modulus of repaired tendon were measured and recorded with a rheometer (Instron 5569, USA). The proximal and distal ends of all Achilles tendons were fixed with two force clips and pulled on until tendons rupture.
2.20. Statistical analysis
All the data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. Statistical differences of experimental results were conducted analyzed using one-way or two-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) and P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant differences and were recorded as *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0005 and ****P < 0.0001.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Construction and characterization of the positively charged layer
Electrostatic interaction is one of the strongest interactions between charged materials [44]. Electrostatic interactions have been utilized to create positively charged multi-stage delivery methods to penetrate the high negative fixed charge density of body tissue such as articular cartilage [24]. Lin et al. [25] used the positively charged liposome carrier to effectively penetrate into the cartilage with the charged guidance. Although rarely reported, inspired by the glomerular filtration barrier, positively charged EFMs can theoretically enhance the barrier effect on positively charged polyplexes via charge repulsion (Fig. S1). CS is the only known natural cationic macromolecule with excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability in vivo [45,46]. Importantly, CS can significantly suppress proliferation of fibroblasts [47], making it a preferred choice for positive charge modification of EFMs. The EFMs were electrospun by mixing CS and PCL solution at different mass ratios (0, 5%, 10% and 15%), named PCL, 5%CS@PCL, 10%CS@PCL and 15%CS@PCL, respectively. The morphologies were observed with SEM. As shown in Fig. 2A, the four groups of fibers were uniform and smooth. Their average diameters were 0.26 ± 0.04 μm, 0.26 ± 0.06 μm, 0.29 ± 0.29 μm and 0.28 ± 0.06 μm, respectively, and no significant difference was found between them (Fig. 2C). Also, there was no significant difference of the porosities of the four EFMs (Fig. 2D), which were closely related to the fiber diameters. In addition, the pore size of EFMs has an important role in facilitating the exchange of nutrients and wastes and in protecting against external pathogens. The above results confirmed that the addition of CS did not affect the morphological characteristics of EFMs.
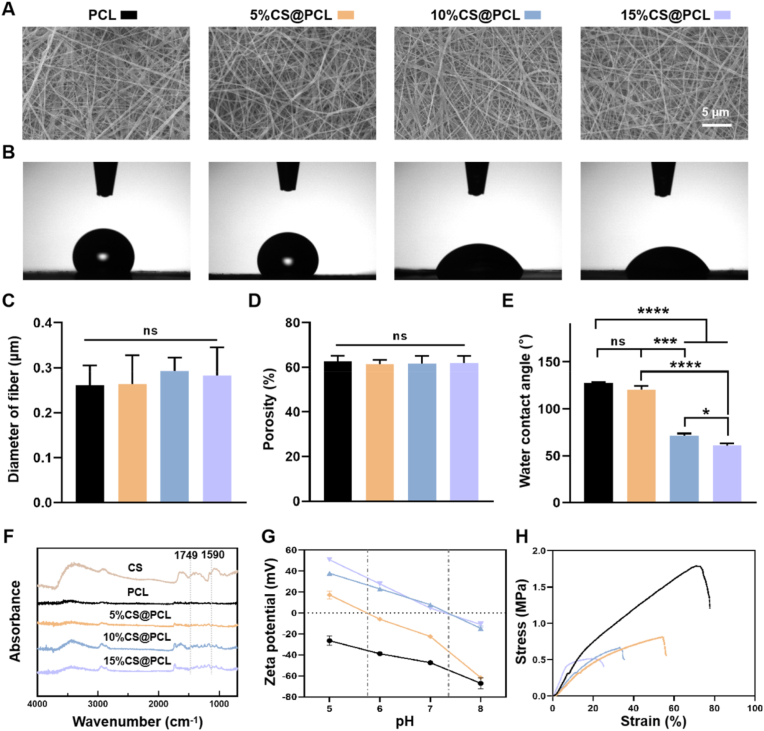
Fig. 2.
Characterization of the positively charged layer. (A) Representative SEM images of four CS@PCL membranes with different mass ratio. (B) Representative water contact angles images of four CS@PCL membranes with different mass ratio. Quantitative analysis of (C) fiber diameter, (D) porosity analysis and (E) hydrophilicity of four CS@PCL membranes with different mass ratio. (F) FTIR spectra analysis of four CS@PCL membranes with different mass ratio. (G) Surface zeta potential of four CS@PCL with different mass ratios. (H) Tensile properties of four CS@PCL with different mass ratios. (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001).
Four EFMs were tested by water contact angle as shown in Fig. 2B. The result showed that the pure PCL was highly hydrophobic, and the hydrophilicity of the membrane became more significant with the increase of CS content (Fig. 2E), which also indicated the successful addition of CS. The FTIR spectrometer analysis of each EFM (in a range of 4000 to 400 cm−1) was further performed and the results were shown in Fig. 2F. The stretching vibration peak of the ester bond could be observed at 1749 cm−1, which is a major characteristic peak of PCL. And the characteristic peak of CS (deformation vibration peak of amino N–H) was located at 1590 cm−1. And both peaks were present in all three groups of CS@PCL EFMs, confirming the successful binding of CS to PCL.
To evaluate the charged state of the membrane surface, the zeta potentials of four EFMs in aqueous media (pH = 5, 6, 7 and 8, which represent the majority of values in the body fluid environment) were measured. As shown in Fig. 2G, the PCL membrane always exhibited a negative charged state due to the presence of negatively charged carboxyl groups. After the addition of CS, the surface potential of the EFMs changed due to the presence of positively charged amino groups of CS. However, 5%CS@PCL exhibited a positive charge state only at pH < 5.87, which is significantly lower than most humoral environments. As the mass ratio of CS increased to 10% and 15%, the isoelectric point (IEP) of EFMs could be roughly increased to pH = 7.2. This makes CS@PCL could retain its positively charged properties in the fluctuating pH environment of the injured tissue. The mechanical properties of the membranes are critical for in vivo applications. Tensile tests were performed on four EFMs and it was found that the mechanical properties weakened with the increase of CS content (Fig. 2H and S2). Based on the results of zeta potentials as well as mechanical properties, 10%CS@PCL was finally selected for the subsequent experiments.
3.2. Construction and characterization of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes
Naked siRNAs suffer rapid clearance in body fluids, so efficient and safe delivery vectors are essential for gene therapy [48]. Dendrimer, such as PAMAM, can deliver siRNA into cells and can also be modified to protect siRNA from enzymatic degradation [3]. In this study, G4 PAMAM dendrimers were chosen to entrap Au nanoparticles (Au NPs) according to the literature [49]. The Au NPs entrapped in the internal cavities of dendrimers facilitate the maintenance of their 3D conformation to improve gene delivery [50]. After entrapment of Au NPs, Au DENPs were obtained and characterized subsequently. Au DENPs-based multifunctional nano-delivery systems were successfully constructed and their safety and efficiency of gene delivery had been demonstrated in our previous study [10]. The UV–vis spectrometer showed that the surface plasma band at 520 nm became prominent, indicating the existence of Au NPs in solution (Fig. S3). The shape and particle size distribution of Au NPs within the Au DENPs were observe using TEM (Fig. 3A). Obviously, Au DENPs displayed spherical Au cores with an average size of 2.626 ± 0.418 nm (Fig. 3B).
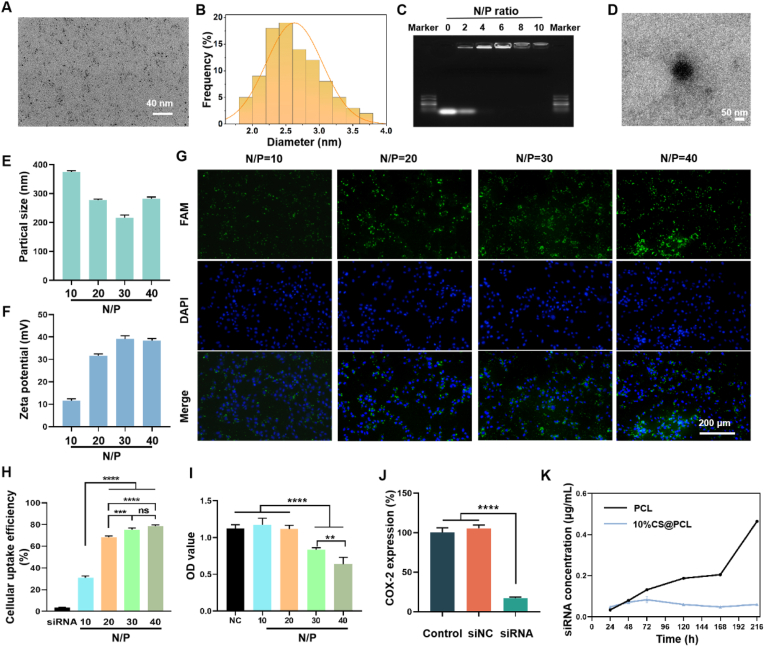
Fig. 3.
Characterization of Au DENPs and siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes. (A) Representative TEM image of Au DENPs. (B) The size distribution of Au DENPs. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis. (D) Representative TEM image of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes. (E) The particle sizes and (F) zeta potentials of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes was measured using dynamic light scattering (DLS). (G) Representative fluorescence staining of 208F cells treated with siRNA@Au DENPs with different N/P ratio. (H) Cellular uptake efficiency of siRNA@Au DENPs with different N/P ratio using flow cytometry. (I) Cytotoxicity of siRNA@Au DENPs with different N/P ratio. (J) Gene silencing efficiency of COX-2 siRNA@Au DENPs with N/P ratio = 20. (K) Using Transwell plates to analyze the concentration of siRNA polyplexes of the lower chamber diffused from the upper chamber to verify the charge repulsion effect. (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001).
Au DENPs were complexed with siRNA by electrostatic attraction. The gene binding capacity of Au DENPs was checked by Agarose gel electrophoresis. This assay revealed that siRNA could be compressed by Au DENPs completely when N/P ratio was greater than or equal to 4 (Fig. 3C). The morphology of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes were further observed using a TEM and exhibit discrete entire spheres (Fig. 3D). The zeta potentials and particle sizes of siRNA polyplexes are critical for effective gene transfection. As shown in Fig. 3E and F, the particle sizes and zeta potentials of siRNA@ Au DENPs polyplexes were in the range of 200–400 nm and 10–40 mV, respectively. The results demonstrated Au DENPs could condense siRNA into the nano-scale and form a positively charged nanoparticle. These favorable biophysical properties greatly facilitate efficient gene delivery [51]. The cellular uptake was observed by fluorescence microscopy, and it was found that the average fluorescence intensity enhanced with the increase of N/P ratio (Fig. 3G). Meanwhile, the cellular uptake efficiency was further quantified using flow cytometry (Fig. S4). The cellular uptake efficiency of siRNA@Au DENP could be increased from 30.9 ± 1.76% to 78.63 ± 1.16% as N/P ratio increased (Fig. 3H).
The cytotoxicity of siRNA@Au DENPs polyplexes was further examined. As shown in Fig. 3I, the OD values decreased as the N/P ratio increased, and Au DENPs exhibited significant cytotoxicity on 208F cells when the N/P ratio exceeded 20. To optimize balance between high transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity, the N/P ratio of 20:1 was selected as appropriate condition to perform the following experiment. The gene silencing efficiency of COX-2 siRNA@Au DENPs was determined by qRT-PCR. As shown in Fig. 3J, the gene silencing efficiency was up to 82.93 ± 1.36% which indicated that COX-2 siRNA@Au DENPs could effectively deliver COX-2 siRNA to silence the expression of COX-2 gene.
The charge repulsion effect of 10%CS@PCL on the above positively charged polyplexes was further verified. As shown in Fig. 3K, the steric hindrance effect of PCL diminished with increasing immersion time, and the concentration of siRNA in the lower chamber of Transwell plates increased dramatically after 7 days. However, 10%CS@PCL could hinder the diffusion of cationic polyplexes for a long time due to the charge repulsion. The unidirectional drug release could be realized due to the presence of hydrophobic eletrospun membrane [19]. The results also showed that the PCL membrane was able to hinder the penetration of cationic polyplexes in the first three days, but after that, this hindering effect gradually weakened. The possible reason for this is that the PCL membrane was saturated with water [19]. Although hydrophilic CS@PCL membrane could not impede water infiltration, it was still able to impede the trans-electrospun membrane transportation of cationic nanoparticles for a long time. The possible reason was the repulsive force of the like charge, similar to that of the glomerular filtration membrane.
3.3. Construction and characterization of the gene-loaded layer
Although the gene-loaded membranes have been successfully constructed by micro-sol electrospinning techniques in our previous study [16], the uncontrolled release of siRNA may lead to reduced biological effects or produce side effects. Compared to conventional materials, smart materials can be activated in response to specific exogenous or endogenous stimuli including ultrasound, pH, temperature, enzymes or specific biomolecules, and can exhibit better selectivity and sensitivity with fewer side effects [[52], [53], [54], [55]]. Thus, based on the significant upregulation of MMP-2 during tendon adhesion formation, a variety of MMP-2-responsive drug release systems have been successfully constructed in our previous works, including MMP-2 responsive hydrogels [22] and MMP-2 responsive GelMA microspheres [38]. Gelatin is a natural polymer which can be degraded by several proteases involving MMPs and GelMA microspheres were also demonstrated to have good MMP-2 responsiveness in our previous study [38]. The synthesis equation of GelMA is shown in Fig. S5. Subsequently, a “core-shell” electrospun fiber with the GelMA-sol particles as the core phase and polylactic acid (PLA) as the shell layer was constructed by micro-sol electrospinning (Fig. 4A and B). TEM also confirmed the core-shell structure of the fibers, as shown in Fig. 4C. The GelMA-sol could not only act as a protective layer to avoid potential damage to gene drugs in the electrospinning process, but also as a gene pool sensitive to MMP-2.
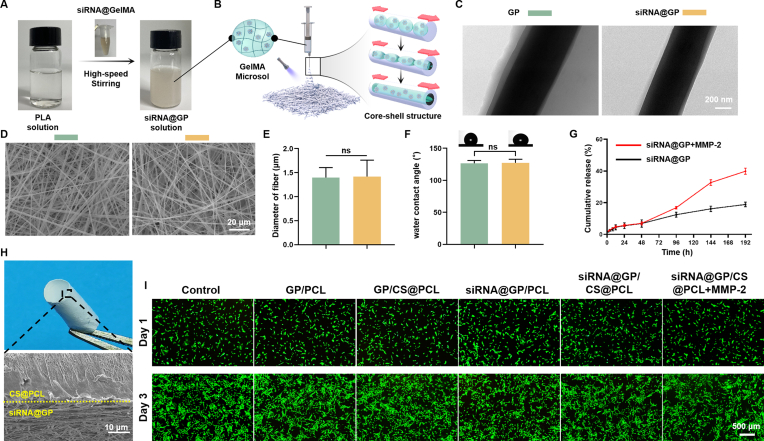
Fig. 4.
Construction and Characterization of the gene-loaded layer. (A) After adding siRNA@GelMA solution and stirring at high speed, the clear PLA solution turned into emulsion-like siRNA@GP solution. GP: GelMA@PLA. siRNA@GP: siRNA@GelMA@PLA. (B) The fabrication process of the gene-loaded layer. (C) TEM images of electrospun fibers with core-shell structure. (D) Representative SEM images of the gene-loaded and non-gene-loaded layers. (E) Fiber diameter analysis of the gene-loaded and non-gene-loaded layers. (F) Water contact angle of the gene-loaded and non-gene-loaded layers. (G) siRNA polyplexes released from the gene-loaded layers with or without MMP-2 (0.1 μg/ml). (H) Representative general and cross-sectional SEM image of double-layer membrane. (I) Cytotoxicity detection of different double-layer membranes used in the following in vitro study.
The fiber morphologies of the EFMs before and after gene loading (GP and siRNA@GP) were observed by SEM. Both groups of the fibers were smooth, uniform and continuous (Fig. 4D), with no significant differences in fiber diameters and porosities (Fig. 4E and S6). The WCAs were observed as (126.5 ± 4.6) ° and (127.4 ± 5.4) ° and no significant difference was found between them (Fig. 4F). The results showed that hydrophilic GelMA was well encapsulated inside the fibers. Subsequently, the property of MMP-2 responsive release was verified. As shown in Fig. 4G, almost 40% of the siRNA nanoparticles were released on Day 8, which was significantly more than the amount released from PBS without MMP-2 (∼20%).
3.4. Construction, characterization, biocompatibility and unidirectional release of the dual-layer EFMs
As shown in Fig. 4H, the dual-layer EFMs constructed by sequential electrospinning technology could be freely curled into a cylindrical structure with a composite tendon shape. The SEM image showed that the two layers were tightly connected with a clear demarcation line. The mechanical properties of the dual-layer EFMs were shown in Fig. S7.
To verify the biocompatibility of the dual-layer EFMs, we incubated 208F cells in the extract liquids of dual-layer EFMs and performed Live/Dead staining on Day 1 and Day 3. As shown in Fig. 4I, only a few cells in any group died, which indicated that dual-layer EFMs had excellent biocompatibilities.
The unidirectional release of the dual-layer EFMs were further evaluated (Fig. S8A). As shown in Fig. S8B, siRNA@GP/10%CS@PCL demonstrated superior unidirectional drug delivery, but siRNA@GP/PCL and siRNA@GP/5%CS@PCL did not. According to the results of the surface potential analysis (Fig. 2G), PCL and 5% CS@PCL did not carry a positive charge, while 10% CS@PCL exhibited a positive charge in PBS solution at pH = 6.8. This demonstrated that charge repulsion is one of the main factors to achieve unidirectional release of positively charged siRNA polyplexes and CS acted mainly by modulating the charge of EFMs.
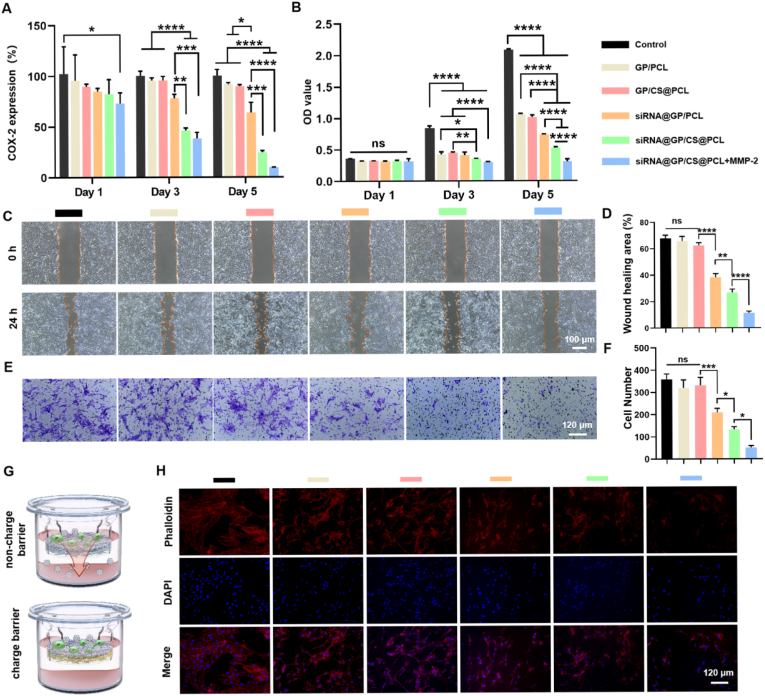
3.5. Long-lasting gene silencing efficiency, cell proliferation, cell migration, cell adhesion and antibacterial activity in vitro
Long-term modulation of chronic inflammation is essential for preventing adhesion formation [56]. Firstly, we evaluated the long-term silencing effect of COX-2 expression in dual-layer EFMs by qRT-PCR on Days 1, 3 and 5 (Fig. 5A). The results showed that all groups did not show gene silencing effect on Day 1, except for the siRNA@GP/CS@PCL + MMP-2 group which significantly knocked down the expression of COX-2. On Day 3, siRNA@GP/PCL did not show gene silencing effect compared with non-gene-loaded membranes, probably because the released siRNA nanoparticles diffused into both upper and lower chambers, reducing the concentration of siRNA polyplexes. In contrast, the positively charged layer could confine more released siRNA polyplexes into the upper chamber, while significantly knocking down the expression of COX-2. With the increase of siRNA polyplexes released, the gene-loaded dual-layer EFMs all showed a significant knockdown effect on Day 5 and the addition of MMP-2 could enhance the knockdown effect, but there was no statistical difference. The above results indicated that siRNA@GP/CS@PCL could effectively inhibit the expression of intracellular target genes and was able to respond to up-regulated MMP-2 for on-demand release.
Fig. 5.
Long-lasting gene silencing efficiency, Cell proliferation, Cell migration, and Cell adhesion of unidirectional gene delivery EFMs in vitro. (A) Long-lasting gene silencing efficiency assessment of different double-layer EFMs. (B) Inhibition efficiency of cell proliferation of 208F cells of different double-layer EFMs. (C) Representative images of 208F cells migration after incubation of 0 and 24 h. (D) Quantitative analysis of wound migration rate on the cell migration results. (E) The cell migration was detected by crystal violet staining. (F) Quantitative analysis of 208F cell migration. (G) The schematic representation of anti-adhesion effect of dual-layer EFMs without or with positively charged layer. (H) Fluorescence images of 208F cells seeded on different dual-layer EFMs for 3 days. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001).
Proliferation and migration of fibroblasts are important biological behaviors in tendon adhesion formation. COX-2 is usually expressed only after harmful stimulation or cytokine induction, such as oxidative stress, mechanical injury and TGF-β stimulation [32]. And it can regulate fibroblast growth, migration, proliferation, autophagy, apoptosis and immune responses [33,57,58]. To further evaluate the effect of knockdown of COX-2 siRNA on the biological behavior of fibroblasts, CCK-8, scratch tests and migration tests on fibroblasts were performed in vitro. Cell proliferation was verified on Days 1, 3 and 5 (Fig. 5B). On Day 1, there was no significant difference in the cell proliferation rate between all the groups. On Day 3, the cell proliferation rate in the control group was significantly higher than that in other groups, which may be due to the anti-cell proliferation effect of the membranes themselves. Furthermore, the siRNA@GP/PCL group showed no differences compared to other non-gene-loaded membranes. However, the presence of the charge barrier could inhibit cell proliferation, and especially the addition of MMP-2 could make the inhibition more pronounced. These results indicated that the charge barrier could concentrate siRNA in the upper chamber, and the addition of MMP-2 allowed more siRNA nanoparticles to be released, which synergistically inhibited cell proliferation more effectively. On Day 5, the cell proliferation inhibition rate of siRNA@GP/CS@PCL + MMP-2 group could reach about 70%. Furthermore, the results of scratch and migration tests also demonstrated that the knockdown of COX-2 inhibited fibroblast migration, and this inhibition was reinforced by a charge barrier and MMP-2 (Fig. 5C–F).
Adhesion of fibroblasts to EFMs affects their therapeutic effect [21]. In the following study, the dual-layer EFMs were placed at the bottom of the upper chamber of the transwell plate with gene-loaded layer facing upward and 208F cells were seeded on the EFMs to exam the anti-cellular adhesion (Fig. 5G). The cell adhesion was observed by fluorescence microscopy (Fig. 5H). It was found that the cell spreading area was significantly reduced in the EFM groups compared with the control group probably due to the hydrophobicity of EFMs. In addition, the cell spreading area was further reduced in the gene-loaded groups compared to the GP/PCL groups. And with the synergistic effect of the positive charge barrier and MMP-2, the siRNA@GP/CS@PCL + MMP-2 group showed the smallest cell adhesion area (Fig. S9). The anti-cellular adhesion effect of EFMs can effectively avoid the formation of fibrous sheath wrapping, while improving the anti-tendon adhesion effect.
The postoperative tendon infection is determined as crucial etiology of adhesion formation and the importance of early prevention of infection is emphasized [39]. Here, we assessed the antibacterial property of different EFMs. As shown in Fig. S10A, GP/CS@PCL and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group present inhibition zone for both E. coli and S. aureus, but GP/PCL and siRNA@GP/PCL group did not. No significant difference was found between GP/CS@PCL and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group in further quantitative comparison (Fig. S10B and C). The bacteria counting assessment showed similar results that the antibacterial effects were only confirmed in GP/CS@PCL and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group (Fig. S10D-F). CS and its various modifications have been demonstrated to own innate antibacterial activity due to the presence of specific functional groups [59]. In our study, the presence of CS in GP/CS@PCL and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL may be one of the reasons why they exhibited antimicrobial activity. The specific antibacterial mechanisms need to be further investigated systematically in future study. In conclusion, the antibacterial properties make our unidirectional gene delivery anti-adhesion membranes even more advantageous.
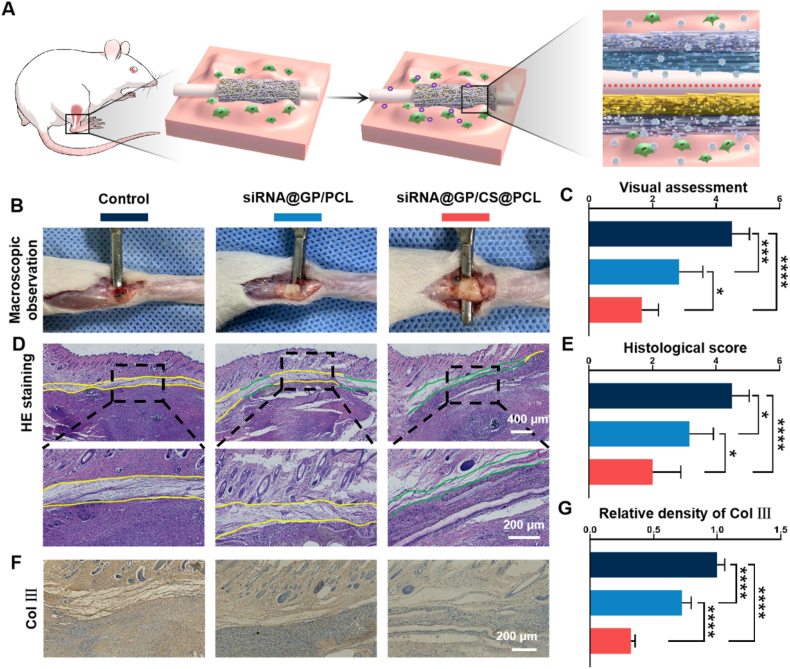
3.6. Histological analysis of the repaired rat achilles tendon
A schematic diagram of tendon injury repair is shown in Fig. 6A. The dual-layer EFMs could release more siRNA nanoparticles with the increasement of MMP-2 while were confined in peritendinous tissue under the charge repulsion of positively charged layer. On postoperative Day 21, all rats were euthanized and the injured tendons were assessed under direct observation. No infected ulcers or necrosis were found. As shown in Fig. 6B, the control group showed significant tissue adhesion, which hindered the penetration of the spatula between the tissues. In the siRNA@GP/PCL group and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group, the adhesion of the peritendinous tissues was reduced attributed to the therapeutic effect of COX-2 siRNA nanoparticles, allowing the spatula to pass easily. According to the macroscopic evaluation standards (Fig. S11), the siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group had lighter tissue adhesion compared to the siRNA@GP/PCL group. This suggested that more siRNA polyplexes were confined to the peritendinous region due to charge repulsion (Fig. 6C).
Fig. 6.
Histological analysis of the rat Achilles tendons. (A) Application of dual-layer EFMs without or with positively charged layer for tendon repair. (B) Gross observation of the degree of tendon adhesion on postoperative Day 21. (C) Visual assessment of peritendinous adhesion of the injured tendon. (D) HE staining images (green lines indicate areas without adhesion, yellow lines indicate adhesion areas). (E) Histologic evaluation of peritendinous adhesion. (F) Representative images of immunohistochemical staining of Col Ⅲ. (G) Quantitative analysis of Col Ⅲ expression in peritendinous tissue. (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001).
The extent of inflammatory reactions, tendon adhesion and tendon healing were further examined via histological analysis including H&E and Masson's staining. The anti-inflammatory effect of dual-layer EFMs was assessed first. A large number of inflammatory cells were recruited in adhesion tissue in the control group and COX-2 siRNA-loaded EFMs showed less inflammatory cells and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group exhibited the least inflammatory cells, indicating the excellent anti-inflammation effect (Fig. S12). Then, we moved to the evaluation of tendon adhesion and the results showed that dense fibrous tissue around the repaired tendon was founded in the control group, and the adhesion was the lightest in the siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group (Fig. 6D and S13). This was also consistent with the visual observation. Furthermore, the degree of tissue adhesion was assessed histologically (Fig. S14). As shown in Fig. 6E, the histological score was significantly lower in the siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group, indicating its excellent anti-adhesion effect. Additionally, the tendon healing outcome was detected and the quantitative results showed the minimal interference with fragile endogenous haling of siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group (Fig. S15). The in vivo biocompatibility of the dual-layer EFMs was also assessed via H&E staining of major organs including heart, lung, liver, etc. at three weeks postoperatively and no obvious impairment by the dual-layer EFMs was found (Fig. S16).
The immunohistochemical staining of Col Ⅲ in peritendinous area was further performed. As shown in Fig. 6F and G, the distribution of brown-yellow Col Ⅲ in the siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group was looser than that in the other two groups.
The inflammatory microenvironment can recruit and drive the differentiation of fibroblasts to myofibroblasts, which secrete large amounts of Col Ⅲ, ultimately resulting in tissue adhesion [33]. Compared with the control group, the on-demand release of COX-2 siRNA could effectively modulate the inflammatory response, while the unidirectional release could enhance the anti-inflammatory effect while reduce interference with endogenous healing.
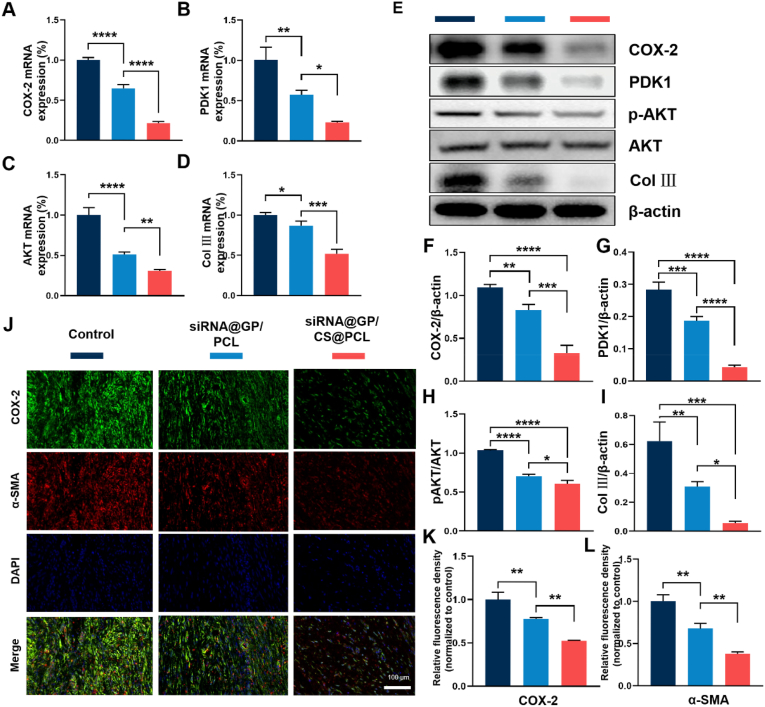
3.7. The assessment of gene and protein expression and PGE2 in peritendinous tissue
In recent years, COX-2 has been reported to exert an essential role in tendon adhesion [60]. Clinically, patients are often advised to take selective COX-2 inhibitors to reduce pain and prevent tendon adhesion. In addition to modulating inflammation, we further explored other pro-fibrotic pathways associated with COX-2. It was reported that PDK1/AKT signaling was closely associated with fibrosis [61] and COX-2 has been reported to involved in this signaling pathway [33]. Hence, to further investigate the mechanisms of adhesion tissue formation, the gene and protein expression of COX-2, PDK1, AKT and Col Ⅲ were verified by qRT-PCR and western blotting. As shown in Fig. 7A, the mRNA expression of COX-2 was significantly silenced in the groups treated with COX-2 siRNA than in the control group, and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL showed the least COX-2 gene expression which proved the charge barrier improve the bioavailability of COX-2 siRNA. The results in Fig. 7B–D showed that the expression of PDK1 and AKT was also decreased, which in turn suppressed Col Ⅲ gene expression. The protein expressions were further verified to explore the cellular mechanism of adhesion tissue formation (Fig. 7 E). As shown in Fig. 7F, siRNA@GP/CS@PCL showed the least expression of COX-2. The expression of PDK1 was also suppressed accordingly which in turn inhibited the phosphorylation of AKT and eventually reduced the expression of Col Ⅲ (Fig. 7G–I). As an important downstream product of COX-2, the concentration of PGE2 was determined in peritendinous tissues by ELISA and the result showed that the knock down of COX-2 suppressed PGE2 expression (Fig. S17). These results suggested that COX-2 is an important target in the regulation of tendon adhesions, and silencing of COX-2 effectively reduced Col Ⅲ formation. Besides by reducing the synthesis of PGE2, an important inflammatory mediator, to modulate inflammation, COX-2 may also intervene in tendon adhesion through PDK1/AKT signaling pathway.
Fig. 7.
Assessment of target genes and protein expression in vivo. (A–D) Quantitative qRT-PCR detection of mRNA expression of COX-2, PDK1, AKT and Col Ⅲ. (E) Expression of COX-2, PDK1, p-AKT, AKT and Col Ⅲ in adhesion tissues determined by Western blotting. (F and G) Quantitative analysis of COX-2 and PDK1 levels normalized to β-actin. (H) Quantitative analysis of p-AKT levels normalized to AKT. (I) Quantitative analysis of Col Ⅲ levels normalized to β-actin. (J) Representative Immunofluorescence double-staining images of COX-2 (green) and α-SMA (red) at 3 weeks. (K and L) Semiquantitative analysis on optical density of COX-2 and α-SMA. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.0005, ****P < 0.0001).
Moreover, we used double-label immunofluorescence staining to assess the relationship between COX-2 and fibrogenesis. The results showed that decreased COX-2 (green) and α-SMA (red) positive areas were distributed in peritendinous tissue in siRNA@GP/PCL and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group, compared with control group (Fig. 7J). The semiquantitative results were shown in Fig. 7K and L, siRNA@GP/CS@PCL group exhibited the significantly decreased positive areas of COX-2 and α-SMA compared with that of control group and siRNA@GP/PCL group. The immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated that COX-2 siRNA significantly decreased the expression of COX-2 to inhibit the formation of adhere tissue.
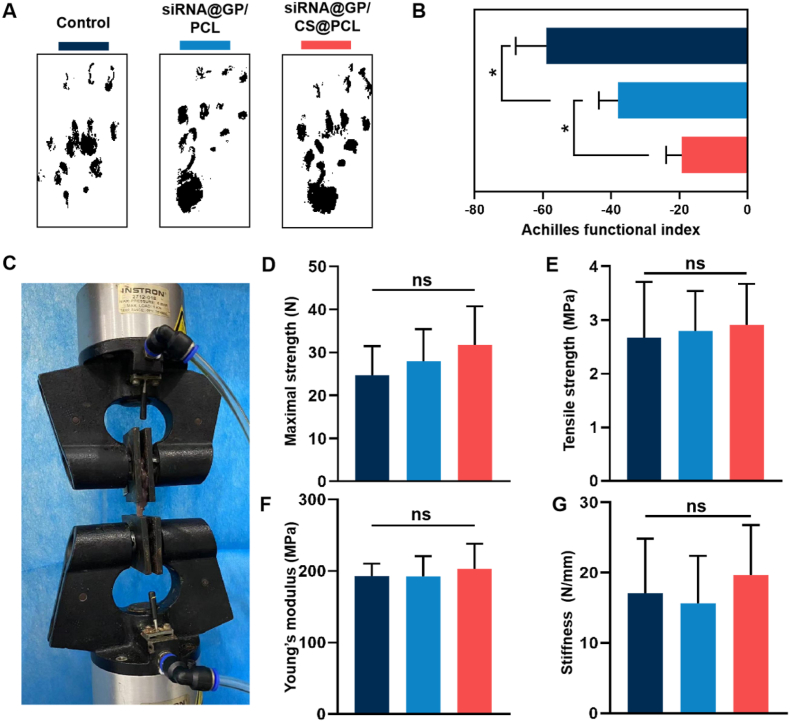
3.8. The assessment of tendon motion and biomechanical function
A gait test was performed to assess the locomotion performance of healing tendon after treating with different dual-layer EFMs (Fig. 8A). To quantitatively assess the extent of functional recovery of the repaired tendons, we then calculated the AFI. As shown in Fig. 8B, the AFI values of all experimental groups decreased with different degrees. Compared with control group, the AFI values of siRNA@GP/PCL and siRNA@GP/CS@PCL were significantly higher at 3 weeks operation, suggesting that COX-2 siRNA could effectively inhibited the deposition of adhesion tissue to improve the motion function of Achilles tendon. Notably, the siRNA@GP/CS@PCL with positively charge barrier showed the highest AFI value, indicating better functional recovery for tendon injuries.
Fig. 8.
Gait tests and Biomechanical testing of the rat Achilles tendon. (A) Gait analysis and (B) Achilles function index (AFI) evaluation of the healed tendon at postoperative Day 21. (C) Biomechanical test of the healed tendon at postoperative Day 21,and Comparison of maximal strength (D), tensile strength (E), Young's modulus (F) and stiffness (G) between the experimental groups.
The effects of the dual-layer EFMs on the tendon healing were investigated by the biomechanical test (Fig. 8C and S18). The important biomechanical parameters such as the maximal strength, stiffness, tensile strength and Youngs’ modulus of the repaired tendon were recorded and analyzed on postoperative Day 21. As shown in Fig. 8D–G, there was no significant difference in the biomechanical properties among the three groups of tendons after injury repaired. This demonstrates that the inhibition of the exogenous healing process is a potential way to reduce tendon adhesions and does not lead to a decrease in tendon strength. However, tendon healing required a longer remodeling period. Further animal study is needed to assess the long-time effect of unidirectional gene delivery EFMs on tendon mechanical properties.
4. Conclusion
In this study, a dual-layer siRNA@GP/CS@PCL with unidirectional siRNA delivery was innovatively constructed by combining microsol-electrospinning, mixed electrospinning and sequential electrospinning technology. Cationic nanocarriers loaded with siRNA in the gene-loaded layer are unidirectionally delivered to target tissues under charge repulsion of the positively charged layer. Meanwhile, the gene-loaded layer enables on-demand release of gene drugs in response to upregulated MMP-2 in the microenvironment (Fig. 9). The siRNA@GP/CS@PCL exhibited significant inhibition of fibroblast proliferation, migration and adhesion in vitro. Moreover, due to the charge repulsion, cationic gene polyplexes could enrich in the peritendinous tissue to effectively modulate the chronic inflammatory response to prevent the formation of tendon adhesion while reduce interference with fragile endogenous tendon healing. This provided an efficient alternative treatment strategy for tissue interface disorders, such as tendon adhesion.
Fig. 9.
Graphic Abstract. The dual-layer positively charged micro-nano electrospun fibrous membrane with unidirectional gene delivery via charge repulsion and MMP-2 responsiveness was fabricated for tendon repair by unidirectional silencing of COX-2 to modulate the inflammation of peritendinous tissue and on-demand release by responding to up-regulated MMP-2.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal procedures were approved by institutional review committee of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (SYXK (Hu)2021-0028).
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Jingwen Liu: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation. Liang Chen: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Conceptualization. Zhenyu Sun: Methodology, Investigation, Conceptualization. Zaijin Tao: Methodology, Investigation. Volotovski Pavel: Investigation. Yusheng Li: Methodology, Investigation. Fei Wang: Supervision, Resources, Project administration, Conceptualization. Wenguo Cui: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Methodology, Conceptualization. Shen Liu: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Resources, Project administration, Methodology, Conceptualization.
Declaration of Competing interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82172408 and 81902234), Shanghai Jiao Tong University Medical College “Two-hundred Talent” Program (No.20191829) , Program of Shanghai Academic/Technology Research Leader (22XD1422600) and Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (Grant No. 2022YQ073).
Footnotes
Peer review under responsibility of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.03.008.
Contributor Information
Fei Wang, Email: wangfeirj@163.com.
Wenguo Cui, Email: wgcui80@hotmail.com.
Shen Liu, Email: liushensjtu@sjtu.edu.cn.
Appendix A. Supplementary data
The following is the Supplementary data to this article.
References
- 1.Hurley E.A., Hull D., Shriver S.P. The next phase of human gene-therapy oversight. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;380:401–402. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1815776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alshaer W., Zureigat H., Al Karaki A., Al-Kadash A., Gharaibeh L., Ma'mon M.H., Aljabali A.A., Awidi A. siRNA: mechanism of action, challenges, and therapeutic approaches. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021;905:174–178. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Paunovska K., Loughrey D., Dahlman J.E. Drug delivery systems for RNA therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022:1–16. doi: 10.1038/s41576-021-00439-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Santos H.S., Rodrigues L., Vera L.N., Poletto E., Filippi-Chiela E., dos Santos Bruschi L.F.R., Schuh R., Baldo G. In situ gene therapy. Curr. Gene Ther. 2021;21:406–430. doi: 10.2174/1566523221666210504103323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tai W., Gao X. Functional peptides for siRNA delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017;110:157–168. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Anthiya S., Öztürk S.C., Yanik H., Tavukcuoglu E., Şahin A., Datta D., Charisse K., Álvarez D.M., Loza M.I., Calvo A. Targeted siRNA lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of KRAS-mutant tumors. J. Controlled Release. 2023;357:67–83. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wu C., Li J., Wang W., Hammond P.T. Rationally designed polycationic carriers for potent polymeric siRNA-mediated gene silencing. ACS Nano. 2018;12:6504–6514. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.7b08777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mohammadinejad R., Dehshahri A., Madamsetty V.S., Zahmatkeshan M., Tavakol S., Makvandi P., Khorsandi D., Pardakhty A., Ashrafizadeh M., Afshar E.G. In vivo gene delivery mediated by non-viral vectors for cancer therapy. J. Controlled Release. 2020;325:249–275. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.06.038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.De Smedt S.C., Demeester J., Hennink W.E. Cationic polymer based gene delivery systems. Pharmaceutical research. 2000;17:113–126. doi: 10.1023/a:1007548826495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li J., Chen L., Xu X., Fan Y., Xue X., Shen M., Shi X. Targeted combination of antioxidative and anti‐inflammatory therapy of rheumatoid arthritis using multifunctional Dendrimer‐Entrapped gold nanoparticles as a platform. Small Methods. 2020;16 doi: 10.1002/smll.202005661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pack D.W., Hoffman A.S., Pun S., Stayton P.S. Design and development of polymers for gene delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005;4:581–593. doi: 10.1038/nrd1775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Li C., Du Y., Lv H., Zhang J., Zhuang P., Yang W., Zhang Y., Wang J., Cui W., Chen W. Injectable amphipathic artesunate prodrug‐hydrogel microsphere as gene/drug nano‐microplex for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022;32 [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lin F., Li Y., Cui W.J.B.T. Injectable hydrogel microspheres in cartilage repair. Biomedical Technology. 2023;1:18–29. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nguyen M.K., Huynh C.T., Gilewski A., Wilner S.E., Maier K.E., Kwon N., Levy M., Alsberg E. Covalently tethering siRNA to hydrogels for localized, controlled release and gene silencing. Sci. Adv. 2019;5 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aax0801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lu M., Zhang X., Luo Z., Zhao Y. Engineered Regeneration; 2023. Developing Hierarchical Microneedles for Biomedical Applications. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu S., Wu F., Gu S., Wu T., Chen S., Chen S., Wang C., Huang G., Jin T., Cui W., Sarmento B., Deng L., Fan C. Gene silencing via PDA/ERK2-siRNA-Mediated electrospun fibers for peritendinous antiadhesion. Adv. Sci. 2019;6 doi: 10.1002/advs.201801217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Du W., Wang T., Hu S., Luan J., Tian F., Ma G., Xue J. Engineered Regeneration; 2023. Engineering of Electrospun Nanofiber Scaffolds for Repairing Brain Injury. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shi S., Si Y., Han Y., Wu T., Iqbal M.I., Fei B., Li R.K.Y., Hu J., Qu J. Deerfield Beach, Fla.; 2021. Recent Progress in Protective Membranes Fabricated via Electrospinning: Advanced Materials, Biomimetic Structures, and Functional Applications, Advanced Materials. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Santocildes-Romero M.E., Hadley L., Clitherow K.H., Hansen J., Murdoch C., Colley H.E., Thornhill M.H., Hatton P.V. Fabrication of electrospun mucoadhesive membranes for therapeutic applications in oral medicine. ACS applied materials & interfaces. 2017;9:11557–11567. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b02337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Stie M.B., Gätke J.R., Chronakis I.S., Jacobsen J., Nielsen H.M. Mucoadhesive electrospun nanofiber-based hybrid system with controlled and unidirectional release of desmopressin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23 doi: 10.3390/ijms23031458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Xiang L., Liang J., Wang Z., Lin F., Zhuang Y., Saiding Q., Wang F., Deng L., Cui W. Motion lubrication suppressed mechanical activation via hydrated fibrous gene patch for tendon healing. Sci. Adv. 2023;9 doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adc9375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cai C., Wang W., Liang J., Li Y., Lu M., Cui W., Fan C., Deng L., Li Y., Wang F., Liu S. MMP‐2 responsive unidirectional hydrogel‐electrospun patch loading TGF‐β1 siRNA polyplexes for peritendinous anti‐adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Suh J.H., Miner J.H. The glomerular basement membrane as a barrier to albumin. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013;9:470–477. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2013.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vedadghavami A., Zhang C., Bajpayee A.G. Overcoming negatively charged tissue barriers: drug delivery using cationic peptides and proteins. Nano Today. 2020;34 doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lin F., Wang Z., Xiang L., Deng L.F., Cui W.G. Charge-guided micro/nano-hydrogel microsphere for penetrating cartilage matrix. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021;31 [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wynn T.A., Vannella K.M. Macrophages in tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity. 2016;44:450–462. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Khanna A., Friel M., Gougoulias N., Longo U.G., Maffulli N. Prevention of adhesions in surgery of the flexor tendons of the hand: what is the evidence? Br. Med. Bull. 2009;90:85–109. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldp013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nichols A.E.C., Best K.T., Loiselle A.E. The cellular basis of fibrotic tendon healing: challenges and opportunities. Transl. Res. : J. Lab. Clin. Med. 2019;209:156–168. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2019.02.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhao X., Jiang S., Liu S., Chen S., Lin Z.Y., Pan G., He F., Li F., Fan C., Cui W. Optimization of intrinsic and extrinsic tendon healing through controllable water-soluble mitomycin-C release from electrospun fibers by mediating adhesion-related gene expression. Biomaterials. 2015;61:61–74. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.05.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wong J.K., Lui Y.H., Kapacee Z., Kadler K.E., Ferguson M.W., McGrouther D.A. The cellular biology of flexor tendon adhesion formation: an old problem in a new paradigm. Am. J. Pathol. 2009;175:1938–1951. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.090380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Manning C.N., Martel C., Sakiyama-Elbert S.E., Silva M.J., Shah S., Gelberman R.H., Thomopoulos S. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells modulate tendon fibroblast responses to macrophage-induced inflammation in vitro. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015;6:74. doi: 10.1186/s13287-015-0059-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Richter K., Konzack A., Pihlajaniemi T., Heljasvaara R., Kietzmann T. Redox-fibrosis: impact of TGFβ1 on ROS generators, mediators and functional consequences. Redox Biol. 2015;6:344–352. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.08.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chen H., Qian Z., Zhang S., Tang J., Fang L., Jiang F., Ge D., Chang J., Cao J., Yang L., Cao X. Silencing COX-2 blocks PDK1/TRAF4-induced AKT activation to inhibit fibrogenesis during skeletal muscle atrophy. Redox Biol. 2021;38 doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang K., Zhang S., Li Q., Yang J., Dong W., Wang S., Cheng Y., Al-Qwbani M., Wang Q., Yu B. Effects of celecoxib on proliferation and tenocytic differentiation of tendon-derived stem cells. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2014;450:762–766. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.06.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fredriksson M., Li Y., Stålman A., Haldosén L.A., Felländer-Tsai L. Diclofenac and triamcinolone acetonide impair tenocytic differentiation and promote adipocytic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2013;8:30. doi: 10.1186/1749-799X-8-30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Prasad T., Shabeena E.A., Vinod D., Kumary T.V., Anil Kumar P.R. Characterization and in vitro evaluation of electrospun chitosan/polycaprolactone blend fibrous mat for skin tissue engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015;26:5352. doi: 10.1007/s10856-014-5352-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yang J., Han Y., Lin J., Zhu Y., Wang F., Deng L., Zhang H., Xu X., Cui W. Ball-bearing-inspired polyampholyte-modified microspheres as bio-lubricants attenuate osteoarthritis. Small. 2020;16 doi: 10.1002/smll.202006356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Cai C.D., Zhang X.S., Li Y.G., Liu X.Z., Wang S., Lu M.K., Yan X., Deng L.F., Liu S., Wang F., Fan C.Y. Self-healing hydrogel embodied with macrophage-regulation and responsive-gene-silencing properties for synergistic prevention of peritendinous adhesion. Adv. Mater. 2022;34 doi: 10.1002/adma.202106564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhang Q., Yang Y., Suo D., Zhao S., Cheung J.C., Leung P.H., Zhao X. A biomimetic adhesive and robust janus patch with anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-bacterial activities for tendon repair. ACS Nano. 2023;17:16798–16816. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cai C., Zhang X., Li Y., Liu X., Wang S., Lu M., Yan X., Deng L., Liu S., Wang F., Fan C. Self-healing hydrogel embodied with macrophage-regulation and responsive-gene-silencing properties for synergistic prevention of peritendinous adhesion. Adv. Mater. 2022;34 doi: 10.1002/adma.202106564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tang J.B., Shi D., Zhang Q.G. Biomechanical and histologic evaluation of tendon sheath management. The Journal of hand surgery. 1996;21:900–908. doi: 10.1016/S0363-5023(96)80212-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li L., Zheng X., Fan D., Yu S., Wu D., Fan C., Cui W., Ruan H. Release of celecoxib from a bi-layer biomimetic tendon sheath to prevent tissue adhesion, Materials science & engineering. C, Materials for biological applications. 2016;61:220–226. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jin S., Wang Y., Wu X., Li Z., Zhu L., Niu Y., Zhou Y., Liu Y. Young exosome bio-nanoparticles restore aging-impaired tendon stem/progenitor cell function and reparative capacity. Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla.) 2023;35 doi: 10.1002/adma.202211602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhou M.Y., Zhang P., Fang L.F., Zhu B.K., Wang J.L., Chen J.H., Abdallah H. A positively charged tight UF membrane and its properties for removing trace metal cations via electrostatic repulsion mechanism. J. Hazard Mater. 2019;373:168–175. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.03.088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Abourehab M.A.S., Pramanik S., Abdelgawad M.A., Abualsoud B.M., Kadi A., Ansari M.J., Deepak A. Recent advances of chitosan formulations in biomedical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23 doi: 10.3390/ijms231810975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Yousefiasl S., Sharifi E., Salahinejad E., Makvandi P., Irani S.J.E.R. Bioactive 3D-printed chitosan-based scaffolds for personalized craniofacial bone tissue engineering. Engineered Regeneration. 2023;4:1–11. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wu W., Cheng R., das Neves J., Tang J., Xiao J., Ni Q., Liu X., Pan G., Li D., Cui W., Sarmento B. Advances in biomaterials for preventing tissue adhesion. J. Contr. Release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society. 2017;261:318–336. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.06.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Salameh J.W., Zhou L., Ward S.M., Santa Chalarca C.F., Emrick T., Figueiredo M.L. Polymer-mediated gene therapy: recent advances and merging of delivery techniques, Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. Nanomedicine and nanobiotechnology. 2020;12:e1598. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wang Y., Shen W., Shi X., Fu F., Fan Y., Shen W., Cao Y., Zhang Q., Qi R. Alpha-tocopheryl succinate-conjugated G5 PAMAM dendrimer enables effective inhibition of ulcerative colitis. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2017;6 doi: 10.1002/adhm.201700276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Shan Y., Luo T., Peng C., Sheng R., Cao A., Cao X., Shen M., Guo R., Tomás H., Shi X. Gene delivery using dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles as nonviral vectors. Biomaterials. 2012;33:3025–3035. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.12.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Puhl D.L., Mohanraj D., Nelson D.W., Gilbert R.J. Designing electrospun fiber platforms for efficient delivery of genetic material and genome editing tools. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2022;183 doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wei H., Cui J., Lin K., Xie J., Wang X. Recent advances in smart stimuli-responsive biomaterials for bone therapeutics and regeneration. Bone research. 2022;10:17. doi: 10.1038/s41413-021-00180-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lin X., Cai L., Cao X., Zhao Y. Stimuli‐responsive silk fibroin for on‐demand drug delivery. Smart Medicine. 2023 doi: 10.1002/SMMD.20220019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Huang D., Cai L., Li N., Zhao Y. Ultrasound‐trigged micro/nanorobots for biomedical applications. Smart Medicine. 2023 doi: 10.1002/SMMD.20230003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Guo J., Luo Z., Wang F., Gu H., Li M. Responsive hydrogel microfibers for biomedical engineering. Smart Medicine. 2022;1 doi: 10.1002/SMMD.20220003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pan G., Liu S., Zhao X., Zhao J., Fan C., Cui W. Full-course inhibition of biodegradation-induced inflammation in fibrous scaffold by loading enzyme-sensitive prodrug. Biomaterials. 2015;53:202–210. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Mitchell J.A., Kirkby N.S., Ahmetaj-Shala B., Armstrong P.C., Crescente M., Ferreira P., Lopes Pires M.E., Vaja R., Warner T.D. Cyclooxygenases and the cardiovascular system. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 2021;217 doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Niranjan R., Mishra K.P., Thakur A.K. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) initiates autophagy and potentiates MPTP-induced autophagic cell death of human neuroblastoma cells, SH-SY5Y: an inside in the pathology of Parkinson's disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018;55:8038–8050. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0950-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dragostin O.M., Samal S.K., Dash M., Lupascu F., Pânzariu A., Tuchilus C., Ghetu N., Danciu M., Dubruel P., Pieptu D., Vasile C., Tatia R., Profire L. New antimicrobial chitosan derivatives for wound dressing applications. Carbohydrate polymers. 2016;141:28–40. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.12.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Chen Q., Hou D., Suo Y., Zhu Z. LncRNA XIST prevents tendon adhesion and promotes tendon repair through the miR-26a-5p/COX2 pathway. Mol. Biotechnol. 2022;64:424–433. doi: 10.1007/s12033-021-00419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Jia S., Agarwal M., Yang J., Horowitz J.C., White E.S., Kim K.K. Discoidin domain receptor 2 signaling regulates fibroblast apoptosis through PDK1/akt. American journal of respiratory cell and molecular biology. 2018;59:295–305. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2017-0419OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.