Figure 1.
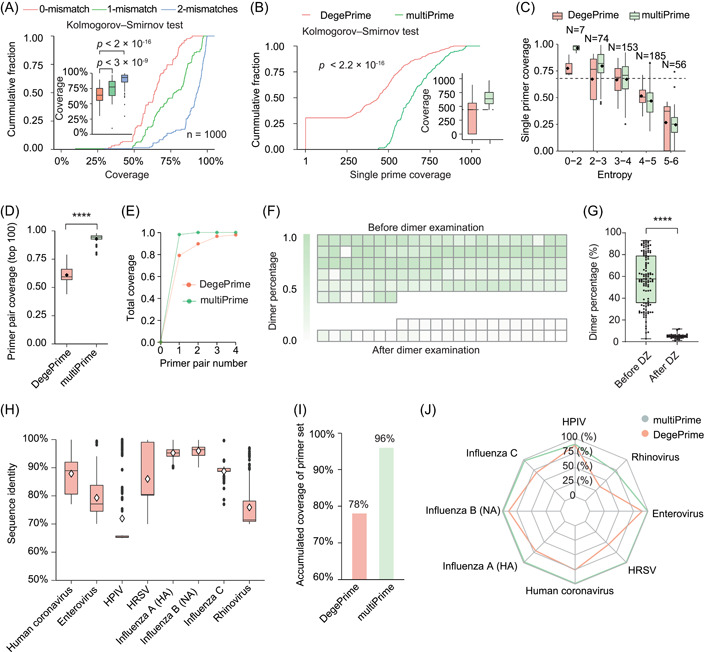
MultiPrime efficiently broadens the spectrum and enhances compatibility. (A) The coverage of primers designed by multiPrime using 1000 sequences, allowing for 0, 1, and 2 mismatches. (B) The cumulative fraction of single primer coverage for primers designed by multiPrime and DegePrime. (C) The coverage of single primers designed by multiPrime and DegePrime in different entropy regions. (D) The top 100 primer pair coverage values for DegePrime and multiPrime. (E) The number of primer pairs required to achieve satisfactory coverage. A heatmap (F) and boxplot (G) were used to show that the percentage of dimers was significantly reduced by dimer examination. Before dimer examination (Before DZ) was defined as the primer set combination without dimer examination. After dimer examination (after DZ) was defined as the primer set combination with dimer examination. (H) The sequence identity of the eight viruses was used for validation. (I) The accumulated coverage of the core primer set was evaluated across all eight viruses. The primer set was designed by multiPrime (v2.0.2) with the following parameters: identity: 0.8; seq_number_ANI: 60; drop: “T”; coordinate: 0; Others: Default. For detailed definitions of the parameters, see YAML files on GitHub. (J) Accumulated coverage of each individual virus by the primer set. HPIV, human parainfluenza virus; HRSV, human respiratory syncytial virus. ****p < 0.0001 by t‐test (two‐sided).
